What Are The Symptoms
Symptoms of PD vary from person to person, as does the rate of progression. A person who has Parkinson’s may experience some of these more common “hallmark” symptoms:
- Bradykinesia – slowness of movement, impaired dexterity, decreased blinking, drooling, expressionless face.
- Tremor at rest – involuntary shaking that decreases with purposeful movement. Typically starts on one side of the body, usually the hand.
- Rigidity – stiffness caused by involuntary increase in muscle tone.
- Postural instability – sense of imbalance. Patients often compensate by lowering their center of gravity, which results in a stooped posture.
Other symptoms that may or may not occur:
Freezing or being stuck in place Shuffling gait or dragging of one foot Stooped posture Cognitive impairment
What Is The Prognosis
The average life expectancy of a person with PD is generally the same as for people who do not have the disease. Fortunately, there are many treatment options available for people with PD. However, in the late stages, PD may no longer respond to medications and can become associated with serious complications such as choking, pneumonia, and falls.
PD is a slowly progressive disorder. It is not possible to predict what course the disease will take for an individual person.
One commonly used scale neurologists use for describing how the symptoms of PD have progressed in a patient is the Hoehn and Yahr scale.
Who Develops Parkinson’s Disease
PD mainly develops in people over the age of 50. It becomes more common with increasing age. About 5 in 1,000 people in their 60s and about 40 in 1,000 people in their 80s have PD. It affects men and women but is a little more common in men. Rarely, it develops in people under the age of 50.
PD is not usually inherited and it can affect anyone. However, one type of PD, which appears in the small number of people who develop it before the age of 50, may be linked to inherited factors. Several family members may be affected.
Also Check: Similar To Parkinsons
Surgery For People With Parkinsons Disease
Deep brain stimulation surgery is an option to treat Parkinsons disease symptoms, but it is not suitable for everyone. There are strict criteria and guidelines on who can be a candidate for surgery, and this is something that only your doctor and you can decide. Surgery may be considered early or late in the progression of Parkinsons. When performing deep-brain stimulation surgery, the surgeon places an electrode in the part of the brain most effected by Parkinsons disease. Electrical impulses are introduced to the brain, which has the effect of normalising the brains electrical activity reducing the symptoms of Parkinsons disease. The electrical impulse is introduced using a pacemaker-like device called a stimulator. Thalamotomy and pallidotomy are operations where the surgeon makes an incision on part of the brain. These surgeries aim to alleviate some forms of tremor or unusual movement, but they are rarely performed now.
How Will The Disease Affect My Life
Most people who have Parkinsonâs live a normal to a nearly normal lifespan, but the disease can be life changing.
For some people, treatment keeps the symptoms at bay, and they’re mostly mild. For others, the disease is much more serious and really limits what you’re able to do.
As it gets worse, it makes it harder and harder to do daily activities like getting out of bed, driving, or going to work. Even writing can seem like a tough task. And in later stages, it can cause dementia.
Even though Parkinson’s can have a big impact on your life, with the right treatment and help from your health care team, you can still enjoy the things you love. It’s important to reach out to family and friends for support. Learning to live with Parkinson’s means making sure you get the backing you need.
