How Does Noninvasive Deep Brain Stimulation Work
Neurons have the ability to send signals to other neurons repetitively. The rate at which the signals are repeated in one second is called the frequency, which is measured in hertz . For example, a frequency of 2 Hz means that the signal occurs twice per second. In practice, when electrodes placed on the skull apply current at a certain frequency, neurons close to the electrodes can sense the stimulation and send signals at that same frequency. This method, however, cannot easily target a specific region deep inside the brain because the neurons near the skull will sense a much stronger stimulation. The MIT researchers circumvented this problem by strategically placing two pairs of electrodes on the skulls of mice and exploiting how their electrical signals interacted or interfered with each other.
This method relies upon two key scientific insights: 1) neurons do not respond to stimulations of very high frequency , and 2) stimulation waves interfere with one another . Interference occurs when two waves meet and form a combined wave of increased or decreased strength, depending on the properties and relative locations of the two original waves. Additionally, when two waves with slightly different frequencies meet, they will form an envelope wave whose frequency equals the difference of the frequencies of the two original waves . This phenomenon is known as temporal interference.
Figure 2: Schematic of temporal interference stimulation.A)B)C)
What You Need To Know
- Surgeons implant one or more small wires in the brain during a surgical procedure.
- The leads receive mild electrical stimulation from a small pulse generator implanted in the chest.
- Proper patient selection, precise placement of the electrodes and adjustment of the pulse generator are essential for successful DBS surgery.
- DBS does not fully resolve the symptoms of PD or other conditions, but it can decrease a patients need for medications and improve quality of life.
Placement Of The Neurostimulator
This procedure takes place under general anesthesia so that the person is asleep. The surgical team inserts the neurostimulator under the outer layers of skin, usually just under the collarbone, but sometimes in the chest or abdomen. The extension wire from the lead is attached to the neurostimulator.
Also Check: Parkinson’s And Mental Health
What Happens During Surgery
For stage 1, implanting the electrodes in the brain, the entire process lasts 5 to 7 hours. The surgery generally lasts 3 to 4 hours.
Step 1: attach stereotactic frameThe procedure is performed stereotactically, which requires attaching a frame to your head. While you are seated, the frame is temporarily positioned on your head with Velcro straps. The four pin sites are injected with local anesthesia to minimize discomfort. You will feel some pressure as the pins are tightened .
Step 2: MRI or CT scanYou will then have an imaging scan, using either CT or MRI. A box-shaped localizing device is placed over the top of the frame. Markers in the box show up on the scan and help pinpoint the exact three-dimensional coordinates of the target area within the brain. The surgeon uses the MRI / CT scans and special computer software to plan the trajectory of the electrode.
Step 3: skin and skull incisionYou will be taken to the operating room. You will lie on the table and the stereotactic head frame will be secured. This prevents any small movements of your head while inserting the electrodes. You will remain awake during surgery. Light sedation is given to make you more comfortable during the initial skin incision, but then stopped so that you can talk to the doctors and perform tasks.
