Exercise For Constipation In Parkinsons Disease
Be guided by your doctor, but general suggestions include:
- Talk with your doctor, physiotherapist, exercise physiologist or healthcare professional when planning your exercise program.
- Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise every day.
- Spend a few minutes warming up and cooling down. This could include marching in place or stretching.
- Start with the easiest exercises first. Slowly introduce the more difficult exercises as your fitness increases.
- Only exercise when other people are at home who can help if necessary.
- Remember: too little exercise and fluid intake with an increase in dietary fibre can worsen constipation for some people.
Management Of Incontinence In Patients With Parkinsons Disease
It is estimated that two-thirds of all patients with PD have some degree of bladder problems ranging from complete inability to empty the bladder to the more common problem of urinating too often and to the ability to make it to the bathroom in time . Common dysfunctions are bladder overactivity, causing urinary urgency, frequency, and incontinence . Getting up at night to use the bathroom is the most prevalently reported non-motor symptom with PD, reported by more than 60%. Weak voiding is also a common dysfunction. Patients may feel like they must go frequently, but when they go it may take longer than average to void. Constipation is another common issue that may arise and being constipated can affect medication absorption. Some studies suggest that 80% of people who have Parkinsons Disease report constipation.
Patients with Parkinsons Disease may also have difficulty eliminating urine. This can be caused by a sphincter that wants to close when the bladder is ready to empty or by a bladder muscle that is too weak to expel urine. This is a concern because incomplete bladder emptying can cause accumulation of urine and the growth of bacteria. The latter can result in an infection. The symptoms of difficulty eliminating urine include weak urinary stream, dribbling or leaking, and feeling that the bladder has not completely emptied.
Patient should be educated to alert their health care provider is they have any of the following signs:
Increased Risk Of Overactive Bladder In Patients With Idiopathic Parkinsons Disease: Insight From A Nationwide Population
-
Roles Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing original draft
Affiliation Department of Neurology, China Medical University Hospital, China Medical University School of Medicine, Taichung, Taiwan
-
Affiliation Department of Neurology, China Medical University Hospital, China Medical University School of Medicine, Taichung, Taiwan
- Cheng-Li Lin,
Roles Data curation, Formal analysis, Project administration
Affiliations College of Medicine, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan, Management Office for Health Data, China Medical University Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan
-
* E-mail:
Affiliations National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Health Research Institutes, Miaoli, Taiwan, Institute of Occupational Medicine and Industrial Hygiene, College of Public Health, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, Ph.D. Program in Environmental and Occupational Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
You May Like: Pfnca Wellness Programs
What Are They Wearing
Although you should allow someone with Parkinsons Disease to assert their individuality, you can ensure they are not wearing awkward clothing. Unnecessary zips and buttons on clothing can make it difficult to remove clothing in time, resulting in leakages. Try and encourage them to wear simple clothing that is fast and efficient to remove.
Treatment For Over Active Bladder In Parkinsons
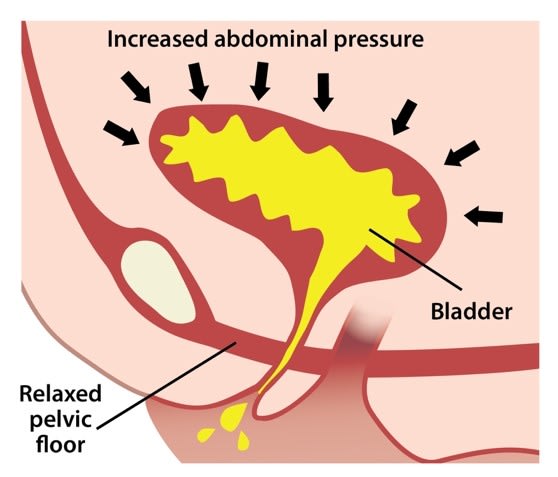
Overactive bladder affects up to 27% of men and 43% of women of the global population. Now, add a neurological condition and the problem becomes more challenging. First, there is a list of medications which make the problem worse, so should be avoided. Then, a thorough evaluation and physical exam. Treatment depends on the cause, but evaluating all medications and an adjustment of dopamine medication is often necessary. If you are still having problems, five further treatment options are included.
