Comparison Of Motor Symptoms
On the Hoehn and Yahr scale as well as on UPDRS III and IV , the PDD group had significantly higher scores than the DLB group, but there was no significant difference in predominant motor subtype between both groups. The tremor severity was higher in the PDD group, but only regarding the tremor at rest, which was marginally significant . Compared to DLB patients, PDD patients also demonstrated a significantly higher score on hand and feet bradykinesia as well as a tendency towards increased rigidity.
Apda In Your Community
APDAParkinson’s Disease SymptomsLewy Bodies, Dementia, and Parkinsons What Does it all Mean?
Here are two common scenarios that may sound familiar:
Scenario 1A patient develops a series of neurologic symptoms, is evaluated by a neurologist and is told that she has Parkinsons disease . She then visits another neurologist for a second opinion and is told she has Lewy Body Dementia .
Scenario 2A patient has his first visit with his neurologist and is told that he has PD, at a subsequent visit the diagnosis is changed to Parkinsons disease dementia , and at a follow up visit the diagnosis is changed yet again to Dementia with Lewy Bodies .
Both of these situations understandably cause great uncertainty and frustration.
What Is Parkinsons Disease
PD is a chronic, neurodegenerative movement disorder. PD affects 1 out of every 100 individuals over the age of 601, and patients commonly experience muscle rigidity, changes in speech and walking, and tremors. Some studies suggest that having PD also increases your risk of developing LBD, but most patients have only one of these conditions.2
You May Like: Yopd Life Expectancy
Causes Of Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Dementia with Lewy bodies is caused by clumps of protein forming inside brain cells. These abnormal deposits are called Lewy bodies.
These deposits are also found in people with Parkinson’s disease, and they build up in areas of the brain responsible for functions such as thinking, visual perception and muscle movement.
It’s not clear why the deposits develop and how exactly they damage the brain. It’s thought that part of the problem is the proteins affecting the brain’s normal functions by interfering with signals sent between brain cells.
Dementia with Lewy bodies usually occurs in people with no family history of the condition, although there have been very rare cases that seem to run in families.
Who Gets Dementia With Lewy Bodies

Around 5% of people with a diagnosis of dementia are recorded as having DLB, but there is good evidence that the condition is under-diagnosed. Scientists think DLB may account for up to 20% of all dementia.
Dementia with Lewy bodies affects men and women roughly equally. As with most other types of dementia, DLB becomes increasingly common over the age of 65. It can also affect people younger than this.
There is not much evidence that anything we might be exposed to during our lives increases the risk of DLB. Having a traumatic head injury may increase the risk of developing Parkinsons disease later in life, but its not known whether this also applies to DLB.
Almost all people who develop DLB have a sporadic form, which means that the main cause is unknown. Some genes may increase the risk of developing DLB.
Also Check: Sam Waterston Parkinson’s
Whats The Difference Between Lewy Body Dementia Parkinsons Disease And Alzheimers Disease
Lewy body dementia is an umbrella term for two related clinical diagnoses: dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinsons disease dementia. These disorders share the same underlying changes in the brain and very similar symptoms, but the symptoms appear in a different order depending on where the Lewy bodies first form.
Dementia with Lewy bodies is a type of dementia that causes problems with memory and thinking abilities that are severe enough to interfere with everyday activities. It specifically affects a persons ability to plan and solve problems, called executive function, and their ability to understand visual information. Dementia always appears first in DLB. The motor symptoms of Parkinsons such as tremor, slowness, stiffness and walking/balance/gait problems usually become more evident as the disease progresses. Visual hallucinations, REM sleep behavior disorder, fluctuating levels of alertness and attention, mood changes and autonomic dysfunction are also characteristic of DLB.
Finally, Alzheimers is characterized by different abnormal clumps called amyloid plaques, and jumbled fiber bundles called tau tangles. These microscopic structural changes in the brain were discovered by Dr. Alois Alzheimer in 1906. These plaques and tangles, together with loss of connections between nerve cells, contribute to loss of coherence and memory, as well as a progressive impairment in conducting normal activities of daily living.
They Are About The Same
Parkinsons Disease and Huntingtons Disease are about the same as far as the impact they have on quality of life. They both begin gradually starting with simple coordination problems. Then that leads on to loss of motor control. Then later they both lead to deterioration of a persons mental capacity. I do not see how one could be any worse than the other. They are both horrible.
