Stage Four Of Parkinsons Disease
In stage four, PD has progressed to a severely disabling disease. Patients with stage four PD may be able to walk and stand unassisted, but they are noticeably incapacitated. Many use a walker to help them.
At this stage, the patient is unable to live an independent life and needs assistance with some activities of daily living. The necessity for help with daily living defines this stage. If the patient is still able to live alone, it is still defined as stage three.
What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Most patients with Parkinsons disease can maintain a good quality of life with medications. However, as the disease worsens, medications may no longer be effective in some patients. In these patients, the effectiveness of medications becomes unpredictable reducing symptoms during on periods and no longer controlling symptoms during off periods, which usually occur when the medication is wearing off and just before the next dose is to be taken. Sometimes these variations can be managed with changes in medications. However, sometimes they cant. Based on the type and severity of your symptoms, the failure of adjustments in your medications, the decline in your quality of life and your overall health, your doctor may discuss some of the available surgical options.
Stage Two Of Parkinsons Disease
Stage two is still considered early disease in PD, and it is characterized by symptoms on both sides of the body or at the midline without impairment to balance. Stage two may develop months or years after stage one.
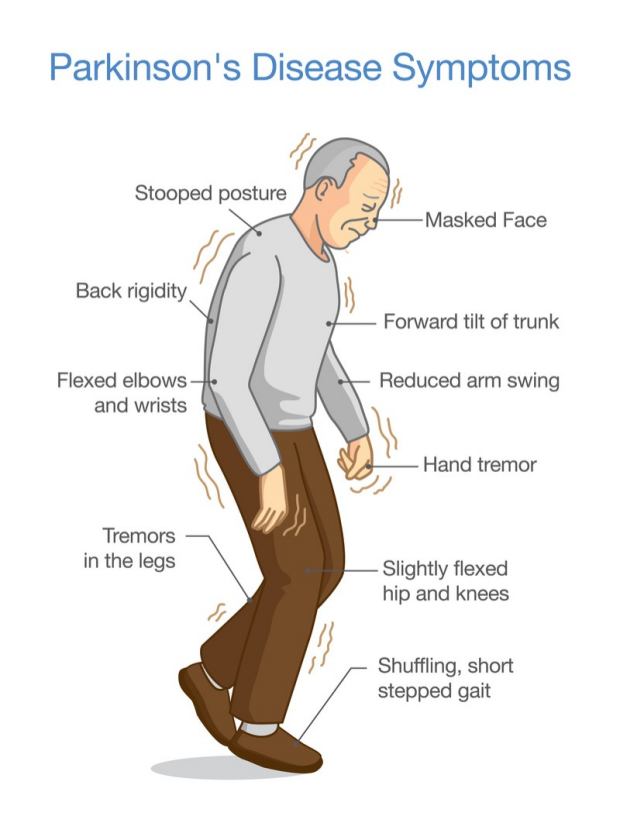
Symptoms of PD in stage two may include the loss of facial expression on both sides of the face, decreased blinking, speech abnormalities, soft voice, monotone voice, fading volume after starting to speak loudly, slurring speech, stiffness or rigidity of the muscles in the trunk that may result in neck or back pain, stooped posture, and general slowness in all activities of daily living. However, at this stage the individual is still able to perform tasks of daily living.
Diagnosis may be easy at this stage if the patient has a tremor however, if stage one was missed and the only symptoms of stage two are slowness or lack of spontaneous movement, PD could be misinterpreted as only advancing age.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Side Effects Of Medication
Depression May Be An Early Symptom Of Parkinsons
Depression is one of the most common, and most disabling, non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease. As many as 50 per cent of people with Parkinsons experience the symptoms of clinical depression at some stage of the disease. Some people experience depression up to a decade or more before experiencing any motor symptoms of Parkinsons.
Clinical depression and anxiety are underdiagnosed symptoms of Parkinsons. Researchers believe that depression and anxiety in Parkinsons disease may be due to chemical and physical changes in the area of the brain that affect mood as well as movement. These changes are caused by the disease itself.
Here are some suggestions to help identify depression in Parkinsons:
- Mention changes in mood to your physician if they do not ask you about these conditions.
- Complete our Geriatric Depression Scale-15 to record your feelings so you can discuss symptoms with your doctor. Download the answer key and compare your responses.
- delusions and impulse control disorders
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinsons disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinsons disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinsons disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
Don’t Miss: Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome Drugs To Avoid
Discuss With Your Physician
Non-motor symptoms can sometimes be difficult to recognize. Therefore, it is important to make your doctor aware of them.
One useful resource is the PD NMS Questionnaire. You can use this to record your symptoms and discuss them with your doctor.
