Lewy Body Dementia Signs And Symptoms
There are many signs and symptoms of LBD. A major hallmark is cognitive impairment. It is defined in the most recent version of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders as cognitive decline in one or more areas . People with problems in these areas might be forgetful, have problems paying attention, have trouble with problem-solving, be unable to learn new facts or skills, have difficulty with speaking or forming sentences, or have behavioral changes. These symptoms can range from mild to major, and in order to make the diagnosis, they must significantly impair a persons day-to-day functioning.
Cognitive impairment isnt the only hallmark of LBD. People with dementia with Lewy bodies and PDD may present very differently because of how the Lewy bodies deposit in the brain.
Dementia with Lewy bodies is characterized by three main features, according to the DSM-5:
- Problems with cognition
- Visual hallucinations
- Spontaneous features of parkinsonism , which begin after the cognitive symptoms appear
Other features that can suggest dementia with Lewy bodies are:
- Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder
- Sensitivity to antipsychotic medications
PDD symptoms are similar, but the timing is different. The important difference is that in PDD, parkinsonian movement symptoms start before cognitive symptoms and dementia appear.
Hallmark symptoms of both diseases include:
How Is Lewy Body Disease Treated
There is no cure for Lewy body disease, but a doctor may treat the symptoms with:
- Alzheimer’s disease medications to reduce hallucinations and behavioural problems
- Parkinson’s disease medications to improve rigid muscles and slow movement
- antidepressants
- sleep medicines
Some medicines, such as antipsychotics, can make symptoms worse and may be dangerous. There are, however, other ways of dealing with symptoms, including:
- learning to manage a person’s behaviour
- learning how to calm the person down
- changing their environment to help them function
- creating daily routines
- using therapies, such as physiotherapy, occupational therapy and speech and language therapy
- providing cognitive stimulation
People with Lewy body disease usually need help at home and eventually care in a nursing home. The disease progresses differently in different people. After they develop symptoms, people live on average for another 6 to 12 years, although some live much longer.
Coping With Cognitive Changes
Some medications used to treat Alzheimer’s disease also may be used to treat the cognitive symptoms of LBD. These drugs, called cholinesterase inhibitors, act on a chemical in the brain that is important for memory and thinking. They may also improve hallucinations, apathy, and delusions. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved one Alzheimer’s drug, rivastigmine, to treat cognitive symptoms in Parkinson’s disease dementia. Several other drugs are being tested as possible treatments for LBD symptoms or to disrupt the underlying disease process.
You May Like: Can Head Injury Cause Parkinson’s
Advice For People Living With Lewy Body Dementia
Coping with a diagnosis of LBD and all that follows can be challenging. Getting support from family, friends, and professionals is critical to ensuring the best possible quality of life. Creating a safe environment and preparing for the future are important, too. Take time to focus on your strengths, enjoy each day, and make the most of your time with family and friends. Here are some ways to live with LBD day to day.
Getting Help
Your family and close friends are likely aware of changes in your thinking, movement, or behavior. You may want to tell others about your diagnosis so they can better understand the reason for these changes and learn more about LBD. For example, you could say that you have been diagnosed with a brain disorder called Lewy body dementia, which can affect thinking, movement, and behavior. You can say that you will need more help over time. By sharing your diagnosis with those closest to you, you can build a support team to help you manage LBD.
As LBD progresses, you will likely have more trouble managing everyday tasks such as taking medication, paying bills, and driving. You will gradually need more assistance from family members, friends, and perhaps professional caregivers. Although you may be reluctant to get help, try to let others partner with you so you can manage responsibilities together. Remember, LBD affects your loved ones, too. You can help reduce their stress when you accept their assistance.
