What Would Happen If I Have Dbs
The duration and surgical steps may vary depending on the type of system used but typically, surgery to implant the DBS system lasts several hours. Your hospital stay is usually a few days and includes a pre-operative assessment, the surgery itself and initial healing before you return home.
Your surgical team will include a neurologist, a DBS specialist neurosurgeon, an anaesthetist, a radiologist and other healthcare professionals.
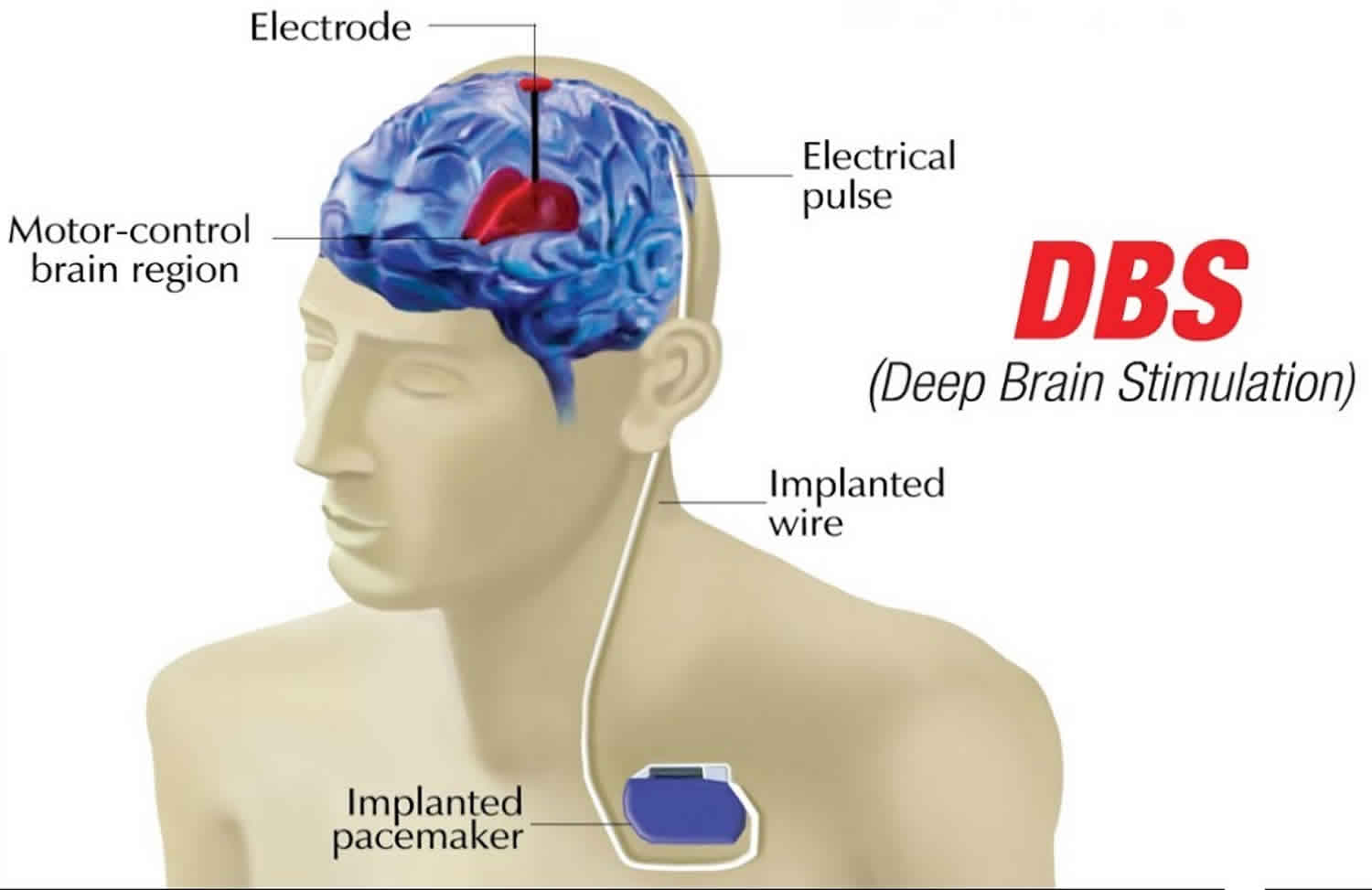
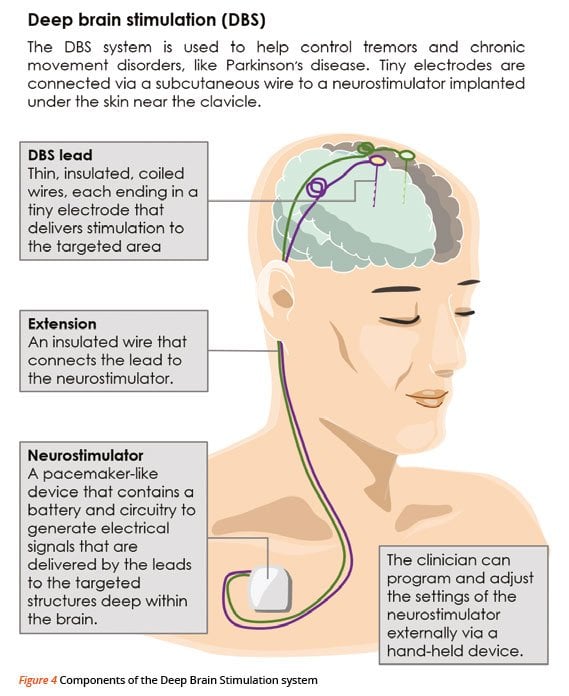
The components of a DBS system are:
- Neurostimulator this pacemaker-like device is the power source for the system. There are several rechargeable and non-rechargeable stimulators. Each contains a small battery and a computer chip programmed to send electrical pulses to control Parkinson’s symptoms.
- Lead an insulated wire terminating in four electrodes which transfer electrical current to your brain .
- Extension an insulated wire placed under your scalp and outside your skull to connect to the lead and run behind the ear, down the neck, and into the chest below the collar- bone where it connects to the neurostimulator.
- Programmer the doctor uses this external programmer to set the parameters for stimulation. Each person responds to DBS in their own way so the programmer will be used to customise the signals to your brain.
- Patient controller in some DBS systems you can use this to turn the neurostimulator on and off. It may also be used to adjust stimulation settings within the limits set by your doctor.
What Results Can I Expect After Parkinson’s Surgery
