Medication Guidelines For Parkinson’s Disease
There is no one best mix of Parkinsonâs medicines. You and your doctor will have to try a few treatment approaches to figure out the best one for you.
But there are some general guidelines for taking your medication. Be sure to ask your doctor or pharmacist for any specific tips for your treatment.
Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease
The causes of Parkinsons disease are still greatly unknown. Scientists who have studied this disorder estimate that 10-15% of cases come from genetics after seeing a series of genetic mutations that were common in Parkinsons patients.
Doctors suspect that environmental factors and lifestyle choices may have effects on the severity of Parkinsons disease symptoms. Exposure to chemicals like pesticides may increase the likelihood of developing Parkinsons disease. On the other hand, a good diet and regular exercise may decrease your chances.
Alternative Treatments For Parkinson’s Disease
Alternative therapy may also be used to treat Parkinson’s disease. The most touted in recent years has been the effect of Vitamin E on reversing the progression of the disease although, this effect is still being debated by the scientific community.
Relaxation and guided imagery have also been suggested to help with stress, depression, and anxiety. Medical studies have shown that relaxation and guided imagery may help slow the progression of symptoms as well as quicken healing time after surgeries or injuries.
Don’t Miss: How Do They Test You For Parkinson’s Disease
Anticholinergics For Early On
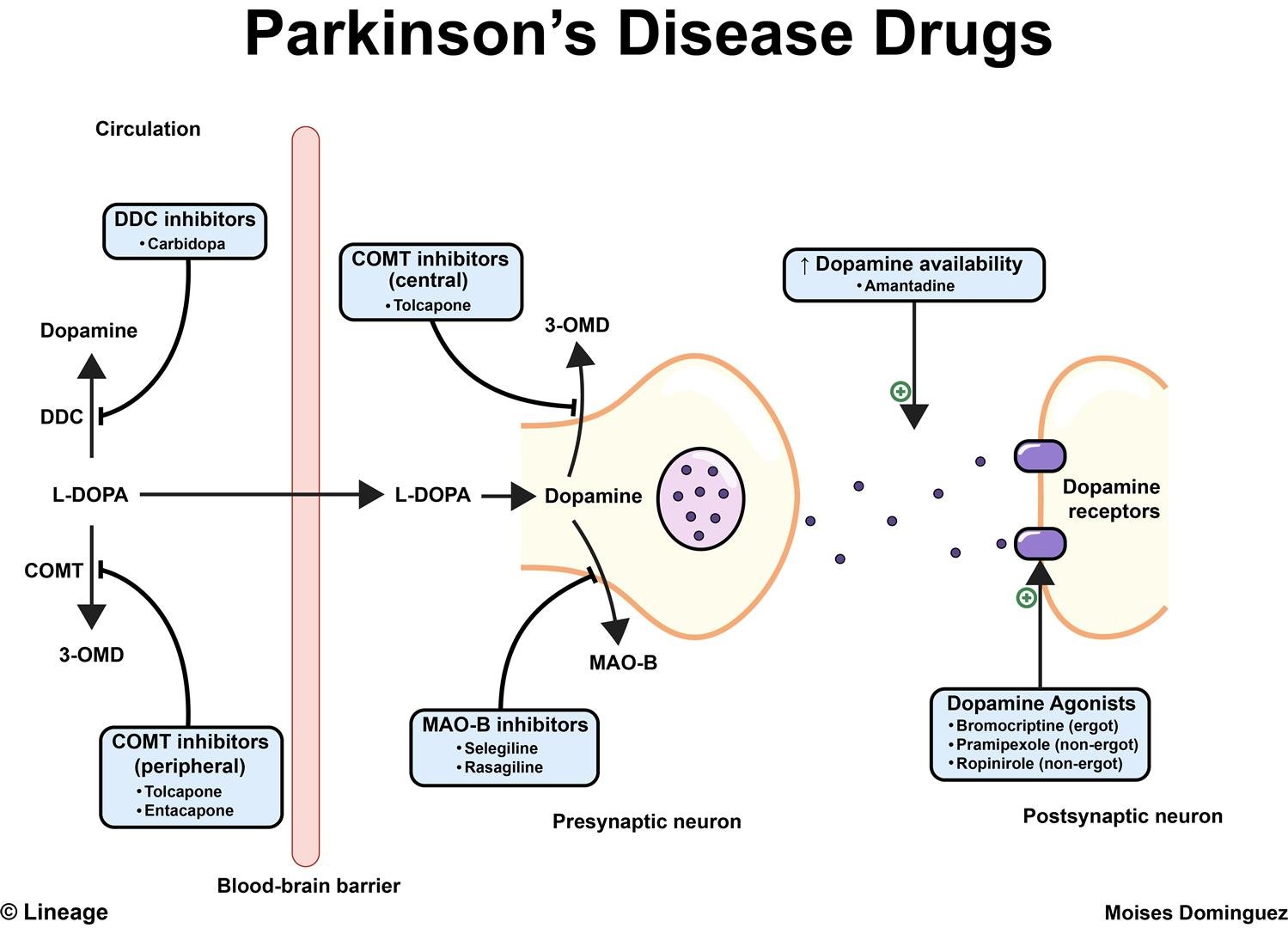
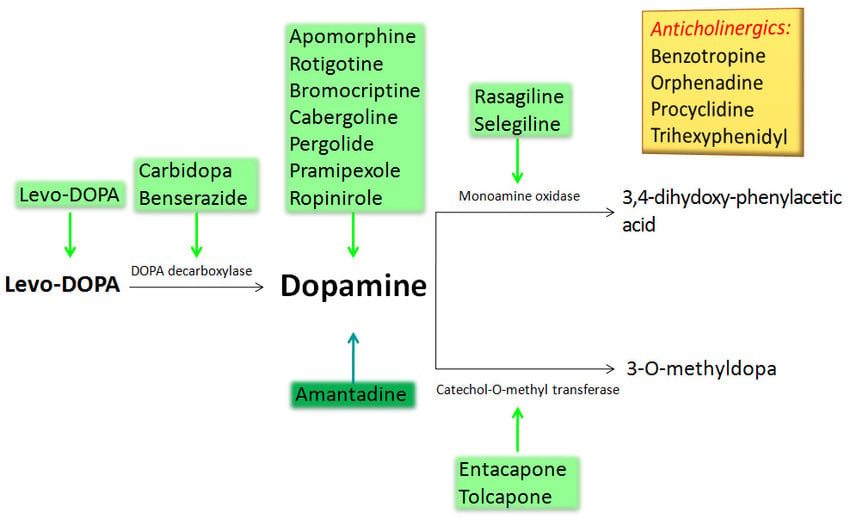
The first pharmacological agents used in PD therapy were anticholinergic drugs. They reduce the activity of acetylcholine by acting as antagonists at choline receptors, hoping to restore the balance between dopamine and acetylcholine levels that was disturbed by PD. These drugs have largely been replaced by L-DOPA and other centrally acting dopaminergic agonists, but they still remain available for use in the treatment of PD. Benztropine, biperiden, diphenhydramine, ethopropazine, orphenadrine, procyclidine, and trihexyphenidyl are included in this therapeutic class of drugs, though there is little pharmacokinetic information available on them because of their low plasma drug concentrations. Typically, anticholinergic drugs have a greater role in tremor-predominant PD and can be a monotherapy in early stages, but are usually done in adjunct with L-DOPA or other prescribed medications.
