What Should I Know About Storage And Disposal Of This Medication
Keep this medication in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. Store it at room temperature and away from excess heat and moisture .
Store cassettes containing levodopa and carbidopa enteral suspension in the refrigerator in their original carton, protected from light. Do not freeze the suspension.
Unneeded medications should be disposed of in special ways to ensure that pets, children, and other people cannot consume them. However, you should not flush this medication down the toilet. Instead, the best way to dispose of your medication is through a medicine take-back program. Talk to your pharmacist or contact your local garbage/recycling department to learn about take-back programs in your community. See the FDA’s Safe Disposal of Medicines website for more information if you do not have access to a take-back program.
It is important to keep all medication out of sight and reach of children as many containers are not child-resistant and young children can open them easily. To protect young children from poisoning, always lock safety caps and immediately place the medication in a safe location â one that is up and away and out of their sight and reach.
Common Drugs For Parkinsons Disease
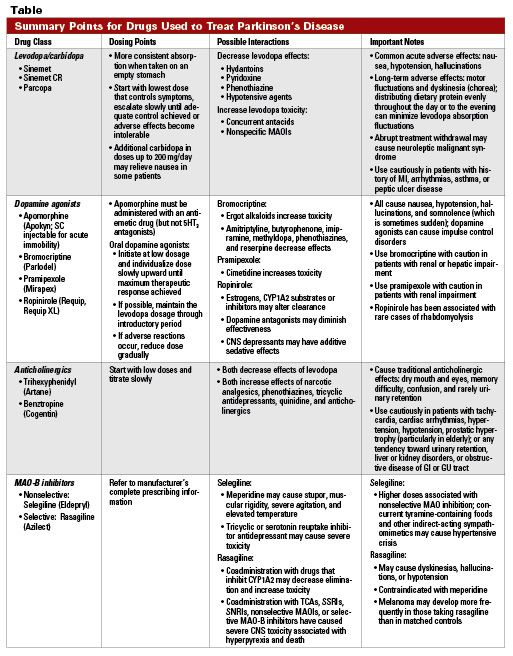
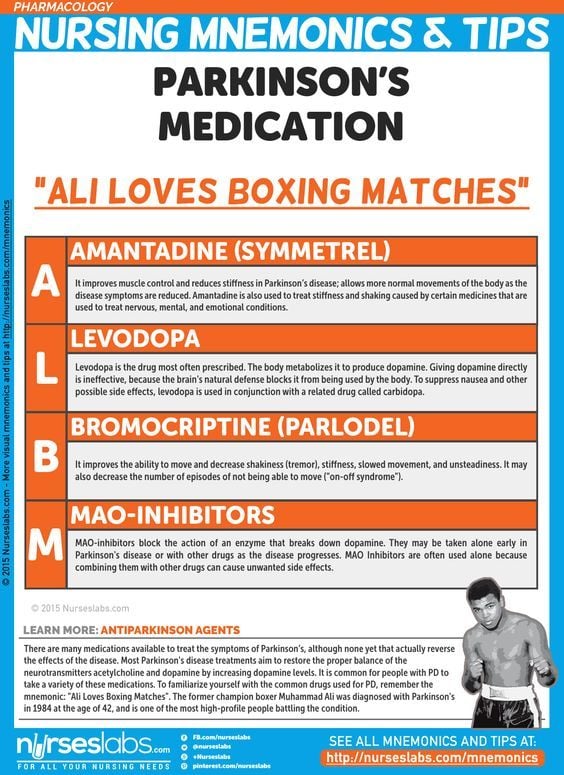
Levodopa and carbidopa . Levodopa is the most commonly prescribed medicine for Parkinsonâs. Itâs also the best at controlling the symptoms of the condition, particularly slow movements and stiff, rigid body parts.
Levodopa works when your brain cells change it into dopamine. Thatâs a chemical the brain uses to send signals that help you move your body. People with Parkinsonâs donât have enough dopamine in their brains to control their movements.
Sinemet is a mix of levodopa and another drug called carbidopa. Carbidopa makes the levodopa work better, so you can take less of it. That prevents many common side effects of levodopa, such as nausea, vomiting, and irregular heart rhythms.
Sinemet has the fewest short-term side effects, compared with other Parkinsonâs medications. But it does raise your odds for some long-term problems, such as involuntary movements. An inhalable powder form of levodopa and the tablet istradefylline have been approved for those experiencing OFF periods, OFF periods can happen when Parkinsonâs symptoms return during periods between scheduled doses of levodopa/carbidopa.