Read Also: Cleveland Clinic Parkinson’s Bicycle Study 2017
So What Do We Know So Far
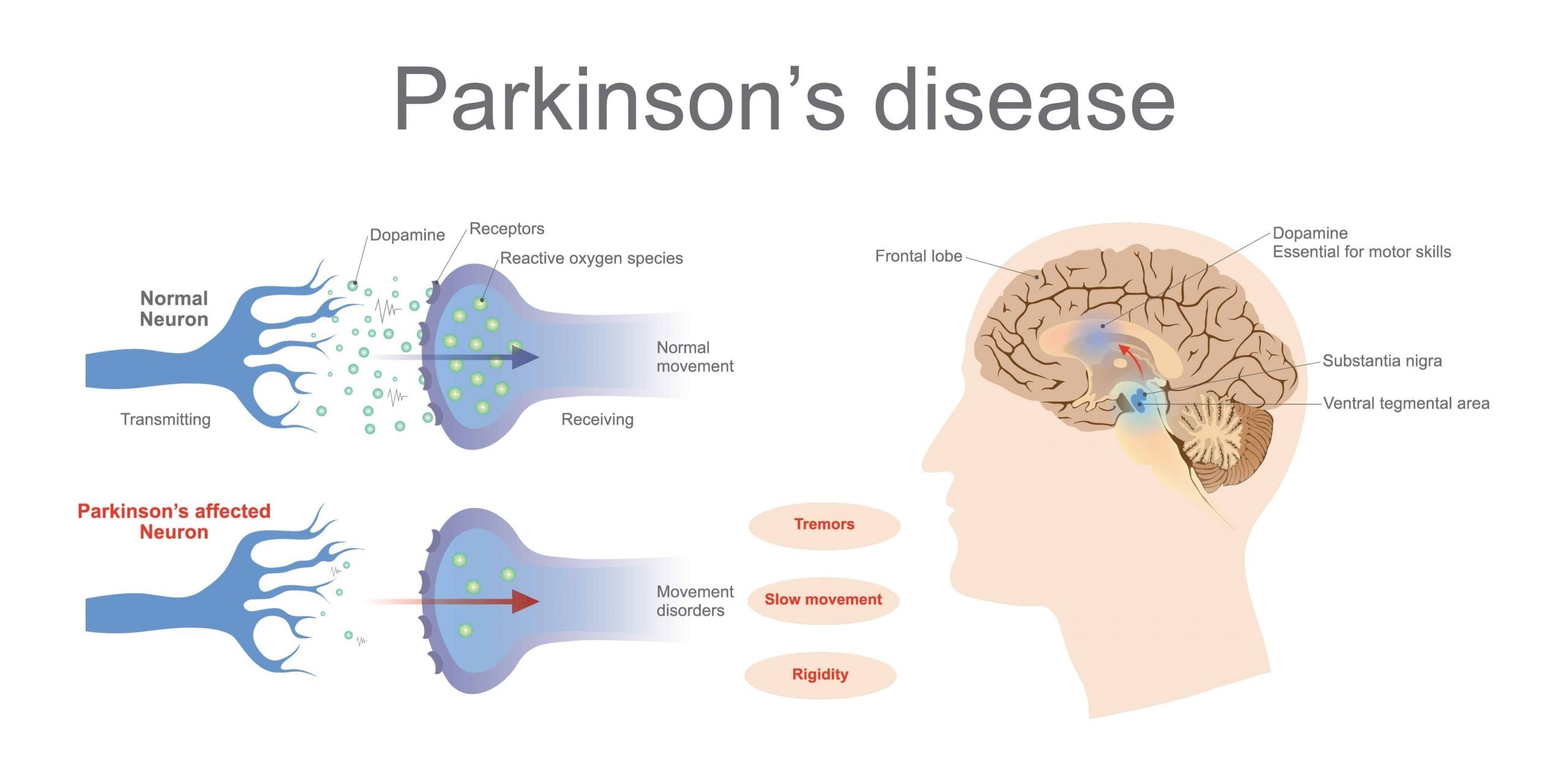
Location of the substantia nigra. FrozenManCC BY-SA 4.0
The substantia nigra is an area of the mid brain located at the top of the spinal cord, which has been the focus of much work into how Parkinsons affects the brain.
There are a right and a left substantia nigra, and often one side is affected before the other. Because of this, people with Parkinsons often experience symptoms primarily on one side of their body, particularly in the early stages. Indeed, this common feature of the condition often helps to distinguish Parkinsons from other similar conditions.
When it comes to confirming a diagnosis, it is the substantia nigra where pathologists look for changes at the end of life in brain tissue that has been donated to research. And the loss of the dopamine-producing cells in this area of the brain, accompanied by the presence of clumps of alpha-synuclein protein , has been the hallmark of Parkinsons for decades.
