What Are The Symptoms
Symptoms include the sense of feeling the heart beat rapidly , light-headedness, fainting, and dizziness.
Symptoms may start during the teen or young adult years.
How often a person has an episode of rapid heart rate varies. A person may have episodes of rapid heart rate once or twice a week, have rare episodes, or never have symptoms.
Episodes of WPW can trigger a life-threatening heart rhythm called ventricular fibrillation, although this is extremely rare. Your doctor may recommend that you wear a medical bracelet to alert medical professionals of your condition if you are at risk for ventricular fibrillation.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Wpw
Your child may have no signs or symptoms, or he may have the following:
- Fast, irregular, or pounding heartbeats
- Chest pain or trouble breathing
- Heavy sweating
- Dizziness or fainting, or not being able to do his activities
- Pale skin, behavior changes, or a fever
- Trouble staying alert, irritability, or a lack of appetite
Causes Of Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome
WPW syndrome is a form of tachycardia that results from an extra electrical bundle, which is called an accessory pathway or bypass tract that runs from the atrium to the ventricles. As a result the conduction runs quickly than in a slower rate because it did not go through the normal pathway, which is the AV node which impedes the flow to facilitate a normal cardiac rate.
You May Like: Vascular Parkinsonism And Cognitive Impairment
Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome Complications
For many people, WPW syndrome doesnt cause significant problems. But complications can occur, and its not always possible to know your risk of serious heart-related events. If the disorder is untreated, and particularly if you have other heart conditions, you may experience:
- Fainting spells
- Rarely, sudden death
Are There Any Specific Tachycardias Associated With Accessory Pathways

Cain, ME, Luke, RA, Lindsay, BD. Diagnosis and localization of accessory pathways. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. vol. 15. 1992. pp. 801-24.
Reyes, W, Milstein, S, Dunnigan, A. Indications for modification of coexisting dual atrioventricular node pathways in patients undergoing surgical ablation of accessory atrioventricular connections. J Am Coll Cardiol. vol. 17. 1991. pp. 1561-7.
Klein, GJ, Bashore, TM, Sellers, TD. Ventricular fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. N Engl J Med.. vol. 301. 1979. pp. 1080-5.
Dreifus, LS, Haiat, R, Watanabe, Y. Ventricular fibrillation: a possible mechanism of sudden death in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Circulation. vol. 43. 1971. pp. 520-7.
Wellens, HJJ, Durrer, D. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome and atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. vol. 34. 1974. pp. 777-82.
Campbell, RWF, Smith, R, Gallagher, JJ. Atrial fibrillation in the preexcitation syndrome. Am J Cardiol. vol. 40. 1977. pp. 514-20.
Sharma, AD, Klein, GJ, Guiraudon, GM. Atrial fibrillation in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: incidence after surgical ablation of the accessory pathway. Circulation. vol. 72. 1985. pp. 161-9.
Dagres, N, Clague, JR, Lottkamp, H. Impact of radiofrequency catheter ablation of accessory pathways on the frequency of atrial fibrillation during long-term follow-up: high recurrence rate of atrial fibrillation in patients older than 50 years of age. Eur Heart J. vol. 22. 2001. pp. 423-7.
You May Like: What Causes Tremors Besides Parkinson’s
Risk Factors For Developing Wpw
Risk factors for developing WPW include:
- Having a family member with pre-excitation or WPW: This is because mutations in certain genes can cause WPW.
- Congenital heart defect: Some people who are born with a specific heart defect known as “Ebstein’s anomaly” can develop WPW. This can occur if their mother was taking certain medications while she was pregnant.
What Are The Long
Overall, the outlook for children with WPW is excellent. The problem resolves in the majority of infants by 12 months of age although SVT may recur later in childhood.
When the problem persists, radiofrequency ablation has proven to be safe and effective.
Exercise guidelines: Guidelines are best made by a patients doctor so that all relevant factors can be included. Participation in vigorous competitive sports may be restricted until the problem is treated by radiofrequency ablation. If the pathway does not conduct rapidly , usually no activity restrictions are needed .
If an episode of SVT occurs during sports, the child should remove herself/himself from participation until the arrhythmia is converted. Also, activities that involve climbing heights should be avoided since an episode may cause dizziness leading to a fall.
References
Bolling S, Morady F, Caukins H, Kadish A, de Buitleir M, Langberg J, Dick M, Lupinetti F, Bove E. Current treatment for Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: results and surgical implications. Ann Thor Surg. 52:461-468,1991.
