Experience And Expertise In Diagnosis And Care
Parkinsonism is a shorthand description for body movements that have become slow, small, stiff, shaky, and unsteady. Most cases of Parkinsonism develop after age 50 and are caused by neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinsons disease . Some Parkinsonisms are the result of strokes, medication side effects, or another neurological condition such as normal pressure hydrocephalus.
UT Southwesterns Movement Disorders team has extensive experience in evaluating and treating Parkinsonism, PD, and other related disorders. Our clinical programs provide patients with access to the latest treatment options and information about medications to manage symptoms, as well as other services as needed.
Living With Parkinsons Disease
Depending on severity, life can look very different for a person coping with Parkinsons Disease. As a loved one, your top priority will be their comfort, peace of mind and safety. Dr. Shprecher offered some advice, regardless of the diseases progression. Besides movement issues Parkinsons Disease can cause a wide variety of symptoms including drooling, constipation, low blood pressure when standing up, voice problems, depression, anxiety, sleep problems, hallucinations and dementia. Therefore, regular visits with a neurologist experienced with Parkinsons are important to make sure the diagnosis is on target, and the symptoms are monitored and addressed. Because changes in your other medications can affect your Parkinsons symptoms, you should remind each member of your healthcare team to send a copy of your clinic note after every appointment.
Dr. Shprecher also added that maintaining a healthy diet and getting regular exercise can help improve quality of life. Physical and speech therapists are welcome additions to any caregiving team.
What Are The Later Secondary Signs And Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
While the main symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are movement-related, progressive loss of muscle control and continued damage to the brain can lead to secondary symptoms. These secondary symptoms vary in severity, and not everyone with Parkinson’s will experience all of them, and may include:
You May Like: Judy Woodruff Parkinson’s
Is There Any Treatment
There is currently no effective treatment for PSP and symptoms usually do not respond to medications.
- Parkinsons disease medications, such as ropinirole, rarely provide additional benefit. In some individuals, other antiparkinsonian medications, such as levodopa, can treat the slowness, stiffness, and balance problems associated with PSP, but the effect is usually minimal and short-lasting.
- Botulinum toxin, which can be injected into muscles around the eyes, can treat excessive eye closing.
- Some antidepressant drugs may offer some benefits beyond treating depression, such as pain relief and decreasing drooling.
Non-drug treatment for PSP can take many forms.
- Weighted walking aids can help individuals avoid falling backward.
- Bifocals or special glasses called prisms are sometimes prescribed for people with PSP to remedy the difficulty of looking down.
- Exercise supervised by a healthcare professional can keep joints limber but formal physical therapy has no proven benefit in PSP.
A gastrostomy may be necessary when there are swallowing disturbances or the definite risk of severe choking.
Deep brain stimulationwhich uses surgically implanted electrodes and a pacemaker-like medical device to deliver electrical stimulation to specific areas in the brain to block signals that cause the motor symptoms of several neurological disordersand other surgical procedures commonly used in individuals with Parkinson’s disease have not been proven effective in PSP.
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosis is difficult at every stage of the disease, but particularly in the early stages. No single test can provide a diagnosis. A diagnosis will likely involve physical and neurological examinations, conducted over time to assess changes in reflexes, coordination, muscle strength, and mental function. Your doctor might also see how you respond to medicine.
You may need to have brain imaging tests to rule out other conditions that might be causing your symptoms. Such tests could include MRI and CT scans and possibly some other types of scans. Blood tests may also be done to exclude other illnesses.
Also Check: Sam Waterston Parkinson’s
Incidence Of Parkinsons Disease
Its estimated that approximately four people per 1,000 in Australia have Parkinsons disease, with the incidence increasing to one in 100 over the age of 60. In Australia, there are approximately 80,000 people living with Parkinsons disease, with one in five of these people being diagnosed before the age of 50. In Victoria, more than 2,225 people are newly diagnosed with Parkinsons every year.
What Causes Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons disease occurs when nerve cells in the basal ganglia, an area of the brain that controls movement, become impaired and/or die. Normally, these nerve cells, or neurons, produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems of Parkinson’s. Scientists still do not know what causes cells that produce dopamine to die.
People with Parkinson’s also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinson’s, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying-down position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinson’s contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons disease and Lewy body dementia.
Recommended Reading: Fitflop Shoes For Parkinson’s
What Is Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
Progressive supranuclear palsy is a rare brain disorder that causes problems with movement, walking and balance, and eye movement. It results from damage to nerve cells in the brain that control thinking and body movement. The disorders long name indicates that the disease worsens and causes weakness by damaging certain parts of the brain above nerve cell clusters called nuclei that control eye movements.
PSP is different than Parkinsons diseaseanother movement disorderalthough they share some symptoms . Currently there is no effective treatment for PSP, but some symptoms can be managed with medication or other interventions.
