Treatment Of Vascular Parkinsonism
The most commonly used medications for vascular Parkinsonism are L-dopa and amantadine. However, some people with Parkinsonism do not experience significant improvement with medication. Some stroke survivors who have vascular Parkinsonism can experience better muscle control with physical therapy. Often, safety measures need to be taken to avoid falls.
If you have already had recurrent strokes resulting in vascular Parkinsonism, you may be at risk of experiencing more strokes over the coming years if no action is taken to reduce your risk. Therefore, if you have been diagnosed with vascular Parkinsonism, it is particularly important to follow up with your doctor in order to prevent additional strokes. You should expect to have testing for stroke risk factors and medical treatment to reduce your risk of stroke.
There are also a number of lifestyle factors that can help reduce stroke risk, such as getting regular moderate exercise and quitting smoking if you smoke. Eating a healthy diet is also important.
Dont Miss: Are There Service Dogs For Parkinsons Patients
Cognitive Symptoms Of Lewy Body Dementia
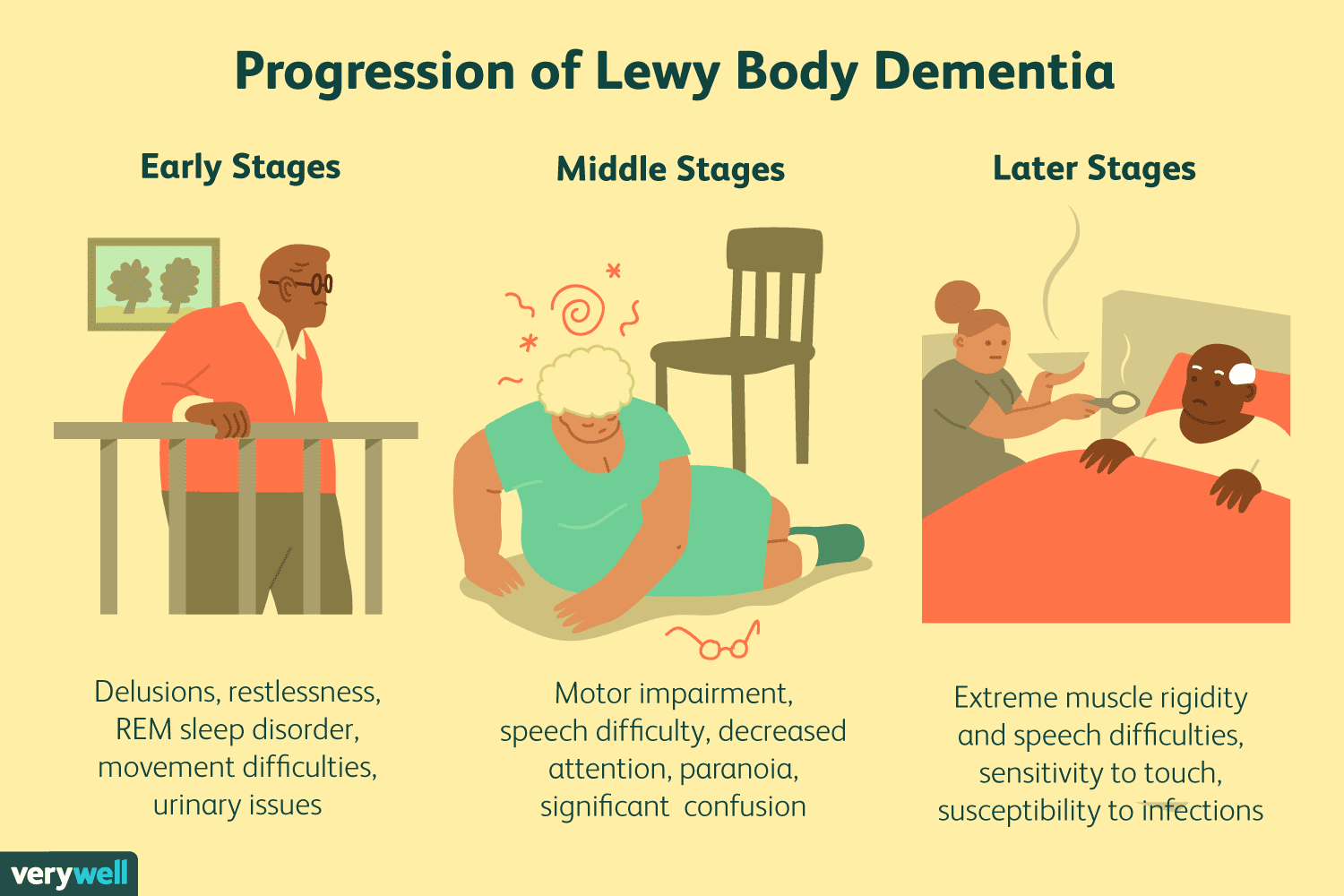
LBD causes changes in thinking abilities. These changes may include:
- Visual hallucinations, or seeing things that are not present. Visual hallucinations occur in up to 80 percent of people with LBD, often early on. Nonvisual hallucinations, such as hearing or smelling things that are not present, are less common than visual ones but may also occur.