Planning And Surgical Technique
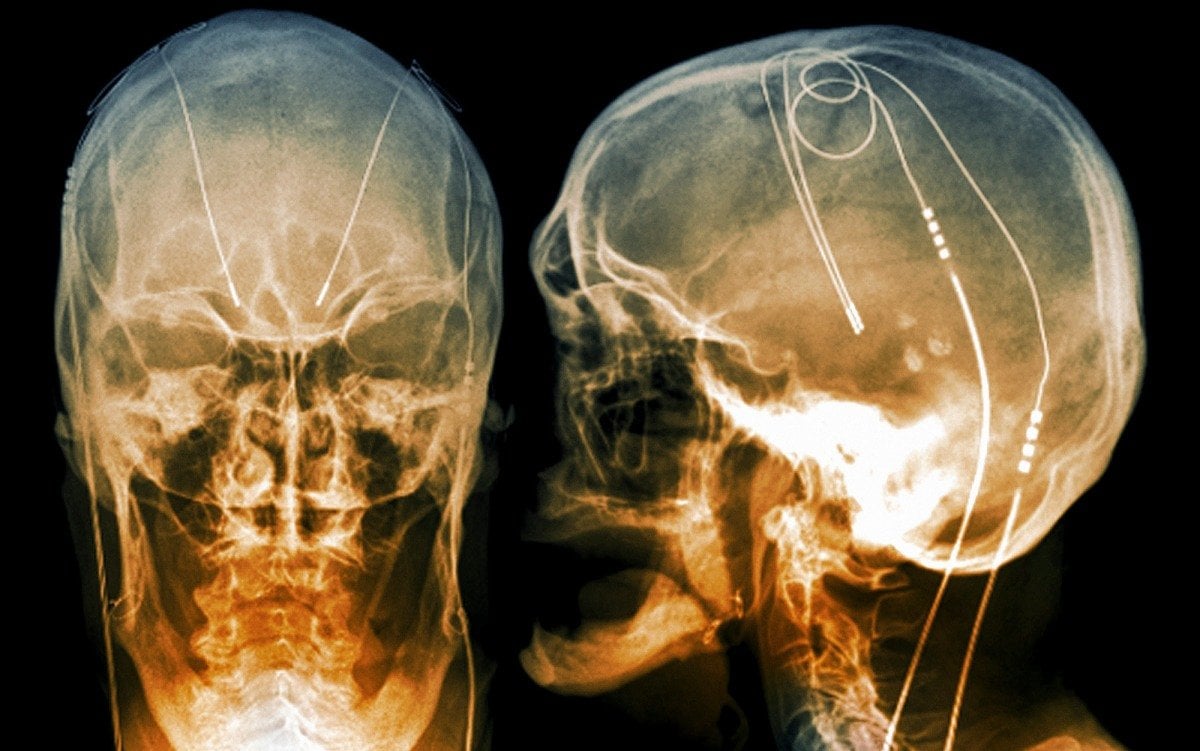
Prior to surgery the operation is planned on a computer using MRI scans. The surgeon chooses targets in the brain . Usually two electrodes are inserted, one on each side of the head. After selecting each target point, an entry point is chosen where a hole will be drilled in the skull to pass the wire through. The entry point is chosen such that the trajectory path avoids blood vessels, thereby reducing the incidence of bleeding complications.
Caption: The Sacramento, Calif. operating room where Parkinson’s disease patient Joel Davis undergoes his deep brain stimulation brain surgery for Parkinsons disease – photo reproduced with permission of the photographer
Also Check: Stage 5 Parkinson’s Disease Life Expectancy
Resources For More Information
- Surgical option a potential life-changer for patients with OCD: Read and watch Erins story as she, a lively 21-year-old woman, fought her battle with OCD. This article explores how deep brain stimulation gave Erin her life back. The procedure was the first of its kind performed at Albany Medical Center the only facility offering this treatment between New York and Boston. In Erins own words, “Now, I can be who I really am and tell people my story and hopefully inspire people and help people along the way.
- Karen and Jims Story: A Shared Journey of Life, Love and DBS: Read about Karen and Jim. They were each diagnosed with Parkinsons before they met. Follow them on their journey as they fall in love after meeting each other from an online support group. See how they embraced each other and DBS.
- Kays Story A Parkinsons Disease Patient: Read about Kay, a 68-year-old woman suffering from Parkinsons disease. The article and video explore how DBS helped her regain her life. In Kays own words, Its like I had been turned on again. It was like a miracle.
Who Is A Candidate For Deep Brain Stimulation
DBS is more than just a surgical procedure. It involves a series of evaluations, procedures, and consultations before and after the actual operation, so people interested in being treated with DBS should be prepared to commit time to the process.
For example, those who do not live close to a medical center that offers DBS surgery may need to spend significant time traveling back and forth to appointments.