Consider Safety
Plan for Your Future
Lewy Body Dementia: Causes And Symptoms
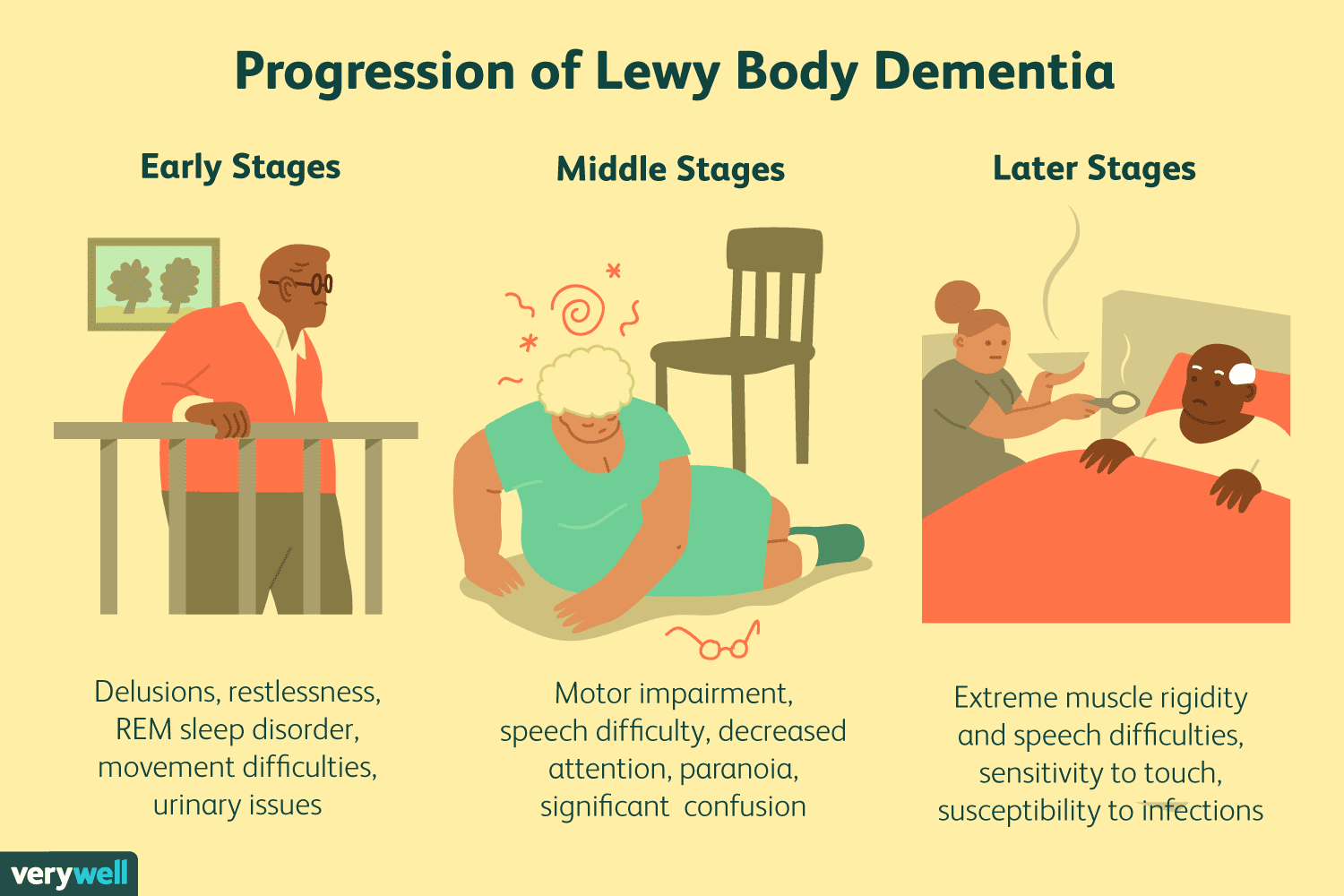
Lewy body dementia is an umbrella term for two related types of dementia dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinsons disease dementia . Dementia is a disease that progressively impairs a persons ability to think, reason, remember, and function. Although these two conditions have overlapping features, there are also important distinctions. Understanding LBD causes and symptoms, as well as how its two subtypes, dementia with Lewy bodies and PDD, differ from one another is critical for proper diagnoses and shortening the time to start treatment.
Read about the diagnosis and treatment of Lewy body dementia.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Donations In Memory Of
Caring For Someone With Lewy Body Dementia
Caring for someone with LBD, or any form of dementia, is hugely challenging. Just as LBD can impact every aspect of a person, caring for someone with the disease can impact every aspect of your daily life. Youll likely face tests of stamina, problem solving, and resiliency. However, your caregiving journey can also be an intensely rewarding experience as long as you take care of yourself and get the support that you need.
