Cognitive Symptoms Of Lewy Body Dementia
LBD causes changes in thinking abilities. These changes may include:
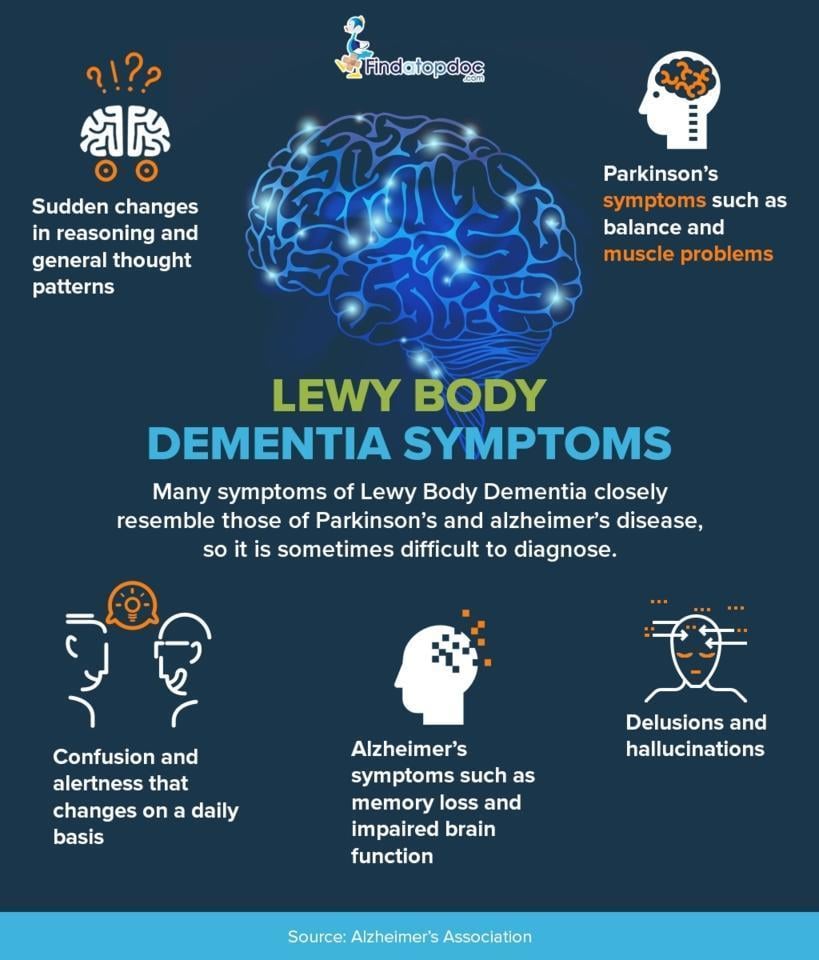
- Visual hallucinations, or seeing things that are not present. Visual hallucinations occur in up to 80 percent of people with LBD, often early on. Nonvisual hallucinations, such as hearing or smelling things that are not present, are less common than visual ones but may also occur.
- Unpredictable changes in concentration, attention, alertness, and wakefulness from day to day and sometimes throughout the day. Ideas may be disorganized, unclear, or illogical. These kinds of changes are common in LBD and may help distinguish it from Alzheimer’s disease.
- Severe loss of thinking abilities that interfere with daily activities. Unlike in Alzheimer’s dementia, memory problems may not be evident at first but often arise as LBD progresses. Other changes related to thinking may include poor judgment, confusion about time and place, and difficulty with language and numbers.
Pd Dementia And Safety Concerns
Safety issues should be considered and monitored from the time of diagnosis. As PDD progresses, ensure that your loved one is not left alone and try to:
- Evaluate driving privileges before safety is a concern. Your doctor can make a driving evaluation referral.
- Work out legal and financial issues and safeguard finances. People with dementia are at greater risk of falling victim to scams and fraud.
- Minimize prescription risks. Confirm with the doctor the medication names and doses of the person with PD. If the person is in dementias early stages and capable, fill up their weekly pill box together and monitor use.
- Look into medical alert systems. These systems can be critical in the event of a fall or if your loved one wanders outside of the home. Many types of systems are available, from bracelets and pendants to smartwatches with fall detection and one-button connections to 911.
- Evaluate gun safety. If your loved one owns a firearm or has one in the home, consider bringing it up with their doctor and taking additional safety precautions.
Whats The Difference Between Drug
Parkinsons is a progressive disorder, which will become worse over time, while DIP does not. In DIP, Parkinson-like symptoms can begin within four days to one month of starting the medication. However, all the symptoms could completely subside once the effecting medication is stopped, though it may take up to 18 months for all the symptoms to subside.
For more information on drug-induced parkinsonism, read this journal article and/or information sheet.