Symptomatic And Neuroprotective Therapy

Pharmacologic treatment of Parkinson disease can be divided into symptomatic and neuroprotective therapy. At this time, there is no proven neuroprotective or disease-modifying therapy.
Levodopa, coupled with carbidopa, a peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor , remains the gold standard of symptomatic treatment for Parkinson disease. Carbidopa inhibits the decarboxylation of levodopa to dopamine in the systemic circulation, allowing for greater levodopa distribution into the central nervous system. Levodopa provides the greatest antiparkinsonian benefit for motor signs and symptoms, with the fewest adverse effects in the short term however, its long-term use is associated with the development of motor fluctuations and dyskinesias. Once fluctuations and dyskinesias become problematic, they are difficult to resolve.
Monoamine oxidase -B inhibitors can be considered for initial treatment of early disease. These drugs provide mild symptomatic benefit, have excellent adverse effect profiles, and, according to a Cochrane review, have improved long-term outcomes in quality-of-life indicators by 20-25%.
Neuroprotective therapy aims to slow, block, or reverse disease progression such therapies are defined as those that slow underlying loss of dopamine neurons. Although no therapy has been proven to be neuroprotective, there remains interest in the long-term effects of MAO-B inhibitors. Other agents currently under investigation include creatine and isradipine.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Education For Nurses
Is Parkinsons Disease Inherited
Scientists have discovered gene mutations that are associated with Parkinsons disease.
There is some belief that some cases of early-onset Parkinsons disease disease starting before age 50 may be inherited. Scientists identified a gene mutation in people with Parkinsons disease whose brains contain Lewy bodies, which are clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to understand the function of this protein and its relationship to genetic mutations that are sometimes seen in Parkinsons disease and in people with a type of dementia called Lewy body dementia.
