Understanding The Basics Of A Parkinsons And How It Affects The Body
A physician looks for the presence or absence of the possible symptoms of Parkinsons disease by interviewing the patient and performing a detailed neurologic examination. While there is presently no definitive test for Parkinsons, it can often be identified by a general neurologist, who is trained to diagnose and treat neurologic disorders. The first signs of parkinsons are often not motor-related, and a physician can help you come to a diagnosis.
To avoid misdiagnosis, consultation with a movement disorder specialist is recommended. After training in general neurology, a movement disorder specialist is a physician who has undergone subspecialty training in the diagnosis and treatment of movement disorders such as Parkinsons.
Symptom History Of Parkinsons Disease
Diagnosis of PD is most often made when a doctor identifies the primary motor symptoms in a patient. Diagnostic criteria for PD called the Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale recommend that the physician assess for symptoms such as tremor, rigidity, balance impairments, freezing episodes , posture, changes in handwriting, difficulty swallowing, and reduced facial expression.3,4
In addition to these primary motor symptoms, the symptom history for diagnosing PD should include investigating the presence of non-motor symptoms of PD, such as constipation, a frequent and urgent need to urinate, sleep disturbances, pain, orthostatic hypotension , reduced sense of smell , sexual dysfunction, and fatigue. In addition, many people with PD experience mood disorders like depression or anxiety and cognitive changes, such as memory difficulties, slowed thinking, or confusion.4,5
Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography
In single photon emission computed tomography , a gamma ray-emitting radioactive isotope is tagged to a molecule of interest , which is given to the person with by intravenous injection. The labelled cocaine derivatives 123I–CIT and 123I-FP-CIT tropane) have most commonly been used, although only the latter is licensed in the UK. These label the presynaptic dopamine re- site and thus the presynaptic neurone, which can be visualised in two-dimensional images. These demonstrate normal uptake in the caudate and putamen in controls and in people with essential tremor, neuroleptic-induced parkinsonism or psychogenic parkinsonism, but reduced uptake in those with PD, PD with dementia, or .
How useful is SPECT in discriminating from alternative conditions?
Also Check: Social Security Disability Parkinson’s
What Is A Datscan And What Role Does It Play In A Parkinsons Diagnosis
In 2011, the FDA approved the use of a scan called a dopamine transporter scan . A DaTscan is an imaging technology that allows visualization of the dopamine system in the brain. It is similar to an MRI, but looks at the function of the brain rather than the structure.
A DaTscan involves injection of a small amount of a radioactive drug that is then measured by a single-photon emission computed tomography scanner . The SPECT scanner measures the levels and location of the drug in the brain.
It is important to know that a negative DaTscan does not rule out PD, especially early in the disease, but a positive DaTscan can help confirm it. A positive DaTscan can differentiate PD from essential tremor as there is no dopamine deficiency in the latter. However, DaTscan abnormalities can be seen in PD as well as other forms of atypical parkinsonism that cause a loss of dopamine . This means that a positive result does not differentiate Parkinsons disease from other forms of atypical parkinsonism.
How Does The Test Work
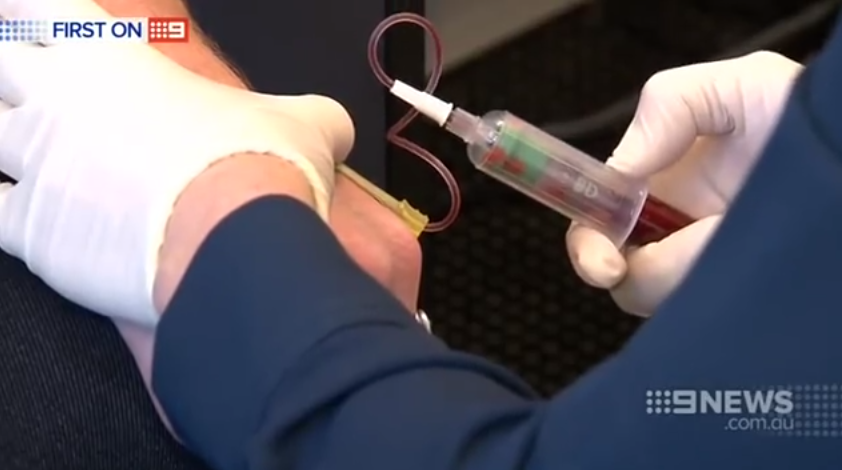
The test works by taking swabs from a patients back which collect samples of an oily secretion known as sebum which originates in the sebaceous glands under the skin.