- Unpredictable changes in concentration, attention, alertness, and wakefulness from day to day and sometimes throughout the day. Ideas may be disorganized, unclear, or illogical. These kinds of changes are common in LBD and may help distinguish it from Alzheimer’s disease.
- Severe loss of thinking abilities that interfere with daily activities. Unlike in Alzheimer’s dementia, memory problems may not be evident at first but often arise as LBD progresses. Other changes related to thinking may include poor judgment, confusion about time and place, and difficulty with language and numbers.
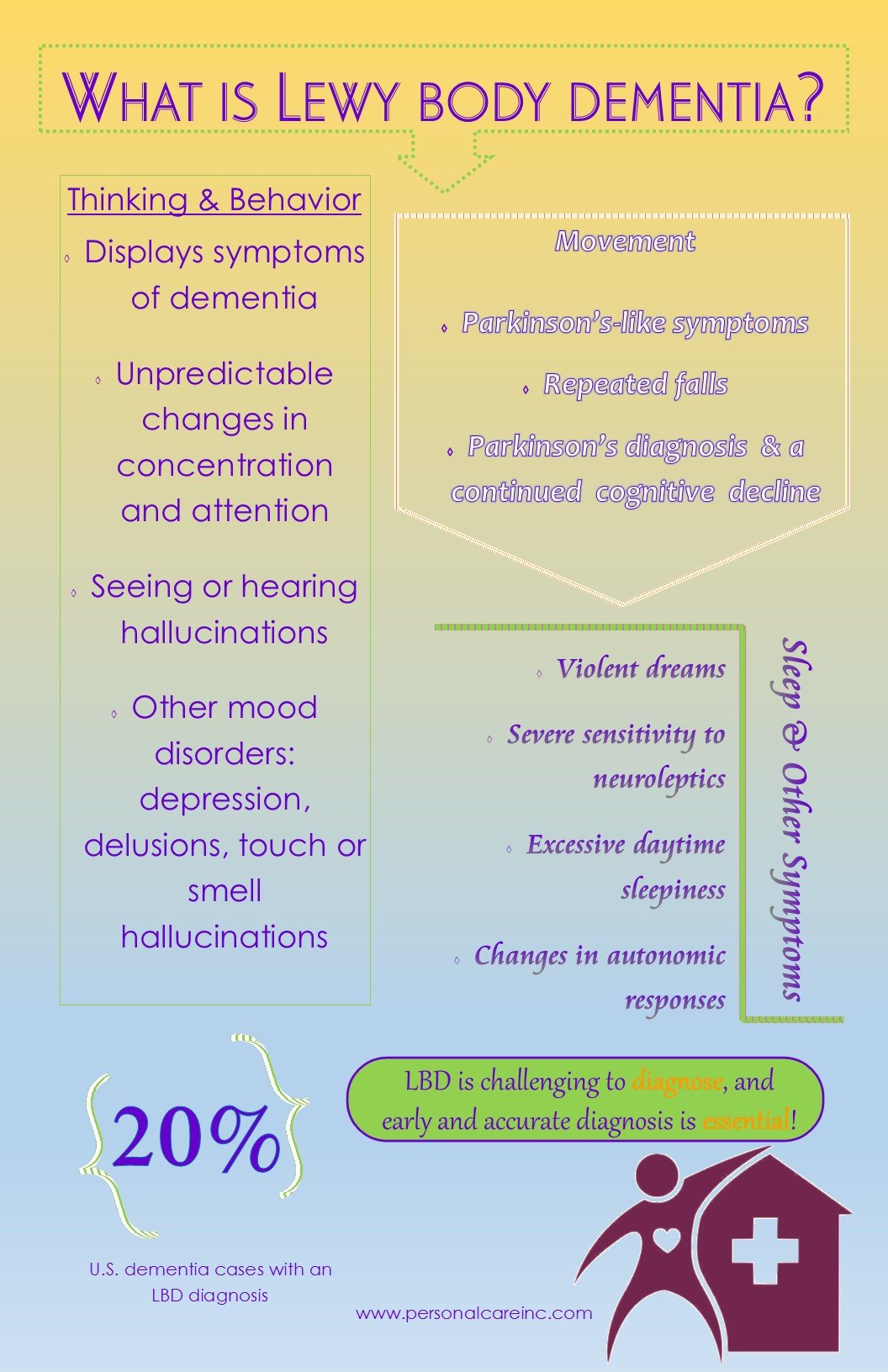
What Are The Symptoms Of Lewy Body Dementia
Lewy body dementia symptoms may resemble those of other neurological disorders, like Alzheimers disease and Parkinsons disease. LBD affects each person differently, and symptoms vary in severity.
Common symptoms of LBD include:
- Visual hallucinations, or seeing things that are not there.
- Reduced alertness, attention and ability to concentrate.
- Parkinsonism, a movement disorder with symptoms including slowness, tremors, stiffness, balance problems, soft voice, difficulty swallowing, reduced facial expression and shuffling walk.
- Visuospatial difficulties, including decreased depth perception, trouble recognizing familiar objects and impaired hand-eye coordination.
- Delusions, or beliefs with no basis in reality.
- Changes in behavior and mood including anxiety, agitation, aggression, apathy, depression and paranoia.
- Changes in sleep patterns.
Other symptoms include:
- Acting out while sleeping. Your loved one may act out their dreams during a phase of sleep cycle called rapid eye movement . Sometimes this happens years before their LBD diagnosis. Often called REM sleep behavior disorder , this condition is described as frequent movements, such as flailing or punching, with yelling or speaking while sleeping. People living with RBD often have difficulty separating dreams from reality when they wake up.
- Changes in normal body functions. Body temperature may waver, blood pressure may fluctuate and loss of bowel and bladder control.
Recommended Reading: Restore Gold Parkinson’s Reviews
Diagnostic Criteria For Parkinson Disease Dementia
Consensus criteria for PDD were developed in 2007 . These criteria require cognitive impairments across multiple domains but emphasize that noncognitive features such as hallucinations are common. As described previously in the article, the clinical and neuropsychological features of DLB and PDD are similar. Indeed, it is the relative timing of dementia and parkinsonism that defines the clinical distinction between DLB and PDD. Controversy exists over how or whether to distinguish these syndromes.
Treatment And Care For Lewy Body Dementia
While LBD currently cannot be prevented or cured, some symptoms may respond to treatment for a period of time. An LBD treatment plan may involve medications, physical and other types of therapy, and counseling. A plan to make any home safety updates and identify any equipment can make everyday tasks easier.
A skilled care team often can suggest ways to improve quality of life for both people with LBD and their caregivers.
Also Check: Everything You Need To Know About Caregiving For Parkinson’s Disease
Tests For Dementia With Lewy Bodies
There’s no single test for dementia with Lewy bodies.
The following may be needed to make a diagnosis:
- an assessment of symptoms for example, whether there are typical symptoms of dementia with Lewy bodies
- an assessment of mental abilities this will usually involve a number of tasks and questions
- blood tests to rule out conditions with similar symptoms
- brain scans, such as an MRI scan, CT scan or a SPECT scan these can detect signs of dementia or other problems with the brain
Treatment Of Pdd And Dlb
Unfortunately, since both types of Lewy Body Dementia often display similar symptoms, patients suffering from either PDD of DLB can get misdiagnosed and subsequently prescribed the incorrect medication and method of treatment. Caregivers and medical professionals alike can increase their understanding of symptoms for each disease to help them more quickly and accurately diagnose and treat each one.
The Lewy Body Dementia Resource Center provides literature, support groups, and help for caregivers grappling with care and treatment of a loved one who has Lewy Body Dementia. Our helpline is available 12 hours a day, 7 days a week for caregivers who have questions or are in need of support. Our online resource center seeks to bring awareness and support to caregivers of those suffering with Lewy Body Dementia. Please dont hesitate to reach out to us.
Don’t Miss: What Are Some Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
Lose Weight & Exercise
Being overweight and sedentary increase your risk of having a stroke, partly because obesity and inactivity are often associated with hypertension, heart disease, and diabetes. All of these things increase the risk of an ischemic stroke.
If youre looking to get into an exercise routine and youre not sure where to start, plan to work out for 30 minutes a day, five days a week.
Also Check: Parkinsons And Immune System
What Are The Causes Of Lewy Body Dementia
The precise cause of LBD is unknown, but scientists are learning more about its biology and genetics. For example, we know that an accumulation of Lewy bodies is associated with a loss of certain neurons in the brain that produce two important chemicals that act as messengers between brain cells . One of these messengers, acetylcholine, is important for memory and learning. The other, dopamine, plays an important role in behavior, cognition, movement, motivation, sleep, and mood.
Scientists are also learning about risk factors for LBD. A risk factor is something that may increase the chance of developing a disease. Some risk factors can be controlled while others cannot. Age is considered the greatest risk factor. No specific lifestyle factor has been proven to increase one’s risk for LBD.
Other known risk factors for LBD include certain diseases and health conditions, particularly Parkinson’s disease and REM sleep behavior disorder, which have been linked to a higher risk of LBD.
Having a family member with LBD also may increase a person’s risk, though LBD is not considered a genetic disease. Variants in three genes APOE, SNCA, and GBA have been associated with an increased risk, but in most cases, the cause is unknown.
Don’t Miss: Psoriatic Arthritis And Parkinson’s Disease
Trial Population And Baseline Characteristics
Of the 640 participants screened for inclusion in the trial, 344 participants were randomly assigned to receive mevidalen or placebo. The single most common reason for screen failure was out of range MoCA score, with most excluded patients recording scores that were above the allowable range. Participant allocation and flow through the trial are shown in Figure . The baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of these 344 participants are well-balanced and shown in Table , although there was an imbalance of participants enrolled with a diagnosis for PDD or LBD, both overall and across treatment arms.
FIG 1
- Abbreviations: N, number of participants SAE, serious adverse event TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event.
Diagnostic Criteria For Dementia With Lewy Bodies
The consensus criteria for a clinical diagnosis of DLB reflect the clinical features described previously in this article . Progressive cognitive decline to dementia is required, often involving attention, executive function, and visual-spatial skills. The core features of these criteria include the following: recurrent visual hallucinations that are well formed and detailed fluctuations in attention and alertness and parkinsonian motor signs. Supportive features, also common in PD, include the presence of REM sleep behavior disorder, severe neuroleptic sensitivity, or low DAT uptake in the basal ganglia on SPECT or PET. A diagnosis of clinically probable DLB requires at least two out of three of the core features to be present or one core feature and one supportive feature. A diagnosis of clinically possible DLB requires only one of the three core features to be present.
Recommended Reading: Best Time To Take Parkinson’s Medication
Management Of Patients With Pdd
Non-pharmacological measures include education of the family about disease symptoms and appropriate care psychopharmacological medication), providing and promoting sufficient mental and physical activities. Before initiating pharmacological treatment conditions including systemic diseases, depression and adverse events of medication should be considered and managed appropriately. In particular, treatments with anticholinergics, tricyclic antidepressants, and benzodiazepines should be minimized and ideally discontinued where possible. The need for pharmacological intervention should be determined based on symptom frequency, severity, and burden.
Memantine, a partial NMDA receptor antagonist used in the treatment of AD, was tested in patients with DLB or PDD in two randomized controlled trials. In one, there was a significant difference in favor of memantine only in the global outcome scale, where patients with PDD had more benefits as compared to those with DLB.95 In the larger study the global outcome scale and behavioural scores were significantly better with memantine in the DLB group, whereas there were no significant differences in the PDD population.166 These results suggest that memantine may have mild beneficial effects in patients with Lewy body-related dementias, possibly more so in the DLB population, in global status and for behavioural symptoms.
What Complications Are Associated With Medications Used To Treat Lewy Body Dementia
Up to 50% of people living with Lewy body dementia can have severe side effects when treated with certain antipsychotic medications. These are known as the typical or traditional antipsychotics and include such drugs as thoridazine, haloperidol, chlorpromazine and perphenazine. This class of older, first-generation antipsychotics can cause sedation and make cognitive symptoms and movement problems worse. A life-threatening reaction to an antipsychotic medication, called neuroleptic malignant syndrome, is possible. Symptoms include rigid muscles, changing blood pressure, high fever, confusion and fast heart rate. Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you or your loved are taking an antipsychotic and develop these symptoms.
Visual hallucinations and behavioral changes may be treated with the newer, atypical antipsychotic medications pimavanserin , quetiapine or clozapine . However, because all antipsychotic medications both older, typical medications and newer atypical medications can increase the risk of death in elderly patients with dementia, you and your healthcare provider should carefully discuss the risks and benefits and using these medications.
Other medications, like antidepressants or sedative antihistamines, may increase confusion in people with LBD.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease Stage 1 Symptoms
What Happens In Dlb
People with DLB may have trouble focusing, remembering things, staying awake during the day, or staying asleep at night. They may become more frustrated or confused because of the lack of sleep. They may also hallucinate and see people, objects, or animals that are not there.
Some people with DLB will need help with walking, while others may have hunched posture or trouble using their hands and feet because of stiff muscles. People with DLB may appear to be better and need less help on some days, only to become worse and more confused again and need more help the next day or in a few days. This is because their energy level and focus will vary.
DLB is a disease that changes with time. A person with DLB can live for many years with the disease. Research suggests that a person with DLB may live an average of 57 years with the disease, although this can vary from person to person.
What Is Lewy Body Disease
Lewy body disease is caused by the degeneration and death of nerve cells in the brain. The name comes from the presence of abnormal spherical structures, called Lewy bodies, which develop inside nerve cells. It is thought that these may contribute to the death of the brain cells. They are named after the doctor who first wrote about them. It is sometimes referred to as Diffuse Lewy body disease.
Also Check: Tell Me About Parkinson’s
How Is Lewy Body Disease Diagnosed
This type of dementia is diagnosed by taking a careful history of the pattern of symptoms, and by excluding other possible causes such as Vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. A brain scan may reveal brain degeneration, but the Lewy bodies can only be identified by examination of brain tissue after death.
Lewy body disease is similar to Alzheimer’s disease in many ways, and in the past it has sometimes been difficult to distinguish the two. It has only recently been accepted as a disease in its own right. It can occur by itself or together with Alzheimer’s disease and/or Vascular dementia. It may be hard to distinguish Lewy body disease from Parkinson’s disease, and some people with Parkinson’s disease develop a dementia which is similar to that seen in Lewy body disease.
Acknowledgments And Conflict Of Interest Disclosure
Data in this manuscript are original and were generated for the purpose of this study. Photomicrographs were taken from tissue provided by the Newcastle Brain Tissue Resource, which is funded in part by a grant from the UK Medical Research Council , by Brains for Dementia research, a joint venture between Alzheimer’s Society and Alzheimer’s Research UK and by the NIHR Newcastle Biomedical Research Centre awarded to the Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust and Newcastle University. DLB research is supported by NIHR Newcastle Biomedical Research Centre in Ageing and Long-Term Conditions. LW is funded by the Alzheimer’s Society. The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
You May Like: Motor And Non Motor Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
What If You Have Parkinsons Disease And A Stroke
Stroke is relatively common and so is Parkinsons disease, so one person can have both. If you or your loved one has a stroke as well as Parkinsons disease, it is normal for you to be concerned.
The conditions have different causes, but the movement problems of Parkinsons disease combined with the effects of a stroke can make it even more difficult for you or your loved one to get around than if you only had one of the two problems.
If you have both conditions, it is more important to pay attention to things such as safeguarding your home to prevent falls and getting a walker or a cane in order to avoid falls.
Pathological And Biochemical Correlates
The core pathological hallmarks include Lewy bodies in neuronal cytoplasm and Lewy neurites. They can be seen in the brainstem nuclei, amygdala, limbic-paralimbic cortices, basal ganglia and cerebral cortex, medulla and peripheral autonomic nervous system may also be involved.46 Gliosis and neuronal loss are also present in these regions. LBs are usually found in the deeper layers of the neocortex: -synuclein is the major protein component 47 neurofilaments, ubiquitin, torsin A, and parkin minor constituents.48 Morphologically, LBs are divided into brainstem and cortical types.46 Brainstem- type LBs, easily detected by standard histological methods such as haematoxylineosin staining, are spherical intraneuronal cytoplasmic inclusions characterized by hyaline eosinophilic core, concentric lamellar band, and a narrow pale halo. Cortical LBs occur in limbic and neocortical regions, mainly in the layer II, III, V, VI of the cortex. They are not readily identifiable with classical histological stainings, and immunohistochemistry with anti–synuclein antibodies is required to detect them. DLB Consortium criteria for a pathological diagnosis of DLB proposes a classification system using -synuclein immunohistochemistry with semiquantitative grading of Lewy-related pathology in brainstem, limbic, and diffuse neocortical areas rather than counting LBs in various brain regions.8
Recommended Reading: Prayers For Parkinson’s Disease
Can Imaging Tests Diagnose Lewy Body Dementia
Imaging tests, such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging , are done to rule out other causes of dementia such as brain tumors, brain bleeds, stroke, hydrocephalus or other structural causes. Imaging studies for Lewy body dementia are usually normal. The only way to make an absolute diagnosis of LBD is by examining the brain at autopsy.
Causes Of Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Dementia with Lewy bodies is caused by clumps of protein forming inside brain cells. These abnormal deposits are called Lewy bodies.
These deposits are also found in people with Parkinson’s disease, and they build up in areas of the brain responsible for functions such as thinking, visual perception and muscle movement.
It’s not clear why the deposits develop and how exactly they damage the brain. It’s thought that part of the problem is the proteins affecting the brain’s normal functions by interfering with signals sent between brain cells.
Dementia with Lewy bodies usually occurs in people with no family history of the condition, although there have been very rare cases that seem to run in families.
Also Check: Pre Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms
What Can I Expect If I Or My Loved One Have A Diagnosis Of Lewy Body Dementia
Each persons experience with Lewy body dementia is unique to them. How slowly or quickly the disease progresses is impossible to know, but may be influenced by your general health and any existing diseases you may have. Because LBD is a progressive disease, difficulties with mind and body functions get worse over time. Currently, there is no known way to stop the progression of the disease. After diagnosis, most people with LBD live between five and seven years. Some people with LBD live up to 20 years after their diagnosis.
However, theres always hope. Research on LBD, dementia with lewy bodies, Alzheimers disease, Parkinsons disease with dementia are ongoing. New medications are being developed and new approaches to treatment are being investigated.