You can read more about the alpha-synuclein protein, and how it plays a role in the spread of Parkinsons, in a previous blog post:
Does Parkinson’s Disease Cause Dementia
The cells in the brain affected in PD are not in the ‘thinking’ parts of the brain and dementia is not a typical early feature of PD. However, if you have PD you have an increased risk of developing dementia. About half of people with PD develop dementia at some stage. If dementia occurs, it tends to develop in older people with PD . Early dementia in younger people with PD virtually never develops. It is thought that PD alone does not cause dementia however, other age-related factors in addition to PD may increase the risk of dementia developing.
You May Like: Sam Waterston Tremor
Beyond The Substantia Nigra
In Parkinsons, other areas of the brain beyond the substantia nigra are involved as the condition progresses. Changes in higher brain areas are linked to non-motor symptoms that can affect people with Parkinsons later on in the condition, and often have a significant impact on quality of life.
For instance, symptoms that affect memory and thinking can be linked to the presence of Lewy bodies in the largest area of the brain the cerebral cortex as well as the limbic system. The limbic system is also believed to be involved in symptoms involving mood and pain, and similar changes in the inferior temporal gyrus, an area of the brain involved in processing what we see, are thought to be the reason for hallucinations.
But research into the spread of Parkinsons through these areas, and how we can stop it , is just one side of the story. There is also ongoing research into where Parkinsons starts, and the effects it is having before it reaches these areas.
The presence of non-motor symptoms many months and maybe even years before the physical symptoms, such as tremor and slowness of movement, points towards the presence of other changes in the body long before the loss of dopamine-producing cells in the substantia nigra. These early symptoms could even help researchers predict those who will go on to be diagnosed with Parkinsons, which would help in the development of new and better treatments.
How Parkinsons Affects The Libido
Parkinsons disease and the sex drive is a complicated issue. is a common complaint in patients with Parkinsons disease. However, certain PD medications particularly dopamine agonists can actually cause an increased sex drive in men and women, known as hypersexuality or sex addiction.
If this happens, and it is out of character for you, it is important to tell your doctor. Other side-effects of PD medications include psychosis and other impulsive behavior such as pathological gambling or heavy drinking. If you experience any of these symptoms, your doctor will most likely change your medication and monitor your mental health.
Don’t Miss: Prayer For Parkinson’s Disease
Related Diagnosis: Lewy Body Dementia
Current research is helping to differentiate dementia related conditions in relationship to Parkinsonâs disease. Doctorâs use a 12-month arbitrary rule to aid in diagnosis. When dementia is present before or within 1 year of Parkinsonâs motor symptoms developing, an individual is diagnosed with DLB. Those who have an existing diagnosis of Parkinsonâs for more than a year, and later develop dementia, are diagnosed with PDD.
In the simplest terms, Lewy bodies are abnormal clumps of proteins that develop in nerve cells. Cholinesterase inhibitors, medications originally developed for Alzheimerâs disease, are the standard treatment today for cognitive DLB and PDD symptoms. Early diagnosis is important, as DLB patients may respond differently than Alzheimerâs disease patients to certain drug, behavioral, and dementia care treatments.
This challenging, multi-system disorder involving movement, cognition, behavior, sleep, and autonomic function requires a comprehensive treatment approach to maximize the quality of life for both the care recipient and their caregiver. It is very important to pay attention to symptoms of dementia and to search for an expert clinician who can diagnose the condition accurately.
Surgery And Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation is a treatment for Parkinsonâs disease that uses an implantable pacemaker-like device to deliver electrical pulses to parts of the brain involved in movement. The DBS system consists of leads precisely inserted into a specific brain target, the neurostimulator implanted in the chest, and extension wires that connect the leads to the neurostimulator. Though implantation of the system requires a neurosurgical procedure, the treatment itself consists of long-term electrical stimulation. Advantages of DBS include its ability to reduce the high doses of medications , its adjustability , and its reversibility DBS was approved by the Food and Drug Administration as a treatment for PD in 2002 and according to Medtronic , more than 80,000 patients have undergone DBS surgery worldwide.
