How Environmental Factors Could Cause Parkinsons Disease
Scientists differ about the extent that brain cells are impacted by environmental factors. However, the statistics associated with the disease show that the environment can play a very large role in whether parkinsons disease develops.
Most often, it is exposure to toxic chemicals that could play a role in the development of Parkinsons disease. Usually, these combine with genetic factors to produce the conditions that cause Parkinsons.
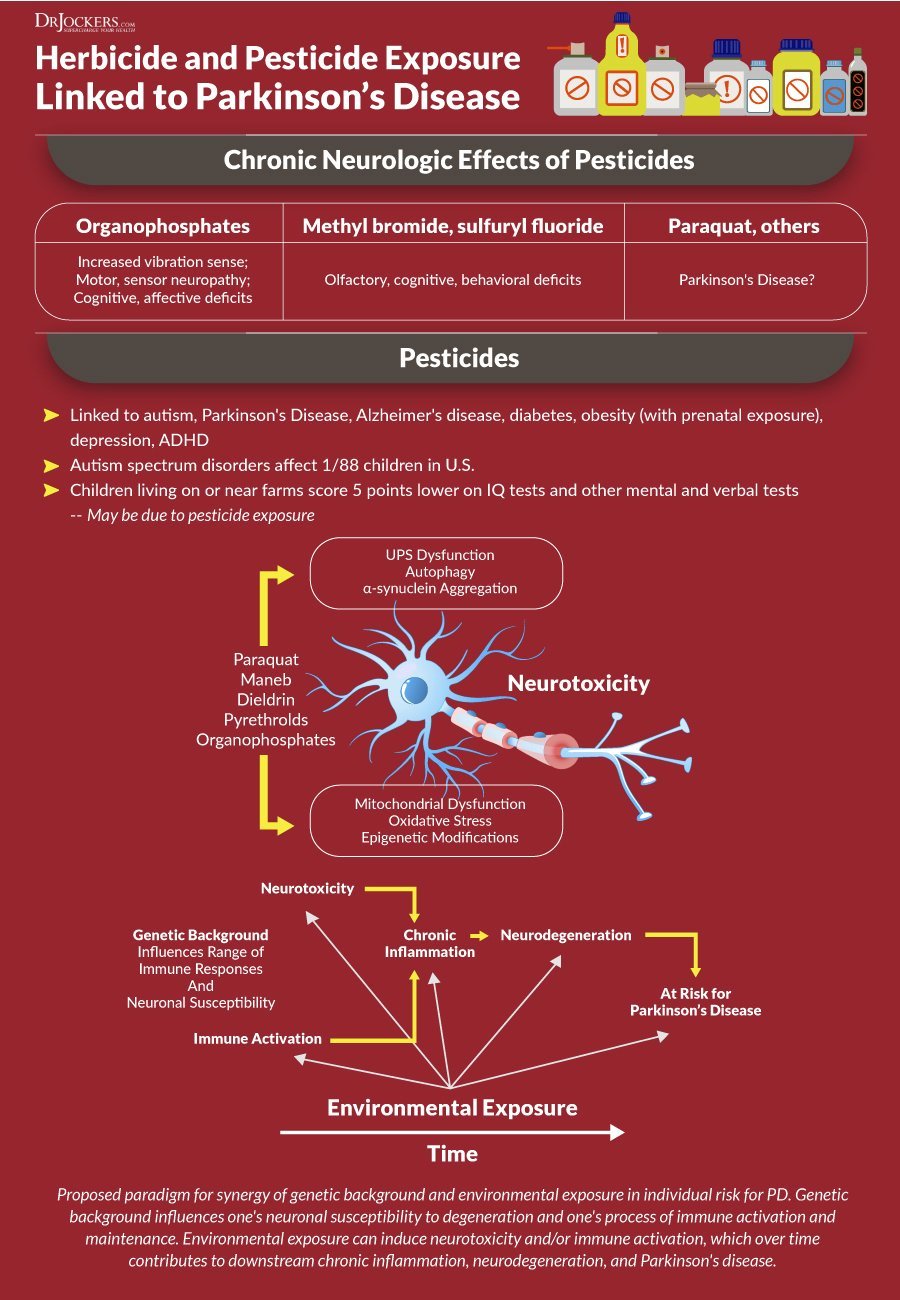
Increasing scientific evidence suggests that Parkinsons may be caused by environmental factors such as exposure to herbicides such as Paraquat.
Exposure To Pesticides In The Military
Agent Orange was an herbicide that US troops sprayed in Vietnam from 1961-1971 to kill trees and crops that provided protection and food to the rival army. It is a mixture of two chemicals: 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Agent Orange was also contaminated with Dioxin, a chemical even more damaging than Agent Orange itself, since it is very long-lasting.
