Using Catecholomethyl Transferase Inhibitors
The inhibitors of the enzyme catecholOmethyl transferase extend the halflife of levodopa. Entacapone and tolcapone are two such agents used in clinical practice. Tolcapone has been associated with significant hepatotoxicity, necessitating regular monitoring of liver function tests. In an animal study using rats, coadministration of entacapone with levodopa attenuated all kinds of dyskinesia when compared to levodopa monotherapy. Stalevo , a commercially available formulation, combines levodopa, dopadecarboxylase inhibitor carbidopa and entacapone in a single tablet. It is hoped that early use of Stalevo might reduce the incidence of dyskinesia.
Continuous Delivery Of Levodopa
Continuous intraduodenal infusion of the levodopa/carbidopa enteral gel has been used successfully in treating patients with advanced Parkinson disease and shows no increase in dyskinesia as compared to oral polypharmacy. Subcutaneous or intramuscular injections of levodopa methyl ester and intravenous infusion of levodopa have also given similar results., However, limitations of such strategies in clinical practice are obvious.
How Can I Manage Or Stop Drug
Managing drug-induced dyskinesia can be challenging. One effective method is to reduce the dose of medication, particularly levodopa. However, this may cause some of the motor symptoms related to Parkinsons to return.
Newer formulations and methods of delivering medications provide a more sustained release of the drug and help reduce the symptoms of dyskinesia. Sustained release formulations and direct intestinal infusions are examples of such methods.
Newer generations of non-levodopa medications, such as safinamide , a monoamine oxidase B inhibitor, and opicapone , a catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitor, have also shown promise in reducing dyskinesia.
Surgery for Parkinsons, such as deep brain stimulation , also results in a reduction of dyskinesia symptoms. This may be because DBS frequently helps to lessen the amount of medication needed for Parkinsons.
You May Like: Is Dizziness A Symptom Of Parkinson’s
How Is It Treated
When dyskinesia is a direct result of taking levodopa, the treatment differs from person to person. Some treatment options may include:
- adjusting the dose of your levodopa to avoid large fluctuations in the amount of dopamine in your system
- taking levodopa in a continuous infusion or an extended release formulation
- taking amantadine extended release , which has been approved to treat dyskinesia
- taking levodopa in smaller doses more often