Deal B, Dick M, Beerman L et al. Cardiac arrest in young patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. PACE 1995 18:815.
Dick M, O’Connor B, Serwer G, LeRoy S, Armstrong B. Use of radiofrequency energy to ablate accessory connections in children. Circulation 84:2318-24, 1991.
Reviewed September, 2012
Also Check: Parkinson’s And Bad Taste In Mouth
Overview And Facts About Wolff
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome is a heart condition that causes a disruption in the hearts normal rhythm causing an arrhythmia . Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is present at birth and those born with it have an extra connection in the heart, known as an accessory pathway.
This extra connection can disrupt the intricate pathway of electrical signals through the heart, leading to changes in heart rhythm, such as increasing the speed of the heartbeat .
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Wolff
Individuals affected by Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome can experience palpitations, rapid heart rates, difficulty breathing, and lightheadedness as well as near loss of consciousness and complete loss of consciousness. For the most part, these symptoms occur all of a sudden and are not associated with warning signs. Usually, there are no dramatic triggers, however, caffeine, alcohol, and exercise can cause the heart to start racing.
Recommended Reading: Stabilizing Spoon For Parkinson’s
Abnormal Electrical System In Wolff Parkinson White
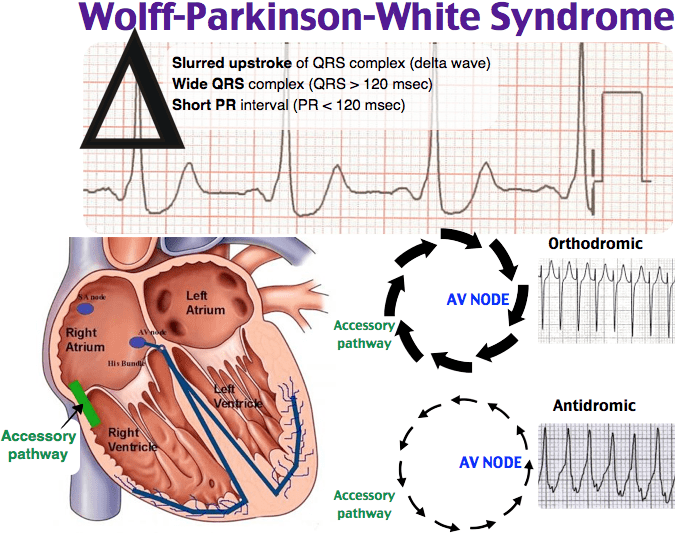
In Wolff Parkinson White syndrome, an extra electrical pathway connects the atria and ventricles, allowing electrical impulses to bypass the AV node. When the electrical impulses use this detour through the heart, the ventricles are activated too early.
The extra electrical pathway can cause two major types of rhythm disturbances:
- Looped electrical impulses. In Wolff Parkinson White, the hearts electrical impulses travel down either the normal or the extra pathway and up the other one, creating a complete electrical loop of signals. This condition sends impulses to the ventricles at a very rapid rate. As a result, the ventricles pump very quickly, causing rapid heartbeat.
- Disorganized electrical impulses. If electrical impulses dont begin correctly in the right atrium, they may travel across the atria in a disorganized way, causing atrial fibrillation. The disorganized signals and the extra pathway of Wolff Parkinson White also can cause the ventricles to beat faster. As a result, the ventricles dont have time to fill with blood and dont pump enough blood to the body.
Figure 2. Wolff Parkinson White syndrome
Note:
Figure 3. Wolff Parkinson White syndrome ECG
Figure 4. Wolff Parkinson White syndrome ECG
Figure 5. WPW syndrome ECG
Figure 6. Preexcited atrial fribrillation
Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome Diagnosis
If your doctor thinks you might have Wolff Parkinson White syndrome after assessing your symptoms, theyll probably recommend having an electrocardiogram and will refer you to a cardiologist .
An ECG is a test that records your hearts rhythm and electrical activity. Small discs called electrodes are stuck onto your arms, legs and chest and connected by wires to an ECG machine. The machine records the tiny electrical signals produced by your heart each time it beats.
If you have Wolff Parkinson White syndrome, the ECG will record an unusual pattern that isnt usually present in people who dont have the condition.
To confirm the diagnosis, you may be asked to wear a small portable ECG recorder so your heart rhythm can be recorded during an episode. A Holter monitor records your heart activity for 24 hours. An event recorder monitors heart activity when you experience symptoms of a fast heart rate. The recorder will trace your heart rate continuously over a few days, or when you switch it on at the start of an episode.
