How Do I Know If I Have A Speech Or Voice Problem
- My voice makes it difficult for people to hear me.
- People have difficulty understanding me in a noisy room.
- My voice issues limit my personal and social life.
- I feel left out of conversations because of my voice.
- My voice problem causes me to lose income.
- I have to strain to produce voice.
- My voice clarity is unpredictable.
- My voice problem upsets me.
- My voice makes me feel handicapped.
- People ask, “What’s wrong with your voice?”
How Are Swallowing Problems Treated
The first step to addressing swallowing issues is to speak to a neurologist about getting an evaluation performed by a SLP. This professional will take a medical history and interview the person with PD about eating and swallowing.
This is typically followed by either a video X-ray or an endoscopic examination, so the medical specialist can observe the swallowing process as an individual sips liquid and eats food, as these substances flow from the mouth, down the throat and esophagus, to the stomach. With these tests it is possible to see where the trouble is occurring and to recommend therapies.
Follow the recommendations of the swallowing specialist, which may include the following:
- Exercise and Swallow Hard. Just as exercise can ease other PD-related movement difficulties, it can also help with swallowing. The Lee Silverman Voice Technique® helps a person exaggerate speaking and swallowing. Working with an SLP on an individualized program helps the person to swallow hard and move food from the mouth down the throat.
- Expiratory Muscle Strength Training. This therapy strengthens respiratory muscles, improves cough and swallowing and reduces aspiration.
- Change in food. Modifying liquids and solids can help. For people who find liquids get into the airway, liquids may need thickening. Taking bigger or smaller bites or sips or pureeing solid foods may help. First get an evaluation, so the SLP can recommend how to modify food and liquid.
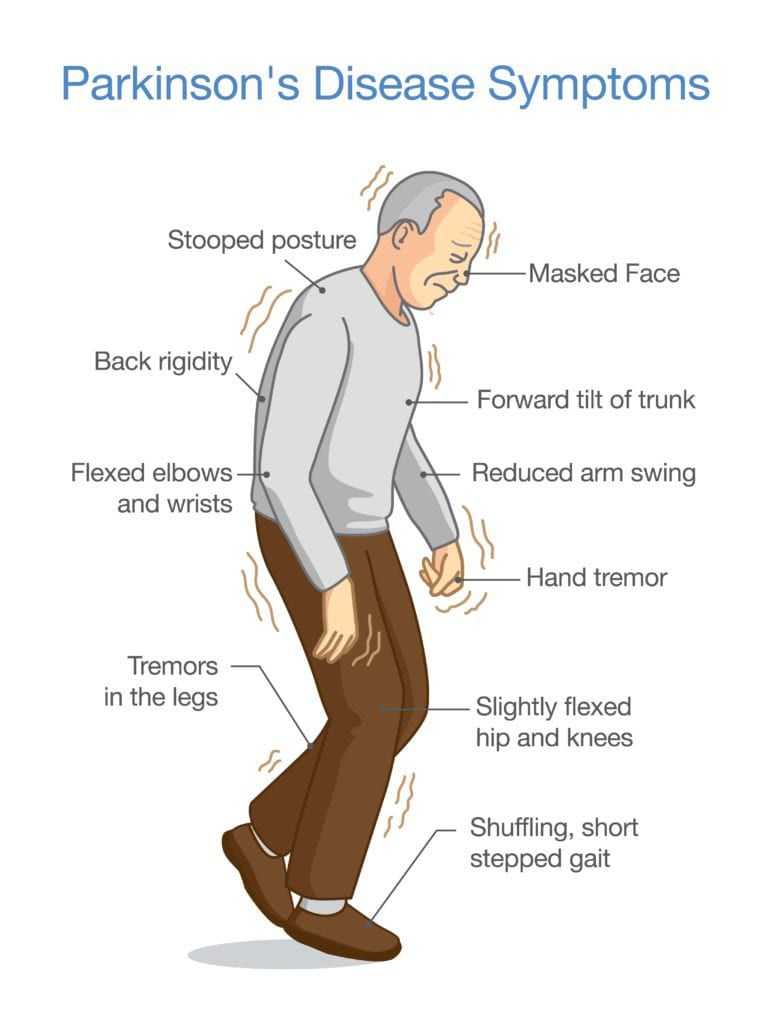
Trouble Moving Or Walking
People without PD do not think about their walking. Their arms naturally swing, and their feet naturally land on the heels with each step. They can walk and talk and carry bags, purses and plates of food without difficulty.
