Living With Postural Hypotension
This 7-page fact sheet was developed for people affected by MSA, but is just as useful to those with Parkinsons disease, who are experiencing drops in blood pressure and postural hypotension. It covers symptoms, when they are likely to happen, what to do, exercise and other tips for daily living with OH, including medication options.
Management Of Noh Includes Three Components:
- Correcting aggravating factors
- Lifestyle changes
- Medication
Stopping medications that can reduce blood pressure, such as diuretics, anti-hypertensives, some medications used for prostate and urinary symptoms, medications for erectile dysfunction, medications for angina and some antidepressants is a first step. Levodopa can lower blood pressure, and adjusting dosage may be necessary in people with Parkinsons and nOH. Anemia can aggravate nOH and should be investigated and treated accordingly.
Symptoms of nOH can improve with time, patience and non-pharmacological changes. It is tempting to try to control nOH only with medications however, this approach is less effective and may have adverse side effects. Treatment of nOH is more successful if lifestyle changes are also made.
Below are lifestyle steps you can take to improve symptoms of nOH. You can adopt all of them at the same time. If performed properly, these actions can lead to a dramatic improvement, even without medications.
What Are The Neurogenic Causes Of Orthostatic Hypotension
Autonomic neuropathy is a common cause of neurogenic OH. Possible etiologies of autonomic neuropathy are too numerous to list but include diabetes mellitus, amyloidosis, toxic neuropathies , infections, autoimmune diseases, hereditary conditions, paraneoplastic syndromes, and metabolic disorders. provides a summary of the most common causes of peripheral autonomic neuropathies to help guide further diagnostic testing based on clinical plausibility.
Relevant causes of peripheral autonomic neuropathies to help guide the diagnostic evaluation
An approach to sorting out the neurogenic causes of OH involves considering the type of associated neurologic findings and whether the onset of the OH was acute/sub-acute or chronic and progressive. Using this approach, the following 5 distinct categories arise:
No neurologic symptoms, acute or sub-acute onset . Consider autoimmune or paraneoplastic ganglionopathy and toxic exposures, particularly neurotoxic drugs. These cases often go undiagnosed. It is essential that these conditions be identified because they often have specific therapy, such as immunomodulatory therapy for autonomic ganglionopathies or removal of a potentially toxic drug.
No neurologic symptoms, chronic, slow progression. Consider pure autonomic failure, a synucleinopathy that usually presents without nonautonomic features but often progresses to Parkinson disease or multiple system atrophy after prolonged follow-up.
Also Check: Test To See If You Have Parkinson’s Disease
Opportunities For Input From Pharmacy Professionals
As there is no cure for PD, medication management is crucial in managing the disease. Pharmacy professionals can play a significant role in both primary and secondary care. It is important that pharmacy professionals are familiar with PD symptoms and are aware of which referral pathway is most suitable for the patient. Many of the symptoms are straightforward to manage for example, constipation, and simple interventions can make a big difference to the patients quality of life.
Pharmacy professionals should also be aware of local services that are available to both patients and themselves. The Parkinsons UK website provides support and resources for healthcare professionals, patients and their family or carers.
Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behaviour Disorder
REM sleep behaviour is associated with PD and is a prodromal symptom in many cases. Patients with REM sleep disorder often physically act out vivid dreams during REM sleep, which can affect their quality of life and that of their family and carers. NICE recommends the off-label use of clonazepam or melatonin . Benzodiazepines are cautioned in the elderly population therefore, this patient cohort must be monitored closely by their care team if started on clonazepam.
Read Also: All About Parkinson’s Disease
Low Blood Pressure In Parkinsons Disease
This 2-page article discusses the frequency of orthostatic hypotension in those with PD, the cause, symptoms and several simple measures that can be used to restore normal blood pressure regulation, including medication evaluation, increase of fluids and salty foods, caffeine, frequent small meals, environment, clothing, slow position change, bed position and medication options.