Don’t Miss: Central Coast Parkinson’s Association
Tips For Communicating With A Person With Pdd
PD-related mood and motor changes can impact communication cognitive changes and Parkinsons disease dementia can further these difficulties.
- Stay calm and be patient. It is not usually helpful to try to reason or argue with someone experiencing a hallucination or delusion. If the person is frightened by the hallucination or delusion, try to redirect their attention to something else.
- Acknowledging what the person is seeing, even if you do not see it, can reduce stress.
- Speak slowly and at eye level. Communicate in simple sentences.
- Ask one question at a time and wait for an answer.
- Limit distractions. Turn off the TV or radio before asking a person with PDD to do something.
- Consider causes behind disruptive behavior. Can your loved one be hungry, thirsty, tired, in pain, frustrated, lonely or bored?
- If the person is stuck on an idea, try agreeing with them, then changing the subject.
- Its okay to use humor to diffuse stressful situations but avoid negative humor or sarcasm these can be misunderstood.
Page reviewed by Dr. Chauncey Spears, Clinical Assistant Professor and Dr. Sydney M. Spagna, Clinical Fellow at the University of Michigan.
Surgical Intervention For Patients With Lewy Body Dementia
Surgical interventions are a common area of concern for patients and caregivers. Dementia in and of itself, and a diagnosis of LBD in particular, does not preclude necessary surgical interventions. This can become more of a gray area when optional procedures such as knee or hip replacements are considered. Clearly, arthritic joints can severely limit QOL but there is a balance when considering potential repercussions from anesthesia and the rehabilitation potential with a pre-existing cognitive and functional impairment. The relationship between general anesthesia and LBD specifically has not been robustly examined. Patients with LBD may respond poorly to certain anesthetics and experience postoperative delirium and/or functional decline . Patients with Parkinsons disease need careful oversight of their drug dosing regimen so it is impacted as little as possible pre- and postoperatively . A discussion with both the surgeon and anesthesiologist prior to surgery about the LBD diagnosis is prudent.
Read Also: Can Parkinson’s Patients Drive
Treating Movement Symptoms In Lewy Body Dementia
LBD-related movement symptoms may be treated with medications used for Parkinson’s disease, called carbidopa-levodopa. These drugs can help make it easier to walk, get out of bed, and move around. However, they cannot stop or reverse the disease itself. Side effects of this medication can include hallucinations and other psychiatric or behavioral problems. Because of this risk, physicians may recommend not treating mild movement symptoms with medication. Other Parkinson’s medications are less commonly used in people with LBD due to a higher frequency of side effects.
People with LBD may benefit from physical therapy and exercise. Talk with your doctor about what physical activities are best.
Movement Problems And Lewy Body Dementia
Some people with LBD may not experience significant movement problems for several years. Others may have them early on. At first, movement symptoms, such as a change in handwriting, may be very mild and easily overlooked. Movement problems may include:
- Muscle rigidity or stiffness
Also Check: List Of Parkinson’s Medications
Managing Sleep Disorders In Lewy Body Dementia
Sleep problems may increase confusion and behavioral problems in people with LBD and add to a caregiver’s burden. A physician can order a sleep study to identify any underlying sleep disorders such as sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, and REM sleep behavior disorder.
REM sleep behavior disorder, a common LBD symptom, involves acting out one’s dreams, leading to lost sleep and even injuries to individuals and their sleep partners. Clonazepam, a drug used to control seizures and relieve panic attacks, is often effective for the disorder at very low dosages. However, it can have side effects such as dizziness, unsteadiness, and problems with thinking. Melatonin, a naturally occurring hormone used to treat insomnia, may also offer some benefit when taken alone or with clonazepam.
Excessive daytime sleepiness is also common in LBD. If it is severe, a sleep specialist may prescribe a stimulant to help the person stay awake during the day.
Some people with LBD have difficulty falling asleep. If trouble sleeping at night persists, a physician may recommend a prescription medication. It is important to note that treating insomnia and other sleep problems in people with LBD has not been extensively studied, and that treatments may worsen daytime sleepiness and should be used with caution. Sleep problems can also be addressed by avoiding lengthy naps, increasing daytime exercise, and avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and chocolate late in the day.
Clinical Manifestations And Diagnostic Criteria
Clinically, DLB is marked by four core symptoms: fluctuating cognition, parkinsonism, visual hallucinations, RBD, and cognitive impairment across multiple domains with moderate memory impairment . DLB is a heterogenous disease. Cluster analysis yielded 3 different groups: cognitive-predominant , neuropsychotic-dominant , and parkinson-predominant . DLB patients with mild cognitive impairment perform worse on visuospatial function and letter fluency tests and better on episodic memory tests than AD-MCI . Cognitive impairment in PD patients being more common in the akinetic/rigid phenotype than in tremor-dominant and mixed phenotypes is similar in quality to what is observed in DLB , but the rate of cognitive decline is faster in DLB than in PDD and AD , and shows more severely impaired frontal and temporal area-associated cognitive profiles . The clinical overlaps and dissimilarities between DLB and PDD have been summarized recently .