Differential Diagnosis Of The Lewy Body Dementias
Few clinically useful biomarkers differentiate DLB and PD from MSA and the parkinsonian tauopathies PSP and CBD, and careful history and examination remain the method of choice. Although unusual, cognitive impairment and dementia have recently been described in MSA and can no longer be used as strong evidence against the diagnosis. The early and profound development of dysautonomia, in association with parkinsonism and/or cerebellar ataxia characterizes MSA and can help in its differentiation from DLB and PDD. When present, ataxia is a strong distinguishing feature of MSA. Conversely, the presence of visual hallucinations and fluctuations would argue in favor of DLB or PDD. Late in the course of MSA, cerebellar atrophy and the hot cross bun pons sign may be appreciated on MRI.
In addition, hallucinations are uncommon in MSA, PSP, and CBS, as are fluctuations of attention and arousal. The presence of these problems should direct the clinician toward DLB and PDD. REM sleep behavior disorder has been described in both PSP and CBD but is more common in the synucleinopathies . In contrast to PD, motor impairments in MSA, PSP, and CBD are rarely responsive to dopamine replacement .
Also Check: Are There Stages Of Parkinson’s Disease
Diagnosing Lewy Body Dementia: For Professionals
Lewy body dementia can be difficult to diagnose. Talking to both patients and caregivers helps doctors make a diagnosis. It is important to ask the patient and their care partners about any symptoms involving thinking, movement, sleep, behavior, or mood. Certain medications can worsen LBD symptoms be aware of all current medications and supplements the patient is taking.
Dementia with Lewy bodies is often hard to diagnose because its early symptoms may resemble those of Alzheimer’s disease or a psychiatric illness. As a result, it is often misdiagnosed or missed altogether. As additional symptoms appear, making an accurate diagnosis may become easier.
The good news is that doctors are increasingly able to diagnose LBD earlier and more accurately, as researchers identify which symptoms and biomarkers help distinguish it from similar disorders.
Visiting a family doctor is often the first step for people who are experiencing changes in thinking, movement, or behavior. If a persons primary doctor is not familiar with LBD, they may have patients seek second opinions from specialists, like a geriatric psychiatrist, neuropsychologist, or a geriatrician to help diagnose LBD. If a specialist cannot be found in your community, ask the neurology department at a nearby medical school for a referral. Neurologists generally have the expertise needed to diagnose LBD.
Difficult as it is, getting an accurate diagnosis of LBD early on is important so that a person:
Relationship With Alzheimers And Parkinsons Dementias
Lewy bodies not only appear in dementia before us, but are also present in Parkinsons disease, multiple systemic atrophy, and Alzheimers disease in the latter case, they are found specifically in the CA2-3 region of the hippocampus, the fundamental structure of memory consolidation.
In addition to Lewy bodies we can find amyloid plaques, One of the typical signs of Alzheimers dementia and dopamine and acetylcholine neurotransmitter deficiencies, as in Parkinsons disease. This is why Lewy disease is often referred to as a midpoint between the other two, etiologically and symptomatically.
Unlike what happens in Alzheimers disease, in Lewy body dementia no atrophy is observed in the cortex of the middle part of the temporal lobes during the early stages of the disease. This fact explains some of the symptomatic differences between the two dementias, especially the evolution of memory problems.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s In Early Stages
What Are The Symptoms Of Lewy Body Disease
The symptoms of Lewy body disease include:
- difficulty concentrating and paying attention
- extreme confusion
- a mental state that switches rapidly between thinking clearly and being confused
- delusions
- disturbed sleep, acting out dreams
- fainting spells, unsteadiness and falls
- problems with understanding, thinking, memory and judgement
If you have the symptoms above, see your doctor.
What Is Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Dementia with Lewy Bodies may account for 10-15 per cent of all cases of dementia. DLB can be diagnosed wrongly and is often mistaken for Alzheimer’s disease.
DLB is sometimes known by other names. These include Lewy body dementia, Lewy body variant of Alzheimer’s disease, diffuse Lewy body disease and cortical Lewy body disease. All these terms refer to the same condition.
What a short video about dementia with Lewy bodies:
Also Check: How Does Occupational Therapy Help Parkinson Disease
How Lewy Body Dementia Differs From Other Types Of Dementia
Dementia is a term that describes the gradual loss of the ability to think, reason or remember. The most common form of dementia in the U.S. is associated with Alzheimers disease, but can also be caused by Lewy body dementia, frontotemporal dementia, and , among others. Although they all have dementia in common, the symptoms of these diseases differ because they affect different parts of the brain.
Lewy body dementia affects many parts of the brain, starting with the outer layer of the brain, called the gray matter or cerebral cortex. The cerebral cortex is responsible for language, thinking, perception and judgment. This is why some of the earlier symptoms of Lewy body dementia include changes in visual perception, delusions or , difficulty paying attention, and misidentifying objects.
As other parts of the brain become affected, more symptoms appear, such as difficulty forming new memories, changes in behavior, difficulty sleeping or excessive sleepiness, and difficulty moving and maintaining balance.
Although overall Lewy body dementia symptoms are similar to other types of dementia like Alzheimers disease or frontotemporal dementia, there are some key differences. For example, early symptoms of Alzheimers disease are or getting lost in familiar places. The earliest symptoms among people with frontotemporal dementia tend to be changes in personality or the inability to bring out the correct words.
How Does Lewy Body Disease Progress
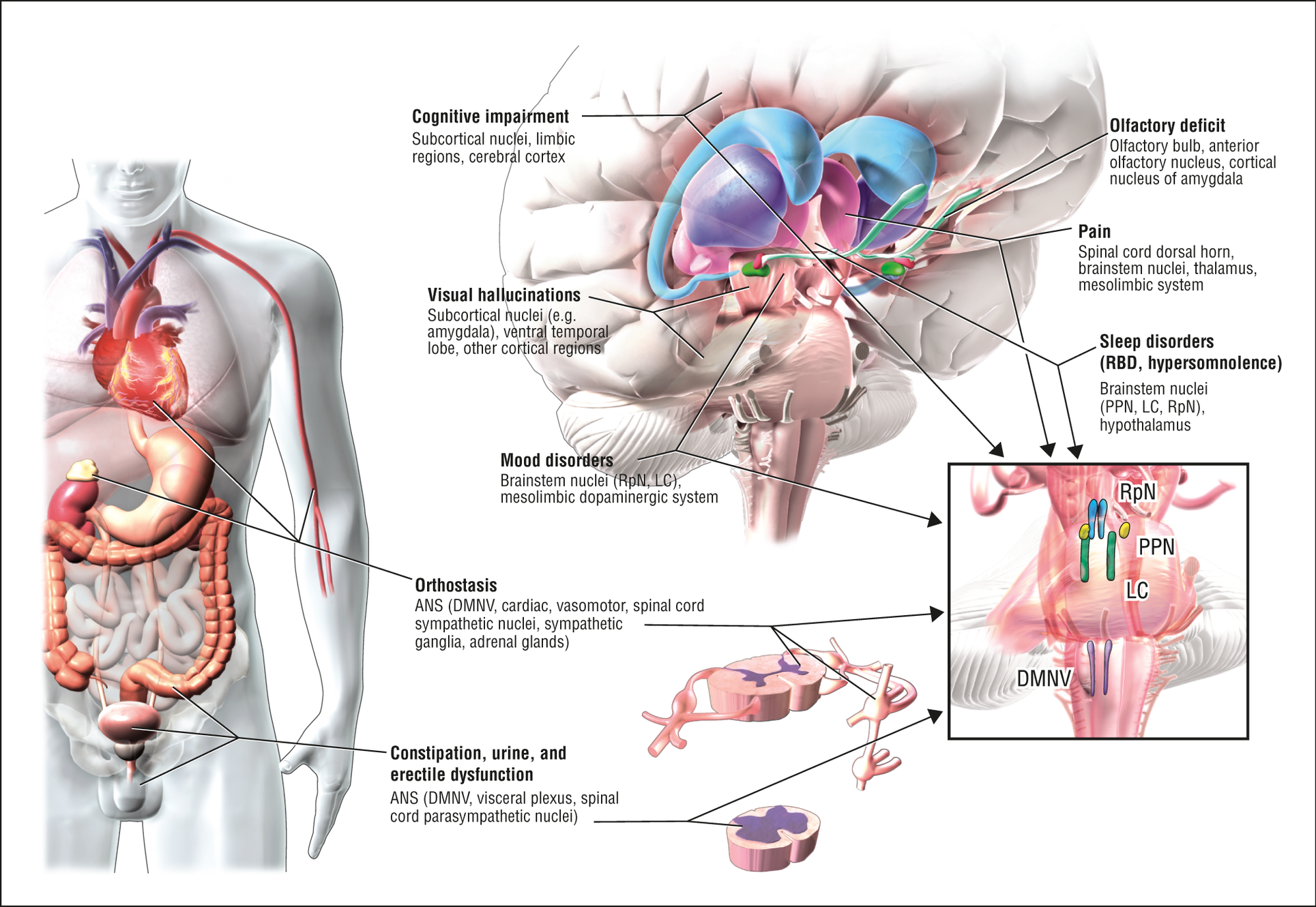
Lewy body disease differs from Alzheimer’s disease in that the progression of the disease is usually more rapid. However, like Alzheimer’s disease it is a degenerative condition, eventually leading to complete dependence. Death is usually a result of another illness, such as pneumonia or an infection. The average lifespan after the onset of symptoms is about seven years.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Foundation Miami Florida
What Is Dementia With Lewy Body Disease
Dementia with Lewy body disease is a condition that causes changes in thinking, behavior, and movement. DLB usually starts with thinking and behavior changes that are followed by problems with movement. The movement problems in DLB are similar to those seen in people with more classical Parkinsons disease.
Lewy Bodies: More Than Lbd
LBD is characterized by the presence of Lewy bodies in the nerve cells of the brain, meaning that LBD patients have Lewy bodies in the brain.2 However, Lewy bodies are also common with other conditions, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinsons disease. In fact, most people with PD also have Lewy bodies in their brain. However, even if they have Lewy bodies, not all Parkinsons patients will also develop LBD.2
You May Like: Can Thyroid Problems Cause Parkinson’s
How Is Lbd Different From Parkinsons Or Alzheimers
These diseases are similar in a lot of ways. But there are some key differences in the symptoms that affect people with LBD and when those symptoms happen.
LBD may not cause short-term memory loss like Alzheimerâs. People with both conditions have trouble with thinking, alertness, and paying attention. But in LBD, those problems come and go. The disease can also cause hallucinations, often in the first few years someone has LBD. People with Alzheimerâs usually donât have hallucinations until the later stages.
People with LBD also often act out their dreams and make violent movements when theyâre asleep. Itâs called REM sleep behavior disorder. Sometimes, itâs the first sign that someone has LBD.
LBD and Parkinsonâs disease both cause movement problems, like stiff muscles and tremors. But most people with Parkinsonâs donât have problems with their thinking and memory until the very later stages of their disease. Sometimes, they donât have it at all. In the type of LBD known as Parkinsonâs disease with dementia, these problems begin much sooner.
People with LBD also need different drugs for their condition than the ones that treat Parkinsonâs or Alzheimerâs.
Parkinsons Disease With Dementia Versus Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Some patients with Parkinsons disease experience no or only subtle cognitive decline, and their primary limitation is their motor disorder. However, other patients with Parkinsons disease develop dementia as a consequence of the disease. When dementia develops after an established motor disorder, we call the disease Parkinsons disease with dementia . In contrast, when dementia develops prior to or at the same time as the motor disorder, we call the disease DLB. Although the initial sequence of symptoms differs in PDD and DLB, as the disorders progress, the symptoms and the underlying brain changes are much more similar than they are different. As such, many researchers and clinicians think of PDD and DLB as being on a continuum of a similar disease process rather than as two distinct entities.
Don’t Miss: How To Test For Early Onset Parkinson’s
Causes And Risk Factors
The precise cause of LBD is unknown, but scientists are learning more about its biology and genetics. For example, they know that an accumulation of Lewy bodies is associated with a loss of certain neurons in the brain that produce two important neurotransmitters, chemicals that act as messengers between brain cells. One of these messengers, acetylcholine, is important for memory and learning. The other, dopamine, plays an important role in behavior, cognition, movement, motivation, sleep, and mood.
Scientists are also learning about risk factors for LBD. Age is considered the greatest risk factor. Most people who develop the disorder are over age 50.
Other known risk factors for LBD include the following:
Memory And Thinking Problems
You may experience forgetfulness, slowed thinking and difficulty concentrating. You might find it harder to follow conversations, and remember some words and names. This can make communication difficult.
You may also find it increasingly difficult to make decisions, plan activities and solve problems. This can make everyday activities harder.
Don’t Miss: How To Test Yourself For Parkinson’s
Lewy Bodies And Parkinsons Disease
A person with Parkinsons disease may develop dementia and have problems with reasoning and thinking. Lewy bodies are a feature of several brain disorders, including Parkinsons disease and Alzheimers disease, and they may cause rigid muscles and problems with movement and posture.
Research suggests that the similarity of the symptoms of Parkinsons disease and Lewy body dementia may be indicative of a shared link to how the brain processes alpha-synuclein.
It is not possible to test for the presence of Lewy bodies, so researchers must try to determine their effects by carrying out postmortem studies.
There is currently no cure for dementia. However, medication can alleviate the symptoms, while a team of medical professionals and therapists may help a person develop strategies to manage their daily activities.
What Other Things Help
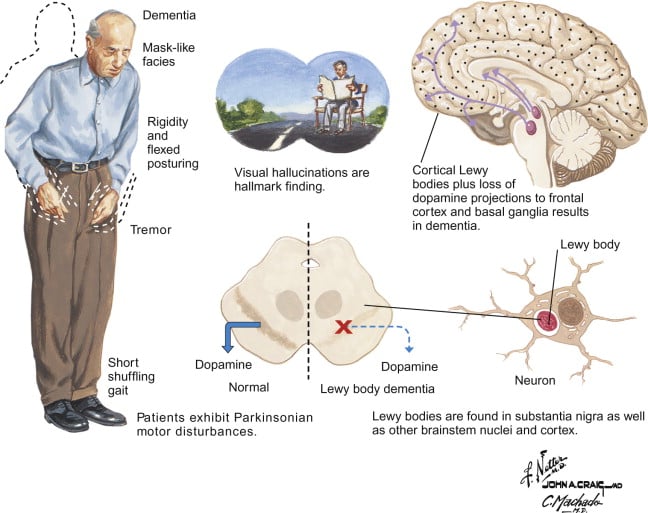
There are various ways to help a person with DLB. Speech therapy may help improve communication between people with DLB and others. Physical therapy may help strengthen and stretch stiff muscles and help to prevent falls.
Research has shown that physical exercise helps to enhance brain health and improves mood and general fitness. A balanced diet, enough sleep, and limited alcohol intake are other important ways to promote good brain health. Other illnesses that affect the brain, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol, should also be treated if present.
You May Like: What’s The Difference Between Parkinson’s And Ms
Treatments For Parkinsons Disease Dementia And Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Treatments for DLB are similar to PDD and are aimed at symptom control. The motor symptoms of slowness, stiffness and walking difficulties can be treated with Levodopa. However, Levodopa can cause or exacerbate hallucinations, making it difficult to use it as a treatment for patients who have or are at risk of having hallucinations. Sometimes, clinicians will need to treat the hallucinations more aggressively in order for a patient to tolerate Levodopa given to help the motor symptoms. On the flipside, anti-psychotic medications to control hallucinations can worsen motor symptoms, so treating all the symptoms of LBD simultaneously can be a tricky balancing act.
Parkinson’s Disease Dementia And Dementia With Lewy Bodies
The key pathological hallmark found in brains of Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s disease dementia patients are abnormal microscopic deposits composed of alpha-synuclein. This protein is found widely in the brain but its normal function is not yet well understood. The deposits are called “Lewy bodies”. Lewy bodies are also found in several other neurodegenerative brain disorders, including dementia with Lewy bodies . Evidence suggests that Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s disease dementia, and dementia with Lewy bodies, may be linked to the same underlying abnormalities in brain processing of alpha-synuclein.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Age Of Onset