Several other gene mutations have been found to play a role in Parkinsons disease. Mutations in these genes cause abnormal cell functioning, which affects the nerve cells ability to release dopamine and causes nerve cell death. Researchers are still trying to discover what causes these genes to mutate in order to understand how gene mutations influence the development of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists think that about 10% to 15% of persons with Parkinsons disease may have a genetic mutation that predisposes them to development of the disease. There are also environmental factors involved that are not fully understood.
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease and the rate of decline vary widely from person to person. The most common symptoms include:
Other symptoms include:
- Speech/vocal changes: Speech may be quick, become slurred or be soft in tone. You may hesitate before speaking. The pitch of your voice may become unchanged .
- Handwriting changes: You handwriting may become smaller and more difficult to read.
- Depression and anxiety.
- Sleeping disturbances including disrupted sleep, acting out your dreams, and restless leg syndrome.
- Pain, lack of interest , fatigue, change in weight, vision changes.
- Low blood pressure.
You May Like: Asbestos And Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Most patients with Parkinsons disease can maintain a good quality of life with medications. However, as the disease worsens, medications may no longer be effective in some patients. In these patients, the effectiveness of medications becomes unpredictable reducing symptoms during on periods and no longer controlling symptoms during off periods, which usually occur when the medication is wearing off and just before the next dose is to be taken. Sometimes these variations can be managed with changes in medications. However, sometimes they cant. Based on the type and severity of your symptoms, the failure of adjustments in your medications, the decline in your quality of life and your overall health, your doctor may discuss some of the available surgical options.
Medical Marijuana And Legislation By State
Thirty-five states and Washington, DC have passed legislation allowing the use of marijuana-based products.
In some states where medical marijuana is legalized, consumers must register to possess and use cannabis. Other states require consumers to acquire a document from a physician stating that the patient has an approved condition. Under federal law doctors cannot prescribe cannabis, but many states authorize them to issue certifications that allow patients to obtain medical marijuana.
PD is listed as a qualifying condition for medical marijuana in Connecticut, Florida, Illinois, Louisiana, Massachusetts, Michigan, Mississippi, Missouri, New Hampshire, New Mexico, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania and West Virginia.
Medical marijuana is legal in Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Hawaii, Illinois, Louisiana, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, South Dakota, Utah, Vermont, Washington, West Virginia and Washington, DC.
Don’t Miss: How Hereditary Is Parkinson’s Disease
Nutritional Factors In Treatment
The most immediate nutritional concerns in Parkinsons disease treatment include changes in the absorption rate, blood levels, and CNS uptake of L-dopa. The protein content of meals, and particularly the distribution of protein intake throughout the day, has emerged as an important consideration in the effectiveness of L-dopa for many patients. Improvement in clinical response varies from 30% with protein redistribution to 82% with low-protein diets.,,
There are eight levels:
- Level 6: Easy to chew
- Level 5: Soft and bit-sized
- Level 4: Extremely thick/pureed
Physical Therapy For Parkinsons Disease
Its well-known that exercise of all kinds is beneficial for patients with Parkinsons disease. But physical therapy, in particular, is key. Why? A professional can guide you through the right moves to increase mobility, strength and balance, and help you remain independent, says Denise Padilla-Davidson, a Johns Hopkins physical therapist who works with patients who have Parkinsons. Here are things a therapist may work on:
Note: Please discuss any exercise program with your physician/neurologist and get a referral to a physical therapist or trainer with expertise in Parkinsons disease before starting any specific program.
Also Check: How Do You Treat Parkinson’s Disease Naturally
Setting Movement Goals With Your Therapist
Every client works with their physical therapist to set individualized movement goals. Physical therapists can help you optimize your exercise routine based on the latest research, re-learn challenging tasks or stay safe and independent in the home. Some of the most common movement goals for people with Parkinsons include:
- Learning about exercises
- Improving walking, balance or posture
- Addressing fall risk
- Treating pain
Before your first visit, think about your movement goals and write down your problems and questions. This will help you to organize your thoughts. You can do this for future visits, too.
