Bob Hoskins: Retirement With Parkinson’s
A British actor best known for his award-winning turn in the 1982 film The Long Good Friday and for his voiceover in 1988’s Who Framed Roger Rabbit, Bob Hoskins announced that having Parkinson’s disease forced him into retirement in 2012. He was quite private about the details of his diagnosis, but in a 2012 interview with Saga Magazine, he said, “I’m trying to retire. I’m not doing very well at it, though.” When he did retire, he announced that he would be focusing on living a healthier lifestyle after leaving the acting profession.
Hoskins died in April 2014 at age 71.
Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
These common symptoms of Parkinson’s disease often begin gradually and progress over time:
- Shaking or tremor
- Poor posture
- Slowing of body movements
As the disease continues to progress, additional symptoms can occur such as slurred or soft speech, trouble chewing and/or swallowing, memory loss, constipation, trouble sleeping, loss of bladder control, anxiety, depression, inability to regulate body temperature, sexual dysfunction, decreased ability to smell, restless legs and muscle cramps.
How Is Parkinsons Diagnosed
Doctors use your medical history and physical examination to diagnose Parkinson’s disease . No blood test, brain scan or other test can be used to make a definitive diagnosis of PD.
Researchers believe that in most people, Parkinson’s is caused by a combination of environmental and genetic factors. Certain environmental exposures, such as pesticides and head injury, are associated with an increased risk of PD. Still, most people have no clear exposure that doctors can point to as a straightforward cause. The same goes for genetics. Certain genetic mutations are linked to an increased risk of PD. But in the vast majority of people, Parkinsons is not directly related to a single genetic mutation. Learning more about the genetics of Parkinsons is one of our best chances to understand more about the disease and discover how to slow or stop its progression.
Aging is the greatest risk factor for Parkinsons, and the average age at diagnosis is 60. Still, some people get PD at 40 or younger.
Men are diagnosed with Parkinsons at a higher rate than women and whites more than other races. Researchers are studying these disparities to understand more about the disease and health care access and to improve inclusivity across care and research.
Aging is the greatest risk factor for Parkinsons, and the average age at diagnosis is 60. Still, some people get PD at 40 or younger.
The Michael J. Fox Foundation has made finding a test for Parkinsons disease one of our top priorities.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease And Weight Loss
Estimation Of The 2020 Global Population Of Parkinsons Disease
N. Maserejian, L. Vinikoor-Imler, A. Dilley
Category:Epidemiology
Objective: To estimate the number of individuals living with PD globally in 2020.
Background: Although previous studies have estimated PD prevalence in many countries, the number of individuals with PD globally in 2020 has not been estimated.
Method: We comprehensively reviewed the literature for recent and reliable prevalence estimates of PD globally. The Global Burden of Disease Study was the only source available that provided an overall global estimate, with 2017 the most recent year available from the published manuscript or online tools . We verified the estimates of the PD prevalence of several countries that comprised the GBD summary estimate, by reviewing the individual publications and comparing them to the GBD estimates. GBD estimates tended to be in the lower range but close to estimates from the individual papers. For all but two countries , we applied the GBD prevalence proportions in 2017. For the US and Canada, we applied more recent prevalence proportions by Marras et al. 2018 . We assessed the worldwide PD population in 2020 by multiplying the most reliable prevalence proportions by the corresponding 2020 population, using CDC data for US, Statistics Canada for Canada, Eurostat for European countries and UN population estimates for the rest of the world.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mov Disord.