- taking Duodopa, a medication that helps stabilize the amount of dopamine in the blood, which may help with smoother motor functions
- undergoing deep brain stimulation, which is a surgical treatment for severe symptoms. Certain criteria must be met for this to be an effective treatment. Ask your doctor if this is an option for you. Deep brain stimulation is only done after other treatments have not worked.
As with any treatment, be sure to discuss all side effects with your doctor before deciding on the best treatment for you.
Dimd Classification And Symptoms
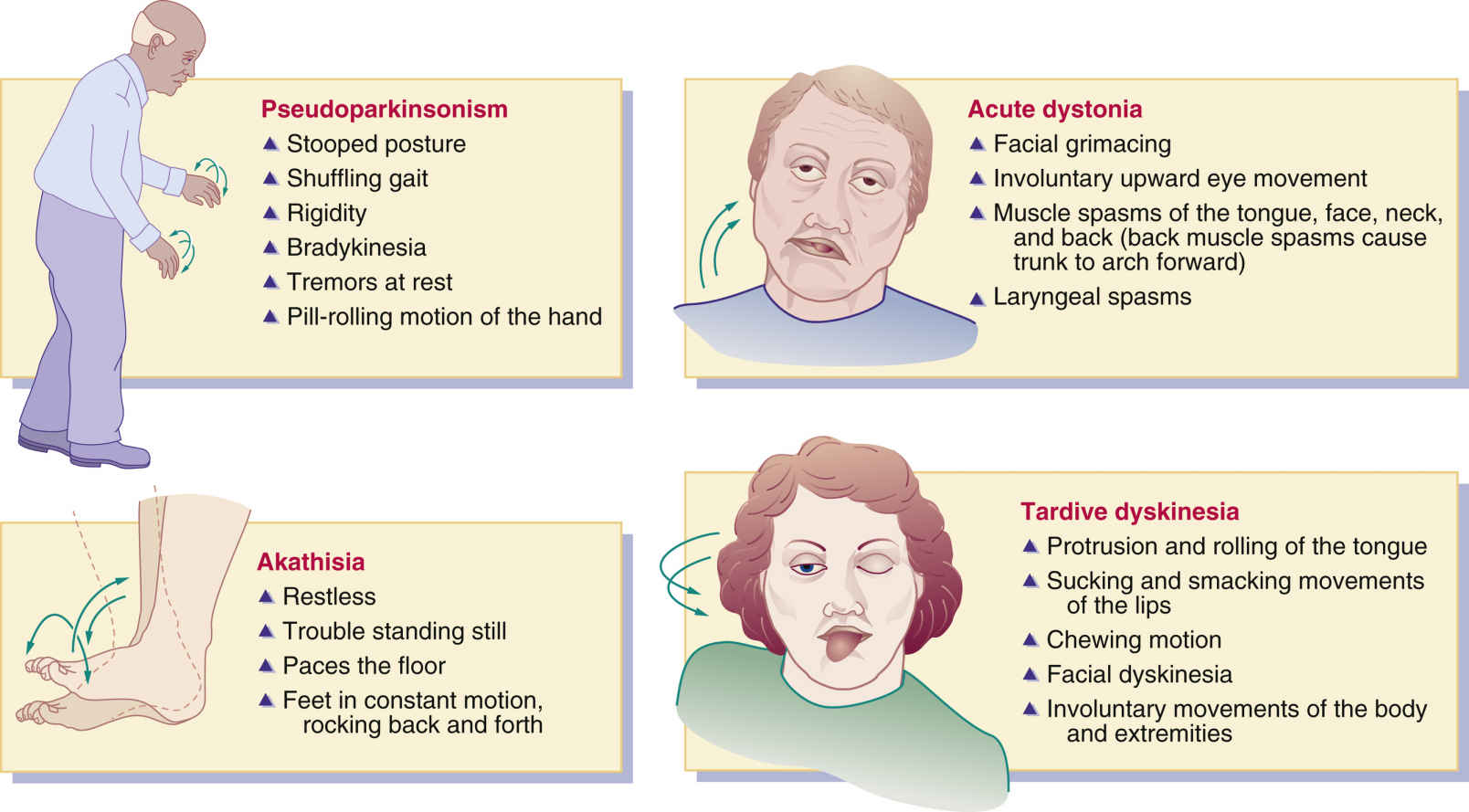
The various movement disorderswhich can be confusing to patients and clinicians alikeare classified based on timing and specific symptomatology. There are two major categories of DIMD: acute and chronic . Acute symptoms occur during the early phase of drug therapy and are frequently short-lived. Chronic symptoms commonly arise with prolonged use of the inciting drug. Some thought leaders believe that permanent movement disorders may arise after a single dose of a dopamine receptor antagonist, but the general consensus supports the chronic-use concept.13
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition , developed and published by the American Psychiatric Association, includes classifications of all currently recognized mental health disorders. In DSM-5, DIMDs are termed medication-induced movement disorders . The MIMDs listed in DSM-5 include neuroleptic-induced parkinsonism and other medication-induced parkinsonism neuroleptic malignant syndrome medication-induced acute dystonia medication-induced acute akathisia TD tardive dystonia and tardive akathisia medication-induced postural tremor and other medication-induced movement disorders .16
Medication-induced postural tremor is expressed as a fine tremor that occurs when the patient attempts to maintain a posture. The tremor is similar to that seen with anxiety and the use of caffeine and other stimulants.16
Read Also: Que Es El Mal De Parkinson
Ataxia / Dysmetria / Asynergia
Ataxia is an unsteady and swaying walk, often with feet planted widely apart. People have difficulty walking a straight line with their heel touching the toe of the shoe in front . Ataxia can occur in a number of neurologic conditions.
Dysmetria is misjudging the distance to a target. A person with dysmetria will have problems reaching out and accurately touching a targeted object.
Asynergia is a breakdown of movement, so that movements of the arms and legs become irregular and clumsy.
For more information, visit the National Ataxia Foundation website at www.ataxia.org.