You May Like: Similar To Parkinsons
Nilotinib Regulates Mirnas Associated With Ubiquitination
Changes of miRNAs associated with the ubiquitination pathways were detected only in nilotinib, 300 vs 150 mg and placebo . We observed disinhibition of SQSTM1, SMURF2, FBXW7, BTRC , and SKP1 , which mediate substrate recognition and recruitment for lysosomal degradation. These specific gene targets show that while initiation of lysosomal-autophagy is functioning, nilotinib, 300 mg, is able to facilitate the completion of these biological waste-control mechanisms. Nilotinib, 300 mg, significantly altered a number of ubiquitination genes and ubiquitin ligases, including NEDD4 , UBEs , MDM , and PSMDs as well as deubiquitination genes and ubiquitin-specific proteases , suggesting regulation of the ubiquitination/deubiquitination cycle, in agreement with previous reports., Alterations of autophagy-ubiquitination genes are also concurrent with significant changes of several heat shock proteins and vesicular transport genes , suggesting facilitation of cellular transport and protein clearance.
You May Like: Parkinsons Double Vision
Is There Treatment Available
At present there is no cure for Lewy body disease. Symptoms such as depression and disturbing hallucinations can usually be reduced by medication. However, medications to relieve hallucinations may increase muscle tremors and stiffness. Conversely, anti-Parkinson drugs may make hallucinations worse.
Emerging evidence suggests that cholinesterase inhibitor drugs may be quite helpful for some people with this condition.
People with this form of dementia are very sensitive to the side effects of neuroleptic drugs such as antipsychotic medications. It is essential all medications are supervised by a specialist to avoid these severe side effects.
Read Also: Pfnca Wellness Programs
What Other Things Help
There are various ways to help a person with DLB. Speech therapy may help improve communication between people with DLB and others. Physical therapy may help strengthen and stretch stiff muscles and help to prevent falls.
Research has shown that physical exercise helps to enhance brain health and improves mood and general fitness. A balanced diet, enough sleep, and limited alcohol intake are other important ways to promote good brain health. Other illnesses that affect the brain, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol, should also be treated if present.
Difference In Parkinsons Disease And Als Diagnosis And Treatment
There is currently no specific test that can be performed to directly diagnose Parkinsons disease, but an array of different tests can help narrow down on a diagnosis. If Parkinsons disease is suspected, a patient will be referred to a neurologist and geriatrician. Diagnosis is commonly confirmed with the presence of at least two of the three most common symptoms: Shaking or tremor that occurs at rest, slowness of movement, and muscle stiffness. A doctor will also perform brain scans to diagnose Parkinsons disease and to check for other conditions that could be causing similar symptoms.
There is also no cure for Parkinsons disease, but treatments are available to manage the symptoms and slow down the disease progression. Alongside traditional treatments, supportive therapies are used to improve different aspects of a persons health.
Common medications prescribed in Parkinsons disease include dopamine replacement therapy, dopamine agonists, anticholinergics, amantadine, monomine oxidase type B inhibitors, and catechol-o-methyl transferase inhibitors.
Surgery is also a treatment option for Parkinsons disease and is best suited for those who had a good response to levodopa, but still have difficulties with movement or who experience large fluctuations in their levodopa levels.
You May Like: On And Off Phenomenon
Recommended Reading: Diseases Similar To Parkinsons
How Is Lewy Body Disease Diagnosed
This type of dementia is diagnosed by taking a careful history of the pattern of symptoms, and by excluding other possible causes such as Vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. A brain scan may reveal brain degeneration, but the Lewy bodies can only be identified by examination of brain tissue after death.
Lewy body disease is similar to Alzheimer’s disease in many ways, and in the past it has sometimes been difficult to distinguish the two. It has only recently been accepted as a disease in its own right. It can occur by itself or together with Alzheimer’s disease and/or Vascular dementia. It may be hard to distinguish Lewy body disease from Parkinson’s disease, and some people with Parkinson’s disease develop a dementia which is similar to that seen in Lewy body disease.
