Search Strategy And Literature Sources
We conducted our systematic review according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Protocols Statement. We searched for research-based articles catalogued in PubMed, the Cochrane Library, Medline, Web of Science, Science Direct, Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health Literature Plus, ProQuest science journals, Scopus, and Wiley from database inception to December 12, 2016, without restriction on year, age, or language. The keywords âdepression,â âParkinson,â and âtreatment OR managementâ were combined with âANDâ to search within the title and abstract fields for each database. We also included relevant keyword derivatives, such as Parkinson’s, Parkinson’s disease, and PD. Bibliographies for all included articles were also searched.
Focus On Depression In Parkinsons Disease: A Delphi Consensus Of Experts In Psychiatry Neurology And Geriatrics
Luis Agüera-Ortiz
1Servicio de Psiquiatría, Instituto de Investigación i+12, Hospital Universitario 12 de Octubre, Madrid, Spain
2Centro de Investigacion Biomedica en Red de Salud Mental , Madrid, Spain
3Movement Disorders Unit, Servicio de Neurología, Hospital Clínico San Carlos, Complutense University, Madrid, Spain
4Movement Disorders Unit, Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón, Madrid, Spain
5Service of Psychiatry, University Hospital Ramón y Cajal. CIBERSAM, IRYCIS. University of Alcalá, Madrid, Spain
6Service of Neurology, HGU Gregorio Marañón, Madrid, Spain
7Memory Disorders Unit, HM Hospitales, Madrid, Spain
8Service of Psychiatry, Hospital Universitario San Jorge, Huesca, Spain
9Neurological Rehabilitation Unit, Clínica Ubarmin, Pamplona, Navarra, Spain
10Service of Neurology, Instituto de Neurociencias, Hospital Clínico San Carlos, San Carlos, IdISSC, Madrid, Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
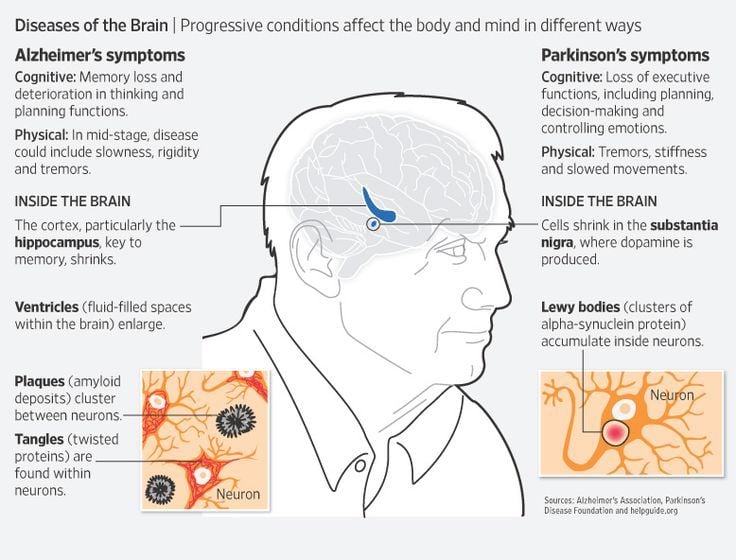
Neuropsychiatric disorders such as depression very often accompany core motor impairments of Parkinsons disease . More and more, they are perceived as significant contributors to PD morbidity and caregiver burden as they have a major impact on patients function, quality of life, and long-term outcomes. In fact, it has been suggested that PD should be classified as a neuropsychiatric disease itself rather than a movement disorder .
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Delphi Methodology
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
N
Medications That Increase The Levels Of Dopamine In The Brain
- Dopamine-like Medications – They are available under the brand names Duopa, Parcopa, Rytary, and Sinemet . Levodopa can effectively manage tremors as well as other motor symptoms at an early stage, but it can also cause serious side effects.
- Dopamine Agonists – They include Apokyn , Mirapex , Neupro , Parlodel , and Requip . These medications mimic the action of dopamine and can be taken either alone or with levodopa.
- MAO-B Inhibitors – MAO enzyme breaks down dopamine in the brain. Its action is inhibited by MAO-B inhibitors. With their action, the dopamine level in the brain remains intact for use. MAO-B inhibitors include Azilect and Eldepryl or Zelapar .
- COMT Inhibitors – Catechol-O-methyltransferase breaks down dopamine in the brain, and its action is inhibited by COMT inhibitors such as Comtan and Tasmar . These drugs inhibit the action of another enzyme that breaks down dopamine.