What Is Dyskinesia In Parkinsons Disease
Dyskinesia is predominately a side effect of a medication called levodopa thats used to treat Parkinsons disease.
To the trained eye, dyskinesias look quite different , says Herrington. Dyskinesias are not rhythmic they have a more writhing quality.
Herrington points out that you can see an example of dyskinesia if you look at videos of Michael J. Fox. Usually, he says, when is on camera, he has some dyskinesia, or extra movements that are involuntary.
Also Check: Dbs Device For Parkinson’s
How Are Tremors And Dyskinesia Experienced By Caregivers
People with Parkinsons disease can experience their condition much differently than do their caregivers or spouses. Sometimes being in the off state looks more comfortable to the caregiver because the person is still, and can even seem kind of calm, says Herrington. But for the person with Parkinsons, they experience that off state as very uncomfortable. They may describe it as feeling trapped because they want to move but and they cant.
In this case, he continues, the person might say, Look, I know I have dyskinesia, but I prefer being free to move than feeling stuck and trapped. The caregiver, however, may feel bothered by the increased movement, he says, and think that the person is taking too much medication.
There can be a real disconnect there between what the patient would want and what the caregiver might think is best, says Herrington. Its not always the best thing to try to get rid of every last bit of dyskinesia, because the person might be less comfortable in that state.
Is Tardive Dyskinesia A Symptom Of Parkinson’s Disease
Tardive dyskinesia is not a symptom of Parkinson’s disease. It’s a separate movement disorder caused by long-term use of anti-psychotic medications.
In addition to being a side effect of different medications, tardive dyskinesia also has its own set of symptoms. The movements associated with tardive dyskinesia tend to be more fluid in appearance compared with Parkinson’s dyskinesia.
- Fluphenazine
- Haloperidol
- Perphenazine
- Prochlorperazine
- Thioridazine
Recommended Reading: Glutathione Injections For Parkinson’s
Overview Of Tardive Dyskinesia
TD is characterized by a delayed onset of involuntary motor movements in the face, trunk, and limbs after exposure to DRBAs.4,17 Involuntary movement are classically peri-oral, including grimacing, tongue protrusion, and lip puckering, but also include neck, shoulder, and limb movements.18 In some cases, symptoms can be severe enough to interfere with breathing, speaking, eating, and ambulation.19,20
TD is often irreversible and can impose long-lasting burdens on psychosocial, physical, and economic health.4, Historically, assumptions that those afflicted are unaware of their symptoms or unconcerned with them have obscured these burdens, especially among persons with schizophrenia who can have limited insight into their physical and mental health.24,25 However, a recent study of those with a history of AP use for the treatment of schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, mood disorder, and other psychiatric disorders, found that nearly 80% of subjects with a clinician-confirmed diagnosis of possible TD reported noticing recent involuntary movements.21 Many of these individuals also felt that the uncontrollable movements impacted their ability to engage in daily activities, talk, or socialize.21
What Causes Dyskinesia In Parkinson’s Disease
Unlike “off” time, patients typically experience dyskinesia in Parkinson’s when medications are working and other symptoms are under control. Researchers aren’t exactly sure what causes dyskinesia, but it is believed to be a side effect of long-term levodopa use, not a symptom itself. Levodopa-induced dyskinesia can look like fidgeting, writhing, wriggling, head bobbing, or body swaying. LID can sometimes be confused with Parkinson’s tremor, which is a back and forth shaking caused by the disease.
Because levodopa is taken throughout the day, dopamine levels in the brain rise and fall. These fluctuating levels of dopamine combined with the continued loss of dopamine in the brain make it difficult to maintain regular dopamine levels, and lead to dyskinesia.
Individuals diagnosed with Parkinson’s at a younger age are more likely to experience dyskinesia. It’s also more common in later stages of Parkinson’s or in those who have taken levodopa for several years.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease Stage 1 Symptoms
Writers Cramp And Musicians Dystonia
Writers Cramp is a focal dystonia of the finger, hand or forearm in which there is a simultaneous contraction of those muscles while writing or doing specific skilled tasks. Writers cramp may begin after repetitive use and is therefore often considered an occupational dystonia, more commonly experienced by typists, draftsmen, musicians and sportsmen.