Dont Miss: Parkinsons Bike Therapy
Is There A Dose
It seems plausible, based on different observational approaches, that higher doses of dopaminergic medications and combined therapies could also increase the chances of manifesting OH. Also some works have suggested that the main effect of medications could be at the beginning of the therapy developing some tolerance thereafter .
Based on all these evidence, the possibility of OH should be especially considered, when starting/adding a new drug or increasing its dose as the probability of symptoms could increase.
Don’t Miss: Survival Rate For Parkinson’s Disease
Understanding Blood Pressure Fluctuations In Parkinson’s Disease
In this 1-hour webinar Anindita Deb, MD, Movement Disorder Specialist, provides an overview of the human nervous system, which controls blood pressure, before explaining what orthostatic hypotension is, how to monitor nOH, medications that can affect blood pressure, lifestyle changes to improve nOH, how nOH affects cognition and mobility. She then spends considerable time sharing physical maneuvers and medications to treat nOH before answering listener questions.
Orthostatic Hypotension In Parkinsons Disease Multiple System Atrophy And Lewy Body Dementia
Movement disorder specialist, Dr. Veronica Santini spoke for a half hour on orthostatic hypotension, a common symptom of Parkinsons disease, Multiple System Atrophy and Lewy Body Dementia. Following her talk, moderator Candy Welch, Brain Support Networks MSA caregiver support group leader, presented Dr. Santini with questions from webinar participants for another half hour.
Also Check: Weighted Silverware
You May Like: Cbd Oil Parkinson’s Disease
Whats Hot In Pd If You Are Dizzy Or Passing Out It Could Be Your Parkinsons Disease Or Parkinsons Disease Medications
This 3-page article, with references, is a personal statement by Dr. Okun describing the mis-diagnoses Parkinsons patients can be given when visiting the ER for symptoms of dizziness or syncope outlining what defines a proper diagnosis of orthostatic hypotension, its frequency in people with Parkinsons, medication and lifestyle changes that can help.
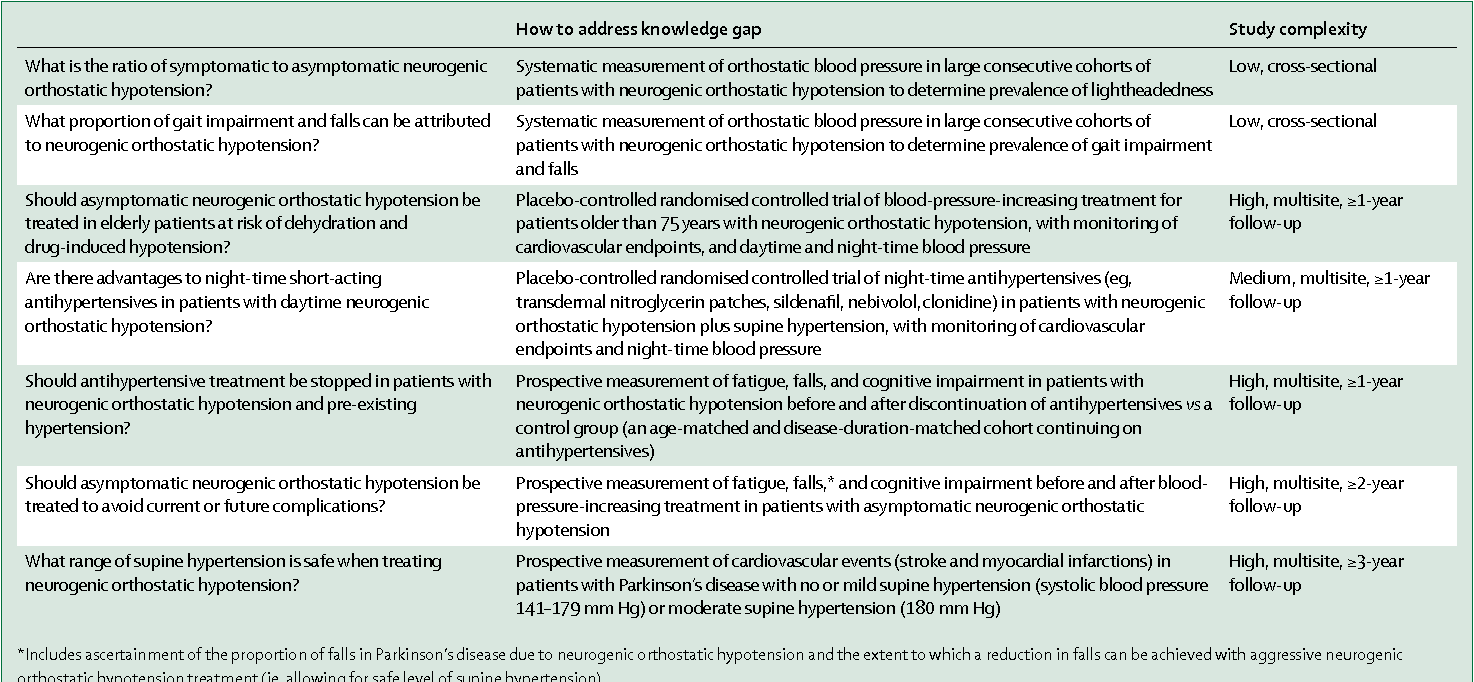
Temporal Variants Of Orthostatic Hypotension