The effects of Agent Orange on both the Vietnamese population and on American soldiers has been studied extensively, but with much variability in the results. Birth defects have been attributed to Agent Orange exposure, as well as multiple types of cancer.
With the understanding that the Veteran community served selflessly on behalf of the American people and therefore deserve the protection and support of the American government, the Agent Orange Act was passed in 1991, allowing the Department of Veteran Affairs to declare certain conditions presumptive to exposure to Agent Orange, even if the scientific data associating Agent Orange with that condition was not airtight.
The list of conditions has grown over the years, and in 2010, PD was added. Read here about how veterans who may have been exposed to Agent Orange and have subsequently developed PD are eligible for VA healthcare and disability compensation. APDA offers a free booklet specifically for veterans to help them find the care and support they need.
Pesticide And Herbicide Exposure
A strong link has been shown between PD and exposure to pesticides and herbicides. We need more Parkinsons-specific research to better understand what causes PD and to work to prevent it and help eliminate the risk of getting the disease, when it comes to all environmental risk factors and whether genetics can cause an increased risk in developing Parkinsons.
One herbicide that has been linked to Parkinsons is paraquat, a widely used commercial herbicide in the U.S. that is banned in 32 countries, including the European Union and China. The Parkinsons Foundation, along with the Unified Parkinsons Advocacy Council, signed two letters to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency encouraging them to cancel the registration of paraquat based on strong scientific research linking the herbicide to Parkinsons disease. In October 2020, the EPA re-approved paraquat for use in the U.S. Without additional action, paraquat will remain legal for sale and use in the U.S. for the next 15 years.
Recommended Reading: How Hereditary Is Parkinson’s Disease
Environmental Factors In Parkinsons Disease
Here are environmental factors that may play a role in the development of Parkinsons disease:
Although environmental exposure to these and other toxins is of continued research interest, its hard to determine if any one substance is a culprit. Most often, individual cases of Parkinsons disease result from a complex interplay between genetics and environmental and other factors.
Targeting Parkinsons-Linked Protein Could Neutralize 2 of the Diseases Causes
Researchers report they have discovered how two problem proteins known to cause Parkinsons disease are chemically linked, suggesting that someday, both could be neutralized by a single drug designed to target the link.
Chemical That Triggers Parkinson’s Disease Discovered
- Date:
- Saint Louis University
- Summary:
- The key brain chemical that causes Parkinson’s disease has been discovered. This is a breakthrough finding that could pave the way for new, far more effective therapies to treat one of the most common and debilitating neurological disorders.
Researchers at the Saint Louis University School of Medicine have discovered the key brain chemical that causes Parkinson’s disease – a breakthrough finding that could pave the way for new, far more effective therapies to treat one of the most common and debilitating neurological disorders.
Currently, the main approach for treating Parkinson’s disease, which afflicts more than 1.5 million Americans, is to replace dopamine that’s lost when the cells that produce it die off and cause the disorder. With this new research, however, scientists can better work toward ‘neuroprotective’ therapies – those that actually block dopamine cells from dying off in the first place.
“We believe this work represents a very significant breakthrough in understanding the complicated chemical process that results in Parkinson’s disease,” said William J. Burke, M.D., Ph.D., professor of neurology at the Saint Louis University School of Medicine and the study’s lead author.
“For the first time, we’ve identified the chemical that triggers the events in the brain that cause this disorder,” Burke added. “We believe these findings can be used to develop therapies that can actually stop or slow this process.”
Story Source:
Don’t Miss: What’s The Difference Between Parkinson’s And Ms
Toxic Substances That Have Been Linked To Parkinsons Disease
There are numerous environmental toxins that researchers have tied to the neurological disorders known as parkinson disease. Here are some that have been linked:
- Agent Orange This was a chemical defoliant used in Vietnam that is already tied to cancer. While there is no definitive link with Parkinsons, the VA at least believes that there is a possibility that the two are tied.
- Solvents Some studies have shown a link between Trichloroethylene, a substance contained in many solvents, and Parkinsons.
- PCBs polychlorinated biphenyls were extensively used in the 1970s. They have been often found in the brains of people who have suffered from Parkinsons.
- Pesticides and herbicides -substances such as insecticides, pesticides and herbicides contain chemicals that researchers have strongly linked with higher incidences of Parkinsons. One of the leading contributors is considered to be Paraquat. For information on Paraquat Parkinsons lawsuits, look here.