Typical candidates are those who have motor fluctuations or periods of âoffâ time with troublesome symptoms alternating with periods of âonâ time with good symptom control, and also with possible periods of excessive movement .
Not all patients with Parkinsonâs disease are good candidates for treatment with DBS. Approximately 10â20% of patients considered for possible treatment with DBS include those:
Read Also: Parkinson’s Hallucinations Commercial
What Are The Complications Of Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease causes physical symptoms at first. Problems with cognitive function, including forgetfulness and trouble with concentration, may arise later. As the disease gets worse with time, many people develop dementia. This can cause profound memory loss and makes it hard to maintain relationships.
Parkinson disease dementia can cause problems with:
- Speaking and communicating with others
- Problem solving
- Forgetfulness
- Paying attention
If you have Parkinson disease and dementia, in time, you likely won’t be able to live by yourself. Dementia affects your ability to care of yourself, even if you can still physically do daily tasks.
Experts don’t understand how or why dementia often occurs with Parkinson disease. Its clear, though, that dementia and problems with cognitive function are linked to changes in the brain that cause problems with movement. As with Parkinson disease, dementia occurs when nerve cells degenerate, leading to chemical changes in the brain. Parkinson disease dementia may be treated with medicines also used to treat Alzheimer’s disease, another type of dementia.
What Can We Do
It would seem to me that there are a number of very vicious circles and negative feedback loops between neck stiffness/rigidity/pain and neck immobilization and posture in PD, which not only impact on each other, but also have neurological and physiological implications much more broadly, including on nervous system, blood pressure and breathing. The principal strategy for progressive symptom reduction would therefore be to increase and maintain mobilization of the neck and to improve posture as much as possible, through daily exercises and therapies, and to address any old injuries elsewhere on the body which may be impacting on posture and hence neck strain.
Dr Farias provides a suite of daily exercises which help to reduce these type of neck problems over time, especially designed for, and tailored to the different types of, cervical dystonia. Many people around the world report that doing his exercise classes daily reduces the symptoms and pain of their neck dystonia, and can eventually even lead to a full recovery. This works through a process of neuroplasticity, which re-wires the connections between the muscles and the brain through movement therapy.
Recommended Reading: Sam Waterston Parkinson’s
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinson’s disease has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Stiffness of the limbs and trunk
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination, sometimes leading to falls
Other symptoms may include depression and other emotional changes difficulty swallowing, chewing, and speaking urinary problems or constipation skin problems and sleep disruptions.
Symptoms of Parkinsons and the rate of progression differ among individuals. Sometimes people dismiss early symptoms of Parkinson’s as the effects of normal aging. In most cases, there are no medical tests to definitively detect the disease, so it can be difficult to diagnose accurately.
Early symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are subtle and occur gradually. For example, affected people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. They may notice that they speak too softly, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. Friends or family members may be the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinson’s. They may see that the person’s face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
People with Parkinson’s often develop a parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward, small quick steps as if hurrying forward, and reduced swinging of the arms. They also may have trouble initiating or continuing movement.
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
We do not know what causes Parkinsons disease. There is some evidence to suggest that there is a genetic factor which increases the risk of Parkinsons disease within some families. Also, there might be an increased risk if people have come into contact with a particular toxin or toxins found in the environment via pesticides and other chemicals used in agriculture. The specific toxin or toxins have not yet been identified but there is ongoing research into this possible cause.
Recommended Reading: What Foods Should Be Avoided When Taking Levodopa
Parkinsons Disease And Sex: What You Need To Know
There is no reason why you cannot continue to have a healthy sex life with Parkinson’s disease. However, studies suggest that around 70 to 80% of those with PD experience sexual dysfunction. These common sexual problems are believed to result from Parkinson’s medication side-effects and psychological issues.
Men and women experience different issues when it comes to Parkinsons disease and sex. In men, common problems include erectile dysfunction, lower sex drive, premature ejaculation and inability to orgasm. Women may experience pain during intercourse, as well as lack of sexual arousal, inability to orgasm and reduced lubrication.