Participants who took part in the study had their samples taken from their upper backs and tested by scientists using a spectrometer from these swabs it took just three minutes for Parkinsons to be diagnosed.
Lead author on the study Professor Monty Silverdale said: This test has the potential to massively improve the diagnosis and management of people with Parkinsons disease.
On the results of the swabs in question, Dr Depanjan Sarkar said: When we do this, we find more than 4,000 unique compounds of which 5,000 are different between people with Parkinsons compared to the control participants.
You May Like: Living With Parkinson’s Documentary
Mri In Parkinson’s Testing
One of the more common tests done during a neurologic workup is an MRI scan and one may think that in the investigation of a disease that affects the brain such as Parkinsons, this imaging test would be a necessity. In the context of Parkinsons disease, however, an MRI is not particularly helpful. It looks at the structure of the brain which, for all intents and purposes, appears normal in this disease. An MRI may, however, be indicated when symptoms appear in younger people or if the clinical picture or the progression of symptoms is not typical for Parkinsons. In these situations, MRI can be used to rule out other disorders such as stroke, tumors, hydrocephalus , and Wilsons Disease .
What Is The Prognosis For Parkinsons Disease
The rate at which Parkinsons progresses varies from patient to patient. Some patients experience its changes over 20 years or more. While others find the disease advances quicker.
Parkinsons is not a fatal disease. However, secondary complications from symptoms may increase falls, blood clots or pneumonia, which can be life-threatening. These are more common in later stages of Parkinsons.
In general, the average life expectancy of Parkinson’s patients is similar to people without the disease.
You May Like: Are There Prenatal Tests For Parkinson Disease
How Is Parkinsons Diagnosed
Doctors use your medical history and physical examination to diagnose Parkinson’s disease . No blood test, brain scan or other test can be used to make a definitive diagnosis of PD.
Researchers believe that in most people, Parkinson’s is caused by a combination of environmental and genetic factors. Certain environmental exposures, such as pesticides and head injury, are associated with an increased risk of PD. Still, most people have no clear exposure that doctors can point to as a straightforward cause. The same goes for genetics. Certain genetic mutations are linked to an increased risk of PD. But in the vast majority of people, Parkinsons is not directly related to a single genetic mutation. Learning more about the genetics of Parkinsons is one of our best chances to understand more about the disease and discover how to slow or stop its progression.
Aging is the greatest risk factor for Parkinsons, and the average age at diagnosis is 60. Still, some people get PD at 40 or younger.
Men are diagnosed with Parkinsons at a higher rate than women and whites more than other races. Researchers are studying these disparities to understand more about the disease and health care access and to improve inclusivity across care and research.
Aging is the greatest risk factor for Parkinsons, and the average age at diagnosis is 60. Still, some people get PD at 40 or younger.
The Michael J. Fox Foundation has made finding a test for Parkinsons disease one of our top priorities.
How Parkinson’s Disease Is Diagnosed
There’s no “gold standard” test that will diagnose Parkinson’s disease . Instead, a healthcare provider relies on their own clinical observations and judgment, along with a patient’s description of possible signs and symptoms, to make the diagnosis. That, of course, makes a physical examination very important in this process. Much of your healthcare provider’s exam will be aimed at assessing whether you have the so-called cardinal signs of Parkinson’s: resting tremor, rigidity , bradykinesia and postural instability .