Table 1: Clinical overlap and dissimilarities between dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson disease with dementia .View Table 1
You May Like: Any New Treatments For Parkinson’s
Whats The Difference Between Vascular Parkinsonism And Parkinsons
As the name implies, vascular parkinsonism is caused by cerebrovascular disease which affects the blood supply to the brain. Vascular parkinsonism is caused by one or more small strokes, while Parkinsons is caused by a gradual loss of nerve cells. One major difference from Parkinsons is that its not progressive, while Parkinsons becomes worse with time. Another difference is that there are no tremors in vascular parkinsonism.
For more information on vascular parkinsonism, read this journal article.
What Is The Treatment For Dementia With Lewy Bodies
There is no cure or treatment that stops or slows dementia with Lewy bodies. Treatment is aimed at relieving symptoms and delaying loss of mental abilities for as long as possible.
An individual with dementia with Lewy bodies should always be under medical care. Much of the day-to-day care, however, is handled by family caregivers. Medical care should focus on optimizing the individualâs health, safety, and quality of life while helping family members cope with the many challenges of caring for a loved one with dementia with Lewy bodies.
Also Check: Does Parkinson’s Make You Forgetful
Coping With Cognitive Changes
Some medications used to treat Alzheimer’s disease also may be used to treat the cognitive symptoms of LBD. These drugs, called cholinesterase inhibitors, act on a chemical in the brain that is important for memory and thinking. They may also improve hallucinations, apathy, and delusions. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved one Alzheimer’s drug, rivastigmine, to treat cognitive symptoms in Parkinson’s disease dementia. Several other drugs are being tested as possible treatments for LBD symptoms or to disrupt the underlying disease process.
Clinical History And Testing

Diagnostic tests can be used to establish some features of the condition and distinguish them from symptoms of other conditions. Diagnosis may include taking the person’s medical history, a physical exam, assessment of neurological function, brain imaging, neuropsychological testing to assess cognitive function,sleep studies, myocardial scintigraphy, or laboratory testing to rule out conditions that may cause symptoms similar to dementia, such as abnormal thyroid function, syphilis, HIV, and vitamin deficiencies.
If DLB is suspected when parkinsonism and dementia are the only presenting features, PET or SPECT imaging may show reduced dopamine transporter activity. A DLB diagnosis may be warranted if other conditions with reduced dopamine transporter uptake can be ruled out.
Since 2001, 123iodine–metaiodobenzylguanidinemyocardialscintigraphy has been used diagnostically in East Asia , but not in the US studies validating its use in differential diagnoses are lacking as of 2022. MIBG is taken up by sympathetic nerve endings, such as those that innervate the heart, and is labeled for scintigraphy with radioactive 123iodine. Autonomic dysfunction resulting from damage to nerves in the heart in patients with DLB is associated with lower cardiac uptake of 123I-MIBG.
Don’t Miss: Can A Blood Test Detect Parkinson’s
How Can We Manage Hallucinations
It may not be necessary to treat all hallucinations of a person with DLB. Hallucinations are often harmless, and it is okay to allow them to happen, as long as they are not disruptive or upsetting to the person or his/her surroundings. Sometimes, recognizing the hallucination and then switching the topic might be an efficient way of handling frustrations that occur because of a hallucination. If hallucinations need medical treatment, your provider may be able to discuss and suggest some options. However, most medications used to treat hallucinations may make movement symptoms worse.
Is Dementia A Symptom Of Both
One of the biggest similarities between PD and LBD is dementia. Some studies have found that approximately 78 percent of PD patients will eventually develop dementia. More specifically, almost half of Parkinsons patients will develop a certain type of dementia called Parkinsons Dementia, usually 10-15 years after their initial PD diagnosis.3,4
People with Parkinsons Dementia commonly experience poor memory and concentration, slowed thinking, confusion, depression, emotional changes, delusions, and visual hallucinations.
Parkinsons dementia is different than LBD, mainly in which symptoms occur first . Patients with Parkinsons Dementia will first show Parkinsons motor symptoms, followed by dementia many years after diagnosis. Conversely, LBD patients will first show dementia symptoms and may show motor symptoms later.3
Read Also: What Age Does Parkinson’s Disease Affect
Dementia With Lewy Bodies : What Is It And What Causes It Dementia With Lewy Bodies : What Is It And What Causes It
Dementia with Lewy bodies is a type of dementia caused by Lewy bodies, which are clumps of protein in the cells of the brain. Read more about what DLB is, and who gets the condition.
Dementia with Lewy bodies Dementia with Lewy bodies .
Dementia With Lewy Bodies And Parkinson Disease Dementia
, MD, PhD, Department of Neurology, University of Mississippi Medical Center
Dementia with Lewy bodiesParkinson disease dementia
Dementia is chronic, global, usually irreversible deterioration of cognition.
Dementia with Lewy bodies is the 3rd most common dementia. Age of onset is typically > 60.
Lewy bodies are spherical, eosinophilic, neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions composed of aggregates of alpha-synuclein, a synaptic protein. They occur in the cortex of some patients who have dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurotransmitter levels and neuronal pathways between the striatum and the neocortex are abnormal.
Lewy bodies also occur in the substantia nigra of patients with Parkinson disease Parkinson Disease Parkinson disease is a slowly progressive, degenerative disorder characterized by resting tremor, stiffness , slow and decreased movement , and eventually gait and/or… read more , and dementia may develop late in the disease. About 40% of patients with Parkinson disease develop Parkinson disease dementia, usually after age 70 and about 10 to 15 years after Parkinson disease has been diagnosed.
Both dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson disease dementia have a progressive course with a poor prognosis.
Also Check: Medical Marijuanas And Parkinson’s
What Are The Symptoms Of These Diseases
The main symptoms of Parkinson’s disease involve motor control, such as tremor , slowness of movement, stiffness of the limbs and trunk as well as postural instability. Many patients develop a decline in thinking and reasoning known as Parkinsons disease dementia if it occurs more than one year after the initial diagnosis of Parkinsons disease. Common symptoms for PDD include decline in memory, concentration and judgment, visual hallucinations, depression, irritability, and anxiety.
The central feature of Lewy body dementia is progressive cognitive decline, combined with pronounced fluctuations in alertness and attention, complex visual hallucinations, and motor symptoms such as rigidity and the loss of spontaneous movement. It can easily be mistaken for Alzheimers disease or for Parkinsons disease dementia .
Pathophysiology Of Cognitive Impairment
The neurobiological basis for cognitive impairment in DLB and PDD is multifocal, related to a synergistic effect of both Syn/LB and AD pathologies and dysfunction of dopaminergic, noradrenalinergic, serotonergic, and cholinergic systems . The emergence of PDD and DLB occurs on the background of severe dopamine deficits and correlates with a marked loss of limbic and cortically projecting dopamine, noradreanaline, serotonin, and ACh neurons. The relationship between these lesions is not yet fully understood.
Severe pathology also involves the noradrenergic locus ceruleus and the serotonergic dorsal raphe nucleus as well as the ventral tegmental area not always associated with coincidental AD lesions . LC neuronal loss and the accompanying norepinephrinergic deficiency are an important cause and pharmacological target for the treatment of PD/PDD/DLB . The prominent role of serotonergic degeneration also involving the anterior caudate nucleus, the orbitofrontal and cingulate cortex for neuropsychiatric symptoms in PD , emphasizes its important role in both PDD and DLB, and stimulates new insight into novel treatments by modulating 5-HT receptors .
Read Also: Meds For Parkinson’s Psychosis
What Is Parkinsons Disease
PD is a chronic, neurodegenerative movement disorder. PD affects 1 out of every 100 individuals over the age of 60, and patients commonly experience muscle rigidity, changes in speech and walking, and tremors.1
Some studies suggest that having PD also increases your risk of developing LBD, but most patients have only one of these conditions.2
Caring For A Person With Lewy Body Dementia

On this page:
As someone caring for a person with Lewy body dementia , you will take on many different responsibilities over time. You do not have to face these responsibilities alone. Many sources of help are available, from adult day centers and respite care to online and in-person support groups.
Below are some actions you can take to adjust to your new roles, be realistic about your situation, and care for yourself.
Read Also: Zofran And Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Symptoms Of Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Symptoms vary from person to person with dementia with Lewy bodies. The one characteristic common to everyone with dementia with Lewy bodies is progressive loss of mental abilities that interferes with everyday activities. This may include the following:
- Loss of recent memory
- Inability to concentrate or pay attention
- Difficulty thinking, reasoning, solving problems
- Misperceptions of space and time
Mental function usually varies in dementia with Lewy bodies, getting better and worse over time. Although the sharpness of our mental function varies in everyone – we all have our good moments and bad moments, or are “morning” persons or “evening” persons – this fluctuation is especially dramatic in dementia with Lewy bodies. This is especially true of alertness and attention.
A person with dementia with Lewy bodies typically has periods of being alert, coherent, and oriented that alternate with periods of being confused and less responsive. This usually is considered more characteristic of dementia with Lewy bodies than of other types of dementia. Other symptoms include the following:
- Abnormal movements of Parkinson’s disease
- Visual hallucinations