People who take levodopa for 3-5 years may eventually have restlessness, confusion, or unusual movements within a few hours of taking the medicine. Changes in the amount or timing of your dose will usually prevent these side effects.
Dopamine agonists. These drugs act like dopamine in the brain. They include pramipexole , rotigotine , and ropinirole , .
When Might I Be Prescribed An Anti
You should only be prescribed an anti-Parkinson’s drug if you have developed Parkinsonism symptoms as a side effect of your antipsychotic, and
- you can’t switch to a different antipsychotic or reduce your dose, or
- you have tried changing the antipsychotic or reducing the dose, but this has not helped your Parkinsonism symptoms.
These drugs should never be prescribed to prevent side effects that you havent already experienced.
You May Like: What Foods Are Good For Parkinson’s Disease
Impulsive And Compulsive Behaviours
People who experience impulsive and compulsive behaviours cant resist the temptation to carry out an activity often one that gives immediate reward or pleasure.
Behaviours may involve gambling, becoming a shopaholic, binge eating or focusing on sexual feelings and thoughts. This can have a huge impact on peoples lives including family and friends.
Not everyone who takes Parkinsons medication will experience impulsive and compulsive behaviours, so these side effects should not put you off taking your medication to control your symptoms.
If you have a history of behaving impulsively you should mention this to your GP, specialist or Parkinsons nurse.
Asking your specialist to make changes to your medication regime or adjusting the doses that you take is the easiest way to control impulsive and compulsive behaviours. So, if you or the person you care for is experiencing this side effect, tell your healthcare professional as soon as possible before it creates large problems.
If you are not able to get through to your healthcare professional straight away, you can call our Parkinsons UK helpline on 0808 800 0303.
We have advice that can help you manage impulsive and compulsive behaviours as well as information on what behaviour to look out for.
An Approach To The Treatment Of Parkinson’s Disease
No treatment can arrest or slow neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. The aim is to relieve symptoms and avoid the complications of therapy.
Early Parkinson’s disease
Many studies have shown that early treatment with dopamine agonists reduces the incidence of dyskinesia.1Fewer motor fluctuations were shown in some but not all of the studies. We recommend a dopamine agonist as the first treatment in younger patients who have mild disease and no cognitive deficit. It is necessary to add levodopa within 1-5 years in most patients. In more severe disease, treatment begins with levodopa but a dopamine agonist may be added to keep the daily dose of levodopa in the lower range if there is no cognitive deficit. Dopamine agonists are used infrequently and with caution in patients more than 70 years old because of the risk of neuropsychiatric adverse effects and postural hypotension. They are contraindicated in the presence of dementia.
Isolated resting tremor is rarely disabling, but if it interferes with function it can usually be managed with levodopa. When this is ineffective at low to moderate doses, the addition of an anticholinergic can sometimes be useful.
Patients with motor fluctuations
Role of physical therapy and surgery
Don’t Miss: Loss Of Balance Parkinson Disease
Dopamine Agonist Withdrawal Syndrome
If you suddenly stop taking dopamine agonists, this can lead to dopamine agonist withdrawal syndrome, which can cause symptoms such as depression, anxiety or pain.
Any withdrawal from Parkinsons drugs needs to be done in a tapered way, under the supervision of a health professional.
Speak to your specialist for advice.
You May Like: How To Support Someone With Parkinsons Disease
What Are The Most Common Medicines Used To Treat Pd
Sinemet®
Levodopa is the most commonly prescribed and most effective medicine for controlling the symptoms of PD, particularly bradykinesia and rigidity.
Levodopa is a chemical found naturally in our brains. When given as a medicine, it is transported to the nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine. It is then converted into dopamine for the nerve cells to use as a neurotransmitter.
Sinemet is made up of levodopa and another drug called carbidopa. Levodopa enters the brain and is converted to dopamine while carbidopa prevents or lessens many of the side effects of levodopa, such as nausea, vomiting, and occasional heart rhythm disturbances. It is generally recommended that patients take Sinemet on an empty stomach, at least ½ hour before or one hour after meals.
There are two forms of Sinemet: controlled-release or immediate-release Sinemet. Controlled-release Sinemet and immediate-release Sinemet are equally effective in treating the symptoms of PD, but some people prefer the controlled release version. Ask your doctor which approach is best for you.
Dopamine agonists
Dopamine agonists are medicines that activate the dopamine receptor. They mimic or copy the function of dopamine in the brain.
