What Are The Causes
The cause of Parkinson’s is largely unknown. Scientists are currently investigating the role that genetics, environmental factors, and the natural process of aging have on cell death and PD.
There are also secondary forms of PD that are caused by medications such as haloperidol , reserpine , and metoclopramide .
Evaluation And Treatment Of Constipation In Neurological Diseases
In evaluation of the neurologically diseased patient with respect to gastrointestinal dysfunction, a combination of a carefully taken history , including actual medication, and physical examination including digital exploration, will be adequate in most cases. Patients may present with abdominal discomfort or pain, and investigations generally do not detect any abnormalities. Based on history alone, it may prove to be difficult to differentiate slow colonic transit time and outlet obstruction. Severe cases of constipation secondary to slow colonic transit, may present with decreased appetite and not uncommonly with nausea, but rarely with vomiting.
Stercoral diarrhoea is a bothersome symptom and though the impaction is evident to the physician, it may prove difficult to treat.
Patients, who have difficulty in evacuating the rectum, generally have outlet obstruction and neoplasia needs to be excluded.
In female patients with severe constipation and difficulty with defecation, it is important to exclude rectoceles, which are mostly asymptomatic but sometimes can cause incomplete emptying.
Further investigation with radiography or manometry depends on the situation. In cases with incomplete emptying, manometry with anal sphincter EMG should be conducted to establish the reason for the prolonged straining.
Table 1
Figure 1 outlines a possible strategy for management and drug treatment in constipated patients.
Figure 1
Clinical And Demographic Features
Table compares the demographic characteristics of the 38 patients with PD and 16 patients with other forms of parkinsonism that completed our work-up. Patients with PD were older than patients with parkinsonism . However, age of onset, disease duration and gender distribution were similar in both groups, despite a trend for higher percentage of women in the parkinsonism group and for older age of onset and longer disease course in the PD group. Mean Hoehn and Yahr scores in the PD group were 2.6±0.1 . Most of the PD patients were treated with levodopa and 68.8 % of the parkinsonism group were taking levodopa. A third of the PD patients and 31 % of the parkinsonism group were treated with pramipexol while 38.9 % of the PD and none from the parkinsonism group were treated with amantadine and only 8.3 and 18.8 were treated with biperiden.
Table 1 Demographic characteristics and risk factors for neuropathy in patients with Parkinsons disease and Parkinsonism
Recommended Reading: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinson
Risk Factor Assessment For Large And Small Fiber Neuropathy
Patients with EMG abnormalities were older: 65.5±3.8 vs. 53±3 years , but abnormalities on SWT scores were not associated with age. In addition, patients with either SWT or EMG abnormalities were not more likely to be older than normal patients. Patients with EMG abnormalities were more likely to be older at the disease onset but there was no significant relationship between EMG abnormalities and disease duration. In addition, there wasnt any significant relationship between the age of disease onset or disease duration and SWT scores .
Regression analysis of tibial and peroneal CMAP amplitudes and conduction velocities or sural SNAP and conduction velocities versus the presence of DM or B12 levels was not significant. In addition, regression analysis also did not disclose any significant relationship between SWT scores and electrodiagnostic parameters, i.e. tibial and peroneal CMAP amplitudes and conduction velocities or between sural SNAP and conduction velocities.
A Constipation In Stroke
Constipation and stroke seems associated, yet no studies have been able to show a direct association either clinically or pathophysiologically. However, the number of studies in this field is limited. It is a general experience, that constipation is frequent in acute admitted stroke patients. There may be several explanations for this: the patients are elderly, often treated with a number of drugs, dehydrated, and immobile already at admittance. Box 1 lists a number of drugs, which themselves or in combination may induce constipation. Bed rest and immobility often give rise to constipation, and may in addition induce deconditioning, resulting in inadequate force to defecate.
Hypovolemia is a common problem, both before and after stroke, the latter as a result of dysphagia and/or impaired thirst mechanisms and lack of attention to drinking possibilities. Diet may be another problem, as the hemiplegic population often has an insufficient intake of dietary fibre.
Lesions affecting the pontine defecatory centre may disrupt the sequencing of sympatical and parasympathical components of defecation, and impair the coordination of the peristaltic wave and the relaxation of the pelvic floor and external sphincter.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Leaning To One Side
Ldopa Iatrogenic Effect: Biochemical Considerations
Data from our systematic review confirm the association between increased Hcy plasma levels and PNP. Hcy may directly cause neurotoxicity through an increased vulnerability to mitochondrial toxins, induction of inflammatory reactions, glutamatergic excitotoxicity, and impairment of DNA repairing mechanisms., , , Multiple evidence supports the notion that Hcy has a neurotoxic effect not only in PD, but also in diabetes, and in the general population of elderly subjects. A possible neuroprotective effect of COMT inhibitors has been postulated in human subjects and supported by animal studies. Cossu and colleagues recently found that PD patients treated with COMT inhibitors had a lower incidence of PNP, lower plasma levels of Hcy, and higher vitB12 plasma levels.
MMA levels were found to be increased in almost all patients with PDassociated PNP, but its pathogenic role in the complex cascade of events associated with ldopaassociated PNP remains unclear. Some researchers suggested that MMA might represent an early marker of cobalamin functional insufficiency, in particular considering that up to 50% of patients with clinically significant cobalamin deficiency have vitB12 plasma levels still comprised within the normal range., ,
Techniques And Experimental Design
The medical charts of all patients were also reviewed, including the risk factors for neuropathy. Basic laboratory tests were requested to pursue the work-up for neuropathy and/or clinical evaluation for the presence of thyroid diseases, diabetes mellitus or vitamin B12 deficiency. Although most of the patients routinely had prior evaluation for diabetes and thyroid disease by primary care physicians , screening for B12 deficiency could only be documented in 63.2 % of the PD and 56.3 % of the parkinsonism group.
Don’t Miss: Wearable Technology For Parkinson Disease
Most Common Causes Of Parkinsons And Neuropathy
Although specific nerve degeneration is different in Parkinsons and Neuropathy, both diseases have the same causes across the general population. Slow bio-accumulation of toxins in the body for years, if not sufficiently flushed, results in nerve degeneration. Risk of these diseases depends on ones overall toxic load and general level of health. There are many individual factors such as where you live, level of exposure, diet, gut health, and exercise. Here are the top causes:
Graph shows Parkinsons deaths correlated to use of Monsantos Glyphosate on crops , and increased consumption of GMO corn and soy in the USA from 1985 to 2009.
Left, a healthy brain with normal dopamine activity.Right, a brain with Parkinsons showing disrupted dopamine signaling.
Ways To Decrease Risk Of Heart Disease
As in the general population, heart disease in people with PD can be decreased by managing traditional risk factors:
- Smoking cessation According to the American Heart Association, smoking is the most preventable cause of premature death in the U.S. Smoking increases the risk of developing many chronic disorders, including atherosclerosis that can lead to heart disease and stroke.3
- Treatment of high blood pressure Approximately 90% of all Americans will develop hypertension, or high blood pressure, over their lifetime. Hypertension puts more stress on arteries and can cause damage over time.3
- Treatment of high cholesterol High cholesterol is one of the major controllable risk factor for heart disease. When too much LDL cholesterol is in the blood, it can build up in the artery walls and narrow the vessels that feed the heart and brain.3
- Control of diabetes Diabetes can affect many major organs in the body, including the heart. Fortunately, diabetes is treatable and often preventable.3
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Support Group For Caregivers
Risk Factors That Increase Risk Of Cardiovascular Disease
Recent research showed that people with Parkinsons who have a high or medium risk of cardiovascular disease tend to have more problems with walking and memory. While both cardiovascular disease and PD become more common as people get older, this study found that people with poorer cardiovascular health also had worse walking and memory problems, even in the early stages of PD. The study authors suggest that assessment and treatment of vascular health may help improve these patients PD symptoms as well.4,5
What Does This Mean
Rajabally and Martey found that people with PD were more likely to have a polyneuropathy than people with other neurologic illnesses. There was a relationship between low vitamin B12 levels and the presence of the nerve problem. There also seemed to be a relationship between the duration of PD and the neuropathy. However, they did not find a clear link between the duration of treatment with levodopa and the occurrence of the neuropathy. Because of this, they were unable to conclusively prove that levodopa causes a polyneuropathy. However, their findings are very important because they showed that more people with PD have polyneuropathy and low vitamin B12 levels. This suggests that doctors need to check vitamin B12 levels in each person with PD.
Don’t Miss: Do People Die From Parkinson’s Disease
Constipation In The General Population
The prevalence of constipation in the population is comparatively high around 15%, with a higher prevalence in the female population and in elderly people. In one study investigating almost 15 000 women, 14% to 27% were found to be constipated, highest prevalence in elderly people. Walking less than 0.5 km a day increases the risk of constipation in elderly people, but the role of exercise in the treatment has been challenged. There seems to be strong beliefs, within both medical professionals and the general population that dietary fibre intake should be around 35 g of fibre a day, and it has been documented, that this volume increases the frequency of defecation. Reports are not unanimous in respect of preventing or changing the course of constipation with dietary fibre, and the beneficial effects in treatment in neurological diseases are not evident.
Other Causes Of Parkinsonism
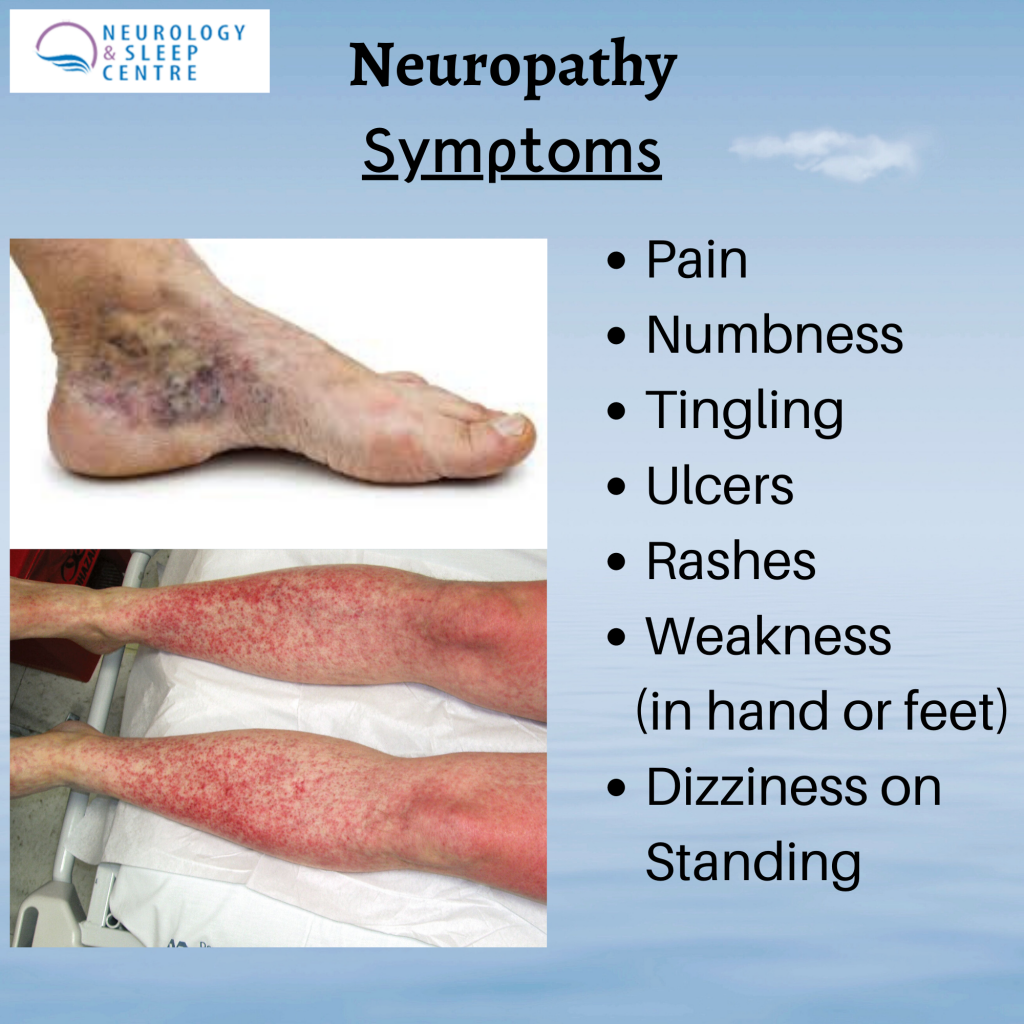
“Parkinsonism” is the umbrella term used to describe the symptoms of tremors, muscle rigidity and slowness of movement.
Parkinson’s disease is the most common type of parkinsonism, but there are also some rarer types where a specific cause can be identified.
These include parkinsonism caused by:
- medication where symptoms develop after taking certain medications, such as some types of antipsychotic medication, and usually improve once the medication is stopped
- other progressive brain conditions such as progressive supranuclear palsy, multiple systems atrophy and corticobasal degeneration
- cerebrovascular disease where a series of small strokes cause several parts of the brain to die
You can read more about parkinsonism on the Parkinson’s UK website.
Page last reviewed: 30 April 2019 Next review due: 30 April 2022
Also Check: What Is The Difference Between Parkinson’s And Alzheimer’s
Peripheral Neuropathy And Parkinsons Disease
A number of studies have tried to determine if PN is more common among people with PD as opposed to people without PD. PN is a relatively common condition in the general population, which makes it difficult to ascertain whether or not it is even more common among people with PD.
The available studies have varying results and are difficult to compare with each other as they:
- Include different types of populations of people with PD
- Assess peripheral neuropathy differently
- Assess for causes of peripheral neuropathy differently
A recent review looked at all the available data and determined that large fiber neuropathy was present in 16% of patients with PD, about double the prevalence of this condition in the general population. Skin biopsy-proven small fiber neuropathy was present in over 50% of people with PD, although this result was based on a small sample of patients.
Patients With Parkinsons Disease Are At Risk For Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Patients with carpal tunnel syndrome experience pain, numbness and tingling that can be characterized as an upper limb neuropathy. CTS is more common in women, with a female to male ratio of 3:1. Various studies have described the incidence of CTS in the general population as between 2.5 and 5 cases per 1,000 person years. Approximately one-third of patients newly diagnosed with CTS receive operative treatment, and this percentage appears to be increasing.1 Although surgery is known to be an effective treatment, the question remains: Which patients are the best candidates for surgery?
You Might Also Like
Individuals with Parkinsons disease may be especially vulnerable to CTS. One study suggests that patients with Parkinsons may be at increased risk of CTS because of the repetitive movement due to tremor.2Others have noted the peripheral neuropathy that is associated with Parkinsons and wondered whether peripheral neuropathy is intrinsic to Parkinsons, a consequence of levodopa exposure or both.3 A body of evidence suggests that a form of small fiber neuropathy is intrinsic to Parkinsons, and thus, experts have suggested that patients with early and advanced Parkinsons be strictly monitored for subtle signs of neuropathy. Such evaluation should make it possible for healthcare providers to detect early symptoms of peripheral neuropathy and potentially provide better management.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease Exercise Program
Preventing Parkinsons And Neuropathy
Biggest Culprits | Digestive Health | Immune system | Movement | Optimizing Health
This article focuses on recent scientific research to isolate the actual roots of these two maladies, which interestingly have many of the same causes. It outlines the most effective ways to prevent them and maintain your health.
When doctors dont know what causes these diseases,theyre called idiopathic.
What is Parkinsons Disease?Parkinsons disease happens when nerve cells in the substantia nigra central area of the brain are damaged and can no longer produce dopamine, a nerve-signaling molecule that helps control muscle movement. People with PD have a variety of symptoms including loss of muscle control, trembling, and lack of coordination. People may also experience anxiety, constipation, dementia, depression, urinary difficulties, and sleep disturbances. Over time, symptoms intensify.
Symptoms of PD include the characteristic hand tremor, slow movement, slurred speech, small handwriting, accelerating small steps when walking, rigidity, decreased facial expression, poor balance, poor reflexes including blinking and swallowing, sleep disturbance, anxiety, depression, difficulty thinking, constipation, and skin problems.
In Parkinsons disease, dopamine-producing cells of the substantia nigra region of the brain basal ganglia slowly die. These cells normally produce dopamine, an essential neurotransmitter.
What is Neuropathy?
Ldopaindependent Peripheral Nervous System Degeneration In Pd: Neuropathological Considerations
There is evidence that PNP might result from a direct involvement of the peripheral nervous system in PD. Skin biopsies showed an increased prevalence of pathological alterations in patients with PD compared to controls, as well as a reduction in density of myelinated fibers, Meissner corpuscles, and intraepidermal nerve fibers, regardless of ldopa exposure. In particular, all neuropathological studies demonstrated signs of small fiber pathology also in ldopanaïve PD patients , whereas only two studies, found a correlation between small fibers neuropathy and ldopa doses. Aggregates of ubiquitin, 1433 protein, and peripheral alphasynuclein were also documented in peripheral axons, as well as in the skin, even in the prodromal phases of PD., , , In a cohort of over 5,000 ldopanaïve PD patients and 20,000 nonparkinsonian controls, Conradt and colleagues found that PD is associated with a 2.4fold higher prevalence of PNP. Moreover, the prevalence of EMGconfirmed PNP, mostly asymptomatic, ranged from 4.8% to 24.0%, in the revised studies that investigated also ldopanaïve PD patients., , , Finally, a recent study from our group found significant differences in the clinical phenotype of PD patients with and without PNP, suggesting that peripheral nervous system involvement represents a clinical endophenotype of a moreaggressive form of PD, characterized by greater cognitive impairment, nonmotor symptoms burden, and daily living functional disability.
You May Like: What Are The Initial Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Symptoms
Symptoms of PD vary from person to person, as does the rate of progression. A person who has Parkinson’s may experience some of these more common “hallmark” symptoms:
- Bradykinesia – slowness of movement, impaired dexterity, decreased blinking, drooling, expressionless face.
- Tremor at rest – involuntary shaking that decreases with purposeful movement. Typically starts on one side of the body, usually the hand.
- Rigidity – stiffness caused by involuntary increase in muscle tone.
- Postural instability – sense of imbalance. Patients often compensate by lowering their center of gravity, which results in a stooped posture.
Other symptoms that may or may not occur:
Freezing or being stuck in place Shuffling gait or dragging of one foot Stooped posture Cognitive impairment
How Was The Study Done
Between October 2010 and February 2011, Rajabally and Martey searched for 2 groups of patients. The first were people with PD. The second group included people who had other neurologic illnesses . The reason they needed to select 2 groups was for comparison.
There are many causes for polyneuropathy. The most common causes are diabetes and long-term alcohol use or abuse. In addition, vitamin deficiencies can cause a polyneuropathy. As the authors were searching for people to study, they excluded those who had diabetes, alcoholism, or a known vitamin deficiency. In this way, they were able to minimize other factors which might make the results more confusing.
Rajabally and Martey identified 37 people with PD. They matched these people with 37 people who were the same age and gender. Both groups were studied in exactly the same way. The participants had blood testing to look for vitamin levels, possible diabetes , and other medical illnesses. Each person had a detailed nerve test called an electromyogram. This test is one way to measure the severity of the nerve problem. Since levodopa was a possible cause of the polyneuropathy, the authors carefully measured the time that the people with PD had been taking this medication.
Also Check: 5 Signs You Ll Get Parkinson’s