Dr. Ron Postuma, whose research was funded by donations to the Parkinson Canada Research Program, has also developed tools to help people with Parkinsons and their physicians identify and manage non-motor symptoms.
Clinical Evaluation Of Motor Symptoms
The motor stage of PD was evaluated according to the UPDRS scale during ON condition. UPDRS I assess mentation, behavior, and mood UPDRS II evaluates Activities of daily living , including speech, swallowing, handwriting, dressing, hygiene, falling, salivating, turning in bed, walking, and cutting food . UPDRS III is a score for motor examination . Each item of those scales scored on a scale from 0 to 4. UPDRS IV assesses the treatments complications in the week preceding the examination . UPDRS V is the Hoehn and Yahrs staging of severity of PD , and UPDRS VI is Schwab and England to assess independency on activity of daily living on OFF and on ON conditions .
The clinical type at onset of the disease was classified as tremor dominant, akinetic-rigid, or mixed form according to criteria used by Rajput et al. . Tremor dominant subtype referred to patients in whom the tremor was the dominant feature compared to bradykinesia and rigidity. Patients with prominent bradykinesia and rigidity with no visible tremor were classified as akinetic-rigid subtype and those who had comparable severity of bradykinesia, rigidity, and tremor were classified as mixed subtype. The first side and limb affected at the onset of the disease were also recorded. Levodopa equivalent daily dose was calculated based on Tomlinson et al. recommendations .
Recommended Reading: What Is The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s In Early Stages
Managing Depression In Parkinsons Disease
People with Parkinsons, family members and caregivers may not always recognize the signs of depression and anxiety. If you are experiencing depression as a symptom of Parkinsons, it is important to know it can be treated.
Here are some suggestions:
- For information and support on living well with Parkinsons disease, contact our Information and Referral line.
- As much as possible, remain socially engaged and physically active. Resist the urge to isolate yourself.
- You may want to consult a psychologist and there are medications that help relieve depression in people with Parkinsons, including nortriptyline and citalopram .
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease is sometimes difficult, since early symptoms can mimic other disorders and there are no specific blood or other laboratory tests to diagnose the disease. Imaging tests, such as CT or MRI scans, may be used to rule out other disorders that cause similar symptoms.
To diagnose Parkinsons disease, you will be asked about your medical history and family history of neurologic disorders as well as your current symptoms, medications and possible exposure to toxins. Your doctor will look for signs of tremor and muscle rigidity, watch you walk, check your posture and coordination and look for slowness of movement.
If you think you may have Parkinsons disease, you should probably see a neurologist, preferably a movement disorders-trained neurologist. The treatment decisions made early in the illness can affect the long-term success of the treatment.
You May Like: How Long Does A Person Live With Parkinson’s Disease
The Clinical Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
Department of Neurology, Broomfield Hospital, Chelmsford, Essex, CM1 7ET UK
Queen Mary School of Medicine and Dentistry, University of London, London, UK
Department of Neurology, Broomfield Hospital, Chelmsford, Essex, CM1 7ET UK
Queen Mary School of Medicine and Dentistry, University of London, London, UK
Cognitive And Psychiatric Symptoms
- depression and anxiety
- mild cognitive impairment slight memory problems and problems with activities that require planning and organisation
- dementia a group of symptoms, including more severe memory problems, personality changes, seeing things that are not there and believing things that are not true
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease And Sleep
Disturbances In Autonomic Function
Autonomic dysfunction may present prior to the diagnosis or become apparent with disease progression or be induced by medication . All areas of autonomic function may be affected and this has been reported to affect daily life of over 50% of patients . The autonomic dysfunction is considered because of involvement of both the central and peripheral postganglionic autonomic nervous system . Orthostatic hypotension affects 30â40% of patients. This is defined as a fall in systolic blood pressure of > 20 mm Hg or in diastolic blood pressure > 10 mm Hg on either standing or head-up tilt to at least 60 degrees within 3 min . On assuming the upright posture, hypotension-induced hypoperfusion of the brain can result in dizziness, visual disturbances and impaired cognition that may precede loss of consciousness. In PD, the blood pressure drop may last several minutes . Duration of PD may be unrelated to the occurrence of orthostatic hypotension . In elderly PD patients, this may mainly occur after food intake .
Gastrointestinal symptoms are common. There is slowing of mobility of the gastrointestinal tract with symptoms such as postprandial fullness and gastric retention, but slow-transit constipation is by far the most common, occurring in 70â80% . Patients may also experience difficulties in rectal evacuation because of rectal sphincter dysfunction .