The procedure, as well as the pre-operative evaluation and post-operative follow-up, can be expensive depending on the persons insurance coverage. DBS surgery is an FDA-approved treatment for Parkinsons disease, and Medicare and most private insurers cover the procedure, but the extent of coverage will depend on each persons individual policy.
Prospective patients should have realistic expectations about DBS results. Although DBS can improve movement symptoms of Parkinsons disease and greatly improve quality of life in properly selected patients, it is not likely to return anyone to perfect health.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Support Group For Caregivers
The Symptoms That Dbs Treats
Deep brain stimulation is used primarily to treat the motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease, but this can vary somewhat between the different placement sites. Symptoms treated include:
- Stiffness
- Abnormal movements : Dyskinesias are often a side effect of medications for Parkinsons disease and include involuntary movements such as twisting, head bobbing, squirming, and more.
DBS is not usually helpful with walking problems or balance, though improvements in the symptoms above can indirectly affect walking. It also does not provide significant benefits for non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons such as cognitive changes, mood changes , or problems with sleeping.
The benefits of DBS can be estimated by looking at how a person responds to levodopa. Symptoms that respond to levodopa will often respond to DBS . But symptoms that are not changed with levodopa are unlikely to be improved by DBS.
DBS often allows for a reduction in the dosage of levodopa, which in turn can result in fewer involuntary movements and a reduction in off time. The result is often improved quality of life.
Advances In Dbs Technology
The treatment can be used to tackle additional neurological problems and other disorders, Wodziak said, including epilepsy, seizures and dystonia, which is the sustained, involuntary contraction of muscles and can lead to painful cramping of the feet or hands, curling toes, or turning and twisting of the neck. A version of the same technology can even be used on the spinal cord. This year, Dr. Andre Machado of the Cleveland Clinic performed the first DBS surgery for stroke recovery using the Boston Scientific Vercise system. It is also considered for depression and weight loss.
Although the treatment has been around since the 90’s, there have been some incremental advances to the technology, including leads capable of focusing electricity to increasingly specific parts of the brain and smaller generators capable of connecting to devices using Bluetooth. Abbott’s DBS system was the first to be approved in the United States with a “directional lead,” which allows physicians to direct current more precisely than traditional DBS. It also allows for system control from an iPod Touch.
Read Also: What Causes Pain In Parkinson’s Patients
Injecting Electronics Into Brain Not As Freaky As It Sounds
No need to wait for the cyborg futureits already here. Adding to a growing list of electronics that can be implanted in the body, scientists are working to perfect the ultimate merger of mind and machine: devices fused directly to the brain.
A new type of flexible electronics can be injected through a syringe to unfurl and implant directly into the brains of mice, shows a study published Monday in Nature Nanotechnologystudy published Monday in Nature Nanotechnology. Researchers injected a fine electronic mesh and were able to monitor brain activity in the mice.
Youre blurring the living and the nonliving, says Charles Lieber, a nanoscientist at Harvard and co-author of the study. One day, he says, electronics might not only monitor brain activity but also deliver therapeutic treatments for Parkinsons disease, or even act as a bridge over damaged areas of the brain. Deep brain stimulation is already used for Parkinsons, but uses relatively large probes, which can cause formation of scar tissue around the probe.
The tiny size of the new devices allow them to be placed precisely in the brain while minimizing damage, a separate team of Korean researchers note in an accompanying article. Ultimately, the goal is to interweave the electronics so finely with brain cells that communication between the two becomes seamless.
An article in the Telegrapharticle in the Telegraph in October 2014 sums up todays state of the art in brain-hacking:
Like A Pacemaker For The Brain
Deep brain stimulation is a surgical treatment sometimes used in Parkinsons and other conditions. In this treatment, small pulses of electrical current are applied to specific locations in the brain through implanted electrodes. These electrodes are connected by wires that run under the skin to a programmable internal pulse generator, which is usually implanted just under the collarbone . It contains a battery and some electronics to generate the pulses, similar to a heart pacemaker. The device delivers electrical stimulation to specific brain areas that are involved in movement control. Electrical stimulation at precise locations in the brain is thought to restore the balance of the circuits that are disrupted in Parkinsons disease.