In addition, the motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease can create physical challenges during sex. Many people with PD experience slowed movement and rigidity that makes any movement difficult. Tremors and involuntary movement can also occur during sexual activity.
What Diseases And Conditions Resemble Parkinsons Disease
PD is the most common form of parkinsonism, in which disorders of other causes produce features and symptoms that closely resemble Parkinsons disease. Many disorders can cause symptoms similar to those of PD, including:
Several diseases, including MSA, CBD, and PSP, are sometimes referred to as Parkinsons-plus diseases because they have the symptoms of PD plus additional features.
In very rare cases, parkinsonian symptoms may appear in people before the age of 20. This condition is called juvenile parkinsonism. It often begins with dystonia and bradykinesia, and the symptoms often improve with levodopa medication.
Read Also: Judy Woodruff Health Problems
Is Parkinson’s Diagnosed In The Brain
Parkinson’s disease is one of the most challenging neurological disorders to diagnose and treat. If your doctor suspects you have Parkinson’s disease, you will usually be referred to a neurologist for further tests. These tests will involve certain movements and exercises to check your symptoms.
A neurologist will look for motor symptoms such as:
- A tremor that occurs at rest
- Slowed movement
- Muscle stiffness
If you have two or more of these symptoms and your doctor has taken blood tests to rule out other causes, it’s likely you will be diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease. Your symptoms will be closely monitored to see any progression of Parkinson’s disease, which can take years.
Causes Of Parkinsons Disease
At present, we do not know the cause of Parkinsons disease. In most people there is no family history of Parkinsons Researchers worldwide are investigating possible causes, including:
- environmental triggers, pesticides, toxins, chemicals
- genetic factors
- combinations of environment and genetic factors
- head trauma.
You May Like: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinsons
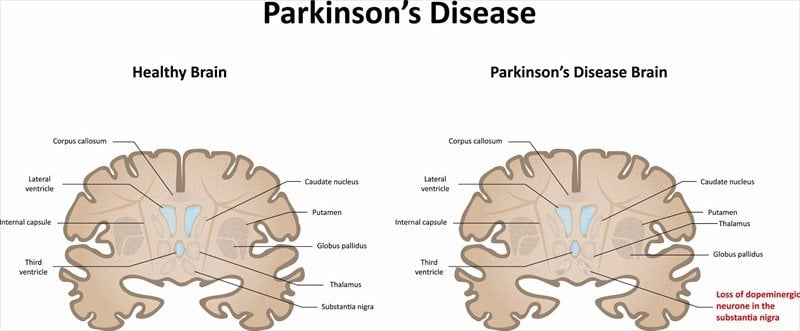
What Part Of The Brain Is Affected By Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease is predominantly a disorder of the basal ganglia, which are a group of nuclei situated at the base of the forebrain. The striatum, composed of the caudate and putamen, is the largest nuclear complex of the basal ganglia. The striatum receives excitatory input from several areas of the cerebral cortex, as well as inhibitory and excitatory input from the dopaminergic cells of the substantia nigra pars compacta . These cortical and nigral inputs are received by the spiny projection neurons, which are of 2 types: those that project directly to the internal segment of the globus pallidus , the major output site of the basal ganglia and those that project to the external segment of the globus pallidus , establishing an indirect pathway to the GPi via the subthalamic nucleus .
For an illustration of the subthalamic nucleus, see the image below.
References
Hauser RA, Grosset DG. FP-CIT SPECT Brain Imaging in Patients with Suspected Parkinsonian Syndromes. J Neuroimaging. 2011 Mar 16. .
Wirdefeldt K, Adami HO, Cole P, Trichopoulos D, Mandel J. Epidemiology and etiology of Parkinson’s disease: a review of the evidence. Eur J Epidemiol. 2011 Jun. 26 Suppl 1:S1-58. .
Anderson P. More Evidence Links Pesticides, Solvents, With Parkinson’s. Medscape Medical News. Available at . Accessed: June 11, 2013.
Grimes DA, Lang AE. Treatment of early Parkinsons disease. Can J Neurol Sci. 1999 Aug. 26 Suppl 2:S39-44. .