Read Also: Can Blows To The Head Cause Parkinson Disease
Diagnosis Of Parkinson Disease: Motor Symptoms
The clinical diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease is based on the presence of characteristic motor symptoms: bradykinesia, rigidity, postural instability, and resting tremor but neuropathology is still considered the gold standard for definite diagnosis. Differentiating PD from other movement disorders can be challenging throughout the disease course, because signs and symptoms often overlap. Indeed, neuropathology studies reveal that clinical diagnosis of PD can be confirmed with an accuracy of about 75%. Good response to levodopa is often used to support the diagnosis of PD. However, cases of pathologically proven PD with poor response to levodopa have also been reported.
Misdiagnosis of PD can occur for several reasons. In a community-based study of patients taking antiparkinsonian medication, the most common misdiagnosis were essential tremor, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular parkinsonism. In addition, many of the prominent features of PD may also occur as a result of normal aging or from comorbid and multifactorial medical conditions .
R. Savica, … G. Logroscino, in, 2016
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
The main symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are:
- tremor or shaking, often when resting or tired. It usually begins in one arm or hand
- muscle rigidity or stiffness, which can limit movement and may be painful
- slowing of movement, which may lead to periods of freezing and small shuffling steps
- stooped posture and balance problems
The symptoms of Parkinson’s disease vary from person to person as well as over time. Some people also experience:
- loss of unconscious movements, such as blinking and smiling
- difficulties with handwriting
- drop in blood pressure leading to dizziness
- difficulty swallowing
Many of the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease could be caused by other conditions. For example, stooped posture could be caused by osteoporosis. But if you are worried by your symptoms, it is a good idea to see your doctor.
Don’t Miss: Living With Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a chronic neurological condition. It is progressive and symptoms worsen over time. It is named after Dr James Parkinson who first described the condition in 1817.
People with Parkinsons disease experience a loss of nerve cells in the part of their brains responsible for controlling voluntary movements. This part of the brain is called the substantia nigra . The nerve cells in the substantia nigra usually produce a chemical called dopamine which helps transmit messages from the brain to the rest of the body via the central nervous system . As these cells are lost, people with Parkinsons disease experience a loss of dopamine and the messages controlling movement stop being transmitted efficiently.
Parkinsons disease is more common as people get older but it can affect younger adults. Men tend to be affected in slightly higher numbers than women.
Can A Blood Test Tell You If You Have Parkinsons Disease
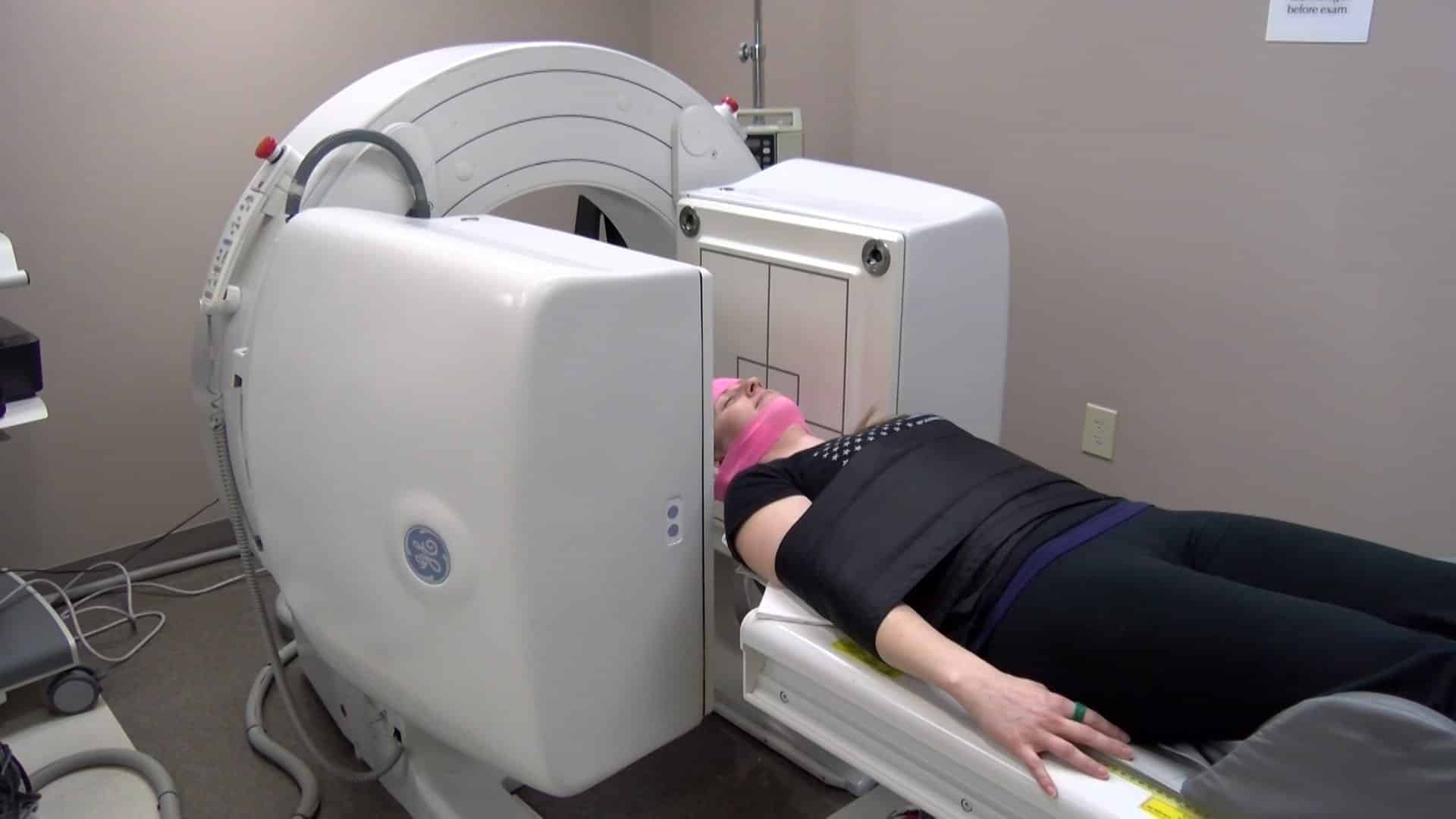
This test cant tell you for sure that you have Parkinsons disease, but it can give your doctor more information to work with. It can take a long time for some people to get a diagnosis. You may need to see your neurologist regularly so she can keep an eye on your symptoms and eventually figure out whats behind them.
You May Like: Cause And Effect Of Parkinson’s Disease
How It All Fits Together
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease can be tricky. The process relies heavily on your doctors judgment. In addition, the causes and risk factors of Parkinsons are not entirely clear yet, which contributes to the difficulty in diagnosing this condition.
However, there have been efforts to try and detect this disease earlier. For instance, clinicians have started focusing more on prodromal symptoms, which are early symptoms that appear before movement-related difficulties begin.
These symptoms include:
- Loss of smell, which can sometimes occur years before other symptoms
- Chronic constipation, without any other explanation
- Rapid eye movement behavior disorder, which causes sleep disturbances
What Are The Symptoms
Each person is affected differently by Parkinsons disease and no two people will experience exactly the same symptoms. The impact of Parkinsons disease can be unpredictable and it is common for people to have good days and bad days.
The main symptoms of Parkinsons disease are:
- balance problems
- problems with posture
Other possible symptoms include difficulty initiating movement , a shuffling gait when walking, and freezing when trying to move . People might experience a loss of facial expression, speech problems , swallowing problems, bowel and bladder problems, difficulties at night and tiredness during the day. Skin can become greasy and people might experience excessive sweating. Sexual problems are common. People often experience depression and anxiety. Another common symptom is small handwriting .
Other less common symptoms can include pain and memory problems.
You May Like: How To Help With Parkinson Disease
Physical And Neurological Examination
Your doctor will conduct a physical and neurological examination. This can involve observing your behavior, movements, and mental state and conducting tests or asking you to perform certain exercises.
These are some of the symptoms of Parkinsons your doctor can determine visually:
- Fewer spontaneous movements or hand gestures
- Reduced frequency of blinking
- Tremors in your hands while they are at rest, often only in one hand
- Hunched posture or forward lean while walking
- Stiff movements
These are some of the exercises your doctor may ask you to do to evaluate your movements, balance, and coordination:
- Opening and closing your fist
- Tapping your fingers, toes, and heels
- Holding your arms out in front of you
- Moving your finger from one point to another
- Rotating your wrists or ankles
- Standing from a chair
Is Early Diagnosis Possible
Experts are becoming more aware of symptoms of Parkinsons that precede physical manifestations. Clues to the disease that sometimes show up before motor symptoms and before a formal diagnosis are called prodromal symptoms. These include the loss of sense of smell, a sleep disturbance called REM behavior disorder, ongoing constipation thats not otherwise explained and mood disorders, such as anxiety and depression.
Research into these and other early symptoms holds promise for even more sensitive testing and diagnosis.
For example, biomarker research is trying to answer the question of who gets Parkinsons disease. Researchers hope that once doctors can predict that a person with very early symptoms will eventually get Parkinsons disease, those patients can be appropriately treated. At the very least, these advances could greatly delay progression.
You May Like: Tai Chi And Parkinson’s
New Diagnostic Standards For Parkinsons
Until recently, the gold-standard checklist for diagnosis came from the U.K.s Parkinsons Disease Society Brain Bank. It was a checklist that doctors followed to determine if the symptoms they saw fit the disease. But thats now considered outdated. Recently, new criteria from the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society have come into use. This list reflects the most current understanding of the condition. It allows doctors to reach a more accurate diagnosis so patients can begin treatment at earlier stages.
Why We Need A Laboratory Test For Parkinsons Disease
It is known that the cell loss of PD begins decades before motor symptoms develop and that often certain non-motor symptoms appear first. Therefore, scientists and clinicians are searching for ways to diagnose PD earlier. Diagnosing the disease earlier may allow people with PD to take measures to improve their health earlier, and may be an essential element to developing a neuroprotective medication, a drug that slows down or reverses the nerve damage of PD. It is possible that such a medication would only work at the earliest stages of the disease.
In addition, there are a number of neurologic syndromes that share features of PD. While neurologists are trained to differentiate between these syndromes, researchers are looking for ways to distinguish between different diagnostic possibilities more accurately.
Theres no consensus for a Parkinsons biomarker, making lab tests difficult.
The major obstacle to earlier and more accurate diagnosis of PD, is the current lack of an agreed-upon, simple biomarker for PD. A biomarker is a measurable characteristic in the body that indicates that disease is present. A biomarker can be a lab test, an imaging test, or a clinical test. Common biomarkers include hemoglobin A1c for diabetes, or ejection fraction for heart failure. You can read more about the development of a biomarker for PD in a prior blog.
You May Like: Living Alone With Parkinson’s
Passive Manipulation Of Limbs
To test for the presence of rigidity, we need to passively manipulate the limbs of the patient. However, If the disease is in its early stage or the symptoms are well controlled with medications, we may not be able to see rigidity. We will need to use some activation maneuvers, that basically consist in performing repetitive movements with the limb contralateral to the one that is being tested.
Also, there are two types of rigidity:
– Lead-pipe rigidity: where the tone is uniformly and smoothly increased throughout the entire range of movement
– Cogwheel rigidity: where a tremor is superimposed on the hypertonia, making the movement irregular due to intermittent increase and reduction of tone
Upper Extremity Testing
For the upper extremity the most sensitive joint where to check for rigidity is the wrist. To uncover rigidity, passively rotate the wrist and feel for a resistance to the movement. It is very important that the arm of the patient is fully relaxed when rotating the wrist. To do this, place your proximal hand under the patients forearm, while your distal hand grabs and rotates the wrist of the patient. When rigidity is present, the range of motion will be preserved but you will feel a resistance in performing the movement.
Wrist rotation with activation maneuver.
It is also possible to test for rigidity in the elbow by passively flexing and extending the forearm.
Elbow flexion-extension with activation maneuver.
Lower Extremity Testing
Gait & Balance Abnormalities
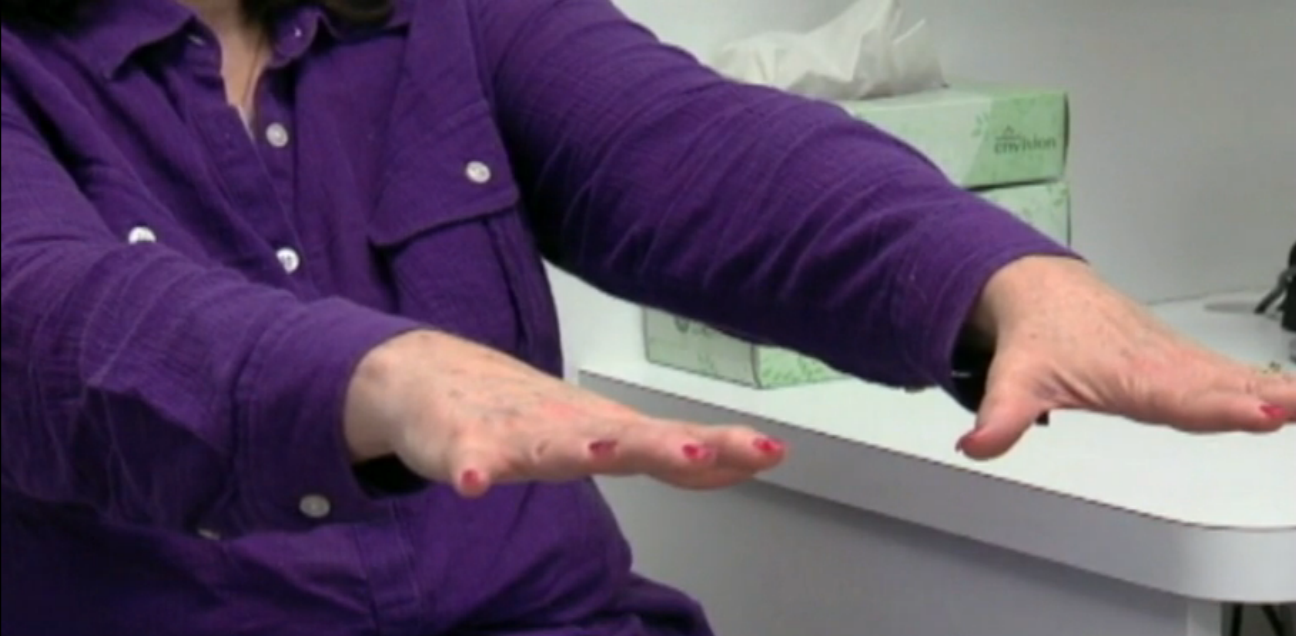

Parkinsons Disease Exam
Patients with Parkinsons disease can develop an alteration of the postural reflexes that causes instability in gait and balance control. Such alterations usually develop later in the course of the illness and are a major cause of disability, especially because of the high risk for falls that derives.
Using the exam to pick up postural instability is of the utmost importance for the management of patients with PD, since it will trigger either a medication adjustment or a physical therapy intervention both aimed at falls prevention.
We have three tests for this part of the PD exam:
1) Standing up from a chair
2) Free walking
3) Provoked pull test maneuver for balance
Also Check: Early Cognitive Signs Of Parkinson’s