Parlodel®, Requip®, and Mirapex® are all dopamine agonists. These medicines might be taken alone or in combination with Sinemet. Generally, dopamine agonists are prescribed first and levodopa is added if the patient’s symptoms cannot be controlled sufficiently.
Symmetrel®
You May Like: Cause And Effect Of Parkinson’s Disease
Delayed Administration And Contraindicated Drugs Place Hospitalized Parkinsons Disease Patients At Risk
Problem: One-third of all patients with Parkinsons disease visit an emergency department or hospital each year, making it a surprisingly common occurrence.1 The disease affects about 1 million people and is currently the fourteenth leading cause of death in the US. Hospitalization can be risky for patients with Parkinsons disease when viewed from the perspective of pharmacological management.
Patients with Parkinsons disease require strict adherence to an individualized, timed medication regimen of antiparkinsonian agents. Dosing intervals are specific to each individual patient because of the complexity of the disease. It is not unusual for patients being treated with carbidopa/levodopa to require a dose every 1 to 2 hours. When medications are not administered on time, according to the patients unique schedule, patients may experience an immediate increase in symptoms.2,3 Delaying medications by more than 1 hour, for example, can cause patients with Parkinsons disease to experience worsening tremors, increased rigidity, loss of balance, confusion, agitation, and difficulty communicating.2 Studies show that three out of four hospitalized patients with Parkinsons disease do not receive their medications on time, or have had doses entirely omitted.4 According to the National Parkinson Foundation, 70% of neurologists report that their patients do not get the medications they need when hospitalized.2
Two case examples
References
Common Drugs For Parkinson’s Disease
Levodopa and carbidopa . Levodopa is the most commonly prescribed medicine for Parkinsonâs. Itâs also the best at controlling the symptoms of the condition, particularly slow movements and stiff, rigid body parts.
Levodopa works when your brain cells change it into dopamine. Thatâs a chemical the brain uses to send signals that help you move your body. People with Parkinsonâs donât have enough dopamine in their brains to control their movements.
Sinemet is a mix of levodopa and another drug called carbidopa. Carbidopa makes the levodopa work better, so you can take less of it. That prevents many common side effects of levodopa, such as nausea, vomiting, and irregular heart rhythms.
Sinemet has the fewest short-term side effects, compared with other Parkinsonâs medications. But it does raise your odds for some long-term problems, such as involuntary movements. An inhalable powder form of levodopa and the tablet istradefylline have been approved for those experiencing OFF periods, OFF periods can happen when Parkinsonâs symptoms return during periods between scheduled doses of levodopa/carbidopa.
People who take levodopa for 3-5 years may eventually have restlessness, confusion, or unusual movements within a few hours of taking the medicine. Changes in the amount or timing of your dose will usually prevent these side effects.
Dopamine agonists. These drugs act like dopamine in the brain. They include pramipexole , rotigotine , and ropinirole , .
Also Check: Utensils For Parkinson’s Patients
Your Parkinson’s Drug Treatment
Dopamine is a chemical messenger made in the brain. The symptoms of Parkinsons appear when dopamine levels become too low. This is because many of the cells in your brain that produce dopamine have died or are dying. Taking dopamine as a drug doesnt work because it cannot cross the blood brain barrier. To get around this, doctors use other medication that can act in a similar way.
How Anticholinergics Are Used
These medications are older and are not used very often for Parkinsons today. Sometimes they are prescribed for reducing tremor and muscle stiffness. They can be used on their own, especially in the early stages of your Parkinsons when symptoms are mild, before levodopa is prescribed.
Anticholinergics can also be used with levodopa or a glutamate antagonist. They are taken as tablets or as a liquid.
Read Also: Symptoms Of Parkinsons In Women
Types Of Parkinson’s Medication
There is currently no cure for Parkinsons, but medication can usually provide good symptom control for a long time. Meanwhile researchers continue to search for a cure, and research into new and improved medicines continues.
Dopamine is a chemical messenger made in the brain. The symptoms of Parkinsons are largely associated with a decrease in the levels of this chemical, due to the death of the nerve cells that make it.
Unfortunately, taking dopamine as a drug treatment would not help you, because it cannot cross into your brain where it is needed. There are a number of approaches that can be taken to try to compensate for the dopamine deficit and therefore alleviate the symptoms of the condition. Ultimately these will increase the levels of dopamine and help to overcome some of the symptoms of the condition. However, many of the medications may have side effects which should be taken into account when being prescribed.
A wide range of Parkinsons medications is available. These may be taken in many different forms. Your doctor will try to find the medication that is most suitable for you throughout your Parkinsons treatment. What is available will also depend on the country in which you live.
