What Are The Stages Of Parkinsons
Doctors sometimes use five stages to describe the progress of Parkinsons disease. Each stage presents changing or new symptoms that a person is likely to encounter.
It is worth noting that not everyone will reach the advanced stages. For some people, the symptoms remain mild, and they can continue to live independently and be mobile.
Dividing the condition into stages helps doctors and caregivers understand and address some of the challenges a person is experiencing as it progresses.
What Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Each person with Parkinsons disease experiences symptoms in in their own unique way. Not everyone experiences all symptoms of Parkinsons disease. You may not experience symptoms in the same order as others. Some people may have mild symptoms others may have intense symptoms. How quickly symptoms worsen also varies from individual to individual and is difficult to impossible to predict at the outset.
In general, the disease progresses from early stage to mid-stage to mid-late-stage to advanced stage. This is what typically occurs during each of these stages:
Early stage
Early symptoms of Parkinsons disease are usually mild and typically occur slowly and do not interfere with daily activities. Sometimes early symptoms are not easy to detect or you may think early symptoms are simply normal signs of aging. You may have fatigue or a general sense of uneasiness. You may feel a slight tremor or have difficulty standing.
Often, a family member or friend notices some of the subtle signs before you do. They may notice things like body stiffness or lack of normal movement slow or small handwriting, lack of expression in your face, or difficulty getting out of a chair.
Mid stage
Mid-late stage
Standing and walking are becoming more difficult and may require assistance with a walker. You may need full time help to continue to live at home.
Advanced stage
Want To Learn More About The Latest Research In Parkinsons Disease Ask Your Questions In Our Research Forum
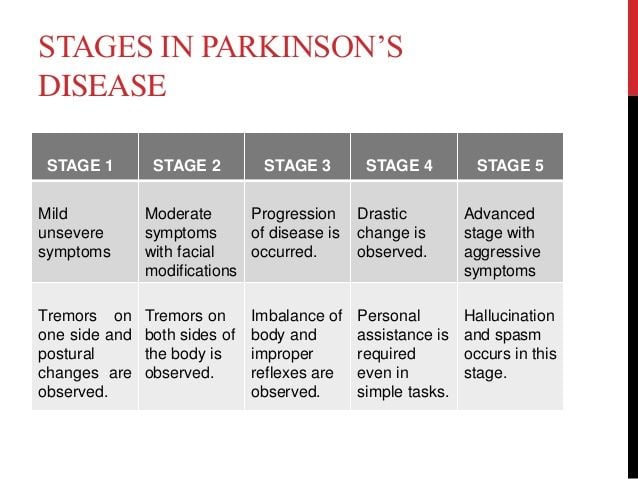
Stage 3As motor symptoms become worse, patients may begin to experience loss of balance leading to falls and movement can become very slow. Although many patients can still live independently they may have difficulty in everyday activities such as eating or dressing.
MORE: How does Parkinsons disease affect the brain?
Stage 4In this later stage, symptoms are now extremely limiting. Many patients can still stand without assistance but movement is greatly impaired. Most will need help with everyday activities and will not be able to look after themselves.
Stage 5This is the most advanced stage of the disease and most patients will experience difficulty in walking and standing, often requiring a wheelchair. Assistance will be needed in all areas of daily life as motor skills are seriously impaired. In addition, people with advanced Parkinsons disease may also begin to suffer hallucinations.
MORE: How Parkinsons disease affects your body.
Parkinsons News Today is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Multiple System Atrophy
Complications Related To Parkinson’s Can Affect Survival
Claudia Chaves, MD, is board-certified in cerebrovascular disease and neurology with a subspecialty certification in vascular neurology. She is an associate professor of neurology at Tufts Medical School and medical director of the Lahey Clinic Multiple Sclerosis Center in Lexington, Massachusetts.
Parkinson’s is a common neurodegenerative disease, and although it is not fatal, research suggests it may influence life expectancy.
A 2012 study in Archives of Neurology examined the six-year survival of nearly 140,000 Medicare beneficiaries with Parkinson’s disease in the United States. During the six-year period, 64% of the participants with Parkinson’s disease passed away.
The risk of death of those with Parkinson’s was then compared to Medicare beneficiaries who did not have Parkinson’s or any other common diseases, including:
When controlling for variables like age, race, and gender, the six-year risk of death among people with Parkinson’s was found to be nearly four times greater than those Medicare beneficiaries without the disease or other common diseases.
At the same time, the rate of death among those with Parkinson’s disease was similar to those with hip fracture, Alzheimer’s dementia, or a recent heart attackalthough it was higher than those who had been newly diagnosed with either colorectal cancer, stroke, ischemic heart disease, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Caring For Your Health With Parkinson’s Disease
In addition to caring for your Parkinson’s health, it is also important to care for your overall health. This means visiting your primary care physician periodically for preventive care like the annual flu shot and cancer screeningsfor example, a mammogram for breast cancer screening and a colonoscopy for colon cancer screening.
A primary care physician can also evaluate for risk factors related to heart attacks and strokes, and provide counseling on exercise, smoking, alcohol use, depression, or other mental health concerns. Regular visits to your primary care physician or neurologist will also allow them to catch bacterial infections like urinary tract infections before they get serious.
Read Also: Parkinson’s And Swollen Feet And Ankles
What Are Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease are typically slow to manifest themselves and may go unnoticed or disregarded until multiple symptoms appear or frequent mishaps begin to occur.
Some of the more common symptoms are:
Involuntary Tremors these tremors may occur while at rest, in the hands, arms, legs, or even through the back affecting posture.
Muscular Affliction The onset of Parkinsons may cause minor to severe:
Muscle Stiffness
Dribbling or Leaking Urine Unintentional Weight Loss
While many of the symptoms above may appear from other afflictions or illnesses, any one or a combination of them should be checked out by your primary care physician.
Is Parkinsons Disease Fatal
Parkinsons disease itself doesnt cause death. However, symptoms related to Parkinsons can be fatal. For example, injuries that occur because of a fall or problems associated with dementia can be fatal.
Some people with Parkinsons experience difficulty swallowing. This can lead to aspiration pneumonia. This condition is caused when foods, or other foreign objects, are inhaled into the lungs.
You May Like: Can Essential Tremor Become Parkinson’s
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder and the most common movement disorder. Characteristics of Parkinsons disease are progressive loss of muscle control, which leads to trembling of the limbs and head while at rest, stiffness, slowness, and impaired balance. As symptoms worsen, it may become difficult to walk, talk, and complete simple tasks.
The progression of Parkinson’s disease and the degree of impairment vary from person to person. Many people with Parkinson’s disease live long productive lives, whereas others become disabled much more quickly. Complications of Parkinsons such as falling-related injuries or pneumonia. However, studies of patent populations with and without Parkinsons Disease suggest the life expectancy for people with the disease is about the same as the general population.
Most people who develop Parkinson’s disease are 60 years of age or older. Since overall life expectancy is rising, the number of individuals with Parkinson’s disease will increase in the future. Adult-onset Parkinson’s disease is most common, but early-onset Parkinson’s disease , and juvenile-onset Parkinson’s disease can occur.
Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale
The Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale has four parts. Each part has multiple points that are individually scored, using zero for normal or no problems, 1 for minimal problems, 2 for mild problems, 3 for moderate problems, and 4 for severe problems.
These scores are tallied to indicate the severity of the disease, with 199 points being the worst and total disability and 0 meaning no disability.3
In 2001, the Movement Disorder Society updated the rating scale with involvement from patients and caregivers. The updated scale is referred to as the UPDRS-MDS, and it was published in 2008. It now includes the following sections:3
You May Like: Interventions For Parkinson’s Disease
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease occurs when nerve cells in an area of the brain called the substantia nigra become impaired or die. These cells normally produce dopamine, a chemical that helps the cells of the brain communicate . When these nerve cells become impaired or die, they produce less dopamine. Dopamine is especially important for the operation of another area of the brain called the basal ganglia. This area of the brain is responsible for organizing the brains commands for body movement. The loss of dopamine causes the movement symptoms seen in people with Parkinsons disease.
People with Parkinsons disease also lose another neurotransmitter called norepinephrine. This chemical is needed for proper functioning of the sympathetic nervous system. This system controls some of the bodys autonomic functions such as digestion, heart rate, blood pressure and breathing. Loss of norepinephrine causes some of the non-movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists arent sure what causes the neurons that produce these neurotransmitter chemicals to die.
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms
Exercise: Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, flexibility, and tremor. It is also strongly believed to improve memory, thinking and reduce the risk of falls and decrease anxiety and depression. One study in persons with Parkinsons disease showed that 2.5 hours of exercise per week resulted in improved ability to move and a slower decline in quality of life compared to those who didnt exercise or didnt start until later in the course of their disease. Some exercises to consider include strengthening or resistance training, stretching exercises or aerobics . All types of exercise are helpful.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This is not only good for your general health but can ease some of the non-movement related symptoms of Parkinsons, such as constipation. Eating foods high in fiber in particular can relieve constipation. The Mediterranean diet is one example of a healthy diet.
Preventing falls and maintaining balance: Falls are a frequent complication of Parkinson’s. While you can do many things to reduce your risk of falling, the two most important are: 1) to work with your doctor to ensure that your treatments whether medicines or deep brain stimulation are optimal and 2) to consult with a physical therapist who can assess your walking and balance. The physical therapist is the expert when it comes to recommending assistive devices or exercise to improve safety and preventing falls.
Also Check: How Long Does A Parkinson’s Patient Live
Parkinsons Disease Treatment And Its Future
Parkinsons disease has no cure. However, millions of dollars are going into research every year to help better understand the disease, from how its defined to how its treated. The ultimate end goal is developing a cure for Parkinsons, but in the meantime, doctors and researchers have developed treatment plans based on what they presume is causing the disease in the first placemost often the lack of certain brain chemicals and cells like dopamine.
The plans vary per patient, and some of these treatment options include:
There isnt any real way to definitively prevent the disease, either. As with prevention for any disease or malady, its suggested that you maintain a healthy lifestyle before and after a diagnosis. Remaining physically engaged through activities like running, yoga, and weight lifting and eating healthy are both ways to provide your body with the best opportunity for a healthy life.
Clinical trials are also viewed as a treatment option because they may give you as good of a chance of relieving symptoms as other already-existent treatments. There are clinical trials happening year-round with various institution and foundations, and your demographic may fit a trial in its beginning pre-clinical stage or an advanced stage.
Talk to your doctor about any available clinical trials that you may qualify for and how to become a part of them. Also stay in contact with your doctor regarding any concerns that you may have with Parkinsons or how to get it treated.
Whats Different About Young

The age of diagnosis matters for a variety of reasons, from probable causes of early cases to symptoms and treatment:
- Genetics. As with any case of Parkinsons disease, the exact cause is usually unknown. That said, The young-onset cases of Parkinsons disease are, on average, a bit more likely to be familial or genetic, says Gregory Pontone, M.D., director of the Johns Hopkins Movement Disorders Psychiatry Clinic.
- Symptoms. In many patients with YOPD, dystonia is an early symptom. People with YOPD also report more dyskinesia . They also tend to exhibit cognitive problems, such as dementia and memory issues, less frequently.
- Progression. Patients with young-onset Parkinsons appear to have a slower progression of the disease over time, says Pontone. They tend to have a milder course, staying functional and cognitively intact for much longer.
- Treatment. Most patients with Parkinsons take the medication levodopa. However, other drugs, such as MAO-B inhibitors, anticholinergics, amantadine, and dopamine receptor agonists, may be used before levodopa.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Disease And Vision Problems
We Compiled The Most Popular Parkinsons Questions And Answers In One Place
As your Parkinsons disease journey evolves, so do your questions about symptoms, treatment options, research and medications. Whether you live with Parkinsons or care for someone who does, you are not alone in looking for answers to your big PD questions.
The Parkinsons Foundation has recently released Frequently Asked Questions: A Guide to Parkinsons Disease, a new and improved booklet that provides answers to the most frequently asked questions our Helpline receives. Pro tip: every section in the booklet provides additional free resources you can check out to learn more. Order the free book now, read it online or check out some questions and answers below:
Q: Can Parkinsons be cured?
A: Not yet. However, many PD symptoms can be treated and researchers are making advances in understanding the disease, its causes and how to best treat it.
Q: What are the stages of Parkinsons?
A: The stages of Parkinsons correspond to the severity of movement symptoms and to how much the disease affects a persons daily activities. At all stages of Parkinsons, effective therapies are available to ease symptoms and make it possible for people with PD to live well.
Q: How can I find a doctor who can treat Parkinsons?
Q: Is it okay to drink alcohol?
A: Consult your doctor first. Generally, moderate consumption should be acceptable for people with PD, if there are no medical conditions or medications that prohibit alcohol use.
Q: Are there any new Parkinsons drugs on the horizon?
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinsons disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare teams efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinsons disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
Also Check: Wearable Technology For Parkinson Disease
Specialized Parkinsons Care At Saint Simeons
Saint Simeons is committed to providing a higher quality of life for those in need of Parkinsons disease. We provide a unique program developed specifically for people with Parkinsons disease. This program is under the direction of Dr. Mary Nole, who develops customized wellness plans for each participant.
The Parkinsons disease program at Saint Simeons is unlike any other in Oklahoma. Our dedicated nursing staff and wellness team have received specialized Parkinsons disease education and training to maintain or restore skills that may have deteriorated. Saint Simeons Parkinsons care is endorsed by the Parkinson Foundation of Oklahoma and the American Parkinson Disease Association. For more information, dont hesitate to contact us today.
How Do I Prevent Falls From Common Hazards
- Floors: Remove all loose wires, cords, and throw rugs. Minimize clutter. Make sure rugs are anchored and smooth. Keep furniture in its usual place.
- Bathroom: Install grab bars and non-skid tape in the tub or shower. Use non-skid bath mats on the floor or install wall-to-wall carpeting.
- Lighting: Make sure halls, stairways, and entrances are well-lit. Install a night light in your bathroom or hallway and staircase. Turn lights on if you get up in the middle of the night. Make sure lamps or light switches are within reach of the bed if you have to get up during the night.
- Kitchen: Install non-skid rubber mats near the sink and stove. Clean spills immediately.
- Stairs: Make sure treads, rails, and rugs are secure. Install a rail on both sides of the stairs. If stairs are a threat, it might be helpful to arrange most of your activities on the lower level to reduce the number of times you must climb the stairs.
- Entrances and doorways: Install metal handles on the walls adjacent to the doorknobs of all doors to make it more secure as you travel through the doorway.
You May Like: Home Exercise For Parkinson Disease
Is Rem Sleep Behavior Disorder An Early Non
If RBD cannot be specifically attributed to the abnormal synuclein staining observed in Braak Stages 1 and 2, then we must evaluate other evidence that RBD, in the setting of neurodegenerative synucleinopathies, is in fact due to involvement of brainstem nondopaminergic systems. One potential source of supportive data would be postmortem analysis in the context of such diseases that RBD can occur in the absence of SN involvement. To date there have been postmortem analyses of 27 RBD brains associated with synucleinopathies. Among these, the SN was examined in 7 brains, and all of these brains exhibited SN neuron loss and synuclein pathology. Thus, we are unaware of a single case in which RBD was associated with a synucleinopathy without co-existing involvement of the SN.
While the occurrence of RBD prior to parkinsonism in PD has often been offered as evidence that specifically supports the Braak staging scheme of PD, it cannot be accepted as such. In many cases, RBD precedes parkinsonism in the multiple system atrophies ,. While MSA is also a synucleinopathy, characterized by synuclein-positive glial inclusions, it does not manifest intraneuronal synucleinopathy, and the Braak staging scheme cannot be proposed to occur.