Recommended Reading: Judy Woodruff Parkinson’s
Treatment Of Bowel Dysfunction In Pd
3.4.1. Dietary Fibers
Although it is not certain whether exercise may facilitate bowel habit in PD, in the healthy population, moderate exercise is reported to shorten mouth-to-anus transit time and improve overall wellbeing . Water content is an important determinant to make stools normal or hard . PD patients are reported to have reduced water intake . Diet and laxatives are the first-line treatment for constipation . Dietary fibers such as psyllium produced an improvement in stool consistency and an increase in stool frequency in healthy population and PD . Polyethylene glycol 3350 , or bulking and highly hydrophilic agent polycarbophil , improve constipation in PD.
3.4.2. Cholinergic Drugs
A prior report has shown that pyridostigmine bromide, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, is effective in the amelioration of constipation in PD .
3.4.3. Dopaminergic Drugs
Levodopa and Other Dopaminergic Agonists
3.4.4. Dopaminergic Blockers
3.4.5. Serotonergic Drugs
3.4.6. Other Drugs
Although prior reports have indicated the effectiveness of motilides , neurotrophin-3 and colchicine on constipation in PD, their use remains limited. Type A botulinum toxin injection into the puborectalis muscle and biofeedback ameliorates anismus in PD.
Why Do Some People With Parkinson’s Disease Experience Urinary Incontinence
Parkinson’s is best known for its effects on balance and movement, but it impacts the autonomic nervous system as well. The autonomic nervous system controls specific bodily functions, like heart rate, blood pressure, libido, and urine production.
Over time, changes to the autonomic nervous system affect your bladder’s ability to store and release urine. That means you might have trouble making it to the bathroom on time or need to urinate more frequently.
You May Like: Zhichan Capsule
Warning Disclaimer Use For Publication
WARNING: Please DO NOT STOP MEDICATIONS without first consulting a physician since doing so could be hazardous to your health.
DISCLAIMER: All material available on eHealthMe.com is for informational purposes only, and is not a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment provided by a qualified healthcare provider. All information is observation-only. Our phase IV clinical studies alone cannot establish cause-effect relationship. Different individuals may respond to medication in different ways. Every effort has been made to ensure that all information is accurate, up-to-date, and complete, but no guarantee is made to that effect. The use of the eHealthMe site and its content is at your own risk.
If you use this eHealthMe study on publication, please acknowledge it with a citation: study title, URL, accessed date.
Physical Therapy For Incontinence
I had the unique and actually most rewarding experience going to physical therapy for my incontinence.
As you can imagine I was a bit hesitant at first but my lovely therapist was wonderful! I think this is very important that you feel very comfortable with your therapist, as this can already be an embarrassing issue. A proper therapist can make you feel more comfortable and less embarrassed, allowing for a greater exchange of ideas. Pelvic floor physical therapy is an effective treatment for symptoms of urinary urgency and urinary incontinence in people with Parkinsons disease.
Read Also: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinson’s
Various Effects Of Dopaminergic Drugs: Improvement Or Worsening
It is possible that levodopa and other antiparkinson medication could affect bladder function in PD. Aranda etâal. studied the effects of 3â8âmg apomorphine injection on the storage function in two de novo PD patients, and found that the bladder capacity increased. They gave oral levodopa to one of the patients, and the bladder capacity increased. We compared the frequency of bladder dysfunction in de novo PD and PD with levodopa. In that study, LUTS was less frequent than in the treated group. In another study, after 3âmonths of treatment with levodopa, the storage urodynamic parameters were slightly improved in de novo PD.
Assessment Of Parkinsonism And Other Adverse Health Outcomes
Parkinsonism was based on the presence of two or more cardinal signs of parkinsonism Trained nurse clinicians administered the mUPDRS. There were 26 items from the mUPDRS which assessed four parkinsonian signs . A sign was considered present if two or more of its respective items had at least a score of 1 indicating a mild abnormality. Parkinsonism was present if two or more of the four signs were present on clinical exam .
Mortality: When an autopsy is obtained, date of death is known promptly. When no autopsy is obtained, we obtain information on date of death from an interview with a knowledgeable informant or searches of public databases as previously described.
Disability was assessed annually via two self-report instruments. Basic activities of daily living were assessed using 6 items from the Katz scale . Mobility disability was assessed using the Rosow-Breslau scale, which assesses three walking performances .
Read Also: Prayers For Parkinson’s Disease
Ui And Adverse Health Outcomes
The mean follow-up of time of the participants was nearly 8 years . We employed a Cox proportional hazards model adjusted for age, sex, and education to examine the association of baseline UI with incident parkinsonism. Baseline UI was associated with incident parkinsonism . Since we treated UI as a numerical scale, inspection of the hazard ratio suggests that an individual with severe incontinence , had about a 30% increased risk of developing parkinsonism as compared to an individual without incontinence.