Individuals with PD tend to lose their automatic movements. Especially as Parkinsons advances, it may bring with it a variety of symptoms that are uncommon in early stages, such as problems with walking and poor balance . Feet begin to shuffle, and performing two tasks at once becomes more difficult. Turning becomes challenging, often leading to a freezing episode and sometimes a fall.
Parkinsons Disease Is a Movement and Sensory Disorder
People with PD have trouble regulating the speed and/or size of their movements. Movements are bradykinetic or hypokinetic .
Changes in the movement system lead to challenges controlling movements, including the following:
- Starting and stopping movements
- Linking different movements to accomplish one task
- Finishing one movement before beginning the next
Changes in the sensory system also lead to challenges, particularly noticing and correcting movement and voice issues, including the following:
- Slowness or smallness of movements
- Lack of movement
- Changes in posture
- Changes in voice volume
Walking Changes
There are many PD-related walking changes:
Managing Walking Changes
Walking Tips
Turning Tips
Freezing
Managing Freezing
Tips for Care Partners
Freezing is a significant cause of falls.
You May Like: Grants For Parkinson’s Patients
These Exercises Have Helped With My Sisters Cognitive Issues
According to the researchers, Nordic walking seems to be an effective, accessible, and safe strategy to help patients with walking difficulties. However, relatively little is understood about the mechanics of how walking with poles might be beneficial.
Their analysis included 11 Parkinsons patients, six men and five women, with an average age of 65.6 and relatively mild symptoms. For comparison, the study also included nine similarly aged adults without Parkinsons.
Analyses showed that the Parkinsons patients took markedly shorter steps, both while Nordic walking and while free walking.
Additionally, when Nordic walking was compared to free walking, the pendulum-like energy recovery was increased in the Parkinson group while external mechanical work remained similar, the researchers reported.
When you walk, the repetitive movements of your steps create a back-and-forth momentum, similar to a pendulum, which helps to decrease the amount of energy needed for walking. Put another way, its more energy-efficient to walk 10 steps consecutively, than to take 10 steps stopping with each step, because your momentum helps propel you along.
In essence, the researchers found that the different gait patterns in Parkinsons patients makes their steps less efficient, and Nordic walking helps to correct this by increasing that pendulum-like momentum.
Availability Of Data And Materials
The data used in this study contains sensitive information about the study participants and they did not provide consent for public data sharing. The current ethical approvals by the Regional Ethical Review Board in Lund, Sweden do not include data sharing. A minimal data set could be shared by request from a qualified academic investigator for the sole purpose of replicating the present study, provided the data transfer is in agreement with EU legislation on the general data protection regulation and approval by the Swedish Ethical Review Authority.
Contact information: Department of Health Sciences, Lund University Box 157, 221 00 Lund, Sweden Principal investigator: Swedish Ethical Review Authority, Box 2110, 75 002 Uppsala, Sweden. Phone: +46 10 475 08 00.