In addition to OH defined as a BP drop within 3 min of standing , thereare two other temporally defined forms of OH that can be identified by clinicalBP measurements. Initial OH is a transient drop in BP that occurs immediatelyupon standing and resolves within 3060 s of active standing, and delayed OH isa sustained drop in BP that occurs beyond 3 min of standing . One large study of delayedOH monitored BP during 45 min of head-up tilt however, there is currently noaccepted standard for the length of time to test in the upright position forthis condition .
Initial OH differs from classical and delayed OH in several ways.Initial OH is defined by a greater magnitude of BP decrease within 15 s of active standing, withrestoration of normotensive BP within 3060 s . Signs and symptoms ofinitial OH are similar to those of the classical form of OH . However, initial OH is notassociated with a particular disease state or with autonomic failure, and theprevalence of initial OH in patients with PD is currently unknown .
Delayed OH occurs in some patients with PD and is thought to be related to, or aprecursor of, classical OH . In one study, more than half ofpatients with delayed OH developed classical OH during 10 years of follow-up. Delayed OH may be a mildor early form of sympathetic adrenergic failure and has been associated with thedevelopment of neurodegenerative disorders andincreased mortality .
Recommended Reading: Zhichan Capsule
Read Also: Healthy Diet For Parkinson’s Disease
How Is Orthostatic Hypotension Treated
Droxidopa . fludrocortisone , or midodrine capsules are approved for the treatment of orthostatic hypotension. Common side effects include headache, dizziness, nausea, high blood pressure, and fatigue.
Another approach in treating orthostatic hypotension is to decrease the pooling of blood in the legs with the use of special stockings called compression stockings. These tight stockings “compress” the veins in the legs, helping to reduce swelling and increase blood flow. There are a number of companies that make these stockings in a wide variety of sizes, and they usually can be found at stores that sell medical supplies, as well as at some pharmacies.
You should wear these stockings when you are up and about. You do not need to wear them when you are in bed. Further, it is recommended that you put the stockings on first thing in the morning while in bed and before getting up for your daily activities. It is important that you do not let the stockings bunch, gather, or roll, since this can compress the veins too much and could harm circulation. You should always watch for signs of decreased circulation, which could include discoloration of the skin, as well as pain or cramping, and numbness of the lower legs and feet.
