Parkinsons Disease Vs Parkinsonism: Understanding The Difference Is Essential For Icd
March 25, 2019 / By Pamela Ewing, CPC
What is Parkinsons disease? It is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects predominately dopamine-producing neurons in a specific area of the brain called the substantia nigra.
The substantia nigra cells produce dopamine, a chemical messenger responsible for transmitting signals within the brain that allow for coordination of movement. Loss of dopamine causes neurons to fire without normal control, leaving patients less able to direct or control their movement. Parkinsons disease is one of several diseases categorized by clinicians as movement disorders.
Parkinsons disease has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Stiffness of the limbs and trunk
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination
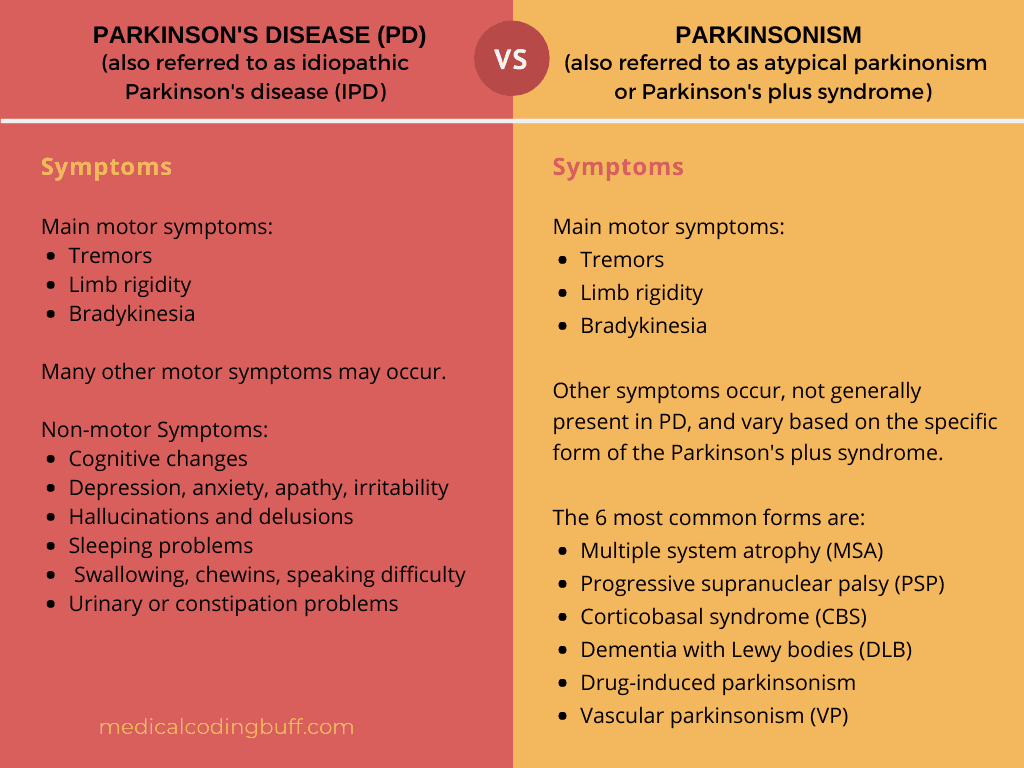
Parkinsonism refers to symptoms of Parkinsons disease , regardless of the cause, and is typically caused by another condition or external agent, such as drugs. These two conditions are not classified the same.
With the Parkinsons Disease progression listed are just a few of many symptoms. Some symptoms may include, but are not limited to:
- Dementia
specified NEC E21.4 Parkinsons G20
We then look in the Alpha index for Parkinsons and it refers us to Parkinsonism.
Parkinsonism G20 with neurogenic orthostatic hypotension G90.3 arteriosclerotic G21.4 dementia G31.83 with behavioral disturbance G31.83
G20 would be used to indicate Parkinsons Disease, and it would be sequenced first, followed by the manifestation.
What Are Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders
Atypical Parkinsonian disorders are progressive diseases that present with some of the signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease, but that generally do not respond well to drug treatment with levodopa. They are associated with abnormal protein buildup within brain cells.