DBS can alleviate tremor, reduce stiffness, and lessen dyskinesias. It can very effectively smooth out on/off fluctuations.
Prior to the introduction of DBS in the 1990s, the main surgical treatment for Parkinsons disease involved inserting a probe into the brain and heating the tip of the probe to burn a very small region of brain tissue. The burn, known as a lesion, was made at the same targets that we now stimulate. Lesional surgery is still a useful option in some cases where DBS is not possible. Recently it has become possible to create lesions noninvasively using focused ultrasound.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease And Eating Problems
Will I Have To Limit My Activity Following Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery
- You should not engage in light activities for 2 weeks after surgery. This includes housework and sexual activity.
- You should not engage in heavy activities for 4 to 6 weeks after surgery. This includes jogging, swimming, or any physical education classes. Anything strenuous should be avoided to allow your surgical wound to heal properly. If you have any questions about activities, call your doctor before performing them.
- You should not lift more than 5 lbs. for at least 2 weeks.
- You should not raise your arms above your shoulders or over bend or stretch your neck.
- Depending on the type of work you do, you may return to work within 4 to 6 weeks.
Currently Available Deep Brain Stimulation Devices
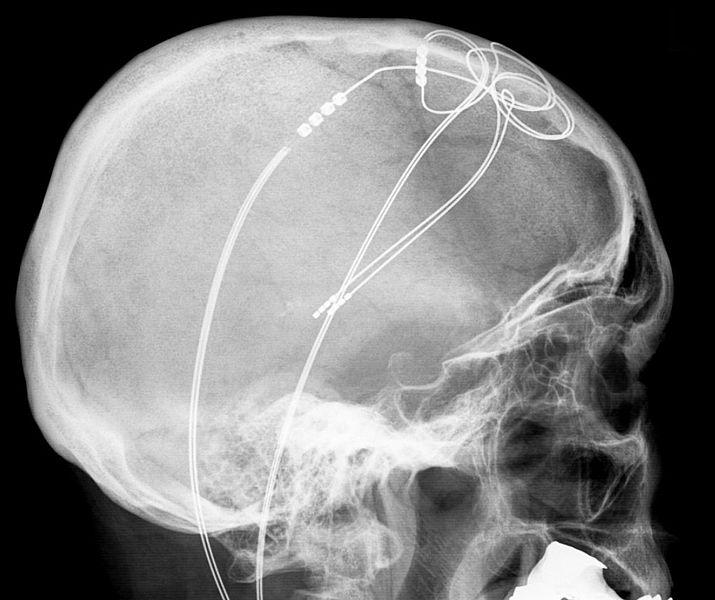
At the current time, the U.S Food and Drug Administration has approved several different deep brain stimulation devices from three separate manufacturers. While all DBS systems have the same basic components and work the same way, each device is unique. The differences are not drastic, but they represent innovation and improvement in care and care delivery. Variations, such as rechargeable batteries or electrodes that can deliver stimulation in novel ways or sense and record your brain signals, may lead you and your doctor to pick one over another. Available DBS devices for Parkinsons include:
ABBOTT
Infinity
Abbotts Infinity DBS was FDA-approved for Parkinsons in 2016. Infinitys brain leads allow directional stimulation, which is a potentially increased ability for the clinician to guide electrical stimulation toward areas associated with symptoms and away from side effects. This device operates with Apple iOS software and controllers. It also uses a non-rechargeable battery.
In 2021, Abbott developed a new technology that enables people with these devices to communicate with their clinician and receive DBS adjustments remotely, from their home or other location through WiFi, using the patient controller device.
For some, knowing they can connect with their doctor and adjustments anytime and anywhere makes life with DBS a little easier.