Deep brain stimulation does not cure Parkinsons disease or stop the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons.
However, deep brain stimulation reduces the severity of some motor symptoms such as severe tremors and slow movements.
Think of your best ON episode, i.e. when levodopa is most effective. This response is a good indicator of the best possible effect of deep brain stimulation on the extent and intensity of your symptoms.
Deep brain stimulation should significantly increase your ON time during the day and reduce your motor fluctuations. Your daily dose of levodopa should then decrease by half and therefore your dyskinesias caused by levodopa overdoses should partially disappear.
Deep brain stimulation substantially improves the quality of life of most patients who undergo surgery and usually gives them more autonomy in the performance of daily tasks.
However, this surgical procedure does not improve or only slightly improves Parkinsons disease non-motor symptoms. Your symptoms that are unaffected by levodopa will most likely not improve after surgery.
Symptoms such as speech disorders, balance problems and cognitive disorders are generally unaffected by deep brain stimulation. These symptoms may even intensify after surgery.
Functional Connectivity Changes At Postdbs And Predbs And Correlation With Clinical Changes
Figure and Table show four principal increases and four critical decreases in brain FC. Brain FC of the Language inferior frontal gyrus with the PreCGR and SMAL SMAL with Cereb7L and AGL SubCalC with Networks Dorsal Attention FEFR and Brainstem with PutamenR, PutamenL, Networks Visual LateralR, and OFusGR was increased .