The Motor Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
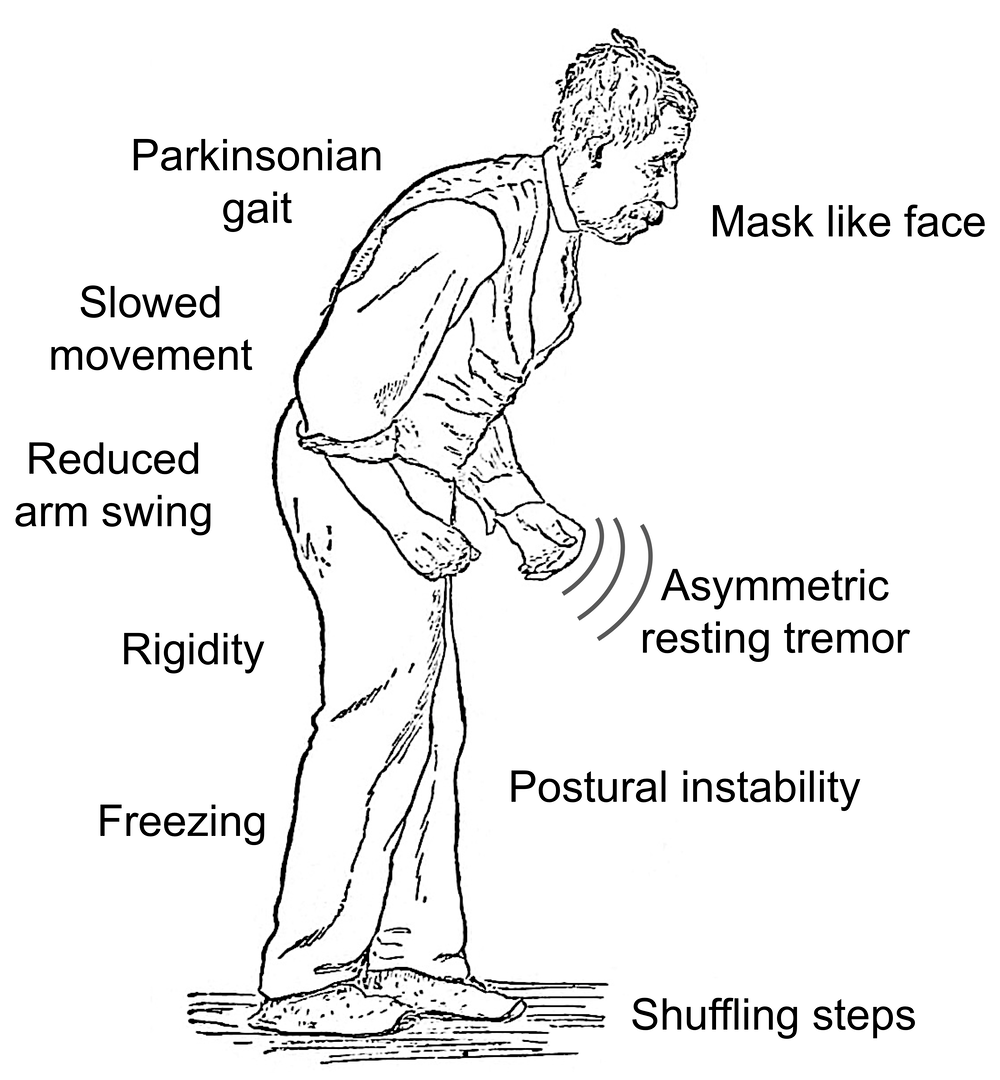
| Step 1: Diagnosis of Parkinsonian syndrome |
| Bradykinesia |
| And at least one of the following |
| Muscular rigidity |
| Levodopa response for 5 years or more |
| Clinical course of 10 years or more |
- Source: Hughes et al. .
Postural stability may be affected either early or later in the disease process and this may lead to falls and injuries. Early falls are atypical for those who are younger at onset but age is an independent risk factor for falls in PD and, in the elderly, the disease is sometimes first diagnosed in hospitals after a fall. A study by Wood et al. showed that falls occurred in 68% of 109 patients with PD with a mean age of 75 years and mean disease duration of 3 years. Another study reported falls in 62% of patients with PD . Predictors of falls other than older age include duration of disease, dementia, symmetrical onset, postural and autonomic instability .
Oral motor disorders are common. Speech disturbances such as very quiet and hurried speech occur in more than half of the patients , swallowing problems have been reported in 40â80% and a quarter of the patients report dribbling of saliva .
You May Like: Keto Diet And Parkinson’s Disease With William Curtis
Support For People With Parkinsons Disease
Early access to a multidisciplinary support team is important. These teams may include doctors, physiotherapists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, dietitians, social workers and specialist nurses. Members of the team assess the person with Parkinsons disease and identify potential difficulties and possible solutions.There are a limited number of multidisciplinary teams in Victoria that specialise in Parkinsons disease management. But generalist teams are becoming more aware of how to help people with Parkinsons disease.