Genetic Forms Of Parkinsons Disease
Despite all this body of evidence, the relatively low incidence of PD suggests that the individual genetic background plays an important role in the pathogenesis of the disease. What are the genetic alterations that predispose to the development of PD and why?
Already a century ago it was noticed that PD patients had affected relatives . The role of genetic inheritance in PD has been increasingly important during the past couple of decades because of different studies. Despite the complexity of achieving good quality epidemiologic studies due to diagnostic difficulties, different studies have confirmed that PD is more common between family members . Generally, the risk of having the disease among relatives is 2 to 3 times greater than in the general population . Also, studies on homozygotic twins have shown that although there is no significant concordance in late onset disease cases , it becomes significant in early onset cases. Therefore, one could say that early PD is usually genetically determined.
Table 1 Known genetic mutations in PD
Recommended Reading: What Is The Life Expectancy Of A Person With Parkinson’s
Rotenone: From Pesticide To Modeling Pd
Among the toxic animal models of PD, rotenone represents one of the most recently used approaches. Rotenone is the most potent member of the rotenoids, a family of natural cytotoxic compounds extracted from various parts of Leguminosa plants. Rotenone’s chemical structure is presented in .
Chemical structure of rotenone.
In contrast to the 6-OHDA and MPTP models, in rotenone-infused rats, some of the remaining substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons contain proteinaceous inclusions.,, Like LBs in PD, these inclusions are immunoreactive for both ubiquitin and -synuclein, and by electron microscopy they appear composed of a dense core with fibrillar peripheral elements. Likewise in PD in which neurodegeneration extends beyond the dopaminergic system, rotenone infusion is associated with 35% reduction in serotonin transporter density in the striatum, 26% reduction of noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus, and 29% reduction in cholinergic neurons in the pedunculopontine nucleus.
Based on this review, it may be concluded that the chronic administration of rotenone has still a long way to go to become a routine PD model, due to its inconsistent and unpredictable effect on the nigrostriatal pathway. Unless these problems are resolved, it is unlikely that preclinical neuroprotection studies could be carried out successfully in such a model.
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
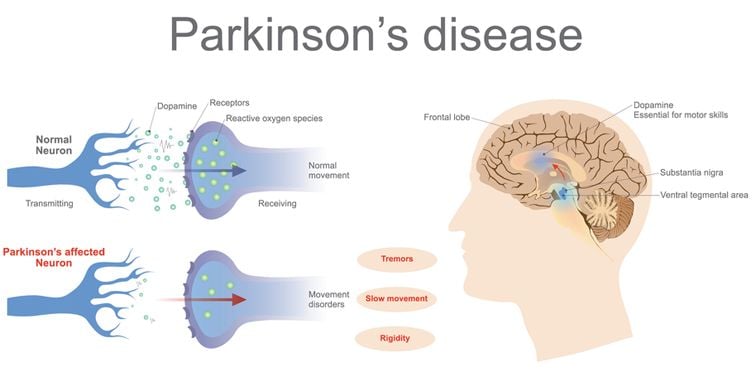
Parkinsons disease is a chronic, progressive neurological disease that currently affects about 1 million Americans. Parkinsons disease involves a small, dark-tinged portion of the brain called the substantia nigra. This is where you produce most of the dopamine your brain uses. Dopamine is the chemical messenger that transmits messages between nerves that control muscle movements as well as those involved in the brains pleasure and reward centers. As we age, its normal for cells in the substantia nigra to die. This process happens in most people at a very slow rate.
But for some people, the loss happens rapidly, which is the start of Parkinsons disease. When 50 to 60 percent of the cells are gone, you begin to see the symptoms of Parkinsons.
Also Check: Can Parkinson’s Psychosis Be Reversed
The Neurotoxic Herbicide Paraquat
The potent herbicide paraquat is another prototypic toxin known to exert deleterious effects through oxidative stress. Indeed, as reviewed elsewhere, paraquat toxicity is mediated by redox cycling with cellular diaphorase such as nitric oxide synthase, yielding ROS. As detailed, the actual reduction-oxidation cycling reaction of paraquat can thus be depicted in . Thus far, there have been several cases of lethal poisoning resulting from ingestion or dermal exposure. For many years, experimental studies using paraquat were focusing on its effects on lung, liver, and kidney probably because the toxicity induced by this herbicide in these organs is responsible for death after acute exposure. However, significant damage to the brain is seen in individuals who died from paraquat intoxication, despite the fact that paraquat poorly crosses the BBB spontaneously. Furthermore, epidemiological studies have suggested an increased risk for PD due to paraquat exposure, raising the possibility that paraquat could be an environmental parkinsonian toxin. In keeping with this, it is relevant to point out that paraquat exhibits a striking structural similarity to MPTP toxic metabolite 1-methyl-4-pheylpyridinium .