Electrophysiological testing. Thin, flexible tubes tipped with electrodes are threaded through your blood vessels to various spots in your heart. The electrodes can precisely map the spread of electrical impulses during each heartbeat and identify an extra electrical pathway.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease And Vision Problems
Prevalence Symptoms And Prognosis Of Wpw Syndrome
An electrocardiographic pattern of preexcitation occurs in the general population at a frequency of around 1.5 per 1000. Of these, 50% to 60% of patients become symptomatic. Approximately one-third of all patients with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia are diagnosed as having an AP-mediated tachycardia. Patients with AP-mediated tachycardias most commonly present with the syndrome of PSVT.
Population-based studies have demonstrated a bimodal distribution of symptoms for patients with preexcitation, with a peak in early childhood followed by a second peak in young adulthood. Nearly 25% of infants who demonstrate preexcitation and/or have AP-mediated arrhythmias will lose evidence of preexcitation and/or become asymptomatic over time as the conduction property of the AP can degenerate with time.
Pappone et al reported that during a mean follow-up of 37.7 months, 18.2% and 30% of noninducible patients have lost the anterograde and retrograde conduction, respectively. The mean age of these patients was 33.6 ± 14.3. Compared to others who had persistent conductibility through the AP, these patients were asymptomatic, noninducible, and had longer minimal 1:1 conduction cycle length through the AP during the baseline EPS.
What Are The Typical Electrophysiologic Findings Of Wpw Syndrome

Electrophysiology study in patients with WPW syndrome can help to confirm the presence of an AP, differentiate this condition from other forms of SVT, and to localize the pathway participating in the tachycardia for ablative therapy.
Figure 8.
Eccentric retrograde conduction through the accessory pathway located in left free wall. Note the eccentric activation of the atrium with pacing from the ventricle, with earliest atrial depolarization at the distal CS lead . The panel shows right ventricular apical pacing at 200 beats/min . His p, proximal His His d, distal His V, ventricular electrogram A, atrial electrogram CS, coronary sinus CS 9-10, the most proximal electrode in the CS catheter RVa, right ventricular apex RVa d, distal right ventricular apex.
Retrograde conduction over most APs is nondecremental. Hence, in the absence of intraventricular conduction delay or the presence of multiple bypass tracts, the VA conduction time is the same over a range of pace cycle lengths. The exception to this is the slowly conducting decremental posteroseptal pathway found in the permanent form of junctional reciprocating tachycardia, in which the VA conduction time increases with increasing ventricular pacing rate.
It is important and often challenging to differentiate retrograde conduction over septal pathway from conduction over the normal AV system. One maneuver that can make this differentiation is differential pacing and measuring the VA conduction time.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s And Marriage Breakdown
How To Manage Or Live With Wpw
There is no way to prevent WPW, but you can prevent complications by learning as much as you can about the disease and working closely with your cardiologist to find the best treatment. Ask your doctor to teach you how to do a Valsalva maneuver.
Here are helpful lifestyle suggestions:
-
Dont smoke.
-
Work with your doctor to keep conditions such as high cholesterol and high blood pressure under control.
-
Eat a heart-healthy diet.
Cleveland Clinic Heart Vascular & Thoracic Institute Cardiologists And Surgeons
Choosing a doctor to treat your abnormal heart rhythm depends on where you are in your diagnosis and treatment. The following Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute Sections and Departments treat patients with Arrhythmias:
- Section of Electrophysiology and Pacing: cardiology evaluation for medical management or electrophysiology procedures or devices – Call Cardiology Appointments at toll-free 800.223.2273, extension 4-6697 or request an appointment online.
- Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery: surgery evaluation for surgical treatment for atrial fibrillation, epicardial lead placement, and in some cases if necessary, lead and device implantation and removal. For more information, please contact us.
- You may also use our MyConsult second opinion consultation using the Internet.
The Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute has specialized centers to treat certain populations of patients:
Don’t Miss: Late Stage Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms
What Are The Potential Complications Of Wolff
Wolff-Parkinson-White can lead to significant symptoms from the rapid heart rates and can be alarming when first experienced. In addition, episodes can be disruptive and can last from minutes to hours and in some rare circumstances even days to weeks. The most serious complication of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is sudden death, which is rare and has been estimated to be around 0.25% per year. This very rare occurrence can happen if the short-circuit of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome triggers another arrhythmia called atrial fibrillation that even more rarely can induce ventricular fibrillation. Ventricular fibrillation can cause sudden death if not treated promptly.
