Introduction Of Bacteria Via Catheterization
Indwelling urinary catheterization provides a direct pathway for pathogenic bacteria to ascend from the external environment to the lower urinary tract. There are three possible mechanisms by which catheterization may lead to bacterial colonization of the lower urinary tract and subsequent infection . First, bacteria may be introduced directly during catheter insertion if aseptic technique is not observed. Secondly, bacteria may travel along the outside of the catheter, between the urethral mucosa and the exterior of the catheter. Lastly, bacteria may ascend directly along the interior lumen of the catheter. Overall, extraluminal tracking of bacteria seems to be the predominant pathophysiologic mechanism of catheter-associated UTI , with biofilm formation playing a role in some cases . Bacteriuria is virtually guaranteed with indwelling urinary catheterization and is more likely with prolonged duration of catheterization.
Dont Miss: Parkinsons Disease Journal Articles
Treatment For Over Active Bladder In Parkinsons
Overactive bladder affects up to 27% of men and 43% of women of the global population. Now, add a neurological condition and the problem becomes more challenging. First, there is a list of medications which make the problem worse, so should be avoided. Then, a thorough evaluation and physical exam. Treatment depends on the cause, but evaluating all medications and an adjustment of dopamine medication is often necessary. If you are still having problems, five further treatment options are included.
Eating the right amount of fibre and drinking enough fluids can help if you have constipation.
To get more fibre in your diet:
- choose a breakfast cereal containing wheat, wheat bran or oats, such as Weetabix, porridge or bran flakes.
- eat more vegetables, especially peas, beans and lentils.
- eat more fruit fresh, stewed, tinned or dried. High fibre fruits include prunes or oranges.
- drink plenty of fluids throughout the day to avoid dehydration. Lots of fluids are suitable, including water, fruit juice,
- milk, tea and squashes. Cut out caffeine to avoid overstimulation of your bladder.
If you find it difficult chewing high-fibre food, you can get some types which dissolve in water. You can also get drinks which are high in fibre.
Try to increase how much fibre you get gradually to avoid bloating or flatulence .
A dietitian can give you further advice. Ask your GP, specialist or Parkinsons nurse for a referral.
Compliance With Ethical Standards
Amit Batla and Natalie Tayim each declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Mahreen Pakzad has been a speaker for Astellas.
Jalesh N. Panicker has received royalties from Cambridge University Press, has been involved in trials supported by FirstKind Ltd, Allergan and Ipsen and has received speaker honoraria from Wellspect, Astellas and Allergan.
You May Like: Prayers For Parkinsons Disease
Recommended Reading: New Cure Parkinson’s Disease
Assessment Of Parkinsonism And Other Adverse Health Outcomes
Parkinsonism was based on the presence of two or more cardinal signs of parkinsonism Trained nurse clinicians administered the mUPDRS. There were 26 items from the mUPDRS which assessed four parkinsonian signs . A sign was considered present if two or more of its respective items had at least a score of 1 indicating a mild abnormality. Parkinsonism was present if two or more of the four signs were present on clinical exam .
Mortality: When an autopsy is obtained, date of death is known promptly. When no autopsy is obtained, we obtain information on date of death from an interview with a knowledgeable informant or searches of public databases as previously described.
Disability was assessed annually via two self-report instruments. Basic activities of daily living were assessed using 6 items from the Katz scale . Mobility disability was assessed using the Rosow-Breslau scale, which assesses three walking performances .
Read Also: Prayers For Parkinsons Disease
Diagnosing A Urinary Tract Infection In Older Adults

Vague, uncommon symptoms such as confusion make UTIs challenging to diagnose in many older adults. Once your doctor suspects a UTI, its easily confirmed with a simple urinalysis.
Your doctor may perform a urine culture to determine the type of bacteria causing the infection and the best antibiotic to treat it.
There are home UTI tests that check urine for nitrates and leukocytes. Both are often present in UTIs. Because bacteria are often in the urine of older adults to some degree, these tests arent always accurate. Call your doctor if you take a home test and get a positive result.
Antibiotics are the treatment of choice for UTIs in older adults and younger people. Your doctor may prescribe amoxicillin and nitrofurantoin .
More severe infections may require a broad-spectrum antibiotic such as ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin .
You should start antibiotics as soon as possible and take them for the entire duration of treatment as prescribed by your doctor. Stopping treatment early, even if symptoms resolve, increases the risks of recurrence and antibiotic resistance.
Antibiotic overuse also increases your risk for antibiotic resistance. For this reason, your doctor will likely prescribe the shortest treatment course possible. Treatment typically lasts no more than 7 days, and your infection should clear up in a few days.
Its important to drink plenty of water during treatment to help flush out the remaining bacteria.
You May Like: Zhichan Capsule
Read Also: Is Parkinson’s Life Threatening
Management Of Sexual Problems By The Physician
Management of sexual problems can be applied in steps. The Open Sexual Communication module is a four-step tool designed to assist physicians in discussing sexual issues with patients and offer them adequate advice or treatment . Sexual advice can go along with medical interventions for the SD, but also can be applied independently. For example, in couples for whom intercourse is not a realistic possibility either because of physical limitations or because of impairments of genital functioning, suggestions about outercourse can be offered. The key to a physicians success in assessing and treating sexual problems is comfort in asking relevant questions and the belief that PD patients are sexual human beings with the ability to share love, intimacy and sexual excitement.
Recommended Reading: Weighted Silverware
Parkinsons And Urinary Incontinence
Parkinsons causes problems with automatic bodily functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and urinary function. Urinary incontinence is much different than fecal incontinence and usually doesnt start to occur until the later stages of the disease. Urinary incontinence due to Parkinsons is a two-fold problem. The bladder has trouble holding urine in, but, at the same time, its difficult to control the release of urine, leading to some serious discomfort and emergency bathroom visits.
Urinary incontinence problems can come in many forms:
A person with Parkinsons may have to urinate very frequently, complicated by an increasingly difficult time with movement. Once they sit down, they may find it difficult to let go of the urine and void their bladder. While nearly 40% of Parkinsons patients may experience some level of urinary incontinence, only 15% of patients should develop a serious urinary condition.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Disease Dementia Prognosis
Parkinsons Drugs And Their Side Effects On Kidneys
Parkinsons drugs have also been researched for kidney damage. Although it can be seen as a side effect of many Parkinsons drugs, There is no solid evidence, and many studies are underway. In a research, a 90-year-old parkinsonian woman treated with
Levodopa-Benserazide and Bornaprine developed rhabdomyolysis and were found unconscious on the floor.
Although there is little evidence, some clinical cases have been observed.
Dont Miss: Housing For Parkinsons Patients
What Are The Symptoms Of A Uti
Sometimes, you can have a UTI and feel no symptoms at all. However, UTIs often cause symptoms such as aburning pain during urination, strong-smelling urine, or a strong, persistent urge to urinate.
Other symptoms may include:
- Pressure in the lower pelvis
- Mental changes or confusion
If the infection impacts your kidneys instead of your bladder and urethra, you may experience different symptoms, such as nausea, back or side pain, chills, and vomiting.
Don’t Miss: Atrial Fibrillation And Parkinson’s
How Can A Neurodegenerative Disease Cause A Kidney Problem Can Parkinsons Cause Kidney Problems
Some studies have shown a relationship between chronic kidney disease and Parkinsons disease. Chronic kidney disease and Parkinsons disease both share many common risk factors, such as:
Although, its not common to come across patients with Parkinsons disease and chronic kidney disease with its associations.
Parkinsons disease has been shown to affect the kidney by causing chronic kidney disease or end-stagerenal disease. This can result in several metabolic derangements, hypoxia, toxins, and acidosis, which cause brain edema, particularly basal ganglia. This will lead to permanent Parkinsons disease due to cytotoxic derangements by damaged kidneys.
A kidney transplant can be a way out of the vicious cycle thought to be created between Parkinsons disease and kidney damage.
Along with the transplant, the immunosuppressants given in the process can act as a preventive measure for the permanent development of Parkinsons disease. This happens by interfering with the pathophysiology and reducing inflammations.
Another cause is triggered acute renal failure, mainly due to rhabdomyolysis. Parkinsons disease can be further more complicated due to rhabdomyolysis. This can lead to a sudden renal shutdown, i.e., Acute renal failure.
There can be two types of cases with rhabdomyolysis, one complicated by oligo-anuric renal failure, and this usually occurs in patients with Parkinsons disease.