Where Can I Get More Information
For more information on neurological disorders or research programs funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, contact the Institute’s Brain Resources and Information Network at:
Office of Neuroscience Communications and EngagementNational Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeNational Institutes of HealthBethesda, MD 20892
NINDS health-related material is provided for information purposes only and does not necessarily represent endorsement by or an official position of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke or any other Federal agency. Advice on the treatment or care of an individual patient should be obtained through consultation with a physician who has examined that patient or is familiar with that patient’s medical history.
All NINDS-prepared information is in the public domain and may be freely copied. Credit to the NINDS or the NIH is appreciated.
Recommended Reading: Zhichan Capsule
How Is Parkinsons Diagnosed
Doctors use your medical history and physical examination to diagnose Parkinson’s disease . No blood test, brain scan or other test can be used to make a definitive diagnosis of PD.
Researchers believe that in most people, Parkinson’s is caused by a combination of environmental and genetic factors. Certain environmental exposures, such as pesticides and head injury, are associated with an increased risk of PD. Still, most people have no clear exposure that doctors can point to as a straightforward cause. The same goes for genetics. Certain genetic mutations are linked to an increased risk of PD. But in the vast majority of people, Parkinsons is not directly related to a single genetic mutation. Learning more about the genetics of Parkinsons is one of our best chances to understand more about the disease and discover how to slow or stop its progression.
Aging is the greatest risk factor for Parkinsons, and the average age at diagnosis is 60. Still, some people get PD at 40 or younger.
Men are diagnosed with Parkinsons at a higher rate than women and whites more than other races. Researchers are studying these disparities to understand more about the disease and health care access and to improve inclusivity across care and research.
Aging is the greatest risk factor for Parkinsons, and the average age at diagnosis is 60. Still, some people get PD at 40 or younger.
The Michael J. Fox Foundation has made finding a test for Parkinsons disease one of our top priorities.
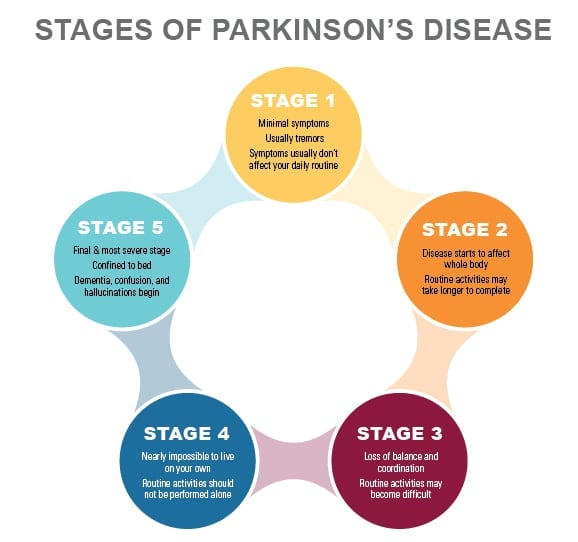
What Are The Five Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
The five stages of Parkinsons disease are called Hoehn and Yahr. Stage one showcases the symptoms affecting one side of the body. In stage two, the symptoms affect both sides of the body with no deterioration or loss of balance. Stage three reveals balance impairment but the person may be physically independent. Stage four depicts a grave disability of movement but the person may still walk unassisted. In stage five, the condition deteriorates further and the person is bound by the wheelchair or bedridden.
Also Check: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinson’s
Diagnosis And Management Of Parkinsons Disease
There are no diagnostic tests for Parkinsons. X-rays, scans and blood tests may be used to rule out other conditions. For this reason, getting a diagnosis of Parkinsons may take some time.
No two people with Parkinsons disease will have exactly the same symptoms or treatment. Your doctor or neurologist can help you decide which treatments to use.
People can manage their Parkinsons disease symptoms through:
- seeing a Doctor who specialises in Parkinsons
- medication
- multidisciplinary therapy provided for example, by nurses, allied health professionals and counsellors
- deep brain stimulation surgery .
Changes In Sleeping Patterns
As Parkinsons progresses, you can also develop problems with sleep patterns. These may not happen in the early stages, but can be noticeable later. You might wake up often in the middle of the night or sleep more during the day than you do at night.
Another common sleep disturbance for people with Parkinsons is rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. This is when you start acting out your dreams in your sleep, such as verbally and physically, which can get uncomfortable if someone is sharing your bed. Dr. Rundle-Gonzalez says many times a bed partner will be the one to notice sleep problems.
REM sleep behavior disorder can also happen in people who dont have Parkinsons. However, if this isnt something youve dealt with before, its likely related to your disease. There are medications your doctor can prescribe to help you sleep comfortably through the night.