When musicians are affected, it is called musicians dystonia . When the muscles involved are around the mouth , it is called embouchure dystonia.
For more information visit the Dystonia Medical Research Foundation www.dystonia-foundation.org.
Connect With Others Who Understand
MyParkinsonsTeam is the social network for people with Parkinsons disease and their loved ones. On MyParkinsonsTeam, more than 74,000 members come together to ask questions, give advice, and share their stories with others who understand life with Parkinsons disease.
Are you living with Parkinsons disease? Have you experienced dyskinesia or dystonia? Share your experience in the comments below, or start a conversation by posting on your Activities page.
Don’t Miss: Can You Recover From Parkinson’s Disease
Are Tremors Or Dyskinesias Painful
Tremors are almost never painful, says Herrington. And unless the dyskinesias are very severe, they also hardly ever cause pain.
However, Herrington says that when a persons medication wears off, the person can experience a condition called dystonia, which is related to dyskinesia. Dystonia is a potentially painful, cramping condition that can occur in the face, arms, or legs and can be very uncomfortable.
What Are Parkinsons Tremors
A tremor is a rhythmic, back-and-forth movement, says Dr. Herrington. While most tremors tend to occur in the hand, he says that they can also involve other parts of the body, including the thumbs, arms, legs, or head.
Tremors also tend to occur when a person isnt otherwise moving, or is at rest. We call that a resting tremor, says Herrington. In such a case, the tremor isnt as pronounced when the person is using the body part affected by the tremor. However, Herrington says, when the hand comes to rest . . . the tremor emerges.
Tremors are usually more prominent when Parkinsons medications are wearing off, he says. During an off time for example, if a person has stopped taking their medicine they can be slow and stiff or stooped over. When they walk, says Herrington, theyll take very short steps. Theyre moving less, and theyre moving small.
Read Also: What Medication Is Used To Treat Parkinson’s Disease
Uncontrolled Movements In Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a disorder that can involve several different kinds of uncontrolled movements. Some are caused by the disease, such as tremor and gait freezing, while dyskinesia uncontrolled jerking or twisting movement is caused by long-term levodopa use. We unpack how dyskinesia affects movement in Parkinsons disease and how its usually treated.
Tardive Dyskinesia: A Distressing Drug
Tricia A. Meyer, MS, PharmD, FASHPDepartments of Pharmacy and AnesthesiologyTravis E. Belson, CPhTThe Texas A& M Health Science Center College of MedicineTemple, Texas
US Pharm. 2014 39:HS13-HS16.
ABSTRACT: Tardive dyskinesia , a drug-induced movement disorder, is a serious side effect resulting primarily from the prolonged use of dopamine-blocking agents. TD is distressing because this adverse effect is likely to be permanent. Age is a consistent risk factor for TD, and the disorder occurs more frequently in women. Most treatments for TD have not proven to be successful, and therefore the best treatment option is prevention of the disorder. If a drug known to cause TD is prescribed, the clinician should monitor the patient for symptoms. Early detection may improve the likelihood of remission.
You May Like: What Kills A Person With Parkinson’s Disease
Other Causes Of Dyskinesia And Dystonia
There are many types of dystonia unrelated to Parkinsons disease. Many forms of dystonia occur with no known cause. Some causes of dystonia are hereditary, while brain injury can also cause dystonia.
Huntingtons disease is a rare, genetic condition in which nerve cells in the brain degenerate over time. This disease causes movement disorders similar to Parkinsons, including chorea and dystonia.
Multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy are other rare, degenerative disorders that affect muscle movements. Dyskinesia can occur when people with MSA or PSP are treated with levodopa, and untreated MSA or PSP can lead to the development of dystonia.
What Does Tardive Dyskinesia Look Like
TD looks like different, uncontrollable movements and patterns of the limbs and face. Sometimes referred to as stereotypy, the activity can be patterned, repetitive, and rhythmic movements that can involve one or more body parts. More than 3/4 of those with TD experience oral-facial-lingual stereotypic movements .1 The Baylor College of Medicine Movement Disorders Clinic conducted a videotape review of 100 people with tardive dyskinesia. The evaluation showed that the majority experienced irregular and chaotic movements in the OFL region, including lip smacking, chewing and other tongue and mouth movements. Other areas of the body can also show signs of TD like nodding and rocking, repeated body movements like crossing and uncrossing arms and legs, and random vocalizations.