Various Effects Of Dopaminergic Drugs: Improvement Or Worsening
It is possible that levodopa and other antiparkinson medication could affect bladder function in PD. Aranda etâal. studied the effects of 3â8âmg apomorphine injection on the storage function in two de novo PD patients, and found that the bladder capacity increased. They gave oral levodopa to one of the patients, and the bladder capacity increased. We compared the frequency of bladder dysfunction in de novo PD and PD with levodopa. In that study, LUTS was less frequent than in the treated group. In another study, after 3âmonths of treatment with levodopa, the storage urodynamic parameters were slightly improved in de novo PD.
You May Like: Parkinson’s And Mouth Problems
Treating And Managing Bowel Problems
The first step in dealing with bowel disorders is to talk to your doctor. He or she will probably review your medication to see if this is a contributory factor. Whilst it is usually possible to control any difficulties with diet, fluid intake and exercise, your doctor, or Parkinsons nurse specialist if you have one, will be able to advise further, and may, for example, prescribe laxatives in severe cases of constipation. If you have any alarm features such as unintentional weight loss or rectal bleeding, then you may need to be referred for specialist assessment.
The following healthcare professionals can also advise on aspects of bowel care:
- A dietician will be able to advise on diet and fluid.
- A physiotherapist may be able to help with advice and abdominal exercises which will help in passing stools.
- A speech and language therapist can help with swallowing problems. They may be able to advise on ways of relaxing your throat, and give guidance on posture and exercises to help overcome any difficulties you have.
- An occupational therapist may also be able to suggest practical ways to overcome any difficulties you have with eating and drinking.
Gi Manifestations In Autonomic Disorders
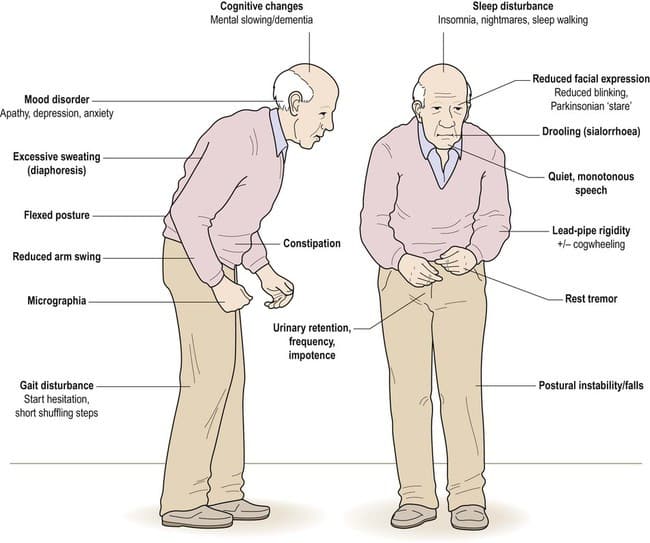
Early PD, when left untreated, is often accompanied by autonomic nervous system impairments among which GI symptoms represent the most common NMS . Indeed, several studies relying on nonmotor rating scales have underscored the particular significance of GI symptoms in assessing the quality of life and have shown that these manifestations occur in 60% to 80% of patients . GI disorders are among the most common causes of emergency admission and often result in severe complications such as malnutrition , pulmonary aspiration , megacolon , intestinal obstruction , and even intestinal perforation . Moreover, older age, DAergic medication, and higher disease severity are usually associated with these nonmotor features . Hence, GI symptoms reflect disturbances of GI tract motility at all levels.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease Smell Test
Gastrointestinal Issues In Advanced Parkinsons Disease
Problems with motility of the gut can be a major source of difficulty throughout the disease course and can be particularly problematic in advanced PD as well. . Constipation, which can be one of the earliest symptoms of PD is a very common problem throughout the disease course. Two gut issues that tend to be particularly problematic in people with advanced PD are abdominal pain and fecal incontinence.
You May Like: Parkinsons Bike Therapy
Evaluating And Treating Urinary Issues In Parkinsons Disease Multiple System Atrophy And The Other Atypical Parkinsonism Disorders
In this hour-long webinar, neuro-urologist Ekene Enemchukwu, MD focuses on urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, urinary retention, and other urinary issues in PD, MSA, and the atypical parkinsonism disorders. Following the presentation, moderator Candy Welch, Brain Support Networks MSA caregiver support group leader, asks Dr. Enemchukwu many questions submitted by webinar participants.