The term refers to several conditions, each affecting particular parts of the brain and showing a characteristic course:
- Dementia with Lewy bodies, characterized by an abnormal accumulation of alpha-synuclein protein in brain cells
- Progressive supranuclear palsy, involving tau protein buildup affecting the frontal lobes, brainstem, cerebellum and substantia nigra
- Multiple system atrophy, another synucleinopathy that affects the autonomic nervous system , substantia nigra and at times the cerebellum
- Corticobasal syndrome, a rare tauopathy that typically affects one side of the body more than the other and makes it difficult for patients to see and navigate through space
Dementia In Other Diseases Classified Elsewhere With Behavioral Disturbance
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific CodeManifestation Code
Recommended Reading: Latest Medication For Parkinson’s Disease
Limitations Of Current Icd
Unlike other neurologic disorders , there is only a single ICD-10-CM code for PD, namely G20.22 The single, nonspecific code for PD cannot accurately capture motor fluctuations and dyskinesia that emerge with PD progression. Based on the limitations of a single ICD-10-CM code for PD, a 7-member panel convened to review ICD-10-CM coding for PD and possible current ancillary codes that could be used to document OFF episodes and dyskinesia in PD. Other potential ICD-10-CM codes were considered for PD but did not provide accuracy or specificity.
Motor Fluctuations and Dyskinesia
As fluctuations and dyskinesia reflect disease progression, codes that specify treatment consequences are not accurate. These motor complications are neither adverse effects of medications nor do they reflect underdosing of medications due to patient nonadherence. OFF episodes are not a result of dose or medication failure and do not indicate that a drug regimen is no longer effective. Therefore, coding PD with dyskinesia and/or OFF episodes using T42.8X5 or T42.8X6 is inconsistent with the nature of these events. In contrast, adverse dopaminergic effects such as nausea or foot edema would be appropriately coded as T42.8X5, and consistent nonfluctuating bradykinesia could be coded with T42.8X6.
Dystonia
Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Dementia with Lewy bodies is named for the presence of abnormal protein deposits of alpha-synuclein that are also seen in people with PD. DLB is the second most common type of dementia after Alzheimers disease, and it is a progressive disorder. In people with DLB, the Lewy bodies are found throughout the brain. DLB is characterized by cognitive impairments, visual hallucinations, inability to focus, inflexible thinking and paranoia. DLB patients initially have these cognitive symptoms but also develop motor symptoms similar to PD such as bradykinesia, tremor, rigidity, and shuffling walk. Similar to PD, DLB patients also have REM sleep behavior disorder in which they act out their dreams. DLB is treated with cholinesterase inhibitors and atypical antipychotics. However, there is no cure for DLB.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease And Vision Problems
Wpw Affects Less Than 1 In 100 People
Normally the heartbeat begins at the sinoatrial SA node located in your right atrium. EX PREEMIE BORN AT 26 WEEKS. ICD-10-CM 2020 Coding Guide from Unbound Medicine. If you have WPW you may have episodes of palpitations or rapid heartbeats. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome WPW is a type of heart condition you are born with congenital. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 BillableSpecific Code.
Genetic Testing Of Fibroblast Growth Factor 20 Rs12720208 Polymorphism
Wang and colleagues noted that many studies had examined the association between fibroblast growth factor 20 rs12720208 polymorphism and the susceptibility of PD. However, published data are still controversial. These researchers performed a meta-analysis to evaluate the association of rs12720208 polymorphism with the risk of PD. Up to April 2016, PubMed, Embase, Web of science, the Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure, and Wanfang Medicine were reviewed to identify appropriate documents. A total of 7 articles involving 11 studies with 3,360 PD cases and 3,681 controls were included based on the strict inclusion and exclusion standards. And STATA 12.0 statistics software was used to calculate available data from each study. The pooled OR and 95 % CI were calculated to assess the association between FGF20 rs12720208 polymorphism and PD risk. When all studies were pooled into this meta-analysis, neither the minor T allele frequencies nor the genotypic distributions were different between PD cases and controls. But the subgroup analysis stratified by ethnicity showed FGF20 rs12720208 polymorphism was associated with increased risk in the allele model and dominant model in Caucasians but not in Asians. The authors concluded that the findings of this meta-analysis indicated that rs12720208 C/T variant might be associated with PD susceptibility in Caucasians.
Recommended Reading: Leg Weakness Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Current Treatment Options
While there is no specific cure for Parkinsons plus syndrome, there are treatments that can control your symptoms. A doctor can develop a plan for your overall health and to treat your specific symptoms. Medications that treat the symptoms of Parkinsons disease often do not work as well for Parkinsons plus syndrome.
Treatment options might include:
- Walking and balance assistance. You might receive physical and occupational therapy to help keep you moving. Therapists can help you build strength and prevent falls. They can also help you learn to use canes, walkers, and other mobility aids, if needed.
- Swallowing and speech assistance. A speech therapist can help you adjust to changes that might make it hard to swallow and speak. They can help you communicate and can recommend foods and beverages that are easier to swallow.
