Bradykinesia And Freezing Impair Gait
Dynamic balance control involves controlling the body CoM with respect to, but not necessarily over a moving base of support. Walking becomes less automatic in PD so it requires more attention, particularly for challenging tasks such as turning, walking between obstacles, and dual-tasking. Newly diagnosed patients with PD show signs of bradykinetic gait features, such as reduced trunk rotation, decreased arm swing, and slow turns, even when walking speed is normal . Extent of arm swing on the most involved side may, in fact, be the most sensitive early sign of gait affected by the disease. Bradykinesia results in slow gait velocity and shuffling of the feet that progresses with the disease. Freezing of gait is not usually only lack of stepping but often includes high frequency trembling of the legs as the patients attempt to get their feet moving. These quick motions may represent repeated, multiple APAs that get larger and larger until a step is finally triggered .
Equipment And Walking Aids
You might find that equipment can help you to walk, such as a walking stick or a rollator .
Before you start using a walking aid, it’s very important to get advice from a physiotherapist. Some walking aids aren’t recommended for people with Parkinsons as they can affect your walking pattern and make you more likely to fall. But, the correct walking aid can increase your confidence and help you to lift your feet better.
What Is Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
Progressive supranuclear palsy is a rare brain disorder that causes problems with movement, walking and balance, and eye movement. It results from damage to nerve cells in the brain that control thinking and body movement. The disorders long name indicates that the disease worsens and causes weakness by damaging certain parts of the brain above nerve cell clusters called nuclei that control eye movements.
PSP is different than Parkinsons diseaseanother movement disorderalthough they share some symptoms . Currently there is no effective treatment for PSP, but some symptoms can be managed with medication or other interventions.
Don’t Miss: Medicinal Plants For Parkinson’s Disease
Walking With Parkinsons: Freezing Balance And Falls
Parkinsons disease can change the way a person walks. Movement Symptoms like stiff muscles, rigidity and slow movement make it harder to take normal steps. In fact, short, shuffling steps are a common sign of PD, as is freezing, the feeling that your feet are stuck to the floor, for people with mid-stage to advanced PD.
On their own, these changes are distressing enough. But add the fact that Parkinsons affects balance and they also become dangerous, putting people with PD at risk of falling. The good news is that with exercise and physical therapy, people with PD can improve their balance. What can you do to minimize freezing and avoid falls? Read on to find out.
The following article is based on the latest research and a Parkinsons Foundation Expert Briefings about Parkinsons-related freezing, balance and falls hosted by Fay B. Horak, PhD, PT, Professor of Neurology at the Oregon Health & Science University, a Parkinsons Foundation Center of Excellence.
Is There A Cure For Parkinsons
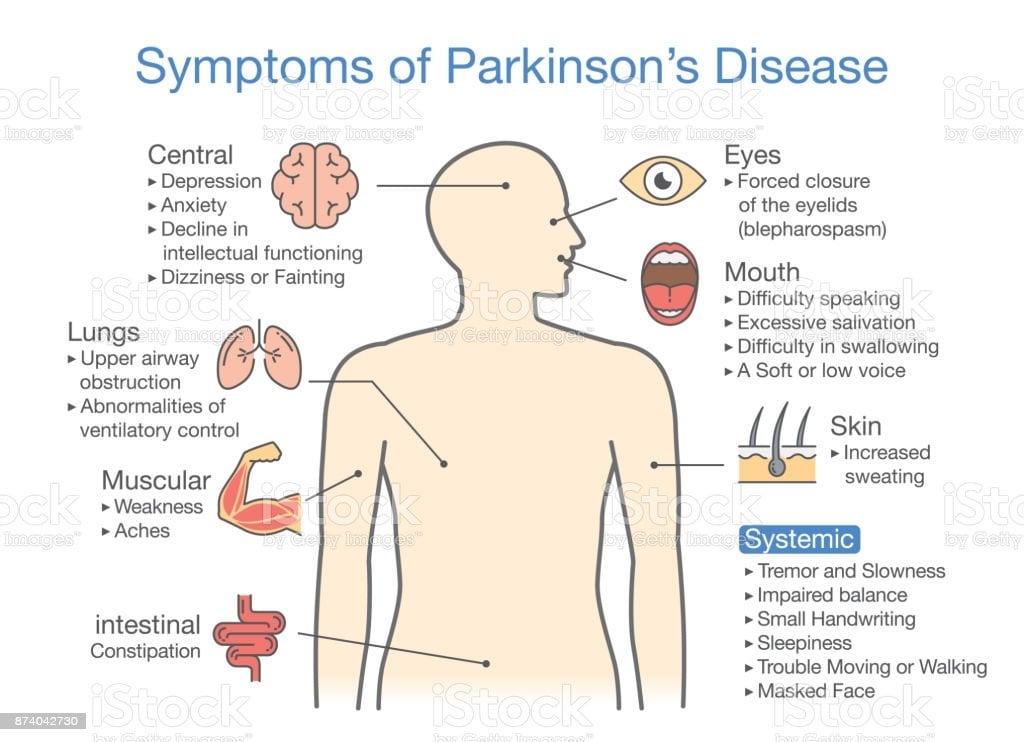
Theres currently no cure for Parkinsons, a disease that is chronic and worsens over time. More than 50,000 new cases are reported in the United States each year. But there may be even more, since Parkinsons is often misdiagnosed.