Show Sources
How Does Pd Cause Orthostatic Hypotension
When you stand, gravity causes your blood to pool in your legs. Your body normally reacts by increasing heart rate and squeezing blood vessels, making sure that enough blood reaches your brain. But for people with orthostatic hypotension, the body does not react like this, and less blood is pumped to the brain.2
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for automatic bodily functions like blood pressure. It helps make sure the body reacts to low blood pressure by increasing heart rate and squeezing blood vessels. Damage in the brain and nerves from PD can affect the function of the autonomic nervous system.4
Drugs that treat PD can cause low blood pressure as well. For example, Mirapex® and those containing levodopa can impact blood pressure. Many other types of drugs can lead to orthostatic hypotension, including:2
- Water pills
- Some anti-depressants
- Drugs for erectile dysfunction
Underlying heart problems, dehydration, increased age, and other factors can also lead to low blood pressure. If you are having episodes of low-blood pressure, it is important for you and your doctor to first ensure your medicines or other medical conditions are not contributing.2
Recommended Reading: No Spill Coffee Cup Parkinson’s
When Is Orthostatic Hypotension Treated
Not all forms of orthostatic hypotension require treatment. If you experience a drop in blood pressure when you stand up, but have no other symptoms you probably wont need treatment. Sometimes all it takes is sitting on the edge of the bed for a minute or steadying yourself for a moment after you stand up. But, if you feel dizzy or lightheaded to the point where you might lose your balance or lose consciousness, you will need treatment.
Because some drugs can cause severe orthostatic hypotension, your doctor may first try reducing some of your medicine or may switch you to another type of medicine. If you have significant symptoms of orthostatic hypotension, and it is not possible to change your medications, then your doctor will likely treat the orthostatic hypotension itself.
Low Blood Pressure And Pd
Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension is a sharp drop in blood pressure that happens when a person gets up from bed or from a chair, causing dizziness or even loss of consciousness. Doctors define it as a blood pressure drop of 20 millimeters of mercury in systolic blood pressure , or a drop of 10 millimeters in diastolic blood pressure , within three minutes after standing up. The condition can put people with Parkinsons at risk of fainting, losing balance, falling and being injured. What can you do? Learn strategies to predict when blood pressure is most likely to fall and also take steps to avoid feeling dizzy in the first place.
Dont Miss: On Off Phenomenon
Recommended Reading: Sex And Parkinson’s Disease
Functional Psychosocial And Healthcare Resource Use Impacts
Falls and their consequences are of high clinical concern inpatients with PD. Falls increase the risk of injuries and increase healthcareresource use . In patients with PD, symptoms of nOHare associated with increased risk of falls and impairment of activities ofdaily living . An increased rate of falls has been demonstrated even inpatients with asymptomatic nOH when compared with patients with PD without nOH . The greater risk of falls in patientswith nOH results in more emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and useof outpatient services . In a retrospective cohortstudy, unadjusted medically attended fall-related costs were significantlyhigher for patients with PD and nOH than for patients with PD alone . Similarly, another retrospective study found thatoverall healthcare costs were more than 250% higher in patients with PD and nOHthan in those with PD alone ,even after adjusting for confounding factors .
Management Of Parkinsons Disease
Overall treatment is specific to the patient and the symptoms they experience. Symptoms can be variable from day to day or even hour to hour therefore, it is important that patients have a good understanding of their treatment, disease, coping mechanism, support system and regular reviews. Life expectancy can be normal however, more advanced symptoms can lead to increased disability and poor health, which may make someone more vulnerable to complications .
Recommended Reading: Best Cbd Oil For Parkinson’s
Is There Any Treatment
There is no cure for multiple system atrophy with orthostatic hypotension. Treatment is aimed at controlling symptoms. Anti-Parkinson medication such as Sinemet may improve the general sense of well-being. Medications to elevate blood pressure while standing are often used, but may cause high blood pressure when lying down. Individuals should sleep with the head of the bed elevated. An artificial feeding tube or breathing tube may be required for problems with swallowing and breathing.
