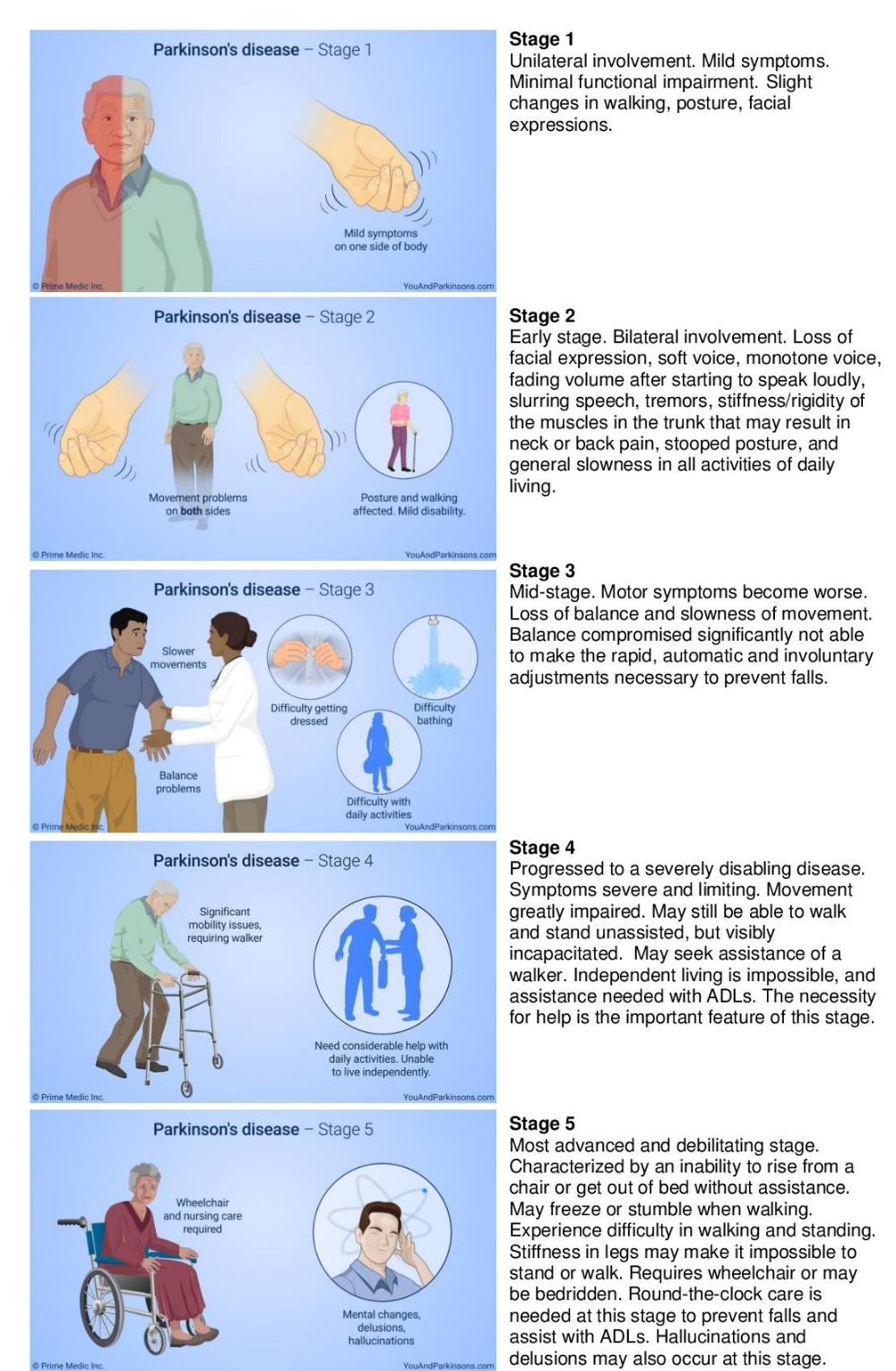
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease and the rate of decline vary widely from person to person. The most common symptoms include:
Other symptoms include:
- Speech/vocal changes: Speech may be quick, become slurred or be soft in tone. You may hesitate before speaking. The pitch of your voice may become unchanged .