Its reported that Parkinsons complications was the
Complications from Parkinsons can greatly reduce quality of life and prognosis. For example, individuals with Parkinsons can experience dangerous falls, as well as blood clots in the lungs and legs. These complications can be fatal.
Proper treatment improves your prognosis, and it increases life expectancy.
It may not be possible to slow the progression of Parkinsons, but you can work to overcome the obstacles and complications to have a better quality of life for as long as possible.
Parkinsons disease is not fatal. However, Parkinsons-related complications can shorten the lifespan of people diagnosed with the disease.
Having Parkinsons increases a persons risk for potentially life threatening complications, like experiencing:
- falls
Parkinsons often causes problems with daily activities. But very simple exercises and stretches may help you move around and walk more safely.
Read Also: Is Drooling A Sign Of Parkinson’s Disease
How Is Parkinsons Disease Treated
There is no cure for Parkinsons disease. However, medications and other treatments can help relieve some of your symptoms. Exercise can help your Parkinsons symptoms significantly. In addition, physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech-language therapy can help with walking and balance problems, eating and swallowing challenges and speech problems. Surgery is an option for some patients.
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinsons disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare teams efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinsons disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
Recommended Reading: Tai Chi For Parkinson’s
How Can I Help Myself
It is important that you do not allow a fear of falling to stop you doing things, provided that you are sensible. Keeping active is good for your mobility and independence, and doing the things you like is good for your morale. Try not to let falls curb your activities too much as this can have a negative impact on your quality of life.
The following information and practical suggestions may help you in adapting your daily routine so as to minimise the risk of falls:
What Are The Causes
The cause of Parkinson’s is largely unknown. Scientists are currently investigating the role that genetics, environmental factors, and the natural process of aging have on cell death and PD.
There are also secondary forms of PD that are caused by medications such as haloperidol , reserpine , and metoclopramide .
Read Also: Insomnia And Parkinson’s Disease
How Postural Instability May Appear
Patients with PD experience symptoms in varying severities, and with the progression of the disease, the severity of the symptoms changes over time. Postural instability may show up during a variety of activities, including:
- When rising from a chair
- When rising from bed
- While turning or pivoting, especially quick movements
- While standing upright1
Postural instability may be apparent at diagnosis, but it is more commonly seen and worsens as PD progresses. The inability to balance and recover from variations in movement often causes falls, which can lead to hospitalization or death in people with PD. Because of this, postural instability is one of the most distressing symptoms of PD and greatly diminishes the individuals level of mobility.2,3
Explorative And Validation Datasets
Two datasets were included in this study. The explorative dataset serves to exploratively analyze the potential balance-improvement predictors after acute DBS. This dataset has a large sample size but contains data in M1 only. The validation dataset was smaller in sample size, but had complete data in both the M1 and M12, serving to validate the factor identified in the explorative dataset in longer follow-ups. This strategy explored the balance response after both the acute and chronic STN stimulation. M1 was chosen because disease progression would not play a role at this timepoint, and stimulation parameters are more variable at M1, helping study the influence of stimulation settings on balance. Besides, factor analysis usually requires a large sample size . The sample size in M1 is large enough to provide sufficient statistical power.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Quality Of Life
Medicines For Parkinson’s Disease
Medicines prescribed for Parkinson’s include:
- Drugs that increase the level of dopamine in the brain
- Drugs that affect other brain chemicals in the body
- Drugs that help control nonmotor symptoms
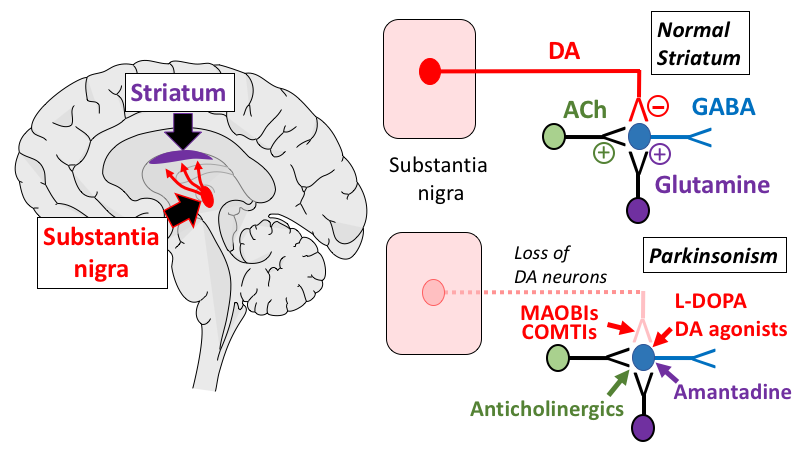
The main therapy for Parkinson’s is levodopa, also called L-dopa. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brain’s dwindling supply. Usually, people take levodopa along with another medication called carbidopa. Carbidopa prevents or reduces some of the side effects of levodopa therapysuch as nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and restlessnessand reduces the amount of levodopa needed to improve symptoms.