- Medications for cognitive issues. Your doctor might prescribe a variety of medications that can help with your focus and memory. Many of these medications are also used for conditions such as Alzheimers or dementia.
- Medications for trouble with movement. You might be prescribed medications that can help you control your muscles and movement. These medications might also address stiffness and balance problems.
- Medications to help with mood symptoms. If youre experiencing depression, anxiety, or other mood-related concerns, your doctor might prescribe medications that can help with these symptoms.
Diagnosis And Management Of Neurodegenerative Atypical Parkinsonism
Rachel Dolhun, MD
“Parkinsonism and parkinsonian are terms broadly used to describe the motor features typically associated with idiopathic Parkinsons disease . While there are other causes of parkinsonism , the neurodegenerative diseases that can cause parkinsonism are deserving of deeper consideration.* These conditions, frequently referred to as the atypical parkinsonianor Parkinsons plussyndromes , include dementia with Lewy bodies , multiple system atrophy , progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration .
Definitive diagnosis of APS can be made only through neuropathological confirmation, the hallmark of which is intracellular protein deposition. Abnormal accumulation of alpha-synuclein is characteristic of PD, DLB, and MSA tau protein aggregates in PSP and CBD .1 The clinical relevance of differentiating synucleinopathies from tauopathies requires further study, but certain generalizations may help clinicians focus on potentially relevant aspects of the history and physical examination and thereby narrow the differential diagnosis.
You May Like: Are Hallucinations A Symptom Of Parkinson’s
Recommendations For Pd Icd
Based on this review, the panel recommends the ICD-10-CM coding structure for PD be expanded to provide specificity to distinguish motor complications of dyskinesia and/or OFF episodes . The proposed changes include delineating between individuals without dyskinesia or fluctuations , without dyskinesia but with fluctuations , with dyskinesia but without fluctuations , and with dyskinesia and fluctuations .
Figure 1. Proposed International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification codes for Parkinson disease.
Understanding The Differences Between Parkinsonism And Parkinson Plus Syndromes
Parkinsonism means looks like Parkinsons disease. To neurologists this means that the person has a somewhat flexed posture, moves slowly, is stiff and usually walks slowly, with small steps and reduced or no arm swing. We call the syndromes atypical because they usually differ from Parkinsons Disease in a few ways:
Very often when the condition is mild, at the earliest stages, we cant tell whether it is Parkinsons Disease or atypical Parkinsons Disease and we treat it as if it is Parkinsons Disease because we dont have treatments for the atypical Parkinson disorders. Sometimes they respond to the usual Parkinsons Disease medications, but usually they dont. And when they do, the response is not as good as it is with PD.
Parkinson plus syndromes refer to syndromes which look like atypical PD, but also include additional abnormalities that are not seen in PD. These include: abnormalities of eye movements, gait ataxia , dystonia , severe problems with low blood pressure on standing, or changes on the neurological exam that are only detected by the neurologist in the form of abnormal reflexes.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease And Sleep Disorders
Measurement Of Telomere Length
Forero et al stated that differences in telomere length have been reported as possible risk factors for several neuropsychiatric disorders, including PD. Results from published studies for TL in PD are inconsistent, highlighting the need for a meta-analysis. In the current work, a meta-analysis of published studies for TL in PD was carried out. PubMed, Web of Science and Google Scholar databases were used to identify relevant articles that reported TL in groups of PD patients and controls. A random-effects model was used for meta-analytical procedures. The meta-analysis included 8 primary studies, derived from populations of European and Asian descent, and did not show a significant difference in TL between 956 PD patients and 1,284 controls . The authors concluded that the findings of this meta-analysis showed that there is no consistent evidence of shorter telomeres in PD patients and suggested the importance of future studies on TL and PD that analyze other populations and also include assessment of TL from different brain regions.
Abnormality Of Tau Protein

PSP has been considered to be a tau protein disorder. Cortical fibrillary tangles of PSP are similar to those observed in Alzheimer disease with regard to the presence of an abnormally phosphorylated tau protein. Tau is a component of a microtubule-associated protein that is responsible for axonal transport of vesicles. The mechanism whereby this is involved in PSP has yet to be determined. PSP overlaps with corticobasal degeneration in this regard, and the latter may have a stronger association with tau protein abnormalities than does PSP.
Tau proteins exist in 6 isoforms encoded by a single gene. Different electrophoretic patterns have been identified in the various disorders associated with tau abnormalities. Thirty-two mutations have been identified in more than 100 families. About half of the known mutations have their primary effect at the protein level. They reduce the ability of tau protein to interact with microtubules and increase its propensity to assemble into abnormal filaments. The other mutations have their primary effect at the RNA level and perturb the normal ratio of 3-repeat to 4-repeat tau isoforms. When studied, this change resulted in a relative overproduction of tau protein with 4 microtubule-binding domains in the brain.