Functional brain changes in PD patients postDBS compared with preDBS shown in the connectome ring . The changes between the regions of interest ROIs are shown in the 3D right and left hemispheres . Brain network FC decreased and increased between ROIROI after STNDBS . *162: Networks Language pSTGR 134: Networks Default Mode LPL 135: Networks Default Mode LPR 136: Networks Default Mode PCC 152: Networks Dorsal Attention FEFR 143: Networks Visual LateralR 156: NetworksFrontoParietal PPC L. Red line: FC increase in postDBS patients compared with preDBS. Blue line: FC decreased in postDBS patients compared with preDBS
Don’t Miss: 1st Sign Of Parkinson’s
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Neuroanatomical And Neurosurgical Considerations
The GPi is also involved in multiple non-motor functions, and probably has a topographical organization mirroring what observed in STN, with an antero-posterior and ventro-dorsal gradient of connectivity . This has been demonstrated thanks to tracing experiments in non-human primates , confirmed in DTI imaging studies . It must be underscored however that GPi does not receive direct cortical inputs this parcellation is based mainly on the distribution of connections to striatum. Therefore, the exact topography of GPi sub territories is less clear than for the STN. Nevertheless, the relative volume of the motor GPi to be targeted by DBS, is definitely greater than the motor STN. Therefore, the probability of stimulating current spreading to non-motor territories is probably lower . In that respect, this might represent an advantage of the GPi over the STN when choosing the stimulating target based on the theoretical risk of non-motor undesired side effects.
Read Also: Parkinson’s And Memory Loss
Management Of Depression In The Preoperative And Postoperative Phases
The existence of depressive symptoms is not per se a contraindication to DBS surgery. However, ongoing severe depression, psychotic symptoms, and suicidal ideation should be considered absolute contraindications as they might worsen and increase suicidal risk, particularly in the first year after surgery . Less evidence is available regarding severe depressive patients who were eventually stabilized by psychotherapy and medication, months or years prior to undergoing DBS: a trend toward a slightly worse motor and mood outcome has been described, but this certainly does not constitute an absolute contraindication to surgery . In any case, most groups and guidelines support the recommendation of a thorough psychiatric assessment before DBS surgery, and of a careful post-operative follow-up. Of note, the post-operative psychiatric assessment should not be limited to the immediate post-operative period, as the occurrence of apathy, for instance, peaks at around 4 months after surgery, often accompanied by depressive symptoms . Particularly after STN-DBS, which allows for a steeper reduction of dopaminergic medication, dopamine withdrawal symptoms should be prevented, when possible favoring the continued treatment with dopamine agonists .
Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinsons Disease
For people with severe motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease that are not adequately controlled by medication, a treatment called deep brain stimulation may offer some relief.
Deep brain stimulation requires the surgical placement of a small conductor called an electrode in the brain. The electrode delivers electrical stimulation that blocks the nerve signals that cause tremors.
Specialists at NYU Langones Center for Neuromodulation perform more than 100 deep brain stimulation procedures each year. Our neurologists, neurosurgeons, and psychiatrists provide a thorough evaluation to ensure youre a good candidate for the procedure.
You May Like: Is Rigidity A Symptom Of Parkinson’s
Testing Before Deep Brain Stimulation
For patients with Parkinsons disease, the doctor must confirm that the PD is levodopa-responsive and determine which symptoms are most likely to respond to DBS and discuss these with the patient.
To accomplish these two objectives, the movement disorders neurologist will examine the patient in the absence of his or her PD medications, then again after having taken them. Seeing the effect of PD medications on the movement and non-motor symptoms helps the physician and patient identify good target symptoms for DBS.
A cognitive assessment can help determine a persons ability to participate in the procedure, which involves providing feedback to the doctor during surgery and throughout the neurostimulator adjustment process. This assessment also informs the team of the risk of having worsened confusion or cognitive problems following the procedure.
Some hospitals also perform an occupational therapy review or speech, language and swallowing assessment. A psychiatrist may examine the person to determine if a condition such as depression or anxiety requires treatment before the DBS procedure.
Having Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation is carried out slightly different at each surgical centre. The team at your hospital will be able to give you information about the specific procedure you will have.
