Baseline Knowledge And Preferences For Disclosure In Participants/patients And Their Families
A few studies provide preliminary evidence that participants of studies, patients, and caregivers are interested in learning about GBA related-conditions as additional or secondary findings . A study of 533 individuals, comprised of individuals with Parkinson disease and their caregivers, found that 93% were interested in hearing results related to Gaucher disease as part of their genetic testing for Parkinson disease. Of note is that after receiving information about Gaucher disease, GBA mutations, and relationships to Parkinson disease, there were gaps in knowledge scores on testing, suggesting more education about the implications of genetic testing is needed . Brothers and colleagues recruited families from a pediatric neurology clinic to explore their preferences in receiving SFs identified by genomic sequencing. Thirteen categories of conditions representing secondary results were provided, including Parkinson disease. They reported that over 90% of participants would be likely to request secondary results regarding Parkinson disease .
| The National Gaucher Foundation: |
| Gaucher Life: ) |
| Parkinson Disease Foundation: |
Clinical Manifestations Of Parkinson Disease
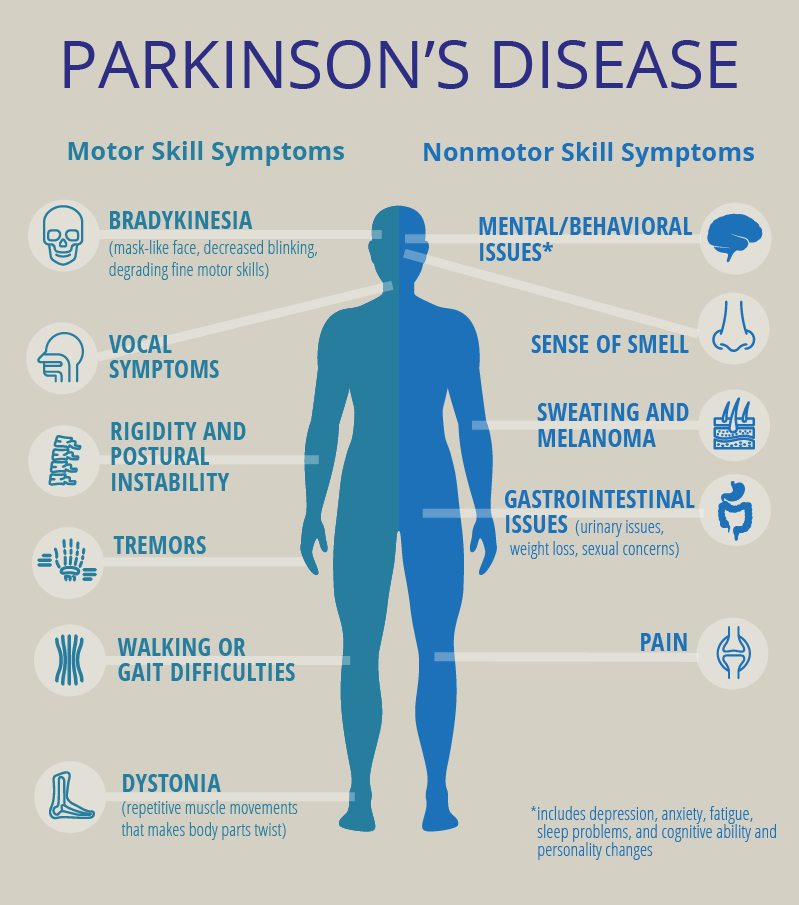
Parkinson disease, a neurodegenerative disorder, is characterized by rest tremor, muscle rigidity, slowed movement , and often postural instability. Onset is typically unilateral and may include other abnormal movements such as postural or action tremor as well as limb dystonia. Common associated non-motor findings include insomnia, depression, anxiety, rapid-eye-movement sleep behavior disorder, fatigue, constipation, dysautonomia, and hyposmia. As part of a prodromal phase, non-motor features may predate formal diagnosis of Parkinson disease by years. With disease progression, bilateral manifestations, balance disturbances, and other complications such as levodopa-induced dyskinesia and motor fluctuations develop. Dementia and/or psychosis occur in 30%-40%.
The diagnosis of Parkinson disease is based on the clinical findings of bradykinesia plus rest tremor and/or rigidity. An important supportive diagnostic feature is an observable response to dopaminergic therapy. Dementia is not an exclusion criterion for diagnosis. While developed for use in a genetic research study, the diagnostic criteria summarized in the following citations are increasingly being used to guide diagnosis in a clinical setting .
Parkinson disease: related terms in use in the clinical setting
The cardinal histopathologic feature of Parkinson disease is the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra with intracytoplasmic inclusions in the remaining intact nigral neurons.
Mri In Parkinson’s Testing
One of the more common tests done during a neurologic workup is an MRI scan and one may think that in the investigation of a disease that affects the brain such as Parkinsons, this imaging test would be a necessity. In the context of Parkinsons disease, however, an MRI is not particularly helpful. It looks at the structure of the brain which, for all intents and purposes, appears normal in this disease. An MRI may, however, be indicated when symptoms appear in younger people or if the clinical picture or the progression of symptoms is not typical for Parkinsons. In these situations, MRI can be used to rule out other disorders such as stroke, tumors, hydrocephalus , and Wilsons Disease .
You May Like: Prayers For Parkinson’s Disease
Whole Genome/exome Sequencing And Genome
Whole genome sequencing is a laboratory test utilized to determine the arrangement of an individuals entire genome at a single time. WGS allows the identification of mutations in the genome without having to target a gene or chromosome region based upon an individuals personal or family history. WGS may also be referred to as full genome sequencing, complete genome sequencing or entire genome sequencing.
Exome sequencing, also referred to as whole exome sequencing or WES, is an alternative to WGS. It is a laboratory test used to determine the sequence of the protein coding regions of the genome. The exome is the part of the genome that encodes protein, where roughly 85% of variants are known to contribute to diseases in humans. Exome sequencing has been proposed as a diagnostic method to identify these genetic variants in patients not diagnosed by traditional diagnostic and genetic testing approaches.
Genome-wide association studies , also referred to as genome-wide analysis, is a method to identify genes involved in human disease by comparing the genome of individuals who have a disease or condition to the genome of individuals without the disease or condition. GWAS are performed using microarrays to search the genome for small variations, called single nucleotide polymorphisms , that occur more often in individuals with a specific disorder than in those who do not have a disorder.
Cooperation With The University Of Lbeck And Denali Therapeutics Inc

CENTOGENEs partners from the University of Lübeck will contribute to further clinical and genetic assessments via the program, LRRK2 International Parkinsons Disease Project . All ROPAD-enrolled participants with any genetic mutation can be enrolled in the LIPAD study. Additionally, the University of Lübeck aims to collect 500 healthy controls , who are recruited from the families of unaffected mutation carrier.
For the idiopathic PD patients, the University of Lübeck aims to collect 1,500 PD patients without a mutation in LRRK2, who are recruited from those who have tested negative.
CENTOGENE’s pharmaceutical partner DENALI Therapeutics Inc. develops investigational therapies for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, as well as others. Any participant testing positive for LRRK2 mutations that meets eligibility criteria may be offered participation in one of their future clinical studies.
Don’t Miss: Ten Steps To Identify Atypical Parkinsonism
New Diagnostic Standards For Parkinsons
Until recently, the gold-standard checklist for diagnosis came from the U.K.s Parkinsons Disease Society Brain Bank. It was a checklist that doctors followed to determine if the symptoms they saw fit the disease. But thats now considered outdated. Recently, new criteria from the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society have come into use. This list reflects the most current understanding of the condition. It allows doctors to reach a more accurate diagnosis so patients can begin treatment at earlier stages.
What Does It Mean
Pregnancy may be uncommon among women with PD, but neurologists should be prepared to treat women who are trying to conceive or who become pregnant. The limited evidence available suggests that levodopa can safely be taken for PD movement symptoms during pregnancy. Possible explanations for worsening of symptoms include PD progression, changes in how PD medications are metabolized during pregnancy, the physical stress of pregnancy, or simply taking too little levodopa.
The study authors caution that their recommendations are based on a relatively small number of cases. There have been no formal clinical trials, which means pregnant women and their providers should rely on available data and use common sense. Medications with limited effects should be avoided, and motor symptoms controlled with physical therapy, occupational therapy and levodopa as needed. Collecting additional data is timely, and the researchers aim to develop a registry. They plan to collect data on women with PD who become pregnant, which would help in developing guidelines for giving them the best care.
Don’t Miss: Drugs Prescribed For Parkinson’s Disease
The Genetic Addiction Risk Score
Blum and associates noted that the Brain Reward Cascade is an interaction of neurotransmitters and their respective genes to control the amount of dopamine released within the brain. Any variations within this pathway, whether genetic or environmental , may result in addictive behaviors or reward deficiency syndrome , which was coined to define addictive behaviors and their genetic components. These investigators searched a number of important databases including: Filtered: Cochrane Systematic reviews DARE PubMed Central Clinical Quaries National Guideline Clearinghouse and unfiltered resources: PsychINFO ACP PIER PsychSage PubMed/Medline. The major search terms included: dopamine agonist therapy for addiction dopamine agonist therapy for reward dependence dopamine antagonistic therapy for addiction dopamine antagonistic therapy for reward dependence and neurogenetics of RDS. While there are many studies claiming a genetic association with RDS behavior, not all are scientifically accurate. The authors concluded that albeit their bias, this Clinical Pearl discussed the facts and fictions behind molecular genetic testing in RDS and the significance behind the development of the Genetic Addiction Risk Score , the first test to accurately predict one’s genetic risk for RDS. The clinical value of the Genetic Addiction Risk Score has yet to be determined.
Conjoined Twins In A Triplet Set
Eighteen-year-old triplets, Mackenzie, Macey and Madeline Garrison from Iowa, are unique in that Mackenzie and Macey were originally part of a conjoined twin pair . The three sisters, who appear to be identical from photographs, differ considerably in height Mackenzie and Macey are of similar stature, but only reach as high as Madelines shoulders. The two were joined at the pelvis and separated in 2003, at age 10 months, by Dr James Stein, the chief medical officer at Childrens Hospital in Los Angeles, California. The operation required 24 hours to complete. The surgery was successful, but both triplets were left with one leg so must rely on prosthetics for mobility. Since then, they have undergone spinal surgery to correct scoliosis. The triplets were adopted by Darla Keller and her family soon after the first surgery the Kellers also have three biological sons. The triplets plan to graduate from high school and attend college, although scholarships will be required.
A recent essay on the unknown paths our lives might have taken, due to personal decisions or chance events, is worth reading in this regard . I would assert that there is an exceptional class of individuals who are able to see themselves living an alternative life they are identical twins reared apart from birth and identical twins discordant for life-changing circumstances, as is true of these triplets. Many illuminating examples of this phenomenon can be found within this rare population .
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease Drugs Side Effects
I Forgot My Password I Would Like My Password Reset How Do I Accomplish This
You can reset your password using the ‘Forgot Password’ feature found on the HIE Gateway Login page. You will enter your Gateway user name and an email containing a temporary password will be sent to the email address associated with your Gateway account. Upon login you will be asked to enter the temporary password then create a new password.
If, after reset, you are still having trouble logging in please send an email to requesting that your password be reset. Be sure to include your user name and the email address with which you registered for reference. Help Desk staff will send you an email response with your new password.
What Are The Symptoms Of Stage 1 Parkinsons
The first stage is the introduction of the product. Mild symptoms do not interfere with daily activities during this initial stage of the disease. There is only one side of the body that is affected by tremors and other movement symptoms. A change in posture, walking, and facial expressions is observed.
Don’t Miss: Nursing Management Of Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons disease is the deterioration of brain nerves that control movement. The symptoms of Parkinsons disease have a slow onset and get worse over time. You may experience a gradual onset of symptoms, or notice several changes all at once.
Perhaps the most well-known symptom of Parkinsons disease is the development of a tremor. You may notice that your fingers, hands, or chin shake uncontrollably. Other symptoms include:
- Change in handwriting specifically smaller handwriting
- Changes in your tone of voice specifically speaking more quietly
- Lack of facial expressions
- Dizziness and fainting
- Beginning to walk with a hunched back
It is important to keep in mind that medications and other medical conditions can cause symptoms similar to those listed above. But, if you are experiencing a combination of these symptoms, it may be a sign of Parkinsons disease.
While there is not currently a cure for Parkinsons disease, many treatment options are available that can help ease your symptoms. Treatments may include medicine, therapy, and even surgery. Each case of Parkinsons disease is unique, and your treatment plan should be, too.
What Do I Do Once I Have The Results
Prenatal test results can help you make important health care decisions. But its important to remember that many of them tell you its possible, but not certain, that your baby will be born with a disorder. No test is 100% accurate.
Talk to your doctor about the results you get and what they mean. A genetics counselor can also help you decide what to do after a positive result and what life will be like for your child if they have a disorder.
You May Like: Early Parkinson’s Symptoms In Young Adults
What Is The Prenatal Screening Program
The activities of the California Prenatal Screening Program are focused on detecting birth defects during pregnancy. PNS is working to assure prenatal screening services and follow-up diagnostic services, where indicated, are available to all pregnant women in California. The Prenatal Screening Program provides pregnant women with a risk assessment for open neural tube defects , Down syndrome , trisomy 18 and SLOS through one or two blood tests. The screening test indicates risk, but does not diagnose fetal birth defects. For women with screening results indicating a high risk for a birth defect, the Program provides free follow-up diagnostic services at State-approved Prenatal Diagnosis Centers . Services offered at these Centers include genetic counseling, ultrasound, and amniocentesis. Participation in the screening testing and follow-up services is voluntary. The cost of the testing through the Prenatal Screening Program is $207.
Prenatal Testing And Preimplantation Genetic Testing
Once the DNAJC6 pathogenic variants have been identified in an affected family member, for a pregnancy at increased risk and are possible.
Differences in perspective may exist among medical professionals and within families regarding the use of . While most centers would consider use of prenatal testing to be a personal decision, discussion of these issues may be helpful.
Don’t Miss: Anesthesia Drugs To Avoid With Parkinson’s
Mitochondrial Recessive Ataxia Syndrome
Gramstad et al noted that mutations in the catalytic subunit of polymerase gamma produce a wide variety of neurological disorders including a progressive ataxic syndrome with epilepsy: mitochondrial SCA and epilepsy . The authors earlier studies of patients with this syndrome raised the possibility of more prominent right than left hemisphere dysfunction. To investigate this in more detail, 8 patients were studied. All completed an intelligence test , and 4 were also given memory tests and a comprehensive neuropsychological test battery. Patients with MSCAE showed significant cognitive dysfunction. Mean Verbal IQ was significantly better than Performance IQ , but memory testing and neuropsychological testing failed to detect a consistent unilateral dysfunction. The authors concluded that further studies are needed to define the profile and development of cognitive symptoms in this disorder.
Furthermore, UpToDate reviews on Overview of the hereditary ataxias and The spinocerebellar ataxias do not mention the use of POLG1 genetic testing.
Ropad Study Rational And Screening Strategy
PD can be caused by several factors, including environmental factors, genetics, and aging. In recent years, a growing number of PD related genes have been described including LRRK2 and GBA. Thus, the identification of new genes and mutations associated with PD will not only improve our understanding of the underlying molecular mechanisms, but may also lead to the development of new drugs and treatments.
- Step 1: The whole GBA gene as well as LRRK2 gene hotspots is analyzed.
- Step 2: If the first step produces a negative result, a comprehensive combined analysis of 68 PD associated genes is applied as a second step. This gene panel covers the known PD-causing genes, along with an additional set of genes, which have been recommended by leading genetic and neurology specialists or are suspected to cause disorders that may mimic PD.
- Step 3: If the first and second steps produce negative results and strong evidence of a genetic cause is present, whole genome sequencing will be carried out. This third step may result in the identification of novel genetic causes of PD.
In the case of a LRRK2 mutation, the participant may be offered participation in future clinical studies.
You May Like: Beginning Signs Of Parkinson’s
Familial Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a progressive neurodegenerative disease involving both the upper motor neurons and lower motor neurons . UMN signs include hyperreflexia, extensor plantar response, increased muscle tone, and weakness in a topographical representation. LMN signs include weakness, muscle wasting, hyporeflexia, muscle cramps, and fasciculations. In the early stage of the disease, the clinical aspects of ALS can vary. Affected individuals typically present with asymmetric focal weakness of the extremities or bulbar findings . Other findings include muscle fasciculations, muscle cramps, and lability of affect but not necessarily mood. Regardless of initial symptoms, atrophy and weakness eventually affect other muscles. Approximately 5,000 people in the U.S. are diagnosed with AML each year.
Most people with ALS have a form of the condition that is described as sporadic or non-inherited. The cause of sporadic ALS is largely unknown but probably involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors. About 10 % of people with ALS have a familial form of the condition, which is caused by an inherited genetic mutation, usually as an autosomal dominant trait. The mean age of onset of ALS in individuals with no known family history is 56 years and in familial ALS it is 46 years.
Familial Cold Autoinflammatory Syndrome
Familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome , also known as familial cold urticaria , is an autosomal dominant condition characterized by rash, conjunctivitis, fever/chills and arthralgias elicited by exposure to cold sometimes temperatures below 22° C . It is rare and is estimated as having a prevalence of 1 per million people and mainly affects Americans and Europeans. Familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome is one of the cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes caused by mutations in the CIAS1/NALP3 gene at location 1q44. Familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome shares symptoms, and should not be confused, with acquired cold urticaria, a more common condition mediated by different mechanisms that usually develop later in life and are rarely inherited. There is insufficient evidence to support the use of genetic testing in the management of patients with FCAS/FCU. UpToDate reviews on “Cold urticaria” and “Cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes and related disorders” do not mention the use of genetic testing.
Read Also: How To Tell Difference Between Parkinson’s And Essential Tremor