- Handwriting changes: You handwriting may become smaller and more difficult to read.
- Depression and anxiety.
- Sleeping disturbances including disrupted sleep, acting out your dreams, and restless leg syndrome.
- Pain, lack of interest , fatigue, change in weight, vision changes.
- Low blood pressure.
Parkinsonism And Brain Pathology
There were 1,373 deaths after an average of nearly 7 years of follow-up with 1,187 autopsies . At the time of these analyses, the uniform neuropathological examination was complete for 1,160 . Mean age at death was 88.3 years 64.5% were women. At their last visit, about 10 months before death, more than 70% had either parkinsonism or possible parkinsonism ).
Description of Neuropathologies: AD pathology was the single most common pathology . One or more of the four vascular pathologies were present in more than 4/5 of the cases . Nigral Lewy body pathology was present in more than 1/5 and moderate/severe nigral neuronal loss was present in more than 1/10 and nigral Lewy bodies together with moderate/severe nigral neuronal loss was present in 1/10 .
Ordinal logistic regression models were employed to examine which neuropathologies were associated with parkinsonism. Each model included terms for one of the seven neuropathologies and controlled for age, sex, and education. Each of the four vascular pathologies was associated with parkinsonism but not AD pathology, Lewy body pathology, or nigral neuronal loss . Arteriolosclerosis and atherosclerosis showed independent associations with parkinsonism when all seven pathologies were included in a single model . These results were unchanged when we excluded cases with a history of PD proximate to death
Parkinsons Disease In The Elderly: How Caregivers Can Help
Parkinsons disease in the elderly is one of the most difficult conditions for patients and caregivers to cope with. A progressive neurological condition, it can affect both movement and cognition. This is part of what makes caring for someone with Parkinsons so difficult, especially in the latter stages of the disease. However, with the right amount of education , you and your loved one can learn how to handle this transition.
Recommended Reading: How To Improve Walking With Parkinson’s
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinson’s disease has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Stiffness of the limbs and trunk
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination, sometimes leading to falls
Other symptoms may include depression and other emotional changes difficulty swallowing, chewing, and speaking urinary problems or constipation skin problems and sleep disruptions.
Symptoms of Parkinsons and the rate of progression differ among individuals. Sometimes people dismiss early symptoms of Parkinson’s as the effects of normal aging. In most cases, there are no medical tests to definitively detect the disease, so it can be difficult to diagnose accurately.
Early symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are subtle and occur gradually. For example, affected people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. They may notice that they speak too softly, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. Friends or family members may be the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinson’s. They may see that the person’s face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
People with Parkinson’s often develop a parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward, small quick steps as if hurrying forward, and reduced swinging of the arms. They also may have trouble initiating or continuing movement.
Caregiving For People Living With Parkinsons

Caring for a loved one with PD can be a challenging job, especially as the disease progresses. Former caregivers of a loved one with PD suggest doing the following : Get prepared, Take care of yourself, Get help , Work to maintain a good relationship with your loved one, and Encourage the person with PD for whom you care, to stay active.
Preparing for caregiving starts with education. Reading this fact sheet is a good start. More resources are available to you in theResources section of this fact sheet. Early Parkinsonâs disease usually requires more emotional support and less hands-on care. It is a good time for family members/caregivers to educate themselves about the disease.
Don’t Miss: Keto Diet And Parkinson’s Disease With William Curtis
Treatment Of Motor Fluctuations
A number of strategies can reduce motor fluctuations in patients with PD. Optimising the amount of levodopa delivered to the brain is the main approach and can be achieved by increasing the levodopa dose, adjusting the timing of administration and/or adding adjunctive agents., Administering levodopa with a low protein meal or empty stomach, if tolerated, can improve absorption. Smaller, more frequent dosing may also help. Changing to a controlled-release formulation could theoretically improve fluctuations however, studies have shown no difference in symptoms compared to immediate-release preparations.