Read Also: Does Caffeine Make Parkinson’s Tremors Worse
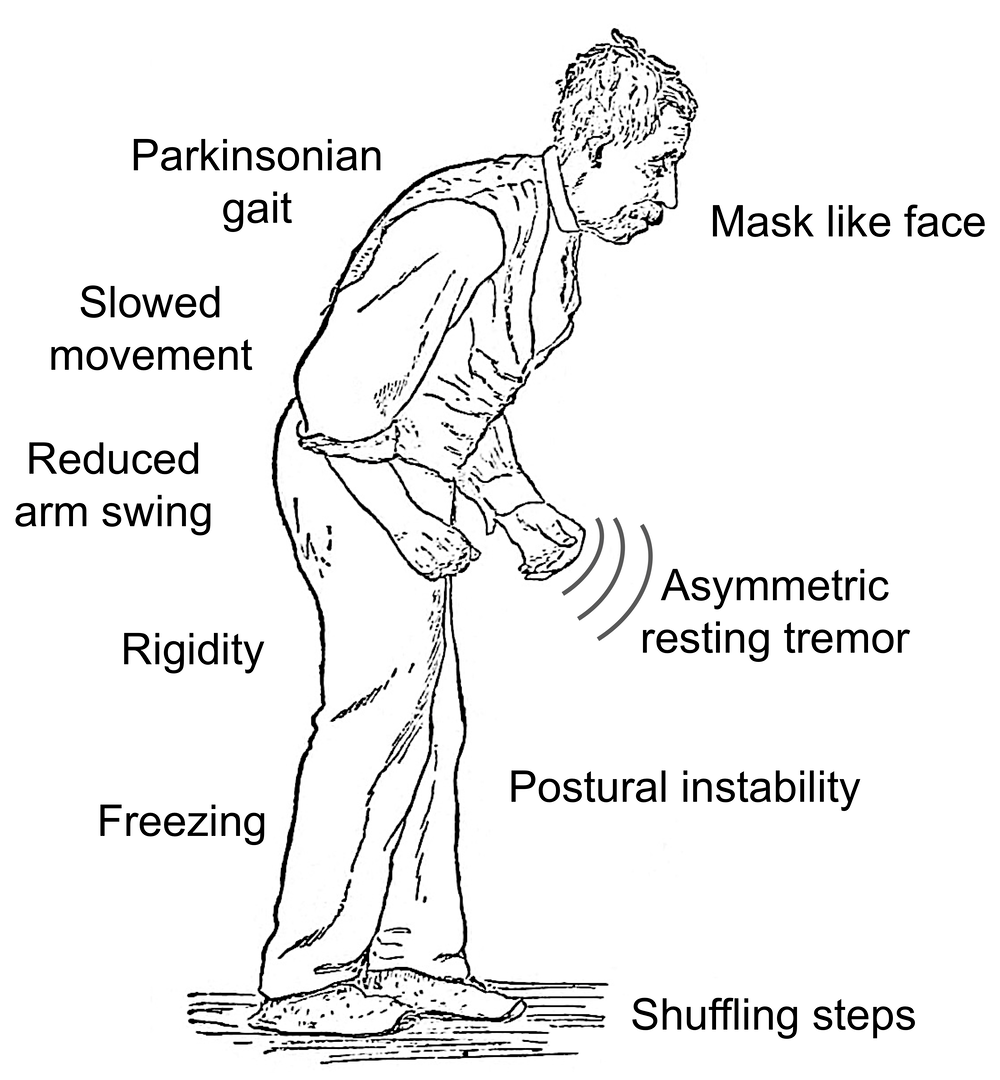
What Does It Look Like
Parkinsonian gait is one of several motor symptoms that are the hallmarks of Parkinsons disease, including slowness of movement and tremors. Motor symptoms in Parkinsons disease come from a lack of control over movements and difficulty initiating muscle movements.
The exact features of Parkinsonian gait can differ from person to person, but there are some very common features that most people have. These include:
- taking small, shuffling steps
- moving more slowly than expected for your age
- festinating, or when your strides become quicker and shorter than normal, which can make it look like youre hurrying
- taking jerky steps
- moving your arms less when walking
- falling frequently
- freezing of gait
People with Parkinsons disease can sometimes lose the ability to pick up their feet, which makes them stuck in place. Freezing of gait can be triggered by environmental factors, such as walking through a narrow doorway, changing directions, or walking through a crowd. It can also be triggered by emotions, especially anxiety or feeling rushed.
Freezing of gait can happen anytime. However, it often occurs when you stand up. You might find that youre unable to pick up your feet and start moving.
Easy Fold And Go Walker
If youre looking for a standard lightweight walker that is ideal for traveling and has an affordable price, think about this Easy Fold and Go walker. This newly designed mobility aid opens and folds up easily for stress-free portability. This easy-to-use rolling walker, with its sturdy design, allows users to walk with confidence, outdoors and indoors!
This walker is so portable that with the lift of a finger, the Easy Fold and Go Walker easily folds allowing it to be stored in a car, shopping cart, the overhead compartment of an airplane, or discreetly by the users side when not in use.
When it comes to the overall framing, the walker looks very stable, secure, and easily cleanable. Its crafted in a way that supports a weight of up to 400 lbs.
The walker has a height adjustment feature that allows the walker height to be easily adjusted to accommodate users from 4 feet 10 inches to 6 feet 8 inches tall. The 6 inches swivel wheels and rear easy-glide feet allow the user to easily maneuver the walker.
Recommended Reading: Is There Pain With Parkinson’s
What Causes Walking Problems
The pattern of how you walk is called your gait. Many different diseases and conditions can affect your gait and lead to problems with walking. They include:
- Abnormal development of the muscles or bones of your legs or feet
- Arthritis of the hips, knees, ankles, or feet
- Cerebellar disorders, which are disorders of the area of the brain that controls coordination and balance
Study Strengths And Limitations
This study is the largest to document gait change in PD over the longest period from diagnosis, in a relatively homogeneous cohort of incident PD participants. The main strength was that gait changes due to aging and disease progression could be parsed, as a well-matched control cohort was assessed alongside people with PD. Relatively precise modeling of gait change in early PD was achieved as PD participants were recruited close to diagnosis, enabling monitoring over the first 6 years of the disease. Inter-individual variation was accounted for through the random effect term included in all models. The inclusion of LEDD in analyses enabled the investigation of gait changes that were related and, arguably, more importantly, not related to changes in dopaminergic medication, to identify potential therapeutic targets for non-dopaminergic interventions. The effects of dopamine on gait progression could be further explored by comparing gait progression for characteristics measured on and off medication. Specifically, testing participants both on and off medication will allow us to better understand the progression of the underlying disease as well as explore the complex relationship between step width variability and dopaminergic medication.
Don’t Miss: Young Onset Parkinson’s Symptoms
How To Improve Walking For The Parkinsons Patient
One of the typical problems for the patient with Parkinsons disease is with walking. The disease damages the part of the brain called the basal ganglia.
This part of the brain is what produces dopamine. As the disease advance and the dopamine levels start to wane, disturbances in movement become common. The patient will start to walk with short, quick scuffling steps. He also will have trouble stopping and starting to move, and may have poor balance and tremors. All of these symptoms make it more likely that he will suffer a fall. So, there are some important tips as the caregiver that you should remember to help him to walk and to prevent falls:
#1 Use Auditory Cues
You may want to try to use helpful phrases with your loved one, such as take long steps, or step up. These gentle reminders can help him to alter his walking pattern. Your patient also may get stuck sometimes, and have trouble with initiating movement. These type of short, firm commands could help him to start moving again. We also have found that the use of a metronome that matches the walking speed of the patient can really help.
#2 Use Visual Cues
#3 Modify the Environment
To cut down on scuffles, try to have a very smooth floor for the patient to walk on. Tile or linoleum work well. Try to avoid carpets if possible, especially ones with a higher nap.
Get rid of throw rugs and any other obstacles, including coffee tables, footstools and magazine racks.
#4 Increase His Mobility
What Is Swelling And What Can People With Parkinsons Do About It
Swelling is a common problem for people with Parkinsons, particularly for those who have movement difficulties. If you dont exercise very much, fluid can build up in your feet, ankles and lower legs. This is known as oedema. Ankle swelling is also a side effect of some Parkinsons medication.
Swelling can get worse during the day and go down overnight. Sometimes this is called postural oedema because gravity causes the build-up of fluid around the ankles when you stand up.
While the swelling is usually mild, some people describe their legs as feeling heavy. They may also have difficulty putting on shoes because they feel tighter than usual.
Wearing footwear that can be loosened during the course of the day may help, but it is important to make sure your shoes still hold firmly on to your feet to avoid the risk of falling.
Being active can help reduce swelling. Try the following:
- When sitting, have your legs raised on a footstool and exercise your ankles regularly .
- Lie flat with your legs slightly raised on a pillow three to four times a day to help reduce excess fluid.
You May Like: Myrbetriq And Parkinson’s Disease
How Are Speech Problems Treated
There are many options to help improve your speech. A speech-language pathologist can help you pick the right approaches for you. Speech-language pathologists are trained health care professionals who specialize in evaluating and treating people with speech, swallowing, voice, and language problems.
Ask your doctor for a referral to a speech-language pathologist. It is also important to contact your health insurance company to find out what therapy and procedures are eligible for reimbursement and to find a list of SLPs covered by your plan. Finally, visit a SLP who has experience treating people with PD.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation For Parkinsons Disease
Vagus Nerve Stimulation has been shown to improve walking in patients with Parkinsons Disease.
What is Parkinsons Disease?
Parkinsons disease is a progressive, neurodegenerative disorder with no known cure. The majority of medical treatment is aimed at relieving the individual of symptoms rather than attempting to cure the disease. Many are often limited by debilitating symptoms that significantly reduce quality of life. Parkinsons symptoms include the following:
- A tremor
- Slowness and incoordination of movement
- Posture, balance and walking difficulties
- Poor executive function and memory loss
- Loss of smell
- Changes in writing and speech
- Weight loss
The Beginning of Parkinsons
Parkinsons disease actually begins outside of the brain, and travels through nerves, such as the vagus nerve, to enter the brain. Classically, Parkinsons is associated with the loss of the neurotransmitter dopamine due to the degeneration of an area of the brain called the substantia nigra . However, there is actually a decrease in norepinephrine before dopamine becomes depleted. There is degeneration in an area of the brain called the locus coeruleus before there is a problem with the substantia nigra.
Existing treatment strategies for Parkinsons disease are purely to relieve symptoms. However, the treatment is often accompanied by terrible side effects. New treatments are vital to developing more effective ways of treating Parkinsons.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Getting Out Of Chair
The Contribution Of Aging To Pd Gait Progression
Understanding how gait changes with normal aging is important as age-related changes cumulatively contribute to gait progression in people with PD alongside disease progression. Three characteristics changed in both PD and control cohorts over 6 years the change was therefore considered to be due primarily to aging mechanisms rather than disease progression. These changes met criteria 2.
Age-related change contributes to gait impairments observed in PD, suggesting that therapies addressing features of aging may be effective in reducing the burden of PD. It is important, therefore, to consider the mechanisms driving age-related gait change. Change may be due to atrophy and loss of muscle strength , physical inactivity , and development of age-related conditions, such as osteoarthritis causing increased pain and stiffness during movement . Age-related changes in the brain such as atrophy and white matter abnormalities also explain the slowing and increased variability of gait during aging . Increasing evidence implies that specific neural regions or networks underpin discrete gait characteristics , which could be specifically targeted to prevent discrete components of age-related gait decline. On this point, gait performance in PD is improved by exercise-based interventions aiming to increase muscle strength and activity speculatively these therapies may, at least partially, be targeting age-related changes which in turn positively impact PD gait.
About Gait And Balance
Gait can be described simply as a persons manner of walking. Most people have a distinctive style of walking. In normal circumstances when people walk, their stance is upright and the center of gravity of the body is positioned in a manner that helps them coordinate their movement. As people walk, they swing their arms on the side, which also helps coordinate their motion.
Because of the bodys inability to coordinate movement in Parkinsons disease, it becomes progressively more difficult for people to maintain proper posture and coordination during walking. Most Parkinsons patients experience a range of walking difficulties, resulting in distinctive gait and balance problems.
Also Check: Best Probiotic For Parkinson’s
How Parkinsons Disease Affects The Autonomic Nervous System And The Heart
In PD, there are two major reasons why the automatic control of the cardiac system is impaired. First, areas of the brain that control this system often contain Lewy bodies and have undergone neurodegeneration. In addition, the autonomic nervous system itself is directly affected by Lewy body-like accumulations and neurodegeneration. This means, when the baroreceptors in the heart and carotid artery sense a drop in blood pressure and try to generate a signal to the heart and blood vessels to increase the blood pressure, the message may not get through. This results in neurogenic orthostatic hypotension , or drops in blood pressure upon standing due to autonomic nervous system dysfunction. There are no medications that can cure nOH by restoring the autonomic nervous system in PD. nOH however, can be treated. Read more about nOH and its treatments here.
Structural problems of the heart such as coronary artery disease or cardiomyopathy are not thought to be part of the pathology of PD, although of course, could co-exist with PD.
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease occurs when nerve cells in an area of the brain called the substantia nigra become impaired or die. These cells normally produce dopamine, a chemical that helps the cells of the brain communicate . When these nerve cells become impaired or die, they produce less dopamine. Dopamine is especially important for the operation of another area of the brain called the basal ganglia. This area of the brain is responsible for organizing the brains commands for body movement. The loss of dopamine causes the movement symptoms seen in people with Parkinsons disease.
People with Parkinsons disease also lose another neurotransmitter called norepinephrine. This chemical is needed for proper functioning of the sympathetic nervous system. This system controls some of the bodys autonomic functions such as digestion, heart rate, blood pressure and breathing. Loss of norepinephrine causes some of the non-movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists arent sure what causes the neurons that produce these neurotransmitter chemicals to die.
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Affect Your Eyesight