Those who experience these involuntary movements may not even realize it. Like other conditions, these stereotypies can get worse under stress. They can manifest as muscle contractions or spasms, inability to be still, facial tics, or other jerking and abnormal movements.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease Education Handout
Drugs Acting On Serotonergic Systems
The basal ganglia have dense serotonergic innervation. It is suggested that serotonergic transmission has an inhibitory effect on dopaminergic transmission. There are reports of successful use of 5HT agents in treating LIDs., However, these studies included very small numbers and were mostly uncontrolled.
Medications And Supplements Used To Treat Tardive Dyskinesia
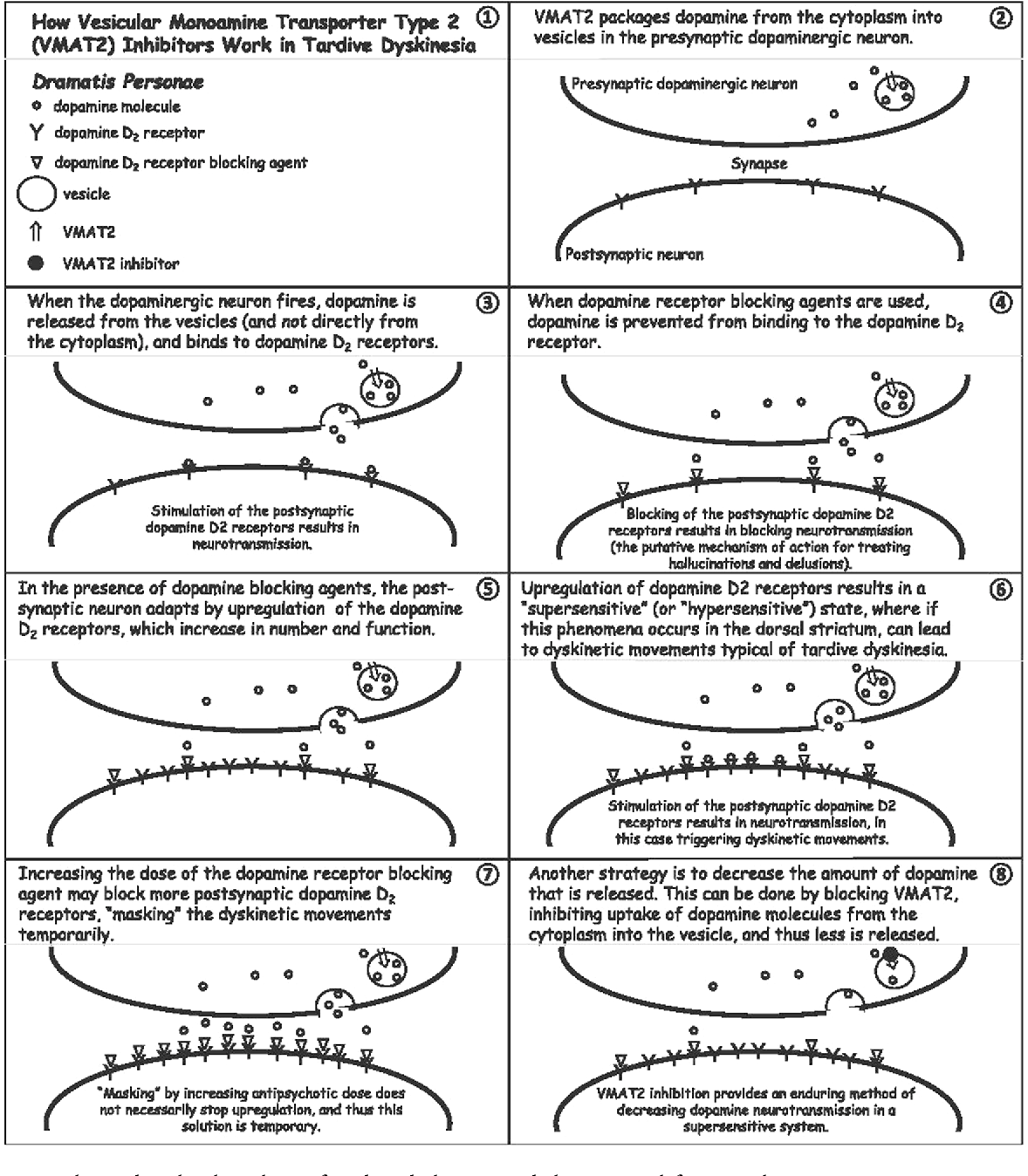
A number of medications and supplements have been identified that ameliorate TD symptoms.