Projected Estimates Of Parkinsons Disease With Aging Population
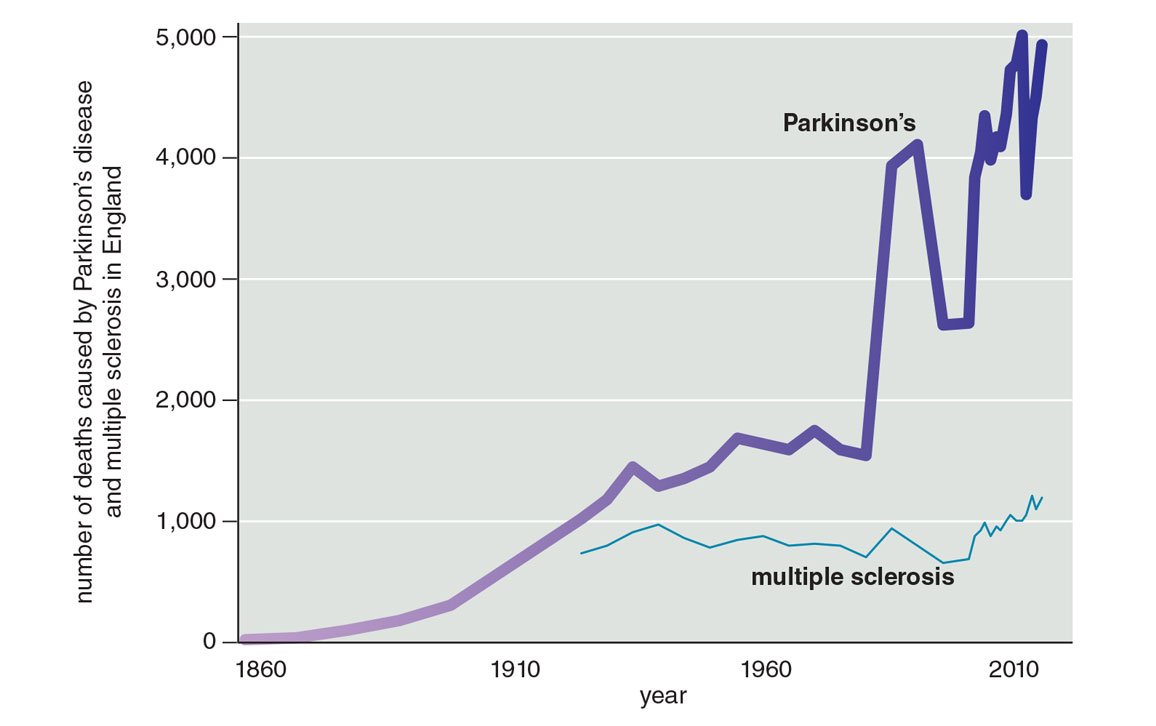
As the life expectancy has increased worldwide, it is expected that the burden of chronic diseases, like PD, will continue to grow. It is estimated that the number of people with PD in 2005 totaled between 4.1 million and 4.6 million and that number will more than double by 2030 to between 8.7 million and 9.3 million.7
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Life Center Of Southern New Jersey
Michael J Fox: Parkinson’s Champion For A Cure
Michael J. Fox is among the most well-known people living with Parkinson’s disease. Many remember him as the fresh-faced young star of the 1980s TV comedy hit Family Ties and the popular Back to the Future movies. Though most people with Parkinson’s are diagnosed between ages 40 and 60, Fox was diagnosed at age 30 but his diagnosis didnt slow him down.
He shared his young-onset Parkinson’s disease diagnosis with the world in 1998 and, two years later, founded the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research. Fox is committed to helping the foundation build Parkinson’s disease awareness and raise funds for research into prevention, treatment, and a cure. In addition to his advocacy work, hes still a working actor some more recent roles have included characters with Parkinson’s in the TV shows The Good Wife and Curb Your Enthusiasm.
“As long as I play a guy with Parkinson’s, I can do anything,” he joked in a 2013 AARP interview.
The Impact Of Parkinsons Disease On Overall Health
Based on the Blue Cross Blue Shield Health Index, the overall health of those affected by Parkinsons is significantly lower than the general population. In 2017, the average BCBS Health Index for someone aged 30-64 with Parkinsons was 57, compared to 88 for the entire commercially insured population in this age range. This translates to an average of 10.7 years of healthy life lost for those with the condition compared to 3.4 years for the 30-64 population as a whole.4
Caring for someone with Parkinsons Disease
The majority of Parkinsons patients are cared for by informal caregivers, such as a family member. The physical, mental and emotional work this requires can be significant. The Impact of Caregiving on Mental and Physical Health found that caregivers have 26% poorer health compared to a benchmark population, as measured by the BCBS Health Index. In addition, a national survey conducted by the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association found that 1 in 4 unpaid caregivers are feeling more stress trying to balance work and family due to COVID-19.5
Also Check: Vagus Nerve Stimulation And Parkinson’s
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinson’s disease has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Stiffness of the limbs and trunk
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination, sometimes leading to falls
Other symptoms may include depression and other emotional changes difficulty swallowing, chewing, and speaking urinary problems or constipation skin problems and sleep disruptions.