Has Anything Changed Over Time
Since most of the studies concerning PD and rural living were done decades ago, a recent study sought to revisit this issue since farming life has changed in recent times. Pesticide use is reduced, there has been a large migration from rural to urban areas, and there is less dependence on well water in rural communities.
The new study was conducted in Finland and looked at the incidence of PD in rural versus urban areas. Interestingly, rural living remained a risk factor for PD. It is possible that current diagnoses of PD continue to reflect the environmental exposures of decades ago, and that risk reduction in rural areas due to decreased pesticide use and other changes in farming life may show more benefits in the future. However, the study suggests that we may not yet fully understand how the rural environment affects Parkinsons risk.
Don’t Miss: How To Check For Parkinson’s Disease
Rural Living And An Increased Risk Of Pd
In the 1980s, studies were conducted that showed that early-age exposure to a rural environment as well as exposure to well water were associated with development of PD later in life. Subsequently, multiple additional studies looked at these questions. The studies are mixed in their conclusions, but overall the evidence supports associations between increased PD risk with each of the following:
- farming as an occupation,
- well water drinking, and
- living in a rural area.
Of course, all these categories are inter-related, since farmers live on farms in rural areas, are exposed to farm animals, are more likely than urban dwellers to drink well water and use pesticides. The studies were attempting to tease out why rural environments increased the risk of PD. Do only those who actually farm have an increased risk or is it enough to live on a farm? Is pesticide exposure the reason for the increased risk? Well water exposure? Exposure to farm animals? Or is it another element of rural life?
In the end, epidemiologic data supports the assertion that each of these elements increases the risk of PD. Of note, all of the increased risks in these studies are small on the order of 1.5-2 times the risk of the general population.
Treatment: Drugs That Make Dopamine
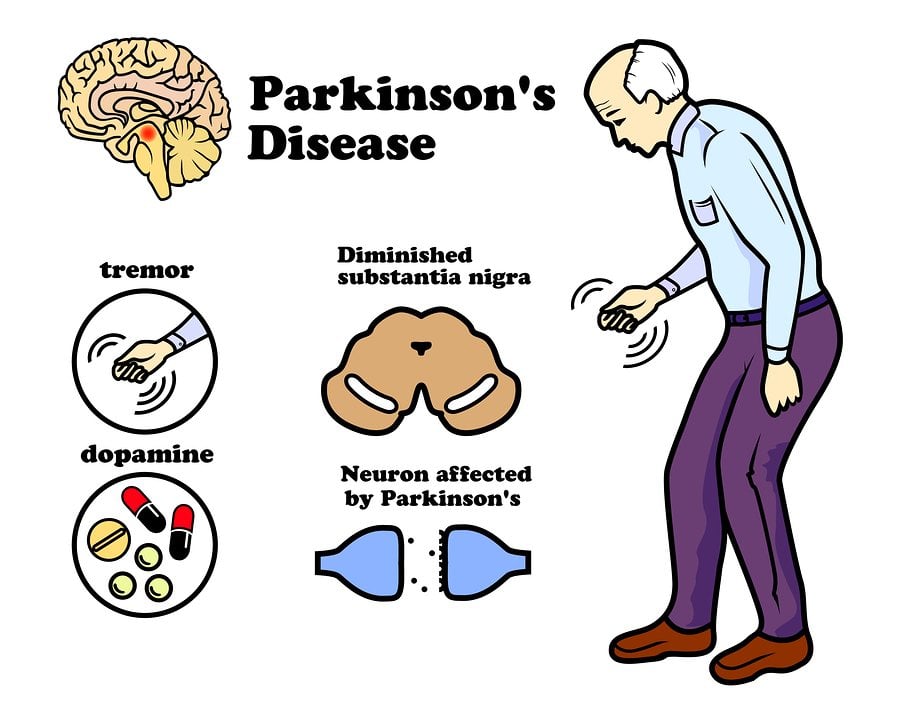
Parkinson’s affects nerve cells in your brain that make a chemical called dopamine. As a result, levels of the chemical fall. Doctors usually start treatment with levodopa . Your brain turns it into dopamine. But it can make you sick to your stomach, so youâll probably take it with another medicine called carbidopa to control these side effects. The combination drug is called carbidopa-levodopa .
Recommended Reading: How Many People In Us Have Parkinsons
Can Parkinsons Disease Be Prevented
Sadly, no.