Recommended Reading: How To Help Someone With Parkinson’s Dementia
How Does Parkinsons Impact The Risk Of Getting Utis
In Parkinsons, the brains control of the urinary sphincter can become disrupted, leading to difficulty holding urine. As a result, people with Parkinsons may experience storage symptoms, which can increase the frequency and/or urgency of urination and lead to nocturia when you wake up multiple times at night to go to the bathroom. Another set of urinary symptoms, called voiding symptoms, can cause urination hesitancy, straining, interrupted stream, and double voiding . You may experience symptoms in both sets, which puts you at a higher risk of developing a UTI.
Voiding symptoms often go unnoticed for longer than storage symptoms do, and they can play a significant role in the development of UTIs. For example, if they keep you from fully emptying your bladder each time you urinate or keep you from urinating as often as you should, bacteria can grow and spread in the remaining urine, leading to UTIs.
Parkinsons motor symptoms can also impact your ability to urinate as frequently. Slowness and stiffness can make it difficult to get to the bathroom. In addition, if you experience significant balance issues, you may not travel to the bathroom as often as you need to for fear of falling.
Identifying And Reporting Uti In Pd
Cognitively intact patients with urinary symptoms should have testing with a urinary dipstick as an initial measure to evaluate for the presence of nitrite or leukocyte esterase or, alternatively, a urinalysis to detect pyuria. Although urinary culture is not required in all cases of uncomplicated UTI, it is preferred to document speciation and susceptibility to antibiotics . In cognitively impaired patients in whom self-reporting of urinary symptoms may be limited, an acute change in mental status, with or without localizable genitourinary symptoms, such as dysuria, urgency, or suprapubic pain, should prompt diagnostic testing for UTI . Heightened suspicion for UTI is appropriate when these symptoms occur in combination, as demonstrated in a study of nursing home residents that showed that the combination of dysuria with either a change in the character of the patients urine or mental status predicted the presence of bacteriuria plus pyuria in 63% of cases . In the future, new technologies may evolve to allow for serial monitoring or automated detection of UTI, perhaps with the use of smart-diapers with built in urinalysis capability .
You May Like: Parkinson’s Disease Boxing Therapy
How Might Parkinson’s Affect Bladder Problems
Bladder difficulties can be common in Parkinsons, particularly in the later stages of the condition. The loss of dopamine and the resulting interruption of signals from the brain can mean that messages telling the bladder to retain or expel urine are disrupted.
However, it is important to stress that bladder problems are not inevitable in Parkinsons. If difficulties do arise, especially in older people, they may be caused by factors totally unrelated to the condition, so a thorough medical evaluation should be carried out with any appropriate tests.
Bladder problems associated with Parkinsons include:
Parkinson’s Disease And Voiding Dysfunction
In this 54-minute webinar, urologist Dr. Sidney Radomski explains how voiding function is affected by Parkinsons disease in both men and women. He discusses how an enlarged prostate contributes to voiding problems and management options of voiding dysfunction for those with Parkinsons disease and MSA.