Symptoms of Parkinsons and the rate of progression differ among individuals. Sometimes people dismiss early symptoms of Parkinson’s as the effects of normal aging. In most cases, there are no medical tests to definitively detect the disease, so it can be difficult to diagnose accurately.
Early symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are subtle and occur gradually. For example, affected people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. They may notice that they speak too softly, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. Friends or family members may be the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinson’s. They may see that the person’s face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
People with Parkinson’s often develop a parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward, small quick steps as if hurrying forward, and reduced swinging of the arms. They also may have trouble initiating or continuing movement.
What Causes Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease occurs when nerve cells, or neurons, in an area of the brain that controls movement become impaired and/or die. Normally, these neurons produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems of Parkinson’s. Scientists still do not know what causes cells that produce dopamine to die.
People with Parkinson’s also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinson’s, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying-down position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinson’s contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons disease and Lewy body dementia.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease Causes Death
Learn More About Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons Disease: The Essentials
If youre new to Parkinsons disease and would like a good overview to help you better understand the disease, please view our Parkinsons Disease: The Essentials presentation. Its a great place to get started with reliable and concise information.
Causes
The exact cause of Parkinsons is still unknown, but there is an enormous amount of research being done to learn more. This research has led scientists to formulate a number of theories on the cause of this disease.
Diagnosing
While there is no definitive test that can be taken to determine whether a person has Parkinsons disease, movement disorder specialists look for symptoms and use brain imaging technology to accurately diagnose Parkinsons.
Symptoms
Even though Parkinsons is classified as a movement disorderand its motor symptoms are the most discussed and well-knownthere are many non-motor symptoms that display in people with Parkinsons as well.
Treatments
As of today, there is no cure for Parkinsons disease. But there are many ways in which the disease can be treated to make symptoms more manageable.
Living With Parkinsons
Number Of People With Parkinson’s
The number of people with Parkinson’s in New Zealand has been steadily increasing, from an estimated 7,000 in 2006 to 11,000 in 2020 . We project that the number of people in New Zealand with Parkinsons is expected to reach 22,000 by 2040. This is due to the ageing population, which puts more people into the highest risk age groups , and also due to people now living longer with the disease.
Figure 1: Number of people in New Zealand that have Parkinson’s.
Read Also: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinson’s
Highlights From The Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System
Parkinsonism, including Parkinsons disease, can have significant impacts for those affected, their caregivers, and society. With a growing and aging population, it is estimated that the number of Canadians living with parkinsonism will double between 2011 and 2031 and that the incidence will increase by 50%.Footnote 1
The Public Health Agency of Canada , in collaboration with all Canadian provinces and territories, conducts national surveillance of parkinsonism to support the planning and evaluation of related policies, programs, and services. This fact sheet presents an overview of the data on diagnosed parkinsonism, including Parkinsons disease, from the Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System .
What Makes Pd Hard To Predict
Parkinsonâs comes with two main buckets of possible symptoms. One affects your ability to move and leads to motor issues like tremors and rigid muscles. The other bucket has non-motor symptoms, like pain, loss of smell, and dementia.
You may not get all the symptoms. And you canât predict how bad theyâll be, or how fast theyâll get worse. One person may have slight tremors but severe dementia. Another might have major tremors but no issues with thinking or memory. And someone else may have severe symptoms all around.
On top of that, the drugs that treat Parkinsonâs work better for some people than others. All that adds up to a disease thatâs very hard to predict.
You May Like: How Does General Anesthesia Affect Parkinson’s
What You Can Expect
Parkinson does follow a broad pattern. While it moves at different paces for different people, changes tend to come on slowly. Symptoms usually get worse over time, and new ones probably will pop up along the way.
Parkinsonâs doesnât always affect how long you live. But it can change your quality of life in a major way. After about 10 years, most people will have at least one major issue, like dementia or a physical disability.
Parkinsons Disease In African Americans: A Review Of The Current Literature
Article type: Review Article
Authors: Bailey, Meagan * | Anderson, Sharlet | Hall, Deborah A.
Affiliations: Rush University Medical Center Department of Neurological Sciences, Chicago, IL, USA
Correspondence: Correspondence to: Meagan Bailey, MD, MS, Department of Neurological Sciences, Rush University Medical Center, 1725 West Harrison, Suite 755, Chicago, IL 60612, USA. Tel.: +1 312 563 2900 Fax: +1 312 563 2024 E-mail: .
Keywords: Parkinsons disease, African Americans, healthcare disparities, epidemiology
DOI: 10.3233/JPD-191823
Journal: Journal of Parkinson’s Disease, vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 831-841, 2020
Abstract
Table 1
Research in African Americans with Parkinsons disease
You May Like: Is Parkinson’s Disease Hereditary
Studies Of Prevalence And Incidence
In a study conducted in Washington Heights in northern Manhattan, information was obtained from a community registry of PD diagnosis originating from multiple sources including clinical settings, health agencies, and senior centers . Information was collected over a four-year period in order to determine prevalence and incidence. All patients who were identified through these sources were contacted and underwent a physical examination to confirm the diagnosis. These investigators reported a lower prevalence in African Americans compared to whites. But, the incidence rates were highest in African American men. The combination of high incidence with low prevalence could have indicated shorter survival times in African Americans diagnosed with PD. However, incidence in this study was calculated with census data, which may underestimate minority populations, so the number may have been inflated . Group differences in co-morbidities between groups were also reviewed in this study, but they did appear to be related to differences in PD prevalence.
Table 3
| 67.54 | 24.35, 187.34 |
How Were These Figures Calculated
We analysed anonymous medical records of over 2.5 million individuals over the age of 20 registered with GPs in the UK from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink database.
Clinical experts helped us assess the records to work out how many patients had a definite diagnosis of Parkinsons and then we adjusted the numbers to make sure they matched the UK population in terms of age profile and gender.
Finally, we used projected population figures from the Office of National Statistics, to estimate how many people have Parkinsons in 2018 and how many will go on to be diagnosed in 2025 and beyond.
The UK population is growing and people are living longer, which means that the number of people of people living with Parkinsons is expected to rise.
For more information, you can
Don’t Miss: Boxing And Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Management Options For Canadians Living With Parkinsonism
There is currently no cure for Parkinsons disease and most other parkinsonism cases. However, treatment options are available to help mitigate the symptoms and health impacts associated with these conditions. Most often the primary treatment is pharmacological, but it may also include other therapeutic options and, in the case of Parkinsons disease, surgical interventions. Studies have shown that specially tailored exercise programs, supervised by physiotherapists or other trained professionals, may help affected individuals maintain or improve their physical functionality and general well-being.Footnote 2 Footnote 3 Footnote 4 Footnote 5
Box 1: What’s in the data?
The data used in this publication are from the Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System , a collaborative network of provincial and territorial chronic disease surveillance systems, led by the Public Health Agency of Canada . The CCDSS identifies chronic disease cases from provincial and territorial administrative health databases, including physician billing claims and hospital discharge abstract records, linked to provincial and territorial health insurance registry records using a unique personal identifier. Data on all residents eligible for provincial or territorial health insurance are captured in the health insurance registries.
Definition of diagnosed parkinsonism, including Parkinsons disease, in the CCDSS
Mortality From Parkinsons Disease
With treatment, the life expectancy of people with PD is similar to that of the general population. However, dementia seems to largely impact life expectancy among people with PD, and about 50 percent to 80 percent of people with PD develop dementia in their lifetime. Risk factors for mortality include later age of onset, male sex, severity of motor impairment, presence of psychotic symptoms, and dementia. Early detection of disease, prevention of motor symptom progression, and treatment of dementia can increase life expectancy.8,9
Engage with the community by asking a question, telling your story, or participating in a forum.
Also Check: Is Thumb Twitching A Sign Of Parkinson’s
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Treated
If a doctor thinks a person has Parkinson’s disease, there’s reason for hope. Medicine can be used to eliminate or improve the symptoms, like the body tremors. And some experts think that a cure may be found soon.
For now, a medicine called levodopa is often given to people who have Parkinson’s disease. Called “L-dopa,” this medicine increases the amount of dopamine in the body and has been shown to improve a person’s ability to walk and move around. Other drugs also help decrease and manage the symptoms by affecting dopamine levels. In some cases, surgery may be needed to treat it. The person would get anesthesia, a special kind of medicine to prevent pain during the operation.