People with Parkinson’s should never stop taking levodopa without telling their doctor. Suddenly stopping the drug may have serious side effects, such as being unable to move or having difficulty breathing.
Other medicines used to treat Parkinsons symptoms include:
- Dopamine agonists to mimic the role of dopamine in the brain
- MAO-B inhibitors to slow down an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain
- COMT inhibitors to help break down dopamine
- Amantadine, an old antiviral drug, to reduce involuntary movements
- Anticholinergic drugs to reduce tremors and muscle rigidity
What Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Each person with Parkinsons disease experiences symptoms in in their own unique way. Not everyone experiences all symptoms of Parkinsons disease. You may not experience symptoms in the same order as others. Some people may have mild symptoms others may have intense symptoms. How quickly symptoms worsen also varies from individual to individual and is difficult to impossible to predict at the outset.
In general, the disease progresses from early stage to mid-stage to mid-late-stage to advanced stage. This is what typically occurs during each of these stages:
Early stage
Early symptoms of Parkinsons disease are usually mild and typically occur slowly and do not interfere with daily activities. Sometimes early symptoms are not easy to detect or you may think early symptoms are simply normal signs of aging. You may have fatigue or a general sense of uneasiness. You may feel a slight tremor or have difficulty standing.
Often, a family member or friend notices some of the subtle signs before you do. They may notice things like body stiffness or lack of normal movement slow or small handwriting, lack of expression in your face, or difficulty getting out of a chair.
Mid stage
Mid-late stage
Standing and walking are becoming more difficult and may require assistance with a walker. You may need full time help to continue to live at home.
Advanced stage
Also Check: How Do They Test You For Parkinson’s Disease
Realities Of Living With Parkinsons
Parkinsons disease is unpredictable, so it can be difficult to make any plansbig or smallwithout worrying you have to cancel at the last minute. Living with the painful symptoms, both physical and mental, can be draining.
Daily tasks may require a lot of energy for someone with Parkinson’s disease to complete or are taken away altogether. For example, a person without a chronic disease can drive to the grocery store, come home and do laundry, cook dinner for their family, and still have time to relax at the end of the day. However, a person with Parkinson’s will have to put much more effort and time into each task and may not be able to drive at all.
As the disease progresses to its later stages, many people are forced to give up their independence and autonomy when it comes to taking care of themselves. This makes coping with a diagnosis and the disease incredibly difficult.
However, with the right treatments, you can slow disease progression and remain independent for as long as possible.
About Gait And Balance
Gait can be described simply as a persons manner of walking. Most people have a distinctive style of walking. In normal circumstances when people walk, their stance is upright and the center of gravity of the body is positioned in a manner that helps them coordinate their movement. As people walk, they swing their arms on the side, which also helps coordinate their motion.
Because of the bodys inability to coordinate movement in Parkinsons disease, it becomes progressively more difficult for people to maintain proper posture and coordination during walking. Most Parkinsons patients experience a range of walking difficulties, resulting in distinctive gait and balance problems.
Don’t Miss: What Age Parkinson’s Disease
Ethics Approval And Consent To Participate
The study was approved by the Ethical Council of Stockholm and stringently followed the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. All the participants were given verbal and written information about the study, and signed a written consent form to participate in the study before data collection commenced.