- Symmetrel – This drug may also increase the levels of dopamine in the brain.
Also Check: Weighted Silverware
Data Extraction And Analyses
The following data were extracted from the selected articles: authors, type of study, participant characteristics, intervention type, diagnostic criteria, primary and secondary outcomes measures, efficacy and safety of the intervention, and summary measures, including risk ratio and difference in means.
Find The Right Strain For You
Whether you want to relieve anxiety, pain or depression, the right strain is out there. Use our online tool to narrow the search.
They also noticed an improvement in non-motor symptoms such as pain, mood, and sleep.
Furthermore, in a similar study, patients noticed an improvement in symptoms just 30 minutes after taking cannabis.
Recommended Reading: Sam Waterston Parkinson’s
Meds Ease Depression In Parkinsons Patients Without Worsening Other Symptoms
- Meds Ease Depression in Parkinsons Patients Without Worsening Other Symptoms
Todays anti-depressant medications can ease depression in Parkinsons patients without worsening other symptoms of the disease, according to a study published online in Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
Depression is the number-one factor negatively affecting the quality of life for people with Parkinsons disease, said Irene Hegeman Richard, M.D., who led the study. It causes a great deal of suffering among patients. The great news here is that its treatable. And when the depression is treated adequately, many of the other symptoms become much more manageable for patients, added Richard, a neurologist at the University of Rochester Medical Center.
The findings are good news for patients with Parkinsons disease, a chronic neurologic disorder best known for causing slow movement, stiffness, balance problems and other motor difficulties. However, about half of Parkinsons patients also struggle with depression.
Its very important to note that these patients are not depressed simply because they are dealing with a chronic neurological condition, said Richard. Rather, the depression is caused by the underlying disease process, which also causes problems with movement and balance.
The Importance Of Diagnosing Depression
Treatment of depression in patients with PD may significantly slow cognitive decline, deterioration in Activities of Daily Living and progression to the more advanced of the Hoehn and Yahr stages. A longitudinal study by Starkstein and colleagues showed that patients with major depression and PD showed a significantly greater decline in ADLs over a 1-year period than patients with PD with minor depression only or no depression. Patients with major depression and PD had significantly longer durations of illness, but when patients were matched for duration and followed longitudinally, those with major depression worsened to a significantly greater extent. Cost-benefit analyses of antidepressant treatment in patients with PD are urgently needed.
You May Like: What Foods Should Be Avoided When Taking Levodopa
Difficulties In Diagnosing Depression In Patients With Parkinson’s
- Certain symptoms of depression overlap with symptoms of PD for example, sleep problems and feeling slowed down occur in both conditions.
- Some experts think that depression in PD often involves frequent, shorter changes in mood versus a constant state of sadness daily.
- Many people with PD express less emotion due to the effect the disease has on the muscles of the face. This symptom, called facial masking, makes a person unable to express emotion through facial expressions.
- Many people with Parkinsons do not seek treatment because they often do not recognize they have a mood problem or are unable to explain symptoms. For these reasons, it is helpful to ask a caregiver or loved one if he or she has noticed any changes commonly reported in depression.
Hospitalization Due To All Cardiovascular Events
The propensity score-adjusted model suggested that there was no significant difference between patients who used antidepressants and non-users in terms of developing cardiovascular events, specifically arrhythmia, heart failure, IHD, stroke, or cardiovascular death . Non-significant associations with all cardiovascular events were also reported among different antidepressant categories and individual drugs .
Recommended Reading: Cleveland Clinic Parkinson’s Bicycle Study 2017
Biomedical Perspective And Brain Imaging
One aspect of the biomedical model argues that depression may be a sequela of changed brain chemistry that is separate from the dopaminergic deficiency associated with PD motor symptoms . This premise is based on the observation that levels of cerebrospinal fluid 5-HIAA, a metabolite of serotonin , are reduced in depressed PD patients . Initially, critics of this hypothesis reported that even non-depressed PD patients showed metabolite reductions , suggesting that either CSF metabolites were inaccurate measures of changes in brain 5-HT or that depressed PD patients were not qualitatively different from non-depressed PD patients. More recent neuroimagining and neuropharmacological research has been used to better understand the biological etiology of PD depression.