Since the pathologic basis for parkinsonism in older adults with and without a clinical diagnosis of PD may vary , we repeated this analysis excluding 65 cases with a clinical diagnosis of PD. Baseline UI remained associated with incident parkinsonism . In a final model, adding terms for seven chronic health conditions and BMI did not attenuate the association of UI with incident parkinsonism .
In further analyses, we examined whether baseline UI was associated with other adverse health outcomes. Baseline UI was also associated with risk of death and incident ADL and mobility disability, but was not associated with incident MCI or AD dementia . These findings were unchanged when we controlled for seven chronic health conditions and BMI .
The Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Associations of Baseline Urinary Incontinence and Global Cognition in Community-Dwelling Older Adults*
| Model Terms . |
|---|
Overactive Bladder Is The Major Symptom In Pd

LUTS are divided majorly into two: storage symptoms and voiding symptoms. Storage symptoms are the most common of the LUTS symptom types in PD. Storage symptoms include nocturia , which is the most prevalent symptom reported by patients with PD ., – Patients also complain of urinary urgency and daytime frequency . Urinary incontinence was present in 26% of male and 28% of female patients with PD.
Read Also: Yopd Life Expectancy
Parkinson’s Disease And Voiding Dysfunction
In this 54-minute webinar, urologist Dr. Sidney Radomski explains how voiding function is affected by Parkinsons disease in both men and women. He discusses how an enlarged prostate contributes to voiding problems and management options of voiding dysfunction for those with Parkinsons disease and MSA.
Sexual Dysfunction In Parkinsons Disease
People with PD may experience sexual dysfunction, including loss of desire, inability to orgasm, erectile dysfunction in men, decreased lubrication in women, or pain with intercourse in women. Some studies have found that sexual dysfunction may occur in 60-80% of men and women with PD. Older patients with PD have more sexual dysfunction than younger patients, although sexual dysfunction is also greater in older adults who do not have PD. In addition to age, conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and depression can factor into sexual dysfunction.3,4
There are several factors that can lead to sexual dysfunction in people with PD. In addition to the motor symptoms of PD, which may create practical barriers to engaging in sexual activity, non-motor symptoms like depression, anxiety, or sleep disturbances can also impact a persons sex drive. Many people with PD express dissatisfaction with their sexual life.3,5
Some people with PD who are treated with dopamine agonists develop impulse control disorders, like hypersexuality. Hypersexuality can lead to unusual or increased sexual behavior, which may have devastating effects on relationships. Changing medications or reducing the dose of medication can help, and people who experience any side effects such as impulse control disorders should bring it to the attention of their doctor.3
You May Like: Parkinson Silverware
Luts Estimated To Be Up To 65% In Patients With Pd
The reported prevalence of LUTS in patients with PD ranges from 38% to 71%.- However, it has been difficult to determine to what extent PD contributes to LUTS. Men older than 60âyears-of-age might have bladder outlet obstruction as a result of prostate hyperplasia. Women might have stress urinary incontinence. âIdiopathic DOâ can occur in men and women aged older than 65âyears due in part to latent brain ischemia. Some of the studies were published before the diagnosis of MSA was recognized. In recent studies of PD patients who were diagnosed according to modern criteria,, – the prevalence of LUTS was found to be 27â63.9% using validated questionnaires,- or 53% in men and 63% in women using a non-validated questionnaire that includes a urinary incontinence category, with all of these values being significantly higher than the incidence rates in healthy controls. The majority of patients had onset of bladder dysfunction after appearance of motor disorder. Correlations have been shown between bladder dysfunction in patients with PD and neurological disability, and bladder dysfunction and stage of disease, both suggesting a relationship between dopaminergic degeneration and LUTS. However, Campos-Sousa etâal. did not find such a correlation.
What Happens To Someone Who Has Urinary Incontinence
The pelvic floor consists of a hammock of muscles, ligaments, and connective tissue, which covers the bottom of the pelvic cavity and assists in supporting the abdominal and pelvic organs. The pelvic floor maintains continence of bowel and bladder and plays an important role in sexual function.
The pelvic floor muscle consists of three layers and has fast and slow-twitch fibers to assist with support and sphincter properties. The muscle is the same in women and men and both sexes benefit from maintaining good strength and tone of the pelvic floor muscle.