How Should This Medicine Be Used
The combination of levodopa and carbidopa comes as a regular tablet, an orally disintegrating tablet, an extended-release tablet, and an extended-release capsule to take by mouth. The combination of levodopa and carbidopa also comes as a suspension to be given into your stomach through a PEG-J tube or sometimes through a naso-jejunal tube using a special infusion pump. The regular and orally disintegrating tablets are usually taken three or four times a day. The extended-release tablet is usually taken two to four times a day. The extended-release capsule is usually taken three to five times a day. The suspension is usually given as a morning dose and then as a continuous dose , with extra doses given no more than once every 2 hours as needed to control your symptoms. Take levodopa and carbidopa at around the same times every day. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take levodopa and carbidopa exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Swallow the extended-release tablets whole do not chew or crush them.
To take the orally disintegrating tablet, remove the tablet from the bottle using dry hands and immediately place it in your mouth. The tablet will quickly dissolve and can be swallowed with saliva. No water is needed to swallow disintegrating tablets.
You May Like: Golf Therapy For Parkinson’s
Medication Guidelines For Parkinson’s Disease
There is no one best mix of Parkinsonâs medicines. You and your doctor will have to try a few treatment approaches to figure out the best one for you.
But there are some general guidelines for taking your medication. Be sure to ask your doctor or pharmacist for any specific tips for your treatment.
What Other Information Should I Know
Keep all appointments with your doctor and the laboratory. Your doctor will order certain lab tests to check your response to levodopa and carbidopa.
Before having any laboratory test, tell your doctor and the laboratory personnel that you are taking levodopa and carbidopa.
Levodopa and carbidopa can lose its effect completely over time or only at certain times during the day. Call your doctor if your Parkinson’s disease symptoms worsen or vary in severity.
As your condition improves and it is easier for you to move, be careful not to overdo physical activities. Increase your activity gradually to avoid falls and injuries.
Levodopa and carbidopa can cause false results in urine tests for sugar and ketones .
Do not let anyone else take your medication. Ask your pharmacist any questions you have about refilling your prescription
It is important for you to keep a written list of all of the prescription and nonprescription medicines you are taking, as well as any products such as vitamins, minerals, or other dietary supplements. You should bring this list with you each time you visit a doctor or if you are admitted to a hospital. It is also important information to carry with you in case of emergencies.
Also Check: What Are The Early Symptoms Of Parkinson’s
Crossing The Blood Brain Barrier
Many molecules are unable to cross the . Molecules must be small, and to cross over. If compounds do not possess these qualities they must have a specific transporter that can transport them over the BBB. Dopamine cannot diffuse across the BBB because of the group, it is too polar and therefore unable to enter the brain. The catechol group is a dihydroxy ring.
The synthesis of dopamine consists of three stages. The synthesis process starts with an amino acid, called . In the second stage is formed by adding a phenol group to the benzene ring of L-Tyrosine. The formation of L-dopa from L-tyrosine is catalyzed by the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase. The third stage is the formation of dopamine by removing the carboxylic acid group from L-dopa, catalysed by the enzyme dopa decarboxylase.
Levodopa is also too polar to cross the blood brain barrier but it happens to be an amino acid so it has a specialized transporter called L-type amino acid transporter or LAT-1 that helps it diffuse through the barrier.
Dopaminergic Features And Their Treatment
Patients with PD usually present with features indicative of degeneration of nigrostriatal pathways. A useful clinical definition for PD is asymmetric onset of an akinetic rigid syndrome with resting tremor and a good response to levodopa. When applied by neurologists with an interest in movement disorders, this definition has a pathological correlation exceeding 98%. When treatment is considered appropriate, and this is a topic discussed in detail below, a variety of options is available. The use of dopaminergic drugs improves motor function, significantly reduces both the morbidity and mortality of PD, and improves quality of life.
Levodopa remains the drug most commonly used in PD. It is very effective in improving bradykinesia and rigidity, and in practice remains the gold standard against which other drugs are judged. Some studies, predominantly in vitro, have suggested that levodopa may be toxic. However, such data are conflicting, and some laboratory studies have suggested a growth factor-like effect for levodopa. Overall, the pre-clinical evidence for levodopa toxicity is not convincing and there are no data to indicate that any toxic action is of clinical relevance.
Table 1
Percentage of patients remaining on dopamine agonist monotherapy at years 14 and years 15 during treatment trials
Recommended Reading: First Stage Of Parkinson’s Disease