Adjunctive agents such as dopamine agonists, catechol-o-methyltransferase inhibitors and monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors have been shown to improve fluctuations. Direct head-to-head studies comparing these medications are lacking however, a Cochrane review involving 44 randomised controlled trials suggested dopamine agonists were most effective in reducing âoffâ time . In older people, choice of adjunctive agent should be based on factors including comorbidities, adverse effects and patient preference.
Dopamine Agonists
COMT Inhibitors
MAO-B Inhibitors
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease symptoms usually start out mild, and then progressively get much worse. The first signs are often so subtle that many people don’t seek medical attention at first. These are common symptoms of Parkinson disease:
- Tremors that affect the face and jaw, legs, arms, and hands
- Slow, stiff walking
You May Like: Is Parkinson’s A Form Of Cancer
Causes Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is caused by a lack of dopamine, a neurotransmitter in the brain that plays a critical role in the nervous system. Dopamine, which essentially serves as a messenger in the brain to produce the controlled, smooth movements most of us enjoy, is lacking in the brain of those suffering from Parkinsons disease the greater the loss of dopamine, the more uncontrolled the symptoms. Further, it is also believed that Parkinsons may also cause other cells in the brain to deteriorate, as well.
Although it is clear that a lack of dopamine causes the symptoms of Parkinsons disease, why these dopamine cells deteriorate is unclear. What is clear is that a number of irregular cellular processes are to blame, although stress has also been attributed to cell damage in Parkinsons disease patients. In other words, it appears as if dopamine loss occurs because of both genetic and environmental factors.
Parkinsons Disease In The Elderly: Symptoms & Care
Parkinsons disease is a neurological disorder that occurs when certain neurons in the brain die or become impaired. These nerve cells, located in a midbrain structure that controls muscle movement, produce dopamine, the chemical responsible for coordinated muscle function. Symptoms of Parkinsons disease begin to appear when 80% of these neurons become damaged.
According to the National Institute of Health , Parkinsons affects 50% more men then women, but impacts people of all ethnicity and socio-economic backgrounds. According to the National Parkinson Foundation , approximately 60,000 new cases of PD are diagnosed each year, joining the 1.5 million Americans who have the disease. The condition usually affects those over age 65. Approximately 1% of seniors have some form of the disease.
Also Check: Fda Approved Parkinson’s Drugs
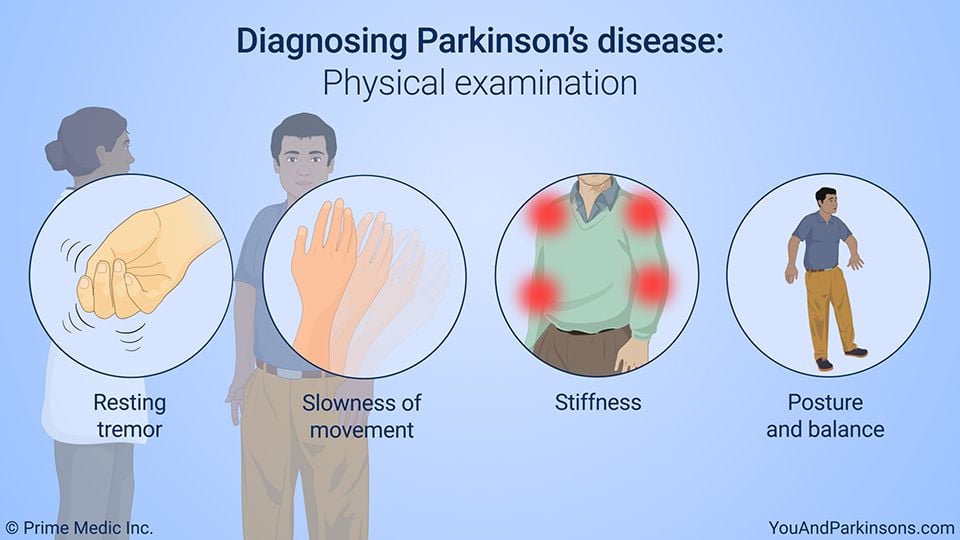
Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease
A number of disorders can cause symptoms similar to those of Parkinson’s disease. People with Parkinson’s-like symptoms that result from other causes are sometimes said to have parkinsonism. While these disorders initially may be misdiagnosed as Parkinson’s, certain medical tests, as well as response to drug treatment, may help to distinguish them from Parkinson’s. Since many other diseases have similar features but require different treatments, it is important to make an exact diagnosis as soon as possible.