During your surgery, a frame will be positioned around your head to help avoid movement during the procedure. Two thin, insulated wires are inserted into the brain. Rarely, when the symptoms mainly affect one side of the body, these leads are only inserted on one side of the brain. The lead implanted in the left side of the brain controls symptoms affecting the right side of the body and the lead implanted in the right side of the brain controls symptoms on the left side of the body.
Your surgeon will implant the leads into a specific area of the brain that is suitable for your Parkinsons the position will not be the same for everyone. After surgery you might have a detailed scan of your brain to make sure that the leads are in the correct place.
Depending on the technique used, the procedure is either completed during one operation or during two separate operations. This might happen so that the device can be implanted a few days after the leads.
There are several deep brain stimulation devices available that transmit the electrical current needed. These are called pulse generators or neurostimulators. Different manufacturers make different devices and the team at your surgical centre will explain which are available and the advantages of each one.
Non-rechargeable pulse generator
You May Like: Is Cbd Good For Parkinson’s
What Happens After Surgery
After surgery, you may take your regular dose of Parkinson’s medication immediately. You are kept overnight for monitoring and observation. Most patients are discharged home the next day.
During the recovery time after implanting the electrodes, you may feel better than normal. Brain swelling around the electrode tip causes a lesion effect that lasts a couple days to weeks. This temporary effect is a good predictor of your outcome once the stimulator is implanted and programmed.
About a week later, you will return to the hospital for outpatient surgery to implant the stimulator in the chest/abdomen. This surgery is performed under general anesthesia and takes about an hour. Patients go home the same day.
Step 7: implant the stimulator You will be taken to the OR and put to sleep with general anesthesia. A portion of the scalp incision is reopened to access the leads. A small incision is made near the collarbone and the neurostimulator is implanted under the skin. The lead is attached to an extension wire that is passed under the skin of the scalp, down the neck, to the stimulator/battery in the chest or abdomen. The device will be visible as a small bulge under the skin, but it is usually not seen under clothes.
You should avoid arm movements over your shoulder and excessive stretching of your neck while the incisions heal. Pain at the incision sites can be managed with medication.
Depression And Parkinson’s Disease
Depression in PD is a common finding, and has an important impact on patient’s quality of life . Published prevalence estimates vary depending on the population studied, but significant depressive symptoms occur in around 35% of patients . The impact of depression on patients’ well-being can hardly be overestimated. It appears to be more distressing for patients and their families than motor symptoms . Treating depression have beneficial effects also on motor performance and conversely depressive symptoms are among the stronger predictors of initiation of dopaminergic therapy .
Recommended Reading: Community Resources For Parkinson’s Disease
How Is Deep Brain Stimulation Performed
Before the actual procedure begins, for most patients, a head frame is positioned on your head, which keeps your head still during brain imaging and is used to deliver the electrode to the target in the brain. Surgical pins or screws are used to secure the frame to your head. Sedation is typically given during this portion of the procedure.
Your neurosurgeon will implant the deep brain stimulation system in one to three stages.
First, a small hole is made in the skull. The leads, which have electrodes at the ends, are passed through this hole and surgically implanted in the areas of the brain identified as the site responsible for the movements caused by Parkinsons disease.
Most people with Parkinson’s disease will require one lead placed on each side of the brain unless symptoms are mostly one-sided . Each side of the brain controls the opposite side of the body, so each lead is inserted on the opposite side of where symptoms are occurring. Sometimes this procedure is done in stages one lead is placed at one time followed by another surgery for the other side. In other patients, both leads are placed during the same operation. Many times patients are awake during lead insertion. An intraoperative MRI is also sometimes used to image the lead location.
Potential Benefits Risks And Side Effects
DBS is not suitable for everyone, so it’s important to talk with your doctor about the potential benefits and risks. You should also discuss with a DBS neurologist the potential risks relating to not treating Parkinson’s, Parkinsons medication and other types of therapies. This information will enable you to make an informed decision on whether DBS is the right treatment to most effectively manage your specific symptoms.
You May Like: Core Exercises For Parkinson’s
Finite Element Method Modeling And Simulation
Electric field simulation was performed using the patient’s individual preoperative T1 and T2 MRI, postoperative CT, and clinical DBS settings. The degree of clinical improvement was defined based on UPDRS-III and combined with the volume of the simulated electric field for the creation of anatomical improvement maps. Figure shows an overview of the total processing workflow.