As we age and with certain diseases such as PD our muscles become weak and the signals do not always tell the muscles to tighten up when they need too. Add a few pounds to the belly region also and you have the perfect storm for Peezing, Peelaughing, as well as a host of other words for embarrassing moments due to urinary incontinence or urgency!
Read Also: Diseases Similar To Parkinsons
Take Control Of Your Parkinsons Treatment
OurEvery Victory Counts® manual gives people living with Parkinsons, their care partners and their family members the tools they need to take control of their own Parkinsons treatment through a proactive approach to self-care.
a powerful new print edition
Its jam-packed with up-to-date information about everything Parkinsons, plus an expanded worksheets and resources section to help you put what youve learned into action. Color coding and engaging graphics help guide you through the written material and point you to complementary videos, podcasts and other materials on the Every Victory Counts companion website. And, it is still free of charge thanks to the generosity of our sponsors.
Request your copy of the new Every Victory Counts manual by clicking the button below.
Urinary Issues In Advanced Parkinsons Disease
Urinary dysfunction and symptoms in PD are most commonly caused by overactivity of the detrusor muscle, or the muscle of the bladder, which contracts excessively despite the fact that it is not filled with urine. This causes an increased urge to urinate and/or an increased frequency of urination, which can be especially prominent at night. In advanced PD, this could culminate in urinary incontinence, or involuntary release of urine. Mobility issues which make getting to the bathroom slower and more cumbersome, compound the problem.
Always remember that people with advanced PD may have other medical problems that affect their urination such as an enlarged prostate. Make sure to have a complete evaluation before assuming that the problem is only related to PD. It is also essential to keep in mind that if changes in urination occur suddenly, there could be a urinary tract infection present.
Once other medical issues and urinary tract infection are ruled out, there are a number of approaches to the issue of urinary incontinence in a person with advanced PD:
Unfortunately, for some, the above available options may not be sufficient to effectively treat urinary incontinence in advanced PD. If this is the reality, it becomes extremely important to keep the skin dry with frequent changes of incontinence products to prevent skin breakdown and the potential development of skin infection.
Recommended Reading: On-off Phenomenon
Management Of Sexual Problems By The Physician
Management of sexual problems can be applied in steps. The Open Sexual Communication module is a four-step tool designed to assist physicians in discussing sexual issues with patients and offer them adequate advice or treatment . Sexual advice can go along with medical interventions for the SD, but also can be applied independently. For example, in couples for whom intercourse is not a realistic possibility either because of physical limitations or because of impairments of genital functioning, suggestions about outercourse can be offered. The key to a physicians success in assessing and treating sexual problems is comfort in asking relevant questions and the belief that PD patients are sexual human beings with the ability to share love, intimacy and sexual excitement.
Recommended Reading: Weighted Silverware
What’s Next For Those Suffering From Urinary Incontinence

I decided I did not want to add another medication to the medicine bag. I was trying to see if there was something I could do besides resigning myself to wearing pads or some other incontinence protection all the time. At 53 years old, I wanted to see if there was a way I could help myself.
Part 2 of this article will address my experiences. I plan to discuss what I lovingly refer to as “PEE PEE PT” – physical therapy to help treat urinary incontinence.
You May Like: Voice Amplifiers For Parkinson’s
Urinary And Fecal Incontinence
I just wanted to say, as a care provider, that this topic should be more discussed as an issue with PD. We have two neurologists, one who is really renowned as a PD specialist in the area, but discuss this topic with them and they get kind of quiet and say that’s not really their domain. But when you read articles like this one: bladderandbowel.org/associa… it clearly indicates that it IS a part of PD. Why don’t more people talk about this or am I just not looking in the right places. The coordination of messaging between the brain and muscles is the thing, right? So both the urinary and bowel systems have muscles and sphincter muscles that need messaging from the brain, hence PD problem. If anyone has any tips with how to help my loved one in this area, I’d greatly appreciate it. It’s demoralizing and wish I could just fix it.
According to a Michael J. Fox podcast several years ago “urinary problems” effect 43% of people with Stage 1 Parkinsons…. 90% of those at stage 4 and 5. So you are on track with your suggestion that these subjects should be talked about more here.
There was an report on a study published last February that might be of interest as it points to a solution. Title was:
Clinical study of the effects of deep brain stimulation on urinary dysfunctions in patients with Parkinsons disease. Briefly . . .
SKCW:
Let me know directly by messaging me.
Sharon