Depression In Pd Versus Other Illnesses
Whether depression is found more frequently in PD relative to other non-neurological illnesses is unclear. If PD patients are at greater risk for developing depression, then the affective disturbances found in PD can be related to neurological disease as opposed to a psychosocial stress response in reaction to having a chronic and disabling illness. Several studies examined rates of depression between PD patients and other disabled clinical populations. Again, the collective evidence does not support either a biomedical or psychological interpretation. For instance, three separate studies found that PD patients were significantly more depressed than paraplegics, amputees, and patients suffering from various medical/surgical conditions . However, the comparison groups in these studies were not equivalent to the PD sample with respect to age and duration of illness.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Double Vision
Longtime Antidepressant Could Slow Parkinson’s
- Date:
- Michigan State University
- Summary:
- Scientists now have early proof that an antidepressant drug that’s been around for more than 50 years could slow the progression of Parkinson’s.
Michigan State University scientists now have early proof that an antidepressant drug that’s been around for more than 50 years could slow the progression of Parkinson’s.
In a proof-of-concept study, published in the journal Neurobiology of Disease, the drug nortriptyline, which has been used to treat depression and nerve pain, stopped the growth of abnormal proteins that can build up in the brain and lead to the development of the disease.
“Depression is a very frequent condition associated with Parkinson’s, so we became interested in whether an antidepressant could modify how the disease progresses,” said Tim Collier, lead author of the federally funded study and a neuroscientist at MSU.
Collier and collaborator Katrina Paumier, an assistant professor of molecular medicine, began looking at previous patient data to see if individuals who were on antidepressants experienced any delay in their need to go on a standard Parkinson’s therapy called levodopa. This type of therapy increases levels of dopamine, a natural chemical in the body that sends signals to other nerve cells and can significantly decrease in cases of Parkinson’s.
The medication also treats many of the symptoms associated with the disease such as tremors and poor muscle control.
Story Source:
The Diagnosis Of Depression In Pd
In most recent research studies, depression in PD has been diagnosed based on standardized criteria for major depression, such criteria from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders , fifth edition . The main problem of using these criteria is that some symptoms of depression, such as psychomotor retardation, insomnia, and loss of energy, are also frequently found in PD. A committee convened by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke raised the important question of whether DSM criteria for major depression, which were designed for individuals without PD, are valid in the context of a disease with a variety of motor and nonmotor manifestations. The committee recommended that depressed mood must be present and that evaluations should be done in the âonâ state for patients who experience fluctuations. Furthermore, to avoid âfalse-negatives,â the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke committee suggested using the âinclusive approachâ to diagnosis, which consist of rating the presence of all symptoms of depression, independent of whether they may be related to the motor disorder.
You May Like: Pfnca Wellness Programs
How Is Depression Treated In Patients With Parkinson Disease
Imaging, cerebrospinal fluid, and autopsy studies indicate that depression in Parkinson disease is associated with dysfunction of basal ganglia dopaminergic circuits that project to the frontal lobes, as well as noradrenergic limbic and brainstem structures. Whether serotonin dysfunction plays a role in depression in PD is unclear.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are the most commonly used medications to treat depression in Parkinson disease in clinical practice. However, several randomized controlled trials, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses have suggested that SSRIs may be no more effective than placebo in this situation.
Positive results in randomized clinical trials have been demonstrated for nortriptyline , desipramine , venlafaxine , citalopram , and paroxetine . For example, in Parkinson disease patients that were diagnosed with depressive disorder or operationally-defined subsyndromal depression, venlafaxine extended release or paroxetine significantly reduced scores on the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression compared to placebo. Both venlafaxine and paroxetine were well tolerated and did not worsen motor function.
There is a suggestion that noradrenergic or dual action antidepressants may be more effective for treating depression in Parkinson disease than SSRIs. However, whether this is an artifact of clinical-trials methodology is not yet clear, and more research is necessary.
References
Indica Vs Sativa For Parkinsons Disease
Cannabis sativa is one of several subspecies of cannabis. Sativa strains are usually recommended for daytime use because of their energizing properties, but they also have strong cerebral effects.
On the other hand, Cannabis indica usually produces sedative effects which makes it favorite among people with sleeping problems.
Indica strains are usually more potent than sativas, making people feel relaxed, sleepy and very hungry. Indica strains are usually recommended for nighttime use, due to higher concentrations of terpenes that cause the high to be felt more in the body than in the head.
But, when it comes to Parkinsons Disease, the first recommendation would be to use indica strains, because of their relaxing and painkilling properties, and since indica is most likely to help with sleep.
