Prognosis Of Als Vs Parkinsons
ALS is considered as a fatal disease. The damage and death of neurons begins to spread throughout the body. In the later stages, nerve damage will affect areas like breathing and swallowing.
Parkinsons disease in itself is not considered fatal but people do die from complications relating to the condition.
Postmortem Evaluation Of Parkin Solubility
Several lines of evidence suggest that the stability of parkin is fragile. Very minor fluctuations within the parkin sequence or the intracellular environment where parkin is expressed can have profound effects on the solubility and activity of the protein. However, many of the studies reviewed here have made exclusive use of cell culture conditions to explore the stability and solubility of parkin, raising the question of whether parkin solubility is an issue within the normal or diseased human brain. Notably, three studies have explored postmortem human brain, and all three reports have found evidence of pathologic changes in parkin solubility in the neurologic disease samples. Two of these studies reported increased levels of insoluble parkin in PD brain tissue, compared to controls , whereas the third found that parkin was elevated in the insoluble fraction of brains taken from patients with diffuse Lewy body disease , indicating that parkin solubility is affected in human neurologic disease and providing the most tantalizing evidence for some link between parkin and -synuclein. Interestingly, the translocation of parkin from a soluble to insoluble state has also been reported in a rodent model of stroke , as well, and is therefore not limited to human neurodegenerative disorders.
Summary Ms Vs Parkinsons
Multiple Sclerosis is a chronic autoimmune, T-cell mediated inflammatory disease affecting the Central Nervous System. Parkinsons disease is a movement disorder characterized by a decline in the dopamine level of the brain. Multiple sclerosis, as stated in its definition, is an autoimmune disease but Parkinsons disease is not an autoimmune disease. This is the major difference between MS and Parkinsons.
Read Also: Can Essential Tremor Become Parkinson’s
Multiple Sclerosis Vs Parkinsons Disease: Us Prevalence And Economic Impact
Anyone can develop multiple sclerosis, but it mostly affects 20- to 40-year-olds. Prevalence of multiple sclerosis in the U.S. is estimated at over 400,000 cases, and nearly 200 new cases are diagnosed each week. Rates of multiple sclerosis are highest in areas furthest away from the equator, so the rates are higher in the Northern U.S.
Direct and indirect costs resulting from multiple sclerosis can range from $8,528 to $54,244.
One million Americans live with Parkinsons disease. The average cost of Parkinsons disease including treatment, lost work wages, and social security payments is $25 billion annually in the U.S.
Is There A Link

Some people have MS and Parkinsonâs, but it could be a coincidence.
Research suggests that the damage that MS causes to your brain can lead some people to develop Parkinsonâs later on.
If you have MS, your immune system triggers ongoing inflammation. This can create lesions in your brain that cause Parkinsonâs disease. If lesions form in certain spots in your brain, they can affect how it makes dopamine.
Read Also: Assisted Living For Parkinson’s Patients
Onset Of Als And Parkinsons
There are several different variants of ALS but it generally affects people between the age of 40 and 70. Juvenile onset ALS, however, can start in childhood or typically before the age of 25, although this form of ALS is particularly rare. The onset of ALS is estimated to be 20% more common in men compared with women and in 10% of cases there is likely to be a genetic component.
Parkinsons disease is usually diagnosed in people over the age of 60, though a small percentage exhibit the symptoms before the age of 50.
Once again, men are more likely to develop Parkinsons than women.
The Impact Of Disease
The clinical mutations in Parkin associated with disease span from genomic deletions to premature truncations and subtle missense mutations in the coding sequence. For this reason, it has been widely accepted that the pathogenicity of these PARK2 mutations derives from a critical loss-of-function. Despite the predicted loss of E3 ligase activity of these parkin mutants, biochemical evidence of parkin E3 ligase activity and the impact of parkin deficiency has been notoriously difficult to establish. Although numerous putative substrates have been reported, many have failed to withstand independent confirmation. The lack of well-founded substrates has also made it difficult to examine the degree to which each mutation alters activity, precluding an analysis of the correlation between the biochemical impact of a given parkin mutation and the severity of the resultant disease in patients. Nonetheless, there have been many valuable observations made regarding the novel PD-associated parkin variants.