You May Like: What Can You Do To Prevent Parkinson’s Disease
Coping With Urinary Problems In Parkinsons Disease
If you have Parkinsons disease, you may end up having to deal with urinary problems which research shows are common in addition to other symptoms of Parkinsons disease.Since urinary symptoms can lead to other problems, such as disrupted sleep and disruption to social activities, its important to be aware of these problems and know what you can do to help with this
You May Like: Sam Waterston Parkinsons
Whats Next For Those Suffering From Urinary Incontinence
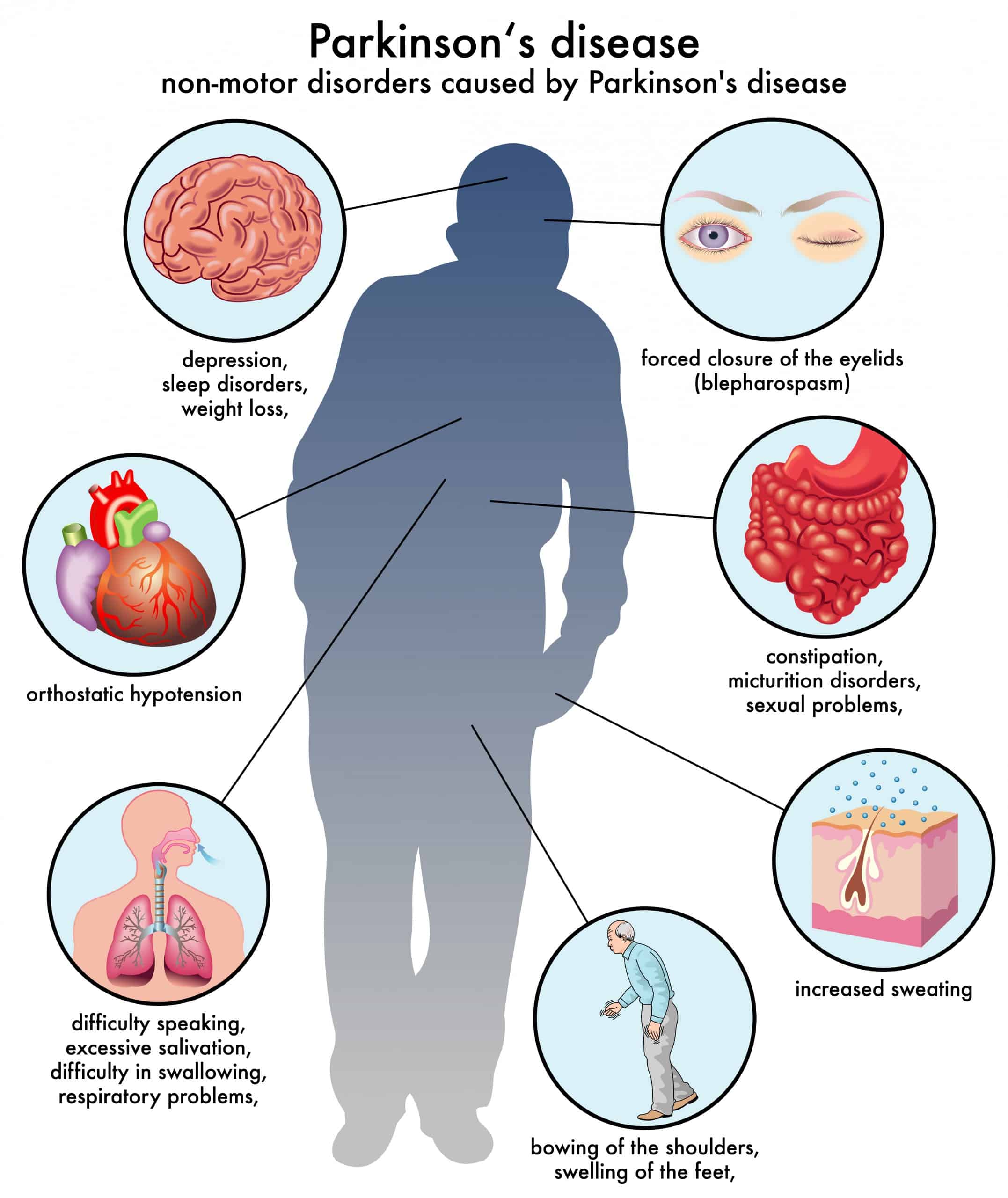
I decided I did not want to add another medication to the medicine bag. I was trying to see if there was something I could do besides resigning myself to wearing pads or some other incontinence protection all the time. At 53 years old, I wanted to see if there was a way I could help myself.
Part 2 of this article will address my experiences. I plan to discuss what I lovingly refer to as PEE PEE PT physical therapy to help treat urinary incontinence.
You May Like: Voice Amplifiers For Parkinsons
Read Also: Scan To Diagnose Parkinson’s
How Might Parkinsons Affect Bladder Problems
Bladder difficulties can be common in Parkinsons, particularly in the later stages of the condition. The loss of dopamine and the resulting interruption of signals from the brain can mean that messages telling the bladder to retain or expel urine are disrupted.
However, it is important to stress that bladder problems are not inevitable in Parkinsons. If difficulties do arise, especially in older people, they may be caused by factors totally unrelated to the condition, so a thorough medical evaluation should be carried out with any appropriate tests.
Bladder problems associated with Parkinsons include:
Recommended Reading: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinsons