Differential Diagnosis Of The Lewy Body Dementias
Few clinically useful biomarkers differentiate DLB and PD from MSA and the parkinsonian tauopathies PSP and CBD, and careful history and examination remain the method of choice. Although unusual, cognitive impairment and dementia have recently been described in MSA and can no longer be used as strong evidence against the diagnosis. The early and profound development of dysautonomia, in association with parkinsonism and/or cerebellar ataxia characterizes MSA and can help in its differentiation from DLB and PDD. When present, ataxia is a strong distinguishing feature of MSA. Conversely, the presence of visual hallucinations and fluctuations would argue in favor of DLB or PDD. Late in the course of MSA, cerebellar atrophy and the hot cross bun pons sign may be appreciated on MRI.
In addition, hallucinations are uncommon in MSA, PSP, and CBS, as are fluctuations of attention and arousal. The presence of these problems should direct the clinician toward DLB and PDD. REM sleep behavior disorder has been described in both PSP and CBD but is more common in the synucleinopathies . In contrast to PD, motor impairments in MSA, PSP, and CBD are rarely responsive to dopamine replacement .
Also Check: Are There Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Pathophysiology Of Cognitive Impairment
The neurobiological basis for cognitive impairment in DLB and PDD is multifocal, related to a synergistic effect of both Syn/LB and AD pathologies and dysfunction of dopaminergic, noradrenalinergic, serotonergic, and cholinergic systems . The emergence of PDD and DLB occurs on the background of severe dopamine deficits and correlates with a marked loss of limbic and cortically projecting dopamine, noradreanaline, serotonin, and ACh neurons. The relationship between these lesions is not yet fully understood.
Severe pathology also involves the noradrenergic locus ceruleus and the serotonergic dorsal raphe nucleus as well as the ventral tegmental area not always associated with coincidental AD lesions . LC neuronal loss and the accompanying norepinephrinergic deficiency are an important cause and pharmacological target for the treatment of PD/PDD/DLB . The prominent role of serotonergic degeneration also involving the anterior caudate nucleus, the orbitofrontal and cingulate cortex for neuropsychiatric symptoms in PD , emphasizes its important role in both PDD and DLB, and stimulates new insight into novel treatments by modulating 5-HT receptors .
Depression May Be An Early Symptom Of Parkinsons
Depression is one of the most common, and most disabling, non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease. As many as 50 per cent of people with Parkinsons experience the symptoms of clinical depression at some stage of the disease. Some people experience depression up to a decade or more before experiencing any motor symptoms of Parkinsons.
Clinical depression and anxiety are underdiagnosed symptoms of Parkinsons. Researchers believe that depression and anxiety in Parkinsons disease may be due to chemical and physical changes in the area of the brain that affect mood as well as movement. These changes are caused by the disease itself.
Here are some suggestions to help identify depression in Parkinsons:
- Mention changes in mood to your physician if they do not ask you about these conditions.
- Complete our Geriatric Depression Scale-15 to record your feelings so you can discuss symptoms with your doctor. Download the answer key and compare your responses.
- delusions and impulse control disorders
Also Check: Fitflop Shoes For Parkinsons
Don’t Miss: Voice Amplifiers For Parkinson’s
What Is Lewy Body Dementia Causes Symptoms And Treatments
On this page:
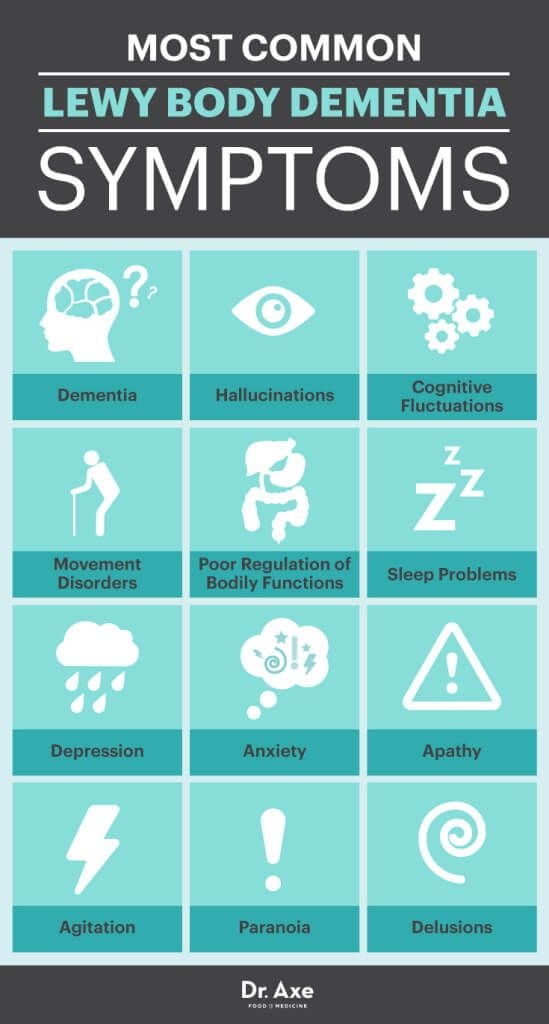
Lewy body dementia is a disease associated with abnormal deposits of a protein called alpha-synuclein in the brain. These deposits, called Lewy bodies, affect chemicals in the brain whose changes, in turn, can lead to problems with thinking, movement, behavior, and mood. Lewy body dementia is one of the most common causes of dementia.
LBD affects more than 1 million individuals in the United States. People typically show symptoms at age 50 or older, although sometimes younger people have LBD. LBD appears to affect slightly more men than women.
Diagnosing LBD can be challenging. Early LBD symptoms are often confused with similar symptoms found in other brain diseases or in psychiatric disorders. Lewy body dementia can occur alone or along with other brain disorders.
It is a progressive disease, meaning symptoms start slowly and worsen over time. The disease lasts an average of five to eight years from the time of diagnosis to death, but can range from two to 20 years for some people. How quickly symptoms develop and change varies greatly from person to person, depending on overall health, age, and severity of symptoms.
In the early stages of LBD, symptoms can be mild, and people can function fairly normally. As the disease advances, people with LBD require more help due to a decline in thinking and movement abilities. In the later stages of the disease, they often depend entirely on others for assistance and care.
Treatment Of Behavior And Mood Problems In Lewy Body Dementia

Behavioral and mood problems in people with LBD can arise from hallucinations, delusions, pain, illness, stress, or anxiety. They may also be the result of frustration, fear, or feeling overwhelmed. The person may resist care or lash out verbally or physically.
Medications are appropriate if the behavior interferes with the person’s care or the safety of the person or others. If medication is used, then the lowest possible dose for the shortest period of time is recommended.
The first step is to visit a doctor to see if a medical condition unrelated to LBD is causing the problem. Injuries, fever, urinary tract or pulmonary infections, pressure ulcers , and constipation can worsen behavioral problems and increase confusion.
Certain medications, such as anticholinergics and antihistamines may also cause behavioral problems. For example, some medications for sleep problems, pain, bladder control, and LBD-related movement symptoms can cause confusion, agitation, hallucinations, and delusions. Similarly, some anti-anxiety medicines can actually increase anxiety in people with LBD. Review your medications with your doctor to determine if any changes are needed.
Antidepressants can be used to treat depression and anxiety, which are common in LBD. Many of them are often well tolerated by people with LBD.
Don’t Miss: On-off Phenomenon
Of Neuroimaging Mibg Scintigraphy And Dat Scan
Here, we briefly describe neuroimaging useful to diagnose Lewy body constipation non-invasively. 123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine myocardial scintigraphy was originally developed to assess postganglionic presynaptic cardiac sympathetic nerve endings in heart disease including: congestive heart failure, ischemic heart disease, and cardiomyopathy. Subsequently, cardiac MIBG uptake was found to be reduced in patients with LBD and is reportedly useful for differentiating LBD from other disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease. MIBG scintigraphy is based on evidence that norepinephrine and MIBG have the same mechanisms for uptake, storage, and release8). There are two types of NE and MIBG uptake: uptake-1 , when the concentration is low, depends on sodium and adenosine triphosphate, and uptake-2 , which takes place only when the concentration is high, represents simple diffusion. Delayed images are less dependent on uptake-2, and more accurately reflect cardiac sympathetic nerve activity as well as pathology9). The sensitivity and specificity of MIBG scintigraphy are around 90% even in very early cases10,11). According to disease progression of LBD, the yearly reduction rate of the heart to mediastinum ratio is 0.0212). When using levodopa for motor disorder in LBD, levodopa might affect MIBG uptake13) .
Representative cases of MIBG myocardial scintigraphy and DAT scan.
Whats The Difference Between Lewy Body Dementia Parkinsons Disease And Alzheimers Disease
Lewy body dementia is an umbrella term for two related clinical diagnoses: dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinsons disease dementia. These disorders share the same underlying changes in the brain and very similar symptoms, but the symptoms appear in a different order depending on where the Lewy bodies first form.
Dementia with Lewy bodies is a type of dementia that causes problems with memory and thinking abilities that are severe enough to interfere with everyday activities. It specifically affects a persons ability to plan and solve problems, called executive function, and their ability to understand visual information. Dementia always appears first in DLB. The motor symptoms of Parkinsons such as tremor, slowness, stiffness and walking/balance/gait problems usually become more evident as the disease progresses. Visual hallucinations, REM sleep behavior disorder, fluctuating levels of alertness and attention, mood changes and autonomic dysfunction are also characteristic of DLB.
Finally, Alzheimers is characterized by different abnormal clumps called amyloid plaques, and jumbled fiber bundles called tau tangles. These microscopic structural changes in the brain were discovered by Dr. Alois Alzheimer in 1906. These plaques and tangles, together with loss of connections between nerve cells, contribute to loss of coherence and memory, as well as a progressive impairment in conducting normal activities of daily living.
Recommended Reading: Sam Waterston Parkinson’s
Lewy Body Dementia: Causes And Symptoms
Lewy body dementia is an umbrella term for two related types of dementia dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinsons disease dementia . Dementia is a disease that progressively impairs a persons ability to think, reason, remember, and function. Although these two conditions have overlapping features, there are also important distinctions. Understanding LBD causes and symptoms, as well as how its two subtypes, dementia with Lewy bodies and PDD, differ from one another is critical for proper diagnoses and shortening the time to start treatment.
Also Check: Parkinsons Donations In Memory Of
How Lewy Body Dementia Differs From Other Types Of Dementia
Dementia is a term that describes the gradual loss of the ability to think, reason or remember. The most common form of dementia in the U.S. is associated with Alzheimers disease, but can also be caused by Lewy body dementia, frontotemporal dementia, and , among others. Although they all have dementia in common, the symptoms of these diseases differ because they affect different parts of the brain.
Lewy body dementia affects many parts of the brain, starting with the outer layer of the brain, called the gray matter or cerebral cortex. The cerebral cortex is responsible for language, thinking, perception and judgment. This is why some of the earlier symptoms of Lewy body dementia include changes in visual perception, delusions or , difficulty paying attention, and misidentifying objects.
As other parts of the brain become affected, more symptoms appear, such as difficulty forming new memories, changes in behavior, difficulty sleeping or excessive sleepiness, and difficulty moving and maintaining balance.
Although overall Lewy body dementia symptoms are similar to other types of dementia like Alzheimers disease or frontotemporal dementia, there are some key differences. For example, early symptoms of Alzheimers disease are or getting lost in familiar places. The earliest symptoms among people with frontotemporal dementia tend to be changes in personality or the inability to bring out the correct words.
Also Check: Fitflop Shoes For Parkinson’s
Diagnosing Lewy Body Dementia
Diagnosing LBD can be challenging. Dementia with Lewy bodies is most often misdiagnosed as Alzheimer’s disease. The biggest difficulty in the diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies is early diagnosis and differentiation from Alzheimer’s. In PDD, the main challenge is timely identification of cognitive impairment in individuals with Parkinson’s disease.
To make a diagnosis, doctors will use specific clinical interview questionnaires, rating scales, and laboratory tests . Neurological and physical exams will also be needed. Imaging techniques can be particularly useful when trying to distinguish LBD from Parkinson’s disease. Careful, accurate assessments and appropriate management plans are necessary components of diagnosing Lewy body diseases.
How Can We Manage Hallucinations
It may not be necessary to treat all hallucinations of a person with PDD. Hallucinations are often harmless, and it is okay to allow them to happen, as long as they are not disruptive or upsetting to the person or surroundings. Sometimes, recognizing the hallucination and then switching the topic might be an efficient way of handling frustrations that occur because of a hallucination. If hallucinations need medical treatment, your provider may be able to discuss and suggest some options. However, many of the medications used to treat hallucinations may make movement symptoms worse.
Read Also: Parkinson Silverware
Coping With A Diagnosis
Being diagnosed with dementia can be an overwhelming experience. While there is no cure at present for LBD, or any medications aimed at specifically treating LBD, doctors are able to treat many of its symptoms. There are also a number of self-help strategies that can help improve symptoms.
If youve been diagnosed with LBD, its normal to feel many strong and painful emotions, including anger, fear, and uncertainty about the future.
Take time to adjust. As with any major life change, its important to give yourself time to adjust. Expect ups and downs as you do. You may feel that youve come to terms with your new situation for a while, and then suddenly feel overwhelmed by stress again.
Reach out for support. Living with Lewy body dementia is not easy, but there is help for this journey. The more support you have from family and friends, the better youll be able to cope with symptoms.
Talk to your loved ones about your wishes. Its never easy to talk about how you want your healthcare handled when youre unable to make decisions for yourself. But its important to let your loved one know what is important to you. Thinking about your choices today can improve your quality of life in the future and ease the burden on your family.
Need to talk to someone?
Get professional help from BetterHelps network of licensed therapists.
Need urgent help? .
Dementia With Lewy Bodies And Parkinson Disease Dementia
, MD, PhD, Department of Neurology, University of Mississippi Medical Center
Dementia with Lewy bodiesParkinson disease dementia
Dementia is chronic, global, usually irreversible deterioration of cognition.
Dementia with Lewy bodies is the 3rd most common dementia. Age of onset is typically > 60.
Lewy bodies are spherical, eosinophilic, neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions composed of aggregates of alpha-synuclein, a synaptic protein. They occur in the cortex of some patients who have dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurotransmitter levels and neuronal pathways between the striatum and the neocortex are abnormal.
Lewy bodies also occur in the substantia nigra of patients with Parkinson disease Parkinson Disease Parkinson disease is a slowly progressive, degenerative disorder characterized by resting tremor, stiffness , slow and decreased movement , and eventually gait and/or… read more , and dementia may develop late in the disease. About 40% of patients with Parkinson disease develop Parkinson disease dementia, usually after age 70 and about 10 to 15 years after Parkinson disease has been diagnosed.
Both dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson disease dementia have a progressive course with a poor prognosis.
Also Check: Sam Waterston Tremor
Building A Lewy Body Dementia Care Team
After receiving a diagnosis, a person with LBD may benefit from seeing a neurologist who specializes in dementia and/or movement disorders. Your primary doctor can work with other professionals to follow your treatment plan. Depending on an individual’s particular symptoms, physical, speech, and occupational therapists, as well as mental health and palliative care specialists, can be helpful.
Support groups are another valuable resource for people with LBD and their caregivers. Sharing experiences and tips with others in the same situation can help people find practical solutions to day-to-day challenges and get emotional and social support.
Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Initial cognitive deterioration in dementia with Lewy bodies resembles that in other dementias. However, dementia with Lewy bodies often manifests with early and prominent deficits in attention, executive function, and visuoperceptual ability prominent or persistent memory impairment tends to occur as the dementia progresses.
Extrapyramidal symptoms occur. However, in dementia with Lewy bodies , cognitive and extrapyramidal symptoms usually begin within 1 year of each other. Also, the extrapyramidal symptoms differ from those of Parkinson disease in dementia with Lewy bodies, tremor does not occur early, rigidity of axial muscles with gait instability occurs early, and deficits tend to be symmetric. Repeated falls are common.
Fluctuating cognitive function is a relatively specific feature of dementia with Lewy bodies. Periods of being alert, coherent, and oriented may alternate with periods of being confused and unresponsive to questions, usually over a period of days to weeks but sometimes during the same interview.
Memory is impaired, but the impairment appears to result more from deficits in alertness and attention than in memory acquisition thus, short-term recall is affected less than digit span memory .
Patients may stare into space for long periods. Excessive daytime drowsiness is common.
Visuospatial and visuoconstructional abilities are affected more than other cognitive deficits.
Don’t Miss: Prayer For Parkinson’s Disease
Lewy Body Dementia Vs Parkinsons Disease Dementia
Diagnoses of Lewy body dementia include dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinsons disease dementia. Symptoms in both of these diagnoses can be similar.
Lewy body dementia is a progressive dementia caused by abnormal deposits of a protein called alpha-synuclein in the brain. Lewy bodies are also seen in Parkinsons disease.
The overlap in symptoms between Lewy body dementia and Parkinsons disease dementia include movement symptoms, rigid muscles, and problems with thinking and reasoning.
This seems to indicate that they could be linked to the same abnormalities, though more research is needed to confirm that.
The later stages of Parkinsons disease have more severe symptoms that may require help moving around, around-the-clock care, or a wheelchair. Quality of life can decline rapidly.
Risks of infection, incontinence, pneumonia, falls, insomnia, and choking increase.
Hospice care, memory care, home health aides, social workers, and support counselors can be a help in later stages.
Parkinsons disease itself isnt fatal, but complications can be.
Research has shown a median survival rate of about
Dementia With Lewy Bodies And Neuroleptics
Neuroleptics, or antipsychotics, are strong tranquillizers sometimes prescribed for people with dementia to treat hallucinations or other behavior problems. However, if taken by people with LBD, neuroleptics may be particularly dangerous. This class of drugs can induce Parkinson-like side-effects, including rigidity, immobility, and an inability to perform tasks or to communicate.
If you or your loved one with Lewy body dementia is not unduly distressed by the hallucinations, it may be better to tolerate them rather than endure the side effects of the medication. If, however, you and your doctor decide to use a neuroleptic, this should be done with the utmost care and monitored carefully and regularly.
According to Lewy Body Dementia Association:
Up to 50% of patients with LBD who are treated with any antipsychotic medication may experience severe neuroleptic sensitivity, such as worsening cognition, heavy sedation, increased or possibly irreversible Parkinsonism, or symptoms resembling neuroleptic malignant syndrome , which can be fatal. .
Read Also: Diseases Similar To Parkinsons