Related
Read Also: On Off Phenomenon
Treatment Of Other Symptoms
- Depression – Antidepressants such as tricyclics are used.
- Psychotic Side Effects – Clozapine and quetiapine are given to treat schizophrenia.
- Dementia – Donepezil and rivastigmine are in some cases used for Parkinsons disease.
- Daytime Sleepiness and Fatigue – Modafinil can be helpful when it comes to treating sleepiness related to Parkinsons disease.
- Erectile Dysfunction – Sildenafil, tadalafil, and vardenafil can be beneficial for men who are suffering from erectile dysfunction due to Parkinsons disease.
- Constipation – Laxatives can be helpful.
- Drooling – Scopolamine and injections of botulinum toxin into the parotid and submaxillary glands can also be used.
Etiology Of Depression In Pd
There have been several explanations for why depression occurs in PD. A psychological explanation suggests that depression is a reaction to the stress of coping with a chronic and progressively disabling disease. A biomedical perspective argues that depression is a primary neurochemical consequence of the neurodegenerative process of PD, attributing depression in PD to deficits in dopaminergic, noradrenergic, and/or serotonergic systems . Evidence from studies that have examined disease correlates of PD, prevalence rates, and brain abnormalities between depressed and non-depressed PD patients have supported both models and are described below.
Recommended Reading: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinson’s
Comparative Efficacy And Acceptability Of Antidepressants In Parkinson’s Disease: A Network Meta
- Jinling Liu ,
Contributed equally to this work with: Jinling Liu, Jiangchuan Dong
Affiliation Department of Neurology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
-
Contributed equally to this work with: Jinling Liu, Jiangchuan Dong
Affiliation Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
-
Affiliation Department of Neurology, Weifang People’s Hospital, Weifang, Shandong, China
-
* E-mail:
Affiliation Department of Neurology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
-
Affiliation Department of Neurology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
-
Affiliation Department of Neurology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Good News For Parkinsons Patients: Drugs May Ease Depression Without Worsening Motor Problems
The American Academy of Neurology is the world’s largest association of neurologists and neuroscience professionals, with 36,000 members. The AAN is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, concussion, Parkinson’s disease and epilepsy.
Don’t Miss: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinsons
Psychosocial Reactivity And Depression
Psychosocial variables, such as coping style and amount of social support, may predict depression more reliably than severity, illness duration, and functional disability . For instance, examined the influence of psychosocial variables in predicting depression in PD patients. Overall, the best predictors of depression were functional disability, low self-esteem, and avoidant coping. These variables accounted for 46% of the variance in depression. Furthermore, positive affect and cognitive coping significantly predicted lower depression. This study found that disease-related variables do not predict a large portion of the variance in the depression that is experienced in PD. The observed inconsistent findings suggest that the reactivity model is in need of revision and should also include psychosocial variables .
In summary, as evidence does not permit discrete choice between the biomedical or psychological position with respect to the etiology of PD depression, a more parsimonious perspective should include a combination of endogenous and exogenous factors . Therefore, we further examined the literature on treatment options for PD depression to understand its etiology towards improving quality of life for this neuropsychiatric population.
Mood Changes In Parkinson’s

When faced with a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease , it is understandable to feel depressed or anxious. But mood disorders such as depression and anxiety are clinical symptoms of Parkinson’s, just as are slowness of movement and tremor. In fact, up to half of all people with Parkinson’s may suffer from depression and/or anxiety at some point during the course of their disease. Like all symptoms of PD, mood changes are different for different people. Some people with depression feel sad and lose interest in things they used to enjoy, while others feel irritable and have difficulty sleeping. People with anxiety often feel overly worried or concerned, or say they are “on edge.”
The good news: Over the past decade, researchers have placed increasing focus on these aspects of PD, and today we have a better understanding of how to treat mood disorders in Parkinson’s.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Bike Therapy
Treating Depression In Parkinson’s Disease: Perspective
The study has ”critical information” for patients and caregivers, says Michael S. Okun, MD, national medical director of the National Parkinson Foundation. He reviewed the findings.
“The bottom-line message is that treatment for depression in Parkinson’s disease matters,” he says. “An important aspect of this particular study was that it had a placebo group, and that the investigators showed that either antidepressant performed better than placebo for Parkinson patients.”
An editorial that accompanies the study concludes that depression in Parkinson’s patients may be as treatable as it is in the general population.
Show Sources