There are currently no blood or laboratory tests to diagnose nongenetic cases of Parkinson’s disease. Diagnosis is based on a person’s medical history and a neurological examination. Improvement after initiating medication is another important hallmark of Parkinson’s disease.
Can Older Adults With Parkinsons Enjoy Normal Lives
By Annette Campbell 9 am on February 10, 2021
Parkinsons disease is classified as a neurological disorder, which means it affects nerve cells that transmit signals to and within the brain. The Parkinsons Foundation estimates about 1 percent of all seniors have some form of this condition. However, having Parkinsons doesnt mean your senior loved one cant still live a normal life. Today, were going to focus on what can be done to achieve this goal.
You May Like: Deep Brain Stimulation Parkinson’s Video
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinsons disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinsons disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinsons disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
Signs Of Early Stage Parkinsons In Seniors
By Lutgarda Mariano 9 am on April 19, 2019
When Parkinsons disease is diagnosed and treated early, its progression may be slowed. Parkinsons is a neurological disorder that causes several noticeable symptoms. However, in the early stages, symptoms may be very subtle. Here are five warning signs of Parkinsons disease in older adults.
Read Also: Is Drooling A Sign Of Parkinson’s
What Can You Do If You Have Pd
- Work with your doctor to create a plan to stay healthy. This might include the following:
- A referral to a neurologist, a doctor who specializes in the brain
- Care from an occupational therapist, physical therapist or speech therapist
- Meeting with a medical social worker to talk about how Parkinson’s will affect your life
For more information, visit our Treatment page.
Page reviewed by Dr. Chauncey Spears, Movement Disorders Fellow at the University of Florida, a Parkinsons Foundation Center of Excellence.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction: A Pivotal Pathological Mechanism Of Parkinsons Disease
Mitochondria are complex cytosolic organelles of eukaryotic cells whose primary function is the generation of cellular energy in the form of ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. Mammalian mitochondria contain between 2 and 10 mitochondrial DNA molecules encoding 22 transfer RNAs, two ribosomal RNAs, and 13 polypeptides, each of which is part of the respiratory chain and the oxidative phosphorylation system . The mitochondrial respiratory chain contains four protein complexes that form the site of oxidative phosphorylation. This site is responsible for NADH and FADH2 oxidation, co-occurring with the movement of protons from the matrix into the intermembrane space. This movement produces an electrochemical gradient denoted as mitochondrial membrane potential . This gradient stimulates the ATP synthase to reduce molecular oxygen and synthesize ATP. This step is fundamental in aerobic metabolism and constitutes the primary provider of ATP at the final stage of cellular respiration . Nevertheless, the biological function of mitochondria goes far beyond energy production and includes the metabolism of lipids and amino acids and the support of intermediate metabolic pathways, such as the Krebs cycle.
Also Check: Working Out With Parkinson’s
What Causes Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease arises from decreased dopamine production in the brain. The absence of dopamine makes it hard for the brain to coordinate muscle movements. Low dopamine also contributes to mood and cognitive problems later in the course of the disease. Experts don’t know what triggers the development of Parkinson disease most of the time. Early onset Parkinson disease is often inherited and is the result of certain gene defects.
Parkinsons Disease In The Elderly May Become More Common
Parkinsons is the second most common neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimers. And unfortunately, cases of Parkinsons disease in the elderly are expected to become more common as baby boomers age. This is because incidents of the disease are highest in those sixty and over. However, it is possible for patients to start having symptoms even younger than forty. As soon as youre aware that someone you love has been diagnosed, take the appropriate steps to cope both for them and for yourself.
If you are unsure of how to best help an aging loved one, the trained and compassionate staff at the Institute on Aging is here to help you make that decision and gain the best in at-home care for older adults. Contact us to find out more.