You May Like: Can Parkinson’s Psychosis Be Reversed
Whats The Outlook For People With Parkinsons Plus
Although there currently isnt a treatment to halt the progression of Parkinsons plus syndrome, there are treatments that can help you manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
The exact outlook for Parkinsons plus syndrome depends on the person and the specific condition they have. Someone who is otherwise healthy when theyre diagnosed will typically have a longer life expectancy than someone who is already facing other health conditions when theyre diagnosed. Your doctor will monitor your condition over time and can let you know how its progressing.
Pd Progression & Motor Complications
PD is a chronic, progressive disorder affecting approximately 1 million people in the US.3-5 Disease progression causes greater morbidities and disabilities because of advancing fluctuations in motor and nonmotor symptoms. These issues are further compounded by the heterogeneous nature of PD in which symptoms, manifestations, and natural history often vary from person to person, thus complicating disease management.
The pathologic hallmark of PD is the presence of Lewy bodies, which are intracellular inclusions of -synuclein.6,7 These -synuclein protein aggregates are associated with the death of dopamine-producing neurons4 and have been implicated in the progressive, neurodegenerative process underlying idiopathic PD.8 Levodopa and other dopaminergic therapies replenish striatal dopamine and provide symptomatic benefit.9 As neurodegeneration progresses over 3 to 5 years, however, progressive striatal denervation coupled with variable intestinal absorption of levodopa due to gastric dysmotilityreflecting enteric nervous system involvementcauses the emergence of motor complications, including motor fluctuations and dyskinesia.10
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Environmental Factors
Measurement Of Urinary Lrrk2 Phosphorylation
Fraser and colleagues examined if phosphorylated Ser-1292 LRRK2 levels in urine exosomes predicts LRRK2 mutation carriers and non-carriers with Parkinson disease and without Parkinson disease . LRRK2 protein was purified from urinary exosomes collected from participants in 2 independent cohorts. The 1st cohort included 14 men . The 2nd cohort included 62 men . The ratio of Ser-1292 LRRK2 to total LRRK2 was compared between LRRK2+/PD+ and LRRK2- in the 1st cohort and between LRRK2 G2019S carriers with and without PD in the 2nd cohort. LRRK2+/PD+ had higher ratios of Ser-1292 LRRK2 to total LRRK2 than LRRK2-/PD- and LRRK2-/PD+ . Among mutation carriers, those with PD had higher Ser-1292 LRRK2 to total LRRK2 than those without PD . Ser-1292 LRRK2 levels predicted symptomatic from asymptomatic carriers with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.844. The authors concluded that elevated ratio of phosphorylated Ser-1292 LRRK2 to total LRRK2 in urine exosomes predicted LRRK2 mutation status and PD risk among LRRK2 mutation carriers. Moreover, they stated that future studies may explore whether interventions that reduce this ratio may also reduce PD risk. In particular, they stated that larger studies that measure Ser-1292 LRRK2 levels over time in asymptomatic carriers will be needed to understand the prognostic potential of this new biomarker.
Diseases Of The Nervous Systemtype 2 Excludes
- Dementia associated with parkinson’s disease
- Dementia in parkinsons disease
- Restrictive lung disease due to parkinsons disease
- Restrictive lung mechanics due to parkinsons disease
- 056 Degenerative nervous system disorders with mcc
- 057 Degenerative nervous system disorders without mcc
- : New code
- 2017
Recommended Reading: Pants For Parkinson’s Patients
What Are The Symptoms Of Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders
Like classic Parkinsons disease, atypical Parkinsonian disorders cause muscle stiffness, tremor, and problems with walking/balance and fine motor coordination.
Patients with atypical Parkinsonism often have some degree of difficulty speaking or swallowing, and drooling can be a problem. Psychiatric disturbances such as agitation, anxiety or depression may also be part of the clinical picture.
Dementia with Lewy bodies can cause changes in attention or alertness over hours or days, often with long periods of sleep during the day. Visual hallucinations typically of small animals or children, or moving shadows in the periphery of the visual field are common in DLB. DLB is second only to Alzheimers disease as a cause of dementia in the elderly, and it most commonly affects patients in their 60s.
Patients with progressive supranuclear palsy may have difficulties with eye movements, particularly when looking downward, and with balance when descending stairs, for instance. Backward falls are common and may occur during the early course of the disease. PSP is not usually associated with tremor, unlike Parkinsons disease.
Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Center