Cholingergic Agents.
Cholinergic agents are used as muscle stimulants to diagnose myasthenia gravis and to treat glaucoma. These agents can also improve the Parkinsonian features of TD. Donepezil, a reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, is currently the only cholinergic medication that has shown benefit against TD. Overall, however, cholinergic agents are not a widely accepted treatment for TD as sufficient evidence is lacking to suggest they are more helpful than other treatments.
Clozapine, Quetiapine, Olanzapine, and Apomorphine.
Clozapine, a serotonin and dopamine receptor antagonist, is an atypical APD used to treat schizophrenia. Clozapine is the best current medication recommended for patients who require antipsychotics and simultaneously have TD, as clozapine has been reported to reverse TD symptoms., Clozapine has been linked to TD however, the incidence is much lower compared to other atypical APDs. Drugs with similar mechanisms of action such as quetiapine, a weak striatal dopamine antagonist, and olanzapine, a dopamine and serotonin receptor antagonist, have also been shown to be effective in ameliorating TD symptoms. Apomorphine, a dopamine receptor antagonist, can be given in conjunction with L-DOPA to decrease dyskinesias.
Tetrabenazine Analogs.
Clonazepam.
Propranolol.
Amantadine.
Branched-Chain Amino Acids.
Ginkgo Biloba.
Antioxidant Medications and Supplements.
Don’t Miss: What Age Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed
How Are Tremors And Dyskinesia Treated
We treat these two kinds of movements very differently, says Herrington. Dyskinesias are usually a problem of too much dopamine medication , and tremors are sometimes a problem of not quite enough.
Its therefore important for a neurologist to be able to tell the difference between the two symptoms, he says, and to adjust the medications accordingly.
Herrington points out that not all people are similarly bothered by tremors or dyskinesia. Take tremors, for example. There are some people who have a very small tremor and it bothers them immensely, he says. Other people have quite a substantial tremor and really dont seem to care about it very much.
When it comes to treating Parkinsons-related tremors, doctors may start out by asking people how much the symptom bothers them. As a physician, you can categorize which symptoms people have or the level of severity, says Herrington, but its always really important to ask the person what bothers them. The most objectively severe symptom may not be the one that bothers them the most.
As for dyskinesia, some people dont notice it at all, he says. there is often a divergence between how much they notice and are bothered by it and how much their loved ones notice and are bothered by it.
How Levodopa Can Impact Uncontrolled Movements In Parkinsons Disease
Carbidopa-levodopa is a drug combination that works to reduce symptoms in Parkinson’s disease for as long as a patient takes it. Levodopa converts into dopamine in the brain, helping to control movement, while carbidopa prevents the breakdown of levodopa in the bloodstream so more levodopa can enter the brain.
In Parkinson’s, dopamine-producing brain cells are lost and dopamine levels decrease, leading to disease symptoms. Levodopa effectively treats motor symptoms, such as tremors, stiffness, and slowness of movement by crossåing into the brain through what is referred to as the blood/brain barrier. It is combined in medications with carbidopa, which slows the breakdown of levodopa in the bloodstream so more medication can reach the brain. Carbidopa can also reduce nausea and vomiting, common levodopa side effects.
While effective at managing some symptoms, it does not slow or stop disease progression or treat non-motor symptoms like sleep issues and depression.
As the underlying disease progresses and symptoms get worse, patients may need to increase their dose or take levodopa more frequently to experience the same reduction in symptoms. Patients may experience what is referred to as “off” time when the medication wears off before it’s time for another levodopa dose. “Off” time can lead to motor fluctuations as well as the return of other symptoms.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease Treatment Guidelines