Treatment Of Pdd And Dlb
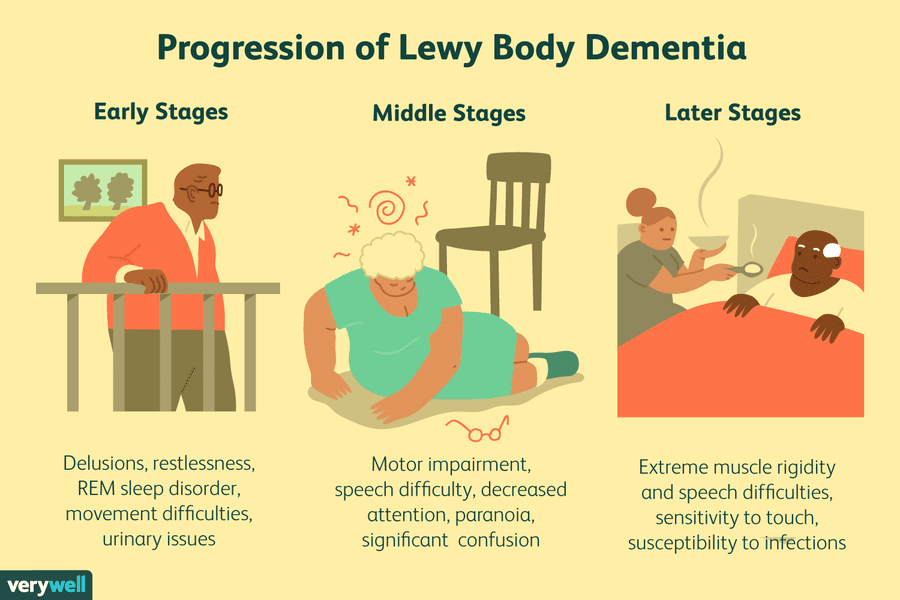
Unfortunately, since both types of Lewy Body Dementia often display similar symptoms, patients suffering from either PDD of DLB can get misdiagnosed and subsequently prescribed the incorrect medication and method of treatment. Caregivers and medical professionals alike can increase their understanding of symptoms for each disease to help them more quickly and accurately diagnose and treat each one.
The Lewy Body Dementia Resource Center provides literature, support groups, and help for caregivers grappling with care and treatment of a loved one who has Lewy Body Dementia. Our helpline is available 12 hours a day, 7 days a week for caregivers who have questions or are in need of support. Our online resource center seeks to bring awareness and support to caregivers of those suffering with Lewy Body Dementia. Please dont hesitate to reach out to us.
Recommended Reading: Prayers For Parkinson’s Disease
Epidemiology And Natural History Of Dlb And Pdd
Approximately 12% of those aged above 65 years are diagnosed with DLB worldwide , affecting approximately 5% of all dementia cases in those over the age of 75 . Its incidence is 0.71.4 new cases/100,000 person-years or 3.5/100,000 person-years . For PDD, the cumulative prevalence is of 75% of PD patients surviving more than 10 years , 83% after 20 years , and up to 95% by age 90 years , with an overall prevalence of 31.1% and incidence rates from 0.43 to 1.13/100,000 person-years , indicating that, annually, approximately 10% of a PD population will develop dementia . The data concerning age at disease or dementia onset are highly variable. Whereas in the Olmsted County study DLB patients were younger at symptom onset than those with PDD and had more hallucinations and cognitive fluctuations, others have reported younger age at disease onset in PDD , or no essential differences between disorders .
Outlook For Dementia With Lewy Bodies
How quickly dementia with Lewy bodies gets worse varies from person to person.
Home-based help will usually be needed, and some people will eventually need care in a nursing home.
The average survival time after diagnosis is similar to that of Alzheimer’s disease around 6 to 12 years. But this is highly variable and some people live much longer than this.
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with dementia, remember that you’re not alone. The NHS and social services, as well as voluntary organisations, can provide advice and support for you and your family.
You May Like: What Foods Should Be Avoided When Taking Levodopa
What Is Vascular Dementia
Vascular dementia is the second most common type of dementia in the UK after Alzheimers disease. It occurs when the brain is damaged due to a lack of blood flow.
Sometimes people have both vascular dementia and Alzheimers, giving them a diagnosis of mixed dementia.
If the vascular system within the brain becomes damaged so that the blood vessels leak or become blocked then blood cannot reach the brain cells and they will eventually die.
This death of brain cells can cause problems with memory, thinking or reasoning, and when these cognitive problems are bad enough to impact on daily life, it is known as vascular dementia.
Dementia symptoms specific to vascular dementia include stroke-like symptoms, suchas as muscle weakness, movement and thinking problems and mood changes, such as depression.
There are several different types of vascular dementia, due to the varying levels of damage on the affected part of the brain.
They include stroke-related dementia, single-infarct and multi-infarct dementia and subcortical vascular dementia.
What Are The Causes Of Lewy Body Dementia
The precise cause of LBD is unknown, but scientists are learning more about its biology and genetics. For example, we know that an accumulation of Lewy bodies is associated with a loss of certain neurons in the brain that produce two important chemicals that act as messengers between brain cells . One of these messengers, acetylcholine, is important for memory and learning. The other, dopamine, plays an important role in behavior, cognition, movement, motivation, sleep, and mood.