The Nervous System & Dopamine
To understand Parkinson’s, it is helpful to understand how neurons work and how PD affects the brain .
Nerve cells, or neurons, are responsible for sending and receiving nerve impulses or messages between the body and the brain. Try to picture electrical wiring in your home. An electrical circuit is made up of numerous wires connected in such a way that when a light switch is turned on, a light bulb will beam. Similarly, a neuron that is excited will transmit its energy to neurons that are next to it.
Neurons have a cell body with branching arms, called dendrites, which act like antennae and pick up messages. Axons carry messages away from the cell body. Impulses travel from neuron to neuron, from the axon of one cell to the dendrites of another, by crossing over a tiny gap between the two nerve cells called a synapse. Chemical messengers called neurotransmitters allow the electrical impulse to cross the gap.
Neurons talk to each other in the following manner :
Also Check: Gene Therapy For Parkinson’s Disease An Update
Reducing The Risk Of Falls
It is important that you take all your Parkinsons medications as prescribed so that symptoms such as poor gait and freezing are well controlled.
Some Parkinsons medications may, unintentionally, lower blood pressure and this can cause dizziness and increase the risk of falling. If this happens you should ask your doctor or nurse to check your blood pressure both when standing and sitting. Your doctor may be able to advise on medication to help with low blood pressure and dizziness, although this can be complicated because of possible interference with Parkinsons medications.
Some dizziness can be avoided. For example, when getting out of bed let your feet dangle over the side of the bed for a few minutes before standing and then rise slowly. When getting up from a chair, pause for a few moments and only start walking when you feel steady.
Some Parkinsons medications can actually aggravate falls by causing dyskinesias Again, it is important to tell your doctor if you fall so that medication can be adjusted if necessary.
Caution!
You are more likely to fracture a bone if you fall frequently, particularly if you have osteoporosis. If you fall frequently, ask your doctor for an osteoporosis assessment. If osteoporosis is diagnosed, he or she will be able to give you s advice on minimising its effects or refer you to another professional who can help.
How Can Parkinsons Disease Affect Mobility And Sense Of Balance
The neurophysiology of Parkinsons Disease proves that it affects balance, gait, movement and can actually cause constraints on mobility. But what do we mean by mobility?
Mobility is a persons ability to move safely in a variety of environments in order to accomplish functional tasks.
Functional tasks like drinking a glass of water or eating can become a problem. And if we think about it, mobility is something we take for granted most of the time. We dont expect to lose it, and we dont expect to get a degenerative disease, such as Parkinsons. Therefore, being able to maintain good mobility is something of utmost importance as we age, and we must take preventive measures to delay mobility impairment as much as possible.
Mobility requires dynamic neural control, a sense of balance, and enough agility to be able to adapt to postural transitions as quickly as possible. What also concerns us today is the several types of mobility deficits caused by the progression of Parkinsons Disease. We need to understand what preventive exercises and preventative measures can be taken to minimize the risk of falls and injury.
Parkinsons Disease and fall prevention
While Parkinsons is not life-threatening, people may experience life-threatening complications, such as choking on food or falling over. We must help our elderly loved ones prevent falls at any cost so that suggested exercise programs can work effectively in combatting the effects of Parkinsons Disease.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease Exercise Program
Tips For Maintaining Balance
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 10/07/2014.
References
- Parkinsons Disease Foundation. Accessed 10/20/2014.Fall Prevention Strategies for People Living with Parkinson’s
- National Parkinson Foundation. Accessed 10/20/2014.Falls Prevention Workbook
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services.Policy
Balance And The Brain

Difficulties with balance and walking are linked to the brain changes that take place with PD. For people who dont have PD, balance is automatic, a reflex. But Parkinsons affects the basal ganglia . To compensate, the brain assigns another brain area an area used for thinking to take over. The thinking part of the brain, mainly the frontal cortex, cant control balance automatically. The result: for many people with PD, balance becomes less automatic.
This means that when people experience freezing and fall, they cant adjust their balance automatically. Taking small steps to try and regain balance can make things worse, because it involves shifting weight with each step. The brain changes from PD inhibit their ability to take a big step to catch their balance and avoid a fall. For some, the drug levodopa can help prevent freezing, but does not improve balance.
A person whose balance is less automatic must pay more attention while walking. For everyone, walking slows down when were talking and thinking slows down when were walking. This is called the dual-task cost and its higher in people with PD. That tells us that people with PD are using more attention and more cognitive control for balance and gait.
Also Check: How Do You Treat Parkinson’s Disease Naturally