What Are The Effects Of This Problem On My Child’s Health
The information about supraventricular tachycardia applies to children with WPW. In babies, the problem resolves on its own about 50% of the time.
Rarely, WPW can cause sudden cardiac death. This can occur only if 1) the extra pathway can conduct an electrical signal very quickly from the atria to ventricles and 2) the person has an arrhythmia called atrial flutter/fibrillation. In atrial fibrillation/flutter, the upper chambers of the heart beat very fast, from 300 to 600 beats per minute. If the pathway can conduct very rapidly to the lower chambers , it could result in a life-threatening heart rhythm called ventricular fibrillation. In patients without WPW, the ventricles are protected from the fast atrial rates by the AV-node since is can only conducts a fraction of the signals . Sudden cardiac death from WPW is extremely rare in the first few years of life.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Donations In Memory Of
What Is The Treatment For Wolff
A range of treatment options is available for the management of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. In the majority of people without any symptoms, there is no need for immediate treatment. However, when or if symptoms suspicious for an episode of rapid heart rate occur, a cardiac electrophysiology study is recommended. A cardiac electrophysiology study is a minimally invasive surgical operation in which special wires inserted through the veins in the legs are used to measure electrical activity inside the heart. During this procedure, the connection can be identified, and importantly, can be eradicated, or ablated . A successful ablation of an extra connection can permanently treat all the symptoms of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, including the risk of sudden death. Finally, in some circumstances, eradication of the extra connection is not possible to perform safely or not desired by the patient. Medications can then be prescribed to help reduce the frequency of rapid heart rate episodes. Of note, the extra connection in the heart can be located on the left side of the heart or on the right side of the heart .
Management Of Asymptomatic And Symptomatic Preexcitation
Blomström-Lundqvist, C, Scheinman, MM, Aliot, EM. ACC/AHA/ESC Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Supraventricular ArrhythmiasExecutive Summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines . Circulation. vol. 108. 2003. pp. 1871-1909.
Klein, GJ, Gulamhusien, SS. Intermittent preexcitation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Am J Cardiol. vol. 52. 1983. pp. 292-6.
Campbell, RWF, Smith, R, Gallagher, JJ. Atrial fibrillation in the preexcitation syndrome. Am J Cardiol. vol. 40. 1977. pp. 514-20.
Auricchio, A, Klein, H, Trappe, HJ. Lack of prognostic value of syncope in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. vol. 17. 1991. pp. 152-8.
Wellens, HJ, Bar, FW, Gorgels, AP. Use of ajmaline in patients with the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome to disclose short refractory period of the accessory pathway. Am J Cardiol. vol. 45. 1980. pp. 130-33.
Brembilla-Perrot, B, Ghawi, R. Electrophysiological characteristics of asymptomatic Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Eur Heart J. vol. 14. 1993. pp. 511-15.
Leitch, JW, Klein, GJ, Yee, R, Murdock, C. Prognostic value of electrophysiology testing in asymptomatic patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White pattern. Circulation. vol. 82. 1990. pp. 1718-23.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Staring Into Space
Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome Causes
When the heart beats, its muscular walls contract to force blood out and around the body. They then relax, allowing the heart to fill with blood again. This is controlled by electrical signals.
In Wolff Parkinson White syndrome, theres an extra electrical connection in the heart, which allows electrical signals to bypass the usual route and form a short circuit. This means the signals travel round and round in a loop, causing episodes where the heart beats very fast.
The extra electrical connection is caused by a strand of heart muscle that grows while the unborn baby is developing in the womb.
Its not clear exactly why this happens. It just seems to occur randomly in some babies, although rare cases have been found to run in families.
Wolff Parkinson White is more common in males than in females.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a rare but dangerous condition. A high index of clinical suspicion and close attention to concerning symptoms may be crucial in making a diagnosis. Once a diagnosis or sufficient concern is established, an interprofessional approach will be necessary for further evaluation and management. This approach, paired with education and shared decision making with patients and their families, will help guide treatment plans.
It is often difficult to develop and carry out well structured and rigorous studies in rare medical conditions. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is no exception, and most of the evidence is drawn from case series and population studies. The pathophysiologic basis is well understood, and surgical or catheter ablation has been shown to be successful and low risk. In high-risk patients, ablation is the most definitive treatment, but more future studies would help delineate medical management and ablation thresholds in some low-risk patients.
Don’t Miss: Is Drooling A Sign Of Parkinson’s