Scientists are also learning about risk factors for LBD. A risk factor is something that may increase the chance of developing a disease. Some risk factors can be controlled while others cannot. Age is considered the greatest risk factor. No specific lifestyle factor has been proven to increase one’s risk for LBD.
Other known risk factors for LBD include certain diseases and health conditions, particularly Parkinson’s disease and REM sleep behavior disorder, which have been linked to a higher risk of LBD.
Having a family member with LBD also may increase a person’s risk, though LBD is not considered a genetic disease. Variants in three genes APOE, SNCA, and GBA have been associated with an increased risk, but in most cases, the cause is unknown.
Recommended Reading: Fitflop Shoes For Parkinson’s
What Causes Dementia With Lewy Bodies
It is not yet known why Lewy bodies develop in the brain or exactly how they cause dementia. But we do know that Lewy body disease:
- can cause different symptoms depending on what parts of the brain have the biggest build-up of faulty proteins
- reduces the levels of important chemicals needed to send messages around the brain
- breaks the connections between nerve cells, eventually causing these cells to stop working
- usually develops over a period of many years typically when a person is approaching old age. Lewy bodies can be developing in the brain for a long time before any symptoms show.
Having Lewy body disease doesnt mean that a persons dementia is only caused by the build-up of Lewy bodies in their brain.
Many people with DLB also have a build-up of other proteins that cause Alzheimers disease. This is common in people over about 80 years old. For people with both DLB and Alzheimers, dementia symptoms are often more severe and progress more quickly.
Lewy Bodies: More Than Lbd
LBD is characterized by the presence of Lewy bodies in the nerve cells of the brain, meaning that LBD patients have Lewy bodies in the brain.2 However, Lewy bodies are also common with other conditions, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinsons disease. In fact, most people with PD also have Lewy bodies in their brain. However, even if they have Lewy bodies, not all Parkinsons patients will also develop LBD.2
You May Like: Voice Amplifiers For Parkinson’s
Dementia With Lewy Bodies Without Parkinsonism
I agree with the proposal of new criteria for the diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies . Previous criteria did not adequately differentiate DLB from Parkinson disease with dementia as outlined in the articles accompanying editorial.
Lewy body disease includes PD and DLB, thus there should be DLB without parkinsonism as well as PDD. The new criteria outlined four core clinical features: fluctuating cognition with pronounced variations in attention and alertness detailed, recurrent visual hallucinations REM sleep behavior disorder, which may precede cognitive decline and one or more spontaneous cardinal features of parkinsonism including bradykinesia, rest tremor, or rigidity. According to this criteria, a patient who has the first three clinical features but does not have parkinsonism may be diagnosed as DLB.
Braak et al. proposed that brainstem synucleinopathy progresses rostrally to affect the substantia nigra, which may cause parkinsonism. . However, these described patterns of synucleinopathy are not often observed in DLB, especially when synucleinopathy occurs in the absence of parkinsonism. Braak et al.s hypothesis would indicate that visual hallucinations are a result of occipital dysfunction. Meanwhile, attention and alertness are due to frontal dysfunction, which does not necessarily follow Braaks hypothesis. In addition, DLB patients with predominantly frontal dysfunction may not have parkinsonism.
How Is Lbd Different From Parkinsons Or Alzheimers

These diseases are similar in a lot of ways. But there are some key differences in the symptoms that affect people with LBD and when those symptoms happen.
LBD may not cause short-term memory loss like Alzheimerâs. People with both conditions have trouble with thinking, alertness, and paying attention. But in LBD, those problems come and go. The disease can also cause hallucinations, often in the first few years someone has LBD. People with Alzheimerâs usually donât have hallucinations until the later stages.
People with LBD also often act out their dreams and make violent movements when theyâre asleep. Itâs called REM sleep behavior disorder. Sometimes, itâs the first sign that someone has LBD.
LBD and Parkinsonâs disease both cause movement problems, like stiff muscles and tremors. But most people with Parkinsonâs donât have problems with their thinking and memory until the very later stages of their disease. Sometimes, they donât have it at all. In the type of LBD known as Parkinsonâs disease with dementia, these problems begin much sooner.
People with LBD also need different drugs for their condition than the ones that treat Parkinsonâs or Alzheimerâs.
Dont Miss: Que Es El Mal De Parkinson
Don’t Miss: Judy Woodruff Parkinson’s