Orthostatic Hypotension: A Prodromal Marker Of Parkinsons Disease
Department of Epidemiology, Erasmus MC University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
Department of Neurology, Erasmus MC University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
Francesco U.S. Mattace Raso PhD
Department of Geriatric Medicine, Erasmus MC University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
Department of Epidemiology, Erasmus MC University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
Department of Neurology, Erasmus MC University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
Correspondence to: Dr. M. Kamran Ikram, Erasmus MC University Medical Center, P.O. Box 2040, 3000 CA Rotterdam, the Netherlands E-mail:
Department of Epidemiology, Erasmus MC University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
Department of Neurology, Erasmus MC University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
Francesco U.S. Mattace Raso PhD
Department of Geriatric Medicine, Erasmus MC University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
Department of Epidemiology, Erasmus MC University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
Department of Neurology, Erasmus MC University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
Correspondence to: Dr. M. Kamran Ikram, Erasmus MC University Medical Center, P.O. Box 2040, 3000 CA Rotterdam, the Netherlands E-mail:
Lisanne J. Dommershuijsen and Alis Heshmatollah contributed equally to this article.
Relevant conflicts of interests/financial disclosures:: Nothing to report.
You May Like: Physical Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Read Also: Physiotherapy Management For Parkinson’s Disease Ppt
Normal Ans Response To Standing
Postural change induces gravitational redistribution of blood volume, leading to changes in blood pressure. Upon standing, pooling of venous blood in the legs is countered by the normal sympathetic ANS to maintain standing blood pressure. Lying supine also causes gravitational redistribution of blood volume, and the normal ANS minimizes blood pressure from rising too high. Norepinephrine is the major neurotransmitter in the ANS regulation of blood pressure in response to postural changes. Sympathetic activation in response to standing leads to: venoconstriction with increased venous return an increase in heart rate and myocardial contractility with increased cardiac output and vasoconstriction with increased blood pressure. Normal activation of the intact ANS, along with sufficient circulating blood volume, prevents the gravity-induced fall in standing systolic blood pressure , maintaining cerebral perfusion and of other vital organs.
You May Like: What Is An Off Period In Parkinsons
How Common Is Noh In People With Parkinsons

An estimated 30 to 50% of people with Parkinsons experience nOH. The prevalence of nOH increases with both age and number of years of living with Parkinsons. Although nOH in Parkinsons is relatively common, not everyone will experience symptoms. For that reason, people with Parkinsons should be screened for nOH, even if they have no symptoms.
Conversely, nOH can be one of the earliest symptoms of Parkinsons and can appear several years even decades before the onset of motor problems like tremor or stiffness. Therefore, people who have nOH, but do not have any significant motor or cognitive symptoms, should also be monitored closely to watch for early signs or symptoms of Parkinsons.
You May Like: Does Parkinson’s Affect Balance
How Low Is Too Low
Sudden drops in blood pressure are dangerous. Blood pressure is a reading of 2 numbers:2
- Systolic pressure is the top number. This is the pressure inside your arteries when your heart pumps.
- Diastolic pressure is the bottom number. This is the pressure in the vessels while your heart is resting in between beats.
While high blood pressure is dangerous, sudden low blood pressure is as well. A sudden drop of 20 mmHg in systolic pressure is enough to cause dizziness and low blood pressure symptoms. If blood pressure remains low, the body can go into shock.2
What Are The Symptoms Of Noh
nOH can appear with or without symptoms. The typical symptoms of nOH are lightheadedness, dizziness, blurry vision and, when theres a significant drop in blood pressure upon standing up, fainting. Symptoms almost always occur when standing up, less frequently when moving from standing to sitting and abate when lying down. People with nOH may also experience weakness, fatigue, leg buckling, headaches, neck and shoulder discomfort and shortness of breath. Severity of symptoms varies from day to day and fluctuates throughout the day. Often, mornings tend to be most difficult since nOH symptoms are aggravated by overnight urination, which is common in people with Parkinsons. Meals, particularly those rich in carbohydrates and sugars, also cause drops in blood pressure.
In people with Parkinsons, symptoms of nOH can also be non-specific, including fatigue and difficultly concentrating, and may sometimes mimic a levodopa off state. Its easy to miss nOH unless your physician measures your blood pressure while you are in a standing position. Conversely, it is important to realize people with Parkinsons can experience lightheadedness that mimics nOH, but may instead be caused by balance problems or other issues. For this reason, careful evaluation of your symptoms by a movement disorder specialist is strongly advised.
You May Like: Pfnca Wellness Programs
Recommended Reading: Motor And Non Motor Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease