Gastrointestinal Transit And Loss Of Levodopa Explained Most Of The Variability In Levodopa Bioavailability
Constipation is a clinical symptom associated with PD, particularly at the later stages. Overall, the GER is inversely proportional to the disease stage. In addition, levodopa is degraded in the stomach and intestine lumen as a consequence of gut microbiota, luminal enzymes, and chemical degradation. The higher residence time of levodopa in the gastrointestinal tract, caused by the slower GER, leads to a higher degraded fraction. The predicted decrease in the maximal concentration was the result of the combination of a slow GER and the luminal degradation . The parameter sensitivity analysis showed that gastric and intestinal processes were the most influential factors for levodopa bioavailability . The GER has been shown to be the main parameter that induces a delay in levodopa absorption. Our observation is further consistent with the reported decrease in levodopa efficiency with pH and Helicobacter pylori infection., The levodopa loss in the stomach also motivated approaches that bypassed the gastrointestinal tract and the intestine, as well as provides a rationale for investigational prokinetics for PD patients.
The Investigation In Mice
In their recent study paper, the scientists refer to research suggesting that neurotrophic factors molecules that help neurons survive and thrive could, in theory, restore the function of neurons that produce dopamine. However, the clinical benefit of these factors had yet to be proven.
The team focused on bone morphogenetic proteins 5 and 7 . They had previously shown that BMP5/7 has an important role in dopamine-producing neurons in mice.
In the latest study, the scientists wanted to see whether BMP5/7 could protect the neurons of mice against the damaging effects of misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins.
To do this, they injected one group of mice with a viral vector that caused misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins to form in their brains. They used other mice as a control group. The scientists then injected the mice with the BMP5/7 protein.
What Is The Effect Of Dietary Protein On Levodopa In Patients With Parkinson Disease
Patients recently diagnosed with Parkinson disease are often confused regarding dietary protein, because they receive conflicting information.
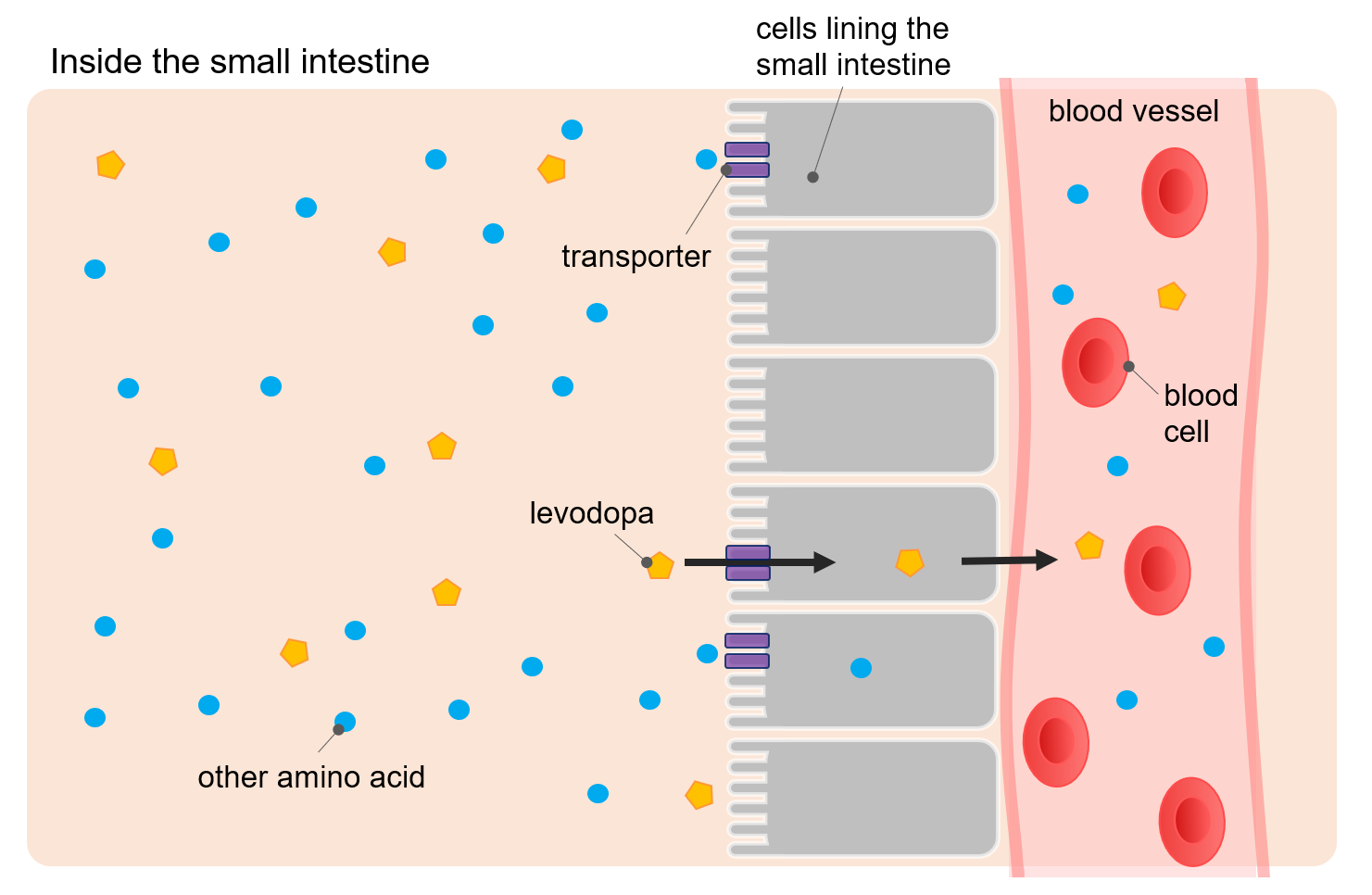
Levodopa is absorbed via a large neutral amino acid active carrier system and therefore competes with dietary proteins for absorption this effect is generally relatively small and is not clinically important for most patients, especially those with early or moderate disease. However, as the disease progresses and patients become more and more sensitive to maintaining relatively narrow therapeutic serum concentrations of levodopa, this effect can become clinically relevant. These patients usually have significant motor fluctuations. Some report that when they are “on” and they eat a meal including protein, they turn “off.” Others find that if they eat a protein meal, their next levodopa dose does not kick in. These patients may benefit from a low protein or a protein redistributed diet.
In a low-protein diet, the total daily protein intake is spread more or less equally over the day. In a protein-redistributed diet, individuals only consume food very low in protein during the day and then eat a high-protein meal in the evening. Unfortunately, these diets are difficult to follow dietary consultation may be beneficial for patients in whom such diets are considered.
References
Hauser RA, Grosset DG. FP-CIT SPECT Brain Imaging in Patients with Suspected Parkinsonian Syndromes. J Neuroimaging. 2011 Mar 16. .
Read Also: Parkinsonism Vs Parkinson’s Disease
Want More Practical Articles Like This
Much more can be found in our Every Victory Counts® manual. Its packed with up-to-date information about everything Parkinsons, plus an expanded worksheets and resources section to help you put what youve learned into action. Request your free copy of the Every Victory Counts manual by clicking the button below.
Nutritional Factors In Treatment
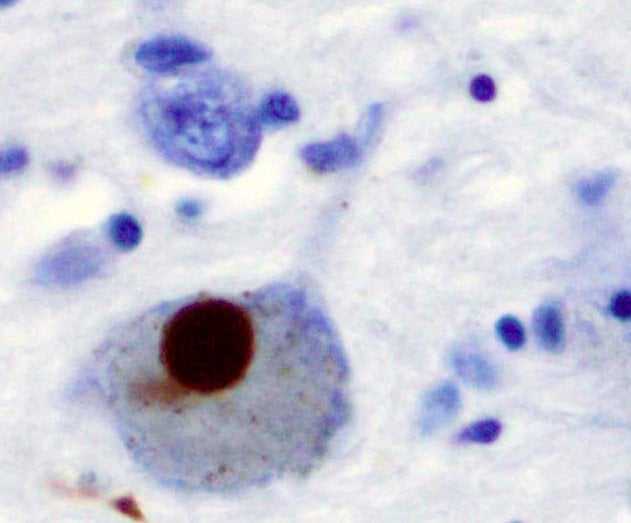
The most immediate nutritional concerns in Parkinsons disease treatment include changes in the absorption rate, blood levels, and CNS uptake of L-dopa. The protein content of meals, and particularly the distribution of protein intake throughout the day, has emerged as an important consideration in the effectiveness of L-dopa for many patients. Improvement in clinical response varies from 30% with protein redistribution to 82% with low-protein diets.,,
There are eight levels:
- Level 6: Easy to chew
- Level 5: Soft and bit-sized
- Level 4: Extremely thick/pureed
Don’t Miss: Early Signs Of Parkinson’s Dementia
Managing Medication Interactions And Side Effects
All prescribed medications can have potential side effects, including those used to treat Parkinsons. Some things you think are symptoms of Parkinsons may actually be side effects of medication. Some peoples side effects will have a big impact on their lives and have to be kept under control along with the symptoms.
Protein And Your Diet
Cutting out wholefood groups, especially protein, is NOT recommended. Foods containing protein provide a valuable source of iron, magnesium, calcium, zinc and vitamin B12. Low protein diets or restricting protein can exacerbate weight loss and malnutrition. The consequence of cutting out protein far outweighs the limited benefits that this can offer. Protein plays an essential role in the body to build the immune system and fight off colds and infections, it helps our body to repair and grow cells, assists in wound healing and helps to maintain lean muscle mass.
You May Like: How Do I Know If I Have Parkinson’s
Quality Assessment And Rob
An overview of the RoB judgment per study is provided in . With the strict Cochrane RoB tool, nonrandomized studies automatically score high risks for domain 1 . To control for this deficit, domain 1 was not included in the overall adjusted RoB judgment for nonrandomized trials and this adjusted RoB was used for the remainder of the review. Three studies were rated as high risk due to significant carryover effects , lack of control groups , and insufficient clarity of reported results . A total of 13 and 6 studies were rated as low and moderate RoB, respectively. The main reasons for moderate RoB judgments were minor protocol adjustments during intervention , specific selection of reported results , and incomplete intervention details . Given the inverse relation between RoB and overall study quality, articles with high RoB were not taken into consideration for the conclusion.
What Are The Different Types Of Pain Experienced By People With Parkinsons
Five main types of pain are common for people with Parkinsons. Multiple types may be present simultaneously or occur at different points throughout a persons path with Parkinsons. Recognizing which kind of pain is present can help you optimize treatment, as can paying attention to what activities or times of day make your pain better or worse.
Musculoskeletal pain
Musculoskeletal pain that affects muscles, bones, tendons, ligaments, and/or nerves. The pain can be localized or generalized and can fade or intensify at different times. Existing musculoskeletal pain can be exacerbated by Parkinsons.
Neuropathic pain
Rather than being caused by a physical injury, this type of pain is caused by damage to the somatosensory nervous system or a disease affecting the somatosensory nervous system, which responds to external stimuli like touch, temperature, and vibration. It tends to be fairly consistent throughout the day and is present no matter what activity youre doing. Unlike the aching you may feel when youre doing a strenuous physical activity, neuropathic pain feels more like a tingly, crawly, uncomfortable sensation.
Dystonic pain
Dystonia, the movement disorder in which involuntary muscle contractions cause repetitive or twisting motions, is often very painful. Many people with Parkinsons experience dystonia as a motor symptom, whether its localized , in multiple nearby body parts , or all over .
Akathisia
Central pain
Also Check: Judy Woodruff Parkinson’s Disease
Eat Plenty Of Protein But Not With Levodopa Medications
If youre taking a levodopa medication, your doctor may tell you to avoid protein when taking your meds. Both animal and plant protein can interfere with the absorption of levodopa medications.
But you should still eat plenty of protein. Just be strategic with the timing. Dont take levodopa medications with meals, Dr. Gostkowski says. Its best to take it on an empty stomach either 30 minutes before your meal or an hour after eating.
If you get nauseous from the medication, eat a small amount of starchy food with it, such as crackers. Make sure whatever you eat with your medicine doesnt have protein. Its a misunderstanding that people with Parkinsons should avoid protein, Dr. Gostkowski says. You definitely need protein in your diet. Just dont eat it when youre taking your levodopa medication.
Foods High In Saturated Fat
The role that foods high in saturated fats play in Parkinsons progression is still under investigation and is often conflicting. We might eventually discover that there are certain types of saturated fats that actually help people with Parkinsons.
Some limited research does show that ketogenic, low-protein diets were beneficial for some with Parkinsons. Other research finds high saturated fat intake worsened risk.
But in general, foods that have been fried or heavily processed alter your metabolism, increase blood pressure, and impact your cholesterol. None of those things are good for your body, especially if youre trying to treat Parkinsons.
Read Also: Is Drooling A Sign Of Parkinson’s Disease
How Much Protein Do I Need
For optimal health, you need about a half gram of protein per pound of body weight every day. Take your weight in pounds and divide it by two to determine the grams of protein you need. For example, if you weigh 140 pounds, you should eat about 70 grams of protein. Since seniors are less efficient at processing protein, spreading protein consumption evenly throughout the day can improve absorption. If you eat three meals a day, divide the 70 grams by three. You should eat about 23 grams of protein in each meal. Of course, if you weigh more, eat more protein. If you weigh less, eat less protein.
You may think 20-25 grams of protein is a lot in one meal however, if you plan ahead, incorporating the amount of protein you need is easy.
Breakfast
Breakfast is the time that most people dont eat enough protein. Just eating oatmeal or cereal with milk isnt enough. Add Greek yogurt, a slice of cheese, peanut butter on your whole-grain toast, an egg, or turkey sausage to increase protein.
Lunch
For lunch, two cups of chili with beans provide 20 grams of protein. Add some cornbread with some honey, and a half cup of milk or a dairy alternative, such as soy milk and you have met your protein requirement for lunch. A grilled cheese sandwich with tomato soup and carrots sticks is another balanced meal idea.
Dinner
Side Effects And Problems Of Anticholinergics

Another reason these drugs are not a first choice for treating Parkinsons are their side effects. Some people may experience confusion, a dry mouth, constipation and blurred vision when taking anticholinergics.
Anticholinergics may interfere with levodopa absorption in the small bowel, which reduces the effectiveness of Madopar or Sinemet, forms of the drug levodopa.
Anticholinergics are not usually prescribed to older people with Parkinsons because there is an increased risk of memory loss and, in men, problems urinating.
Read Also: Is There A Medical Test For Parkinson’s
Advantages Of Comt Inhibitors
When used with levodopa, COMT inhibitors can reduce the daily off time and increase the on time.
In many cases, the dose and frequency of levodopa can also be reduced.
The terms on/off or motor fluctuations refer to the period when people can no longer rely on the smooth and even symptom control that their drugs once gave them.
What Is The Effect Of Dietary Protein On Carbidopa
The main medication for people with Parkinsons is carbidopa-levodopa. In the body, protein is broken down into building blocks called amino acids. In order to absorb and use these amino acids, your body needs a carrier to transport them to the blood and the brain. Imagine that this carrier is like a bus. Because carbidopa-levodopa and amino acids have a similar shape, they use the same bus to transport them to the blood and brain. Since the bus has limited seats, when you eat protein and take carbidopa-levodopa in the same meal, the seats in the bus are full and less carbidopa-levodopa is absorbed. When less carbidopa-levodopa reaches the brain, your motor and non-motor symptoms can worsen.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Treat Parkinson’s Disease Naturally
What Exactly Is The : 1 Diet And How Is It Planned
The 7:1 diet balances carbohydrate and protein, allowing for 7 parts carbohydrate for one part protein. Each meal and snack is planned in this ratio for best results. The total number of grams of protein from each of the food items to be eaten at the meal is calculated. This is determined by reading the food labels or consulting lists of protein content of foods. Based on the amount of protein at that meal, the number of grams of carbohydrate needed is calculated. For example, if 10 grams of protein is included at breakfast, 7 times that amount or 70 grams of carbohydrate needs to be included at breakfast as well.
Protein is found in a wide variety of foods. Foods highest in protein include milk and other dairy products and meats . But even starchy foods such as breads, dried beans or peas, grains and cereals have protein which needs to be accounted for. They are, however, relatively high in carbohydrate.
Foods high in carbohydrate and low in protein include fruits and juices, sugar and syrups, sorbet and sherberts, soda and other sweetened beverages. These can be added to your meals to help shift the balance to 7:1. A rule of thumb is to keep meat and dairy portions small and fruit/juice and starch servings large to help improve your ratio.
Rule Of Thumb To Improve Absorption:
- Take carbidopa-levodopa one hour before a meal
| 3rd dose | Drink with a large glass of water. |
As Parkinsons progresses, you may need to take carbidopa-levodopa four to six times a day. The goal is to create a steady-state level of medicine in your blood. Thus, it becomes more challenging with protein and medication timing. Be practical. Try to take your medication at least 30 minutes before you eat, and flush it down with a big glass of water . Since carbidopa-levodopa isnt absorbed in your stomach but rather in your small intestine, drinking water helps move the medication quickly to your small intestine. If the carbidopa-levodopa stays in your stomach for an hour, it will not work as effectively.
Recommended Reading: Do Parkinson’s Patients Get Violent
Modeling Intestinal Absorption Of Levodopa Using A Combined Pbpkcobra Model
Figure 1
The multiscale PBPKCOBRA model used in this study. We combined a spatially and temporally refined PBPK model of the gastrointestinal tract with seven copies of a mechanistically accurate and detailed metabolic model of small intestinal epithelial cells . COBRA, constraint-based reconstruction and analysis PBPK, physiologically based pharmacokinetic WB-ACAT, whole-body advanced compartmental absorption and transit.
Using the WB-ACAT-sIEC model, we predicted that the addition of serine in the systemic circulation could improve the bioavailability of levodopa as shown by the increase of the AUC above the efficacy threshold . The subsequent increase of amino acids concentration in the plasma improved the bioavailability of the next dose through a higher absorption in the basolateral side of the seven compartments of the small intestine. Taken together, we propose that a serine-rich meal after a levodopa dose could improve the brain bioavailability of levodopa.
Protein Shows Promise In Treating Parkinson’s Disease
by Kayla Zacharias, Purdue University
The true cause of Parkinson’s disease is still a mystery to researchers, although they do know that in many patients, a protein called alpha-synuclein tends to aggregate in brain cells. But a different protein could help stop that aggregation, according to a new study in the Journal of Molecular Biology.
HYPE, the only Fic protein found in humans, is a key regulator of whether cells live or die under stress. In order to work properly, proteins need to fold in the correct shape. When cells are stressed, their proteins can become misfolded, at which point they can aggregate and become toxic. Cells sense stress by assessing the amount of misfolded proteins within them.
“Since HYPE plays such an important role in how cells deal with stress from misfolded proteins, we wondered whether diseases that result from protein misfolding were likely to need HYPE,” said Seema Mattoo, an assistant professor of biological sciences at Purdue University. “We know that in Parkinson’s disease, often the misfolded protein is aSyn. So we asked if HYPE could modify aSyn, and if so, what are the consequences?”
The study shows that HYPE does modify aSynand that this new modification, called AMPylation, decreases aggregation.
Clumps of aSyn, known as Lewy bodies, are the pathological hallmark of Parkinson’s disease. Aggregated aSyn can poke holes in the membranes of neurons, which causes a decline in nerve function and messes up how nerve cells communicate.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Donations In Memory Of
Why Not Just Take Dopamine
In theory, the simplest way to treat Parkinsons would be to directly replace the dopamine lost via supplements. But, theres a complication. Dopamine itself is unable to cross the blood-brain barrier a natural barrier that protects the brain from bacteria and viruses that may be in the blood. This means that taking dopamine directly is ineffective as it cant get from the blood into the brain.
Fortunately, levodopa can cross the blood-brain barrier, into the brain, where its turned into dopamine.
Taking Levodopa Medication: Co
Co-beneldopa is a type of generic levodopa medication. Madopar is the brand name for co-beneldopa.
It contains two ingredients, levodopa and benserazide. The benserazide ingredient helps levodopa get in to the brain where it can be converted to dopamine.
The dose of co-beneldopa is expressed with the levodopa content first and then the benserazide content. For example, Madopar 50/12.5 contains 50 mg levodopa and 12.5 mg of benserazide.
Below we have included the different forms of co-beneldopa medication and some key points on taking them. The most recent and complete information on your specific drug will be on your patient information leaflet that comes with your medication packet. Always read it carefully before you start your treatment.
For detailed information you should follow the advice of your specialist or Parkinsons nurse about how to take co-beneldopa so that it works well for your Parkinsons.
Read Also: Nutrition For Parkinson’s Disease