Figure 1
- CSF, cerebrospinal fluid.
Electrical Field Simulation
The brain conductivity model was used as input to FEM simulation in Comsol Multiphysics . The geometry of the leads was modeled and placed in the brain model based on the lead artifact in the CT images, co-registered to the preoperative MRI . The clinical DBS setting one year after surgery was used as input parameters for the simulations. The electric field distribution around the active contact was computed using the equation of continuity for steady currents, details of which are available in previous work . From the resulting electrical field an isolevel, according to Table , was applied to represent the volume of tissue affected by the active contact corresponding to stimulation of axons with a diameter of approximately 34 m . For the bipolar cases, the electric field on the anodic side was scaled with a factor of 0.6 to account for anodic stimulation being less effective than cathodic stimulation .
Improvement Maps
Issues With Spatial Analyses And Improvement Maps
The PSA is a small area where slight changes to stimulation parameters or electrode positioning theoretically may affect different structures. Since the zona incerta can be considered as a central hub, with wide connections to various brain areas , different pathways may be stimulated with the possibility to affect different PD symptoms.
Several other studies have used electric field simulation as input for creating probabilistic improvement maps and in some cases also prediction analysis . This was not addressed in this study due to the low level of significance in the statistical test, but the result can be seen as a spatial visualization of the improvement in the cohort. To further elucidate the improvement of different PD symptoms, data from monopolar review would give more spatial information and smaller fields in comparison to more complicated settings like double monopolar stimulation. The downside however is that one only sees the acute effects of stimulation and has lower external validity than chronic stimulation parameters.
You May Like: Nocturnal Leg Cramps Parkinson’s
What Are The Benefits
- Symptom reduction: DBS often reduces symptoms significantly. These include motor symptoms like stiffness, tremor, slowness and dyskinesia. DBS has also been shown to aid in on/off fluctuations, improve mood and quality of life, and increase overall energy level.
- Little to no damage: In contrast to previous methods, DBS does not damage portions of the brain, nor remove nerve cells.
- Utilizing DBS in addition to levodopa could decrease a persons need for medication, thus, decreasing medication access and cost issues, as well as levodopa side effects.
- Individualized treatment: Electrodes and stimulation frequency and intensity can be controlled by physicians and the individual with DBS, and can be subjectively altered when needed.
How Does It Work
Essentially, electrodes are placed deep into the brain and deliver electrical impulses and signals to specific brain cells. The exact mechanism by which DBS works is not completely known.
However, it is theorized that the electrical impulses delivered by the electrodes work to regulate and reset faulty electrical communication between brain cells that leads to PD symptoms such as tremor and dyskinesia.
A team of healthcare providers will determine if DBS is right for your specific situation. In most cases, it becomes an option for those who have had PD for at least 4 years, and who have breakthrough symptoms while on levodopa, leading to significant ‘off” time.
As with any procedure, there are risks and benefits to DBS. Check out the lists below for some of these pros and cons!
Also Check: Who Discovered Parkinson’s Disease
Instability And Rarely Falling
Let us think about two things that can cause you to fall if you have Parkinsons:
- Imbalance increases in 1/3rd of patients after DBS.
- Freezing decrease in most patients after DBS.
Overall, the beneficial effects outweigh the increased imbalance. So, usually patients fall less often after DBS.
But if the most important reason for you falling is that you are unstable, you should pause.
And think.
You should ask your doctor these 3 questions, BEFORE DBS.
If instability is the cause of your falls, proceed only after understanding the pros & cons.
If you have a Parkinsons plus syndrome, consider not getting DBS.
1. Falling: If you are falling because of instability.
2. Thinking/memory: If you already have these problems.
3. Depression: If you already have uncontrollable depression.
No one is perfect. Most patients with Parkinsons have these symptoms, in greater or lesser severity. This does not mean nobody can get DBS.
But if you have very severe/uncontrollable problems with any of these three symptoms, you should discuss the pros/cons of DBS in detail with your doctor before proceeding.