You May Like: What Diseases Are Similar To Parkinson’s
Serotonergic Degeneration In Pd And Als
Staging of brain pathology in PD demonstrated an early involvement of Lewy body depositions within the RN. In more detail, Halliday et al. firstly described a 56% loss of serotonergic neurons in the median RN of PD compared to control brain. Afterwards, Braak et al. determined six stages in the evolution of PD-related pathology, with lesions being present in the median RN in the caudal brainstem already from stage two onwards. Furthermore, 5-HT depletion was observed in various target areas of the RN, such as in the basal ganglia, hypothalamus, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex . This was later confirmed by in vivo imaging studies, revealing new insights. For instance, Politis et al. applied 11C-DASB-PET to early-stage PD patients, and demonstrated reduced SERT binding in the caudate nucleus, thalamus, and anterior cingulate cortex, whereas PD subjects with established disease showed additional 11C-DASB binding reductions in the putamen, insula, posterior cingulate cortex, and, prefrontal cortex. Further binding reductions were noticed in the ventral striatum, RN, and amygdala of advanced PD patients. Interestingly, the loss of SERT binding in the RN occurred in later stages, pointing to an earlier loss of serotonergic projections instead of the neurons themselves.
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is caused by a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. A deficiency in the chemical dopamine can cause symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
In about 15% of cases, Parkinsons occurs in individuals with a family history of the disease, due to gene mutations and alterations that are passed down.
Age is a large risk factor for developing Parkinsons. People over the age of 60 have the highest risk of developing the disease.
Studies show that men are 1.5 times more likely to develop Parkinsons than women.
Other environmental risk factors that can lead to Parkinsons include:
- Head injury
- Exposure to pesticides and herbicides
- Exposure to toxins such as trichlorethylene and polychlorinated biphenyls
Recommended Reading: Best Food For Parkinson Patient
Key Difference Parkinsons Vs Huntingtons Disease
The key difference between Parkinsons and Huntingtons disease is that Parkinson disease is a disorder with rigidity, tremors, slowing of movements, postural instability and gait disturbances usually occurring in old age due to degeneration of the substantia nigra of the midbrain while Huntingtons disease is a familial neurodegenerative disorder usually occurring in a younger population, characterized by emotional problems, loss of thinking ability and abnormal choreiform movements .
Introduction: Neurologic Disorders Of Movement
More than two million Americans are believed to suffer from some form of neurodegenerative movement disorder, the total cost of which is estimated to exceed $10 billion annually. Because no society on earth is spared the effects of these crippling diseases, the figures for other countries are similar, adjusted for population differences. The neurodegenerative diseases Parkinsons disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are the most important of the movement disorders from a proteostasis perspective. ALS is often classified separately, as a motor neuron disease, but there are a number of reasons for considering them together, of which perhaps the most important is that the two sometimes present together, as in the Parkinsonism-dementia complex of Guam . This movement disorder occurs among the Chamorro populations of Guam and the Mariana Islands and is frequently accompanied by a motor neuron disease resembling ALS. The course of the disease is rapid, with death typically occurring within 5 years .
In the following sections, we will review the evidence that links dysfunction in the proteostasis of certain proteins to the pathology of ALS and PD. Recent data support the notion that at least most forms of Parkinsons disease may be amenable to therapeutic strategies aimed at proteostasis of -synuclein or proteins called parkin or LRRK2, while the situation with ALS is still far from clear.
You May Like: Dopamine Supplements For Parkinson’s
What Makes Them Different
MS and Parkinsonâs have different causes. They usually start to affect you at different ages, too.
MS often affects people between ages 20 and 50, but children get it, too. Parkinsonâs usually starts at age 60 or older, but some younger adults get it.
MS is an autoimmune disease. That means your bodyâs immune system goes haywire for some reason. It attacks and destroys myelin. As myelin breaks down, your nerves and nerve fibers get frayed.
In Parkinsonâs, certain brain cells start to die off. Your brain makes less and less of a chemical called dopamine that helps control your movement. As your levels dip, you lose more of this control.
Some genes may put you at risk for Parkinsonâs, especially as you age. Thereâs a small chance that people who are exposed to toxic chemicals like pesticides or weed killers can get it, too.
These symptoms are more common if you have MS. They not usually found in Parkinsonâs:
Changes In Levels Of Creatinine And C
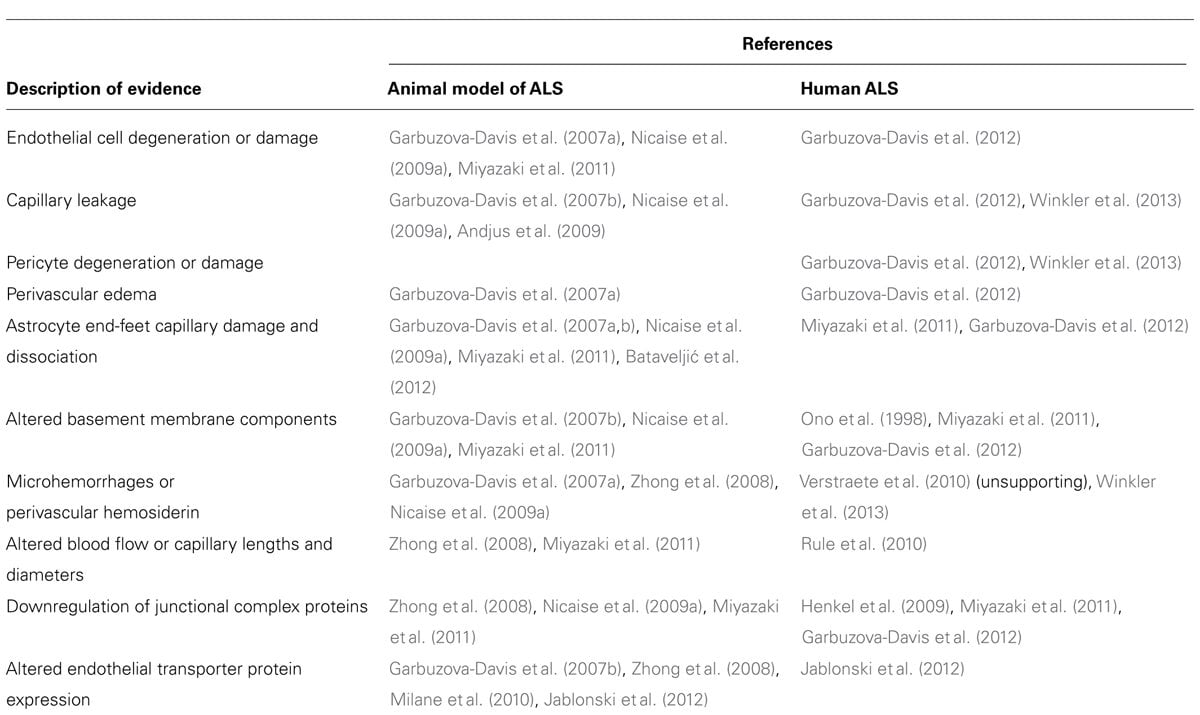
The patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis showed statistically significantly decreasing levels of creatinine from 1year before until 2years after diagnosis . Controls of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients had, on the other hand, increasing levels of creatinine during large part of these 4years, although the annual change was not always statistically significant. Patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis had increasing levels of C-reactive protein from diagnosis until 2years after diagnosis . Controls of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis demonstrated, however, no clear change of C-reactive protein during the 4years.
Temporal changes of creatinine levels from 2years before to 2years after diagnosis among patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and their matched controls
| Group . |
|---|
No clear change in either creatinine or C-reactive protein was noted among patients with Parkinsons disease or multiple sclerosis or their respective controls, apart from the increasing levels of creatinine and C-reactive protein from 1year before until 2years after the index date among controls of patients with Parkinsons disease .
Also Check: Parkinson’s Loss Of Balance
Possible Link To Alzheimers
Though Alzheimers, Huntingtons, and Parkinsons are distinctly different diseases, some evidence has emerged that shows a common link between the three.
All three diseases have proteins within the cells that do not assemble properly. Though the molecular and cellular changes that occur in each disease vary greatly, this protein degradation has been shown to precede early clinical signs in each disease. This is promising news, as more studies are being done to determine whether this can either predict or prevent these neurodegenerative diseases.
Posttranslational Modifications That Inactivate Parkin
The reports summarized above raise the intriguing possibility that idiopathic PD pathogenesis or disease risk may arise by processes whereby neuronal stress might inactivate parkin via insolubility and aggregation. As a biochemical phenocopy of PARK2-associated familial PD, a severe loss of active, soluble parkin could compromise the viability of nigral neurons in the sporadic disease.
The one problem with this model is that Lewy bodies have generally not been observed in PARK2-associated familial PD brains, whereas they are almost always present to some extent in postmortem analyses of sporadic PD patients. No biochemical or genetic evidence has yet conclusively tied parkin into -synuclein aggregation, raising the possibility that neither protein is the direct cause of any form of PD, but that each may act independently through either the same or different downstream initiators of cell death. Of course, the other possibility is that macroscopic -synuclein aggregates are not involved in pathogenesis, and that loss of parkin function causes disease by producing whatever the actual toxic -synuclein species is.
Recommended Reading: Emotional Symptoms Of Parkinson’s
Muscle Weakness In Arms And Legs
ALS always advances to cause muscle paralysis . The muscles eventually atrophy . Eventually, everyone who has ALS will need an assistive device, such as a walker, wheelchair, or scooter.
Many people with MS experience mild or moderate muscle weakness, but only rarely experience paralysis. MS can affect your walking, and you may need an assistive device to get around, but most people with MS have more independence than those with ALS.
Similarities Between Als And Parkinsons Disease
There are several similarities between these two diseases. Both affect neurons in the body and have a detrimental impact on the motor system, that is, how we move, speak, eat and breathe.
Individuals with ALS can often show Parkinson like symptoms, such as tremors, rigidity and slow movement. Beyond this, however, the ALS vs Parkinsons disease differences tend to be much starker than the similarities.
You May Like: Does Parkinson’s Get Worse
What Is The Life Expectancy For Ms Vs Als
In general, the prognosis for MS is much better than for ALS. People with MS may have a lifespan that is relatively normal, but is about six or seven years shorter than in those without the disease. Depending upon the response to treatment and the presence of complications, the prognosis for MS patients may range from good to poor. In contrast, the life expectancy of a person with ALS is only about 2 to 5 years after the time of diagnosis, although about 20% may live somewhat longer than five years. ALS progresses more rapidly than MS, and because nerve cells are the targets that become damaged, the prognosis is at best, fair to poor.
Treatment Of Als Vs Parkinsons Disease
There is currently no cure for ALS and much of the treatment is aimed at managing the symptoms and trying to slow down the progression of the disease. Ultimately the disease will be fatal and once bodily functions such as swallowing and breathing are affected, the prognosis is very poor.
Typically, around half of those diagnosed with ALS will die within the first three years following their diagnosis. Only 10% of those diagnosed will live beyond 10 years.
Treatment of Parkinsons disease has received a lot more attention with its higher profile in the media. As with ALS, there is currently no cure but there are a wide range of different medications and treatments that are available.
This includes brain stimulation therapy which sends an electrical stimulus to the brain from a device embedded by the collarbone to help alleviate symptoms such as tremors.
Don’t Miss: Link Between Sciatica And Parkinson’s
Training With Iqoro A Complement To Rehabilitation
IQoro is a new and unique neuromuscular treatment method that requires just 30 seconds exercise, three times per day. Exercising with IQoro can contribute to retaining and maintaining as much as possible of the normal functions for an extended period.
This is possible because IQoro activates the internal involuntary muscles in the same way that traditional physiotherapy strengthens arms and legs. Training with IQoro therefore it makes a positive difference in the ability to continue to eat via the mouth, chew, use facial expressions and to form sounds for an extended time.
IQoro is unique in being able to effectively activate the involuntary musculature from the face, oral cavity, pharynx, and the esophagus, down to the diaphragm.
The treatment is a good complement to physiotherapy as only a short exercise period is required one and a half minutes per day, and that the training has no negative side effects except for possible exercise stiffness in the early days. IQoro cannot, of course, treat the underlying disease.