Recommended Reading: Weighted Silverware
No One Definitive Cause Of Parkinsons
There are no biomarkers or objective screening tests that indicate one has Parkinsons. That said, medical experts have shown that a constellation of factors are linked to it.
Parkinsons causes are likely a blend of genetics and environmental or other unknown factors. About 10 to 20 percent of Parkinsons disease cases are linked to a genetic cause, says Ted Dawson, M.D., Ph.D., director of the Institute for Cell Engineering at Johns Hopkins. The types are either autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive .
But that leaves the majority of Parkinsons cases as idiopathic, which means unknown. We think its probably a combination of environmental exposure to toxins or pesticides and your genetic makeup, says Dawson.
Age. The biggest risk factor for developing Parkinsons is advancing age. The average age of onset is 60.
Gender. Men are more likely to develop Parkinsons disease than women.
Genetics. Individuals with a parent or sibling who is affected have approximately two times the chance of developing Parkinsons. Theres been an enormous amount of new information about genetics and new genes identified over the past 10 or 15 years that have opened up a greater understanding of the disease, says Dawson.
Sidebar: Advances In Circuitry Research
The brain contains numerous connections among neurons known as neural circuits.
Research on such connections and networks within the brain have advanced rapidly in the past few years. A wide spectrum of tools and techniques can now map connections between neural circuits. Using animal models, scientists have shown how circuits in the brain can be turned on and off. For example, researchers can see correlations between the firing patterns of neurons in a zebrafishs brain and precise behavioral responses such as seeking and capturing food.
Potential opportunities to influence the brains circuitry are starting to emerge. Optogenetics is an experimental technique that involves the delivery of light-sensitive proteins to specific populations of brain cells. Once in place, these light-sensitive proteins can be inhibited or stimulated by exposure to light delivered via fiber optics. Optogenetics has never been used in people, however the success of the approach in animal models demonstrates a proof of principal: A neural network can be precisely targeted.
Thanks in part to the BRAIN Initiative, research on neural circuitry is gaining momentum. The Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies Initiative is accelerating the development and application of new technologies that enable researchers to produce dynamic pictures of the brain that show how individual brain cells and complex neural circuits interact at the speed of thought.
NIH Publication No. 15-5595
Don’t Miss: Prayer For Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms: Life Expectancy
Even though Parkinson’s disease is a serious, progressive condition, it is not considered a fatal illness. People who have Parkinson’s disease usually have the same average life expectancy as people without the disease.
But when the disease is in its advanced stages, Parkinson’s symptoms can lead to life-threatening complications, including:
- Falls that lead to fractured bones
- Pneumonia
- Choking
Thinking about the progression of Parkinson’s disease can be frightening. But proper treatments can help you live a full, productive life for years to come. And researchers hope to one day find ways to halt the progression of Parkinson’s and restore lost functioning.
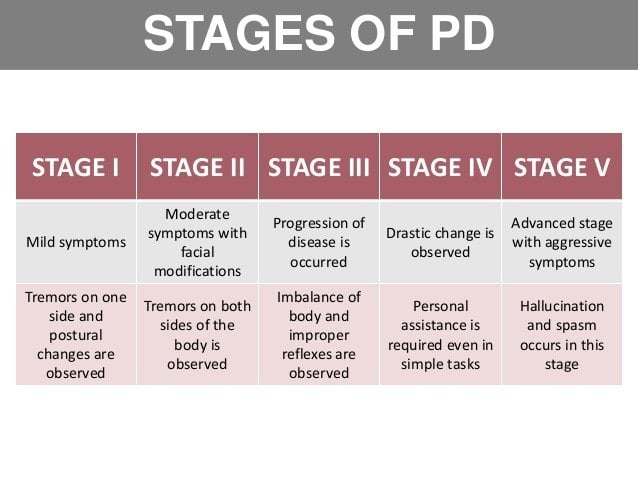
Stage Four Of Parkinsons Disease
In stage four, PD has progressed to a severely disabling disease. Patients with stage four PD may be able to walk and stand unassisted, but they are noticeably incapacitated. Many use a walker to help them.
At this stage, the patient is unable to live an independent life and needs assistance with some activities of daily living. The necessity for help with daily living defines this stage. If the patient is still able to live alone, it is still defined as stage three.
Also Check: Yopd Life Expectancy
Parkinsons Disease Is A Progressive Neurodegenerative Disorder The Current Treatment Options For The Disorder Have Focused On Symptom Control Research Is Now Focusing On Developing Ways To Modify The Disease Progression And Possibly Provide A Cure In
APA format, 3 references, at least 300 words
Parkinsons disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder. The current treatment options for the disorder have focused on symptom control. Research is now focusing on developing ways to modify the disease progression and possibly provide a cure. Investigate the current research on Parkinsons disease treatments, including stem-cell research and the use of fetal tissue implants. Share your thoughts on the evolving therapies. What are the current controversies?