General Approach To Management
The primary goal in the management of PD is to treat the symptomatic motor and nonmotor features of the disorder, with the objective of improving the patients overall quality of life. Appropriate management requires an initial evaluation and diagnosis by a multidisciplinary team consisting of neurologists, primary care practitioners, nurses, physical therapists, social workers, and pharmacists., It is also important that the patient and his or her family have input into management decisions.
Effective management should include a combination of nonpharmacological and pharmacological strategies to maximize clinical outcomes. To date, therapies that slow the progression of PD or provide a neuroprotective effect have not been identified., Current research has focused on identifying biomarkers that may be useful in the diagnosis of early disease and on developing future disease-modifying interventions.,
You May Like: What Happens If Parkinson’s Is Left Untreated
Diagnosis And Management Of Parkinsons Disease
There are no diagnostic tests for Parkinsons. X-rays, scans and blood tests may be used to rule out other conditions. For this reason, getting a diagnosis of Parkinsons may take some time.
No two people with Parkinsons disease will have exactly the same symptoms or treatment. Your doctor or neurologist can help you decide which treatments to use.
People can manage their Parkinsons disease symptoms through:
- seeing a Doctor who specialises in Parkinsons
- medication
- multidisciplinary therapy provided for example, by nurses, allied health professionals and counsellors
- deep brain stimulation surgery .
Stiffness And Slow Movement
Parkinsons disease mainly affects adults older than 60. You may feel stiff and a little slow to get going in the morning at this stage of your life. This is a completely normal development in many healthy people. The difference with PD is that the stiffness and slowness it causes dont go away as you get up and start your day.
Stiffness of the limbs and slow movement appear early on with PD. These symptoms are caused by the impairment of the neurons that control movement. A person with PD will notice jerkier motions and move in a more uncoordinated pattern than before. Eventually, a person may develop the characteristic shuffling gait.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s And Similar Diseases
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinsons disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare teams efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinsons disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a nervous system disease that affects your ability to control movement. The disease usually starts out slowly and worsens over time. If you have Parkinsons disease, you may shake, have muscle stiffness, and have trouble walking and maintaining your balance and coordination. As the disease worsens, you may have trouble talking, sleeping, have mental and memory problems, experience behavioral changes and have other symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s And Restless Leg Syndrome
Stage Three Of Parkinsons Disease
Stage three is considered mid-stage and is characterized by loss of balance and slowness of movement.
Balance is compromised by the inability to make the rapid, automatic and involuntary adjustments necessary to prevent falling, and falls are common at this stage. All other symptoms of PD are also present at this stage, and generally diagnosis is not in doubt at stage three.
Often a physician will diagnose impairments in reflexes at this stage by standing behind the patient and gently pulling the shoulders to determine if the patient has trouble maintaining balance and falls backward . An important clarifying factor of stage three is that the patient is still fully independent in their daily living activities, such as dressing, hygiene, and eating.
How Is Parkinsons Disease Treated

There is no cure for Parkinsons disease. However, medications and other treatments can help relieve some of your symptoms. Exercise can help your Parkinsons symptoms significantly. In addition, physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech-language therapy can help with walking and balance problems, eating and swallowing challenges and speech problems. Surgery is an option for some patients.
Don’t Miss: New Cure For Parkinson’s Disease
Stage Five Of Parkinsons Disease
Stage five is the most advanced and is characterized by an inability to rise from a chair or get out of bed without help, they may have a tendency to fall when standing or turning, and they may freeze or stumble when walking.
Around-the-clock assistance is required at this stage to reduce the risk of falling and help the patient with all daily activities. At stage five, the patient may also experience hallucinations or delusions.
While the symptoms worsen over time, it is worth noting that some patients with PD never reach stage five. Also, the length of time to progress through the different stages varies from individual to individual. Not all the symptoms may occur in one individual either. For example, one person may have a tremor but balance remains intact. In addition, there are treatments available that can help at every stage of the disease. However, the earlier the diagnosis, and the earlier the stage at which the disease is diagnosed, the more effective the treatment is at alleviating symptoms.
Stage One Of Parkinsons Disease
In stage one, the earliest stage, the symptoms of PD are mild and only seen on one side of the body , and there is usually minimal or no functional impairment.
The symptoms of PD at stage one may be so mild that the person doesnt seek medical attention or the physician is unable to make a diagnosis. Symptoms at stage one may include tremor, such as intermittent tremor of one hand, rigidity, or one hand or leg may feel more clumsy than another, or one side of the face may be affected, impacting the expression.
This stage is very difficult to diagnose and a physician may wait to see if the symptoms get worse over time before making a formal diagnosis.
Read Also: Working Out With Parkinson’s