Don’t Miss: What Foods Are Good For Parkinson’s Disease
Clinical Diagnoses And Adverse Health Outcomes
The annual uniform structured clinical evaluation includes a medical history and a neurologic examination that includes a modified version of the United Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale . A diagnosis of PD was based on the history of the disease for which the participant was treated with levodopa.
Mortality: When an autopsy is obtained, date of death is known promptly. When no autopsy is obtained, we obtain information on date of death from an interview with a knowledgeable informant of searches of public databases as previously described .
Dementia or mild cognitive impairment was diagnosed in a three-step process. Nineteen cognitive tests were scored by a computer and summarized as a composite measure of global cognition . These data were reviewed by a neuropsychologist to diagnose cognitive impairment. Then participants were evaluated by a clinician who used all cognitive and clinical data to diagnose dementia status .
Disability was assessed annually via two self-report instruments. Basic activities of daily living were assessed using six items from the Katz scale . Mobility disability was assessed using the RosowBreslau scale, which assesses three walking performances .
Are There Medicines To Treat Pdd
Though there is no cure for PDD yet, there are medications that help manage the symptoms. These medications are called cholinesterase inhibitors, and they can help if a person with PDD is having memory problems. Some examples of these medicines are donepezil, rivastigmine and galantamine. Sleep problems may be managed by sleep medications such as melatonin.
Because people with PDD are usually very sensitive to medications, any new medication, even one that is not being used for the brain, needs to be reviewed with the persons provider to avoid potential contraindication.
Also Check: Ed Begley Jr Parkinson’s
Can Parkinsons Disease Be Prevented
Unfortunately, no. Parkinsons disease is long-term disease that worsens over time. Although there is no way to prevent or cure the disease , medications may significantly relieve your symptoms. In some patients especially those with later-stage disease, surgery to improve symptoms may be an option.
Treatment For Parkinsons Disease In The Elderly
Unfortunately, the disease is difficult to diagnose in many cases, and is incurable. The good news that older adults can live with Parkinsons disease comfortably with the proper types of treatment.
- Regular Medication. A treatment plan will most likely include at least one medicine for the patient. Fortunately, advances in medicine have given those with Parkinsons disease hope for a relatively normal life.
- Surgery. Treating Parkinsons disease in older adults with surgery is usually only an option when medication has become less effective and the symptoms have begun to get worse.
- Therapy. In addition to following a medication routine, several types of therapy may improve a patients overall health and help minimize Parkinsons toll on the persons lifestyle. Physical, occupational, and speech therapy have all been successful in helping Parkinsons disease patients maintain a high quality of life for longer. Psychological therapy is also helpful in working through the emotions that such a debilitating disease brings on.
- Exercise. By exercising several times a week, an older adult battling Parkinsons disease can help improve their balance, keep their muscles strong, and release some stress. Water exercises are good choices, along with simple walking. Pilates is another good option.
You May Like: Que Es El Mal De Parkinson
Parkinsons Disease In The Elderly: Symptoms And Treatment
Older adults must face many health challenges as they age, and one that rears its ugly head is Parkinsons disease. Around 60,000 people are diagnosed with the disease each year, and there are around 1 million people currently living with and battling it.
Understanding Parkinsons disease is the first step toward formulating a game plan for you or your loved one. Watching for symptoms of Parkinsons disease in your elderly loved ones, and being aware of the treatment, can help decrease worry and stress, and make the situation a bit more comfortable.
Symptoms of Parkinsons Disease in Older Adults
- Rigid Muscles. Stiffness in the persons extremities and neck may be a symptom of Parkinsons. If these muscles are aching for seemingly no reason for more than a few days, its time to visit the doctor.
- Balance Issues. Feeling unsure on your feet when you have been sure-footed before, is a sign. Being unbalanced so you lean forward or backward to stay upright may signal Parkinsons disease.
- Tremors. This is perhaps the most well-known of symptoms of Parkinsons disease in the elderly. You may notice uncontrollable hand tremors that may start small and gain power. They might even move up through the arms. If you notice even small tremors, schedule a doctors appointment immediately.
- Slow Movements. Many of us slow down as we get older, so this symptom is more difficult to pinpoint. If there is a quick progression, however, it may be more than a simple by-product of aging.