Stage Two Of Parkinsons Disease
Stage two is still considered early disease in PD, and it is characterized by symptoms on both sides of the body or at the midline without impairment to balance. Stage two may develop months or years after stage one.
Symptoms of PD in stage two may include the loss of facial expression on both sides of the face, decreased blinking, speech abnormalities, soft voice, monotone voice, fading volume after starting to speak loudly, slurring speech, stiffness or rigidity of the muscles in the trunk that may result in neck or back pain, stooped posture, and general slowness in all activities of daily living. However, at this stage the individual is still able to perform tasks of daily living.
Diagnosis may be easy at this stage if the patient has a tremor however, if stage one was missed and the only symptoms of stage two are slowness or lack of spontaneous movement, PD could be misinterpreted as only advancing age.
Don’t Miss: Prayers For Parkinson’s Disease
Sidebar: Ninds Steps Up Pursuit Of Pd Biomarkers
In 2012, the NINDS dramatically accelerated efforts to identify biomarkers by establishing the Parkinsons Disease Biomarkers Program . This unprecedented program unites a range of stakeholders from basic and clinical researchers to healthcare professionals, the NINDS staff, information technology experts, and people living with PD and their families.
PDBP supports research and builds resources aimed at accelerating the discovery of biomarkers to ultimately slow the progression of PD. For example, the program has established a repository of biological specimens and a Data Management Resource system maintained by the NIH Center for Information Technology. The DMR allows researchers to access clinical, imaging, genetic, and biologic data, while a complementary PDBP-supported project develops statistical tools to analyze vast quantities of data so that patterns can be identified across these diverse sources of information.
Parkinson And Its Hallmark Symptoms
Parkinsons is a neurodegenerative disease that leads to shaking, stiffness, and difficulty with walking, and causes a person to lose control over some body functions.
Syndrome progresses gradually and differs from individual to individual. Parkinsons patients also experience mood swings accompanied by depression and anxiety.2
You May Like: Parkinson Silverware
How Is Parkinson Disease Diagnosed
Parkinson disease can be hard to diagnose. No single test can identify it. Parkinson can be easily mistaken for another health condition. A healthcare provider will usually take a medical history, including a family history to find out if anyone else in your family has Parkinson’s disease. He or she will also do a neurological exam. Sometimes, an MRI or CT scan, or some other imaging scan of the brain can identify other problems or rule out other diseases.
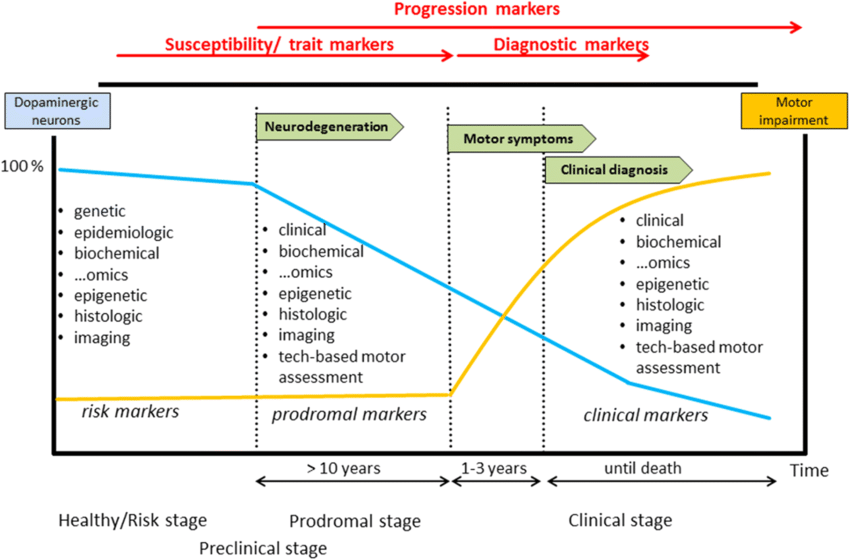
Theory Of Pd Progression: Braaks Hypothesis
The current theory is that the earliest signs of Parkinson’s are found in the enteric nervous system, the medulla and the olfactory bulb, which controls sense of smell. Under this theory, Parkinson’s only progresses to the substantia nigra and cortex over time.
This theory is increasingly borne out by evidence that non-motor symptoms, such as a loss of sense of smell , sleep disorders and constipation may precede the motor features of the disease by several years. For this reason, researchers are increasingly focused on these non-motor symptoms to detect PD as early as possible and to look for ways to stop its progression.
Page reviewed by Dr. Ryan Barmore, Movement Disorders Fellow at the University of Florida, a Parkinsons Foundation Center of Excellence.
Don’t Miss: Similar To Parkinsons