MEDTRONIC
+ Activa
+ Percept
BOSTON SCIENTIFIC
Vercise
Learn more about Boston Scientific DBS.
You May Like: What Causes Death In Parkinson’s
How Does Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinsons Work
Deep brain stimulation works by modifying abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It was first approved for Parkinsons tremors in 1997 and has become an established treatment to control additional motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
DBS involves three main components:
- Leads: Leads are implanted in the brain in a region responsible for motor activity.
- Implantable pulse generator : A separate procedure is performed to implant a battery-operated device in the chest or in the abdomen. An IPG is similar to a pacemaker for the heart and has been coined by some as a pacemaker for the brain.
- Extension: A thin, insulated wire is passed beneath the skin between the leads and implantable pulse generator to deliver the electrical stimulation from the pulse generator to the leads.
The target area in the brain is first identified by magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography . Then, the leads are placed via small holes that a surgeon drills in the skull.
This is considered a minimally invasive surgery that is done in the operating room with local anesthesia. It usually requires an overnight stay.
The IPG is inserted in a separate surgical procedure in the operating room roughly a week later.
After a few weeks, a neurologist begins to program the unit. This process can take several additional weeks to months. When this is completed, people are able to manage the device with a handheld remote control.
What Is Deep Brain Stimulation Or Dbs
Deep brain stimulation, or DBS, is often described as a pacemaker for the brain. It works much like a pacemaker, sending electrical signals to the brain instead of the heart. DBS is primarily utilized for patients who have Parkinsons disease, dystonia, or essential tremor, and who cant adequately control their disease with medication. Before any patient is considered for the surgery, they are evaluated by the U-M interdisciplinary team. That team includes a neurosurgeon, neurologist, clinical neuropsychologist, speech pathologist, social worker, and other team members who ensure that you and your family understand the procedure and discuss your expectations and concerns.
Its important to understand that DBS does not offer a cure for your disease, but a way to manage it more effectively. It can offer many benefits, including the need to take less medication and therefore experience fewer medication side effects.
Don’t Miss: Deep Brain Stimulation Parkinson’s Side Effects
How Is Deep Brain Stimulation Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Deep brain stimulation delivers electrical impulses to a targeted area of the brain that is responsible for the movement symptoms caused by Parkinsons disease. The electrical impulses disrupt the abnormal activity that occurs in the brains circuitry, which is causing the symptoms.
There are three areas in the brain that can be targets for deep brain stimulation in patients with Parkinsons disease. They are the subthalamic nucleus, the globus pallidus internus, and the ventral intermediate nucleus of the thalamus. Each of these areas plays a role in the brains circuitry that is responsible for the control of movement.
The specific area in the brain to target in an individual with Parkinsons disease depends on symptoms that need to be treated. For example, deep brain stimulation of subthalamic nucleus is effective for all major movement symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, such as tremor, slowness of movement , stiffness , and problems with walking and balance. Deep brain stimulation of globus pallidus is another effective target for a wide range of Parkinson’s symptoms. The thalamic target is sometimes selected for patients with tremor symptoms. The recommended target for each patient is made collaboratively with the neurologist, neurosurgeon and other caregivers involved in the decision making process.
What Are The Risks And Complications Of Deep Brain Stimulation
As with any surgical procedure, there are risks and complications. Complications of DBS fall into three categories: surgery complications, hardware complications, and stimulation-related complications.
- Surgical complications include brain hemorrhage, brain infection, wrong location of the DBS leads, and less than the best location of the leads.
- Hardware complications include movement of the leads, lead failure, failure of any part of the DBS system, pain over the pulse generator device, battery failure, infection around the device and the device breaking through the skin as the thickness of skin and fat layer change as one ages.
- Stimulation-related complications occur in all patients during the device programming stage. Common side effects are unintended movements , freezing , worsening of balance and gait, speech disturbance, involuntary muscle contractions, numbness and tingling , and double vision . These side effects are reversible when the device is adjusted.
Read Also: Parkinson’s And Muscle Cramps