It is not possible to prevent Parkinsons disease, but some believe that lifelong healthy habits may reduce ones risk of developing the condition. Some medications may also relieve some of its symptoms.
In some PD patients, particularly those who are at the late stage of the disease, surgery may be an option to help improve symptoms.
Some experts also advise doing rpeventive measures such as wearing gloves and other protectvie equipment when applying pesticides as it may help protect you against the disease.
Treatment: Boosting Dopamines Effects
Your doctor might give you one of these, alone or with another drug:
- Dopamine agonists: They act like dopamine but donât raise levels of it in your brain. You can take them with any drug that has levodopa. You might try pramipexole or ropinirole .
- COMT Inhibitors: They help levodopa last longer. You might get entacapone or tolcapone .
- MAO-B inhibitors: These stop your brain from breaking down levodopa. You could get selegiline or rasagiline .
Don’t Miss: What Happens With Parkinson’s
What Are The Causes
Drug-induced parkinsonism is caused by medications that reduce dopamine levels in the brain. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that works to control bodily movements.
Dopamine is also part of the brains reward system. It helps you feel pleasure and enjoyment, and it supports your ability to learn and focus.
Medications that bind to and block dopamine receptors are called dopamine antagonists. These medications arent used to treat Parkinsons disease. Rather, theyre used to treat other conditions that might seriously impact your quality of life.
If your doctor has prescribed a medication that causes unwanted side effects, you may have options. You may also decide that the side effects are worth it if the medication effectively treats your condition.
Some medications that cause drug-induced parkinsonism include:
How You Lose Dopamine Production
Damaged nerve cells can be what results in a decreased ability of the brain to create dopamine. Generally, some kind of degradation of the brain cells will reduce dopamine production.
There is some genetic link to parkinsons disease. For example, specific genetic mutations can impact the dopamine production. Far more common is that exposure to something in the environment can impact the brain.
Read Also: Lewy Body Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms
Environmental Toxins Linked To Parkinson’s
New Studies Support Link Between Chemicals and Parkinson’s Disease
Researchers say the findings support evidence of a possible link between environmental toxins and Parkinson’s disease and may help explain why some people with genetic risk factors for the disease get it while others do not.
Parkinson’s disease is a common neurological disorder that can occur randomly or as the result of inherited gene mutations.
In the study, which appears in Current Biology, researchers looked at fruit flies lacking both forms of a gene that is associated with the inherited form of Parkinson’s disease. These specially bred fruit flies became extremely sensitive to the herbicide paraquat and the insecticide rotenone and died after exposure.
The Human Parkinsonian Neurotoxin 1
In the early 1980s, several drug users from Northern California developed an acute state of akinesia following the intravenous injection of a street preparation of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-4-propionpiperidine , an analog of the narcotic meperidine. After fine detective work, it was found that MPTP, which was inadvertently produced during the illicit synthesis of MPPP, was the culprit behind this dramatic clinical picture. The chemical structures of MPPP and MPTP are shown in .
Comparison of chemical structures of MPPP and MPTP.
Read Also: Nursing Home Care For Parkinson’s Patients
What Helps Parkinson Causes What Protects Dopamine Cells
Turns out that no, it is not the caffeine!
Researchers at the Kinsmen Laboratory of Neurological Research, University of British Columbia, tested the ingredients in coffee.
- They discovered that a compound called quercetin is in fact the main neuro protective compound in coffee against Parkinson’s disease as well as Alzheimer’s disease.
How does it work?
They found that the quercetin actually reduced the amount of damage to the DNA, and the fats and proteins in the brain cells. .
- The quercetin in the coffee, in turn increased the amount to GSH, or glutathione in the cells.
- It is already known that improving glutathione is very important for PD patients. Glutathione, GSH is the protective molecule that reduces damage inside brain and nerve cells, and keeps them healthy.
So, drink more coffee!!
But protecting your brain is also multi-factoral! You may need a different Parkinson diet and supplements than others.
- Improving the protective molecule in the brain, glutathione is one of the best things you can do against Parkinson causes.
Unfortunately, it is not as simple as taking a pill! You have to take the pre-cursors, or building blocks.
Is Surgery An Option
If medicine doesnât work well enough, your doctor may suggest deep brain stimulation . In DBS, your doctor implants electrodes deep in the brain. A device connected to them delivers electrical pulses. Those pulses can help control the tremors caused by Parkinson’s.
In the past, doctors sometimes used other operations to damage the brain in ways to help with movement symptoms. But they rarely use those surgeries now.
Recommended Reading: Does Parkinson’s Cause Pain In Legs