Understanding The Differences Between Parkinsons And Lou Gehrigs Disease
By Angie Kunnath 7 pm on June 5, 2015
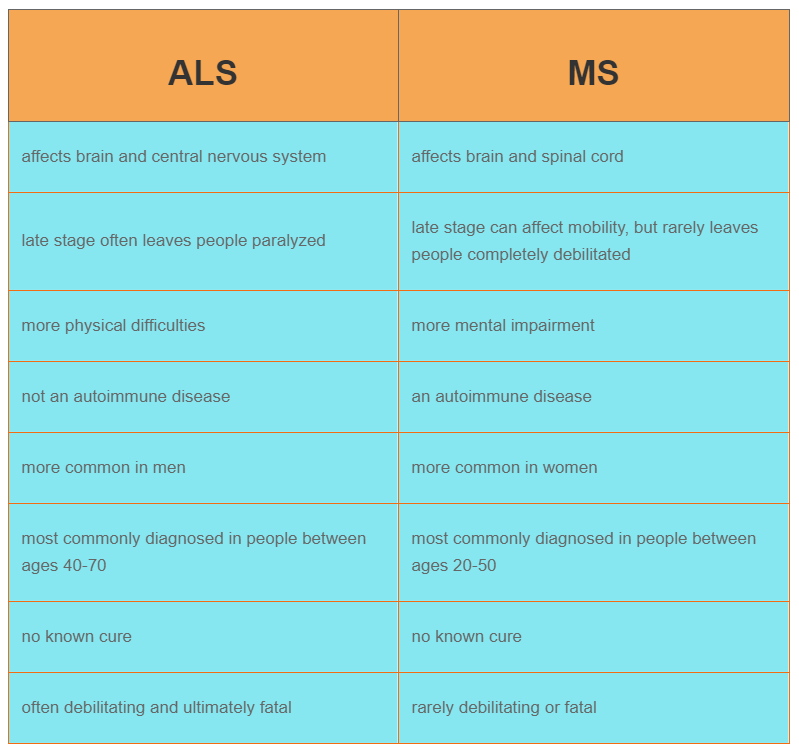
As Parkinsons disease and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis are both progressive neurodegenerative diseases, many people confuse the terms. Below, senior care experts at Home Care Assistance of Mississauga provide information on the basic differences between Parkinsons and ALS to help you better understand the two diseases.
Recommended Reading: Lifespan Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Difference In Parkinsons Disease And Als Diagnosis And Treatment
There is currently no specific test that can be performed to directly diagnose Parkinsons disease, but an array of different tests can help narrow down on a diagnosis. If Parkinsons disease is suspected, a patient will be referred to a neurologist and geriatrician. Diagnosis is commonly confirmed with the presence of at least two of the three most common symptoms: Shaking or tremor that occurs at rest, slowness of movement, and muscle stiffness. A doctor will also perform brain scans to diagnose Parkinsons disease and to check for other conditions that could be causing similar symptoms.
There is also no cure for Parkinsons disease, but treatments are available to manage the symptoms and slow down the disease progression. Alongside traditional treatments, supportive therapies are used to improve different aspects of a persons health.
Common medications prescribed in Parkinsons disease include dopamine replacement therapy, dopamine agonists, anticholinergics, amantadine, monomine oxidase type B inhibitors, and catechol-o-methyl transferase inhibitors.
Surgery is also a treatment option for Parkinsons disease and is best suited for those who had a good response to levodopa, but still have difficulties with movement or who experience large fluctuations in their levodopa levels.
Serotonergic Modulation Of Basal Ganglia And Mesencephalic Dopaminergic Activity In Pd
The basal ganglia are composed of the striatum , subthalamic nucleus , internal and external globus pallidus and SN, and are part of the BG-cortico-thalamic circuits. This highly organized network is important for motor control, emotion, and cognition. It has been firmly established that BG nuclei receive vast serotonergic input mainly coming from the rostral RN clusters , with effects on mesencephalic dopaminergic activity depending on the specific nucleus and its receptor distribution . In PD, lesioning of the RN in addition to DA depletion in the striatum and SNparticularly of the pars compacta are hallmarks of the disease, leading to overactivation of the output regions of the BG, i.e., GPi and SN pars reticulata , which contain large GABAergic neurons. This cascade results in a net decreased activity of the supplementary motor areas, premotor, and primary motor cortices, triggering parkinsonian symptoms . Overall, the loss of 5-HT neurons is not as profound as the loss of DA neurons, and may not be sufficient to cause motor or non-motor symptoms per se, however, both systems closely interact, and combined depletion certainly seems to aggravate the situation, as was shown in a parkinsonian rat model . Moreover, 5-HT and 5-HIAA levels, as well as SERT expression, are reduced in various BG nuclei , and the serotonergic system is strongly involved in the mechanism of action of antiparkinsonian therapeutics, such as levodopa , and high frequency stimulation of the STN .
Read Also: Asbestos And Parkinson’s Disease