Can Parkinsons Disease Be Prevented
Unfortunately, no. Parkinsons disease is long-term disease that worsens over time. Although there is no way to prevent or cure the disease , medications may significantly relieve your symptoms. In some patients especially those with later-stage disease, surgery to improve symptoms may be an option.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Age Of Onset
Medical Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease
Enormous progress has been made in the treatment of Parkinsons disease over the past half century, but levodopa remains the most potent drug for controlling PD symptoms . Prior to instituting medical therapy, a correct diagnosis of PD must be established and the level of impairment determined . Each patients therapy is to be individualized, and diverse drugs other than levodopa are presently available. Among these are the dopamine agonists , catechol-o-methyl-transferase inhibitors and nondopaminergic agents . Head-to-head comparisons of drugs within classes are rare, and the differences that have emerged are related to the effects on motor fluctuations, dyskinesias, on/off times and adverse effects of the specific agents within each class .
Iron Chelators In Current Clinical Use
The naturally occurring siderophore, deferrioxamine , contains three bidentate hydroxamate ligands and forms a very stable hexadentate complex with ferric iron. First introduced for transfusional iron overload in the early 1970s, DFO initially gave poor results because it was not orally active and had a short half-life . The development of continuous subcutaneous infusion of DFO by a portable pump combined with sensible schedules for the optimal use of the pump resulted in three independent studies demonstrating prolonged cardiac-disease-free survival in patents by the 1990s . Unfortunately, patients who could not or would not comply developed cardiac failure or arrhythmia much more rapidly . There was clearly a need for an orally active chelator, thereby improving compliance, which was as effective in iron chelation as DFO.
Chemical structures of chelators.
You May Like: How To Prevent Getting Parkinson’s Disease
Treating Parkinsons With Complementary Medicine
Complementary medicine incorporates many different practices that can be used alongside conventional medicine to try to ease PD symptoms. There is typically not as much rigorous data to support the use of complementary medicine techniques, as compared to conventional medicine, but many patients find them helpful. These include yoga and massage.
Medication For Parkinsons Disease
Once the doctor diagnoses Parkinsons disease, the next decision is whether a patient should receive medication, which depends on the following:
-
The degree of functional impairment
-
The degree of cognitive impairment
-
Ability to tolerate antiparkinsonian medication
-
The advice of the attending doctor
No two patients react the same way to a given drug, therefore, it takes time and patience to find an appropriate medication and dosage to alleviate symptoms.
You May Like: Effect Of Exercise On Parkinson’s Disease
Surgery For Parkinsons Disease
Based on the severity of the condition and the medical profile, the doctor may recommend surgery as one treatment option for Parkinson’s disease.
There are several types of surgery that may be performed that can help patients with Parkinson’s disease. Most of the treatments are aimed at helping the tremor or rigidity that comes with the disease. In some patients, surgery may decrease the amount of medication that is needed to control the symptoms.
There are three types of surgeries that may be performed for Parkinson’s disease, including the following:
It is important to remember that surgery may help with symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, but does not cure the disease or stop the progression of the disease.
Assembling Your Care Team
Assembling a team that will provide you with physical and emotional support and adapt to your needs over time is one of the best ways to remain healthy. Parkinsons disease is complex and requires an interdisciplinary approach to care. The care team may include, but is not limited to:
- Movement disorder specialist
- Rehabilitation specialists including physical, occupational, and speech therapists
- Nurse
You May Like: Israeli Treatment Of Parkinson Disease
The Evolution Of Treatments
The history of Parkinson’s disease is tightly linked to therapeutic interventions, ranging from serendipitous observations to controlled clinical trials of specifically designed agents.
Parkinson devoted a chapter of his monograph to considerations respecting the means of cure . In humility and perhaps with a vision toward current concepts of neuroprotection, he hoped for the identification of a treatment by which the progress of the disease may be stopped . To this end, he advocated very early therapeutic intervention when signs were largely confined to the arms without balance and gait impairments. Reflecting therapeutic approaches of the early nineteenth century, Parkinson recommended venesection, specifically advocating bloodletting from the neck, followed by vesicatories to induce blistering and inflammation of the skin. Small pieces of cork were purposefully inserted into the blisters to cause a sufficient quantity of purulent discharge . All these efforts were designed to divert blood and inflammatory pressure away from the brain and spinal cord, and in this way, decompress the medulla that Parkinson considered the seat of neurological dysfunction.
Treatment Of Late Stage Complications Of Parkinson’s Disease
Postural hypotension
Levodopa and dopamine agonists worsen postural hypotension and it may be necessary to lower the dose of levodopa or withdraw the agonist. Treatment is difficult, but patients should be advised to sleep with the head of the bed raised by one or two bricks and to add salt to their diet. Fludrocortisone can then be added at a dose of 0.1 mg in the morning, increasing if necessary up to 0.5 mg in the morning. If these measures are ineffective, the alpha agonist midodrine 10-20 mg four hourly can be useful but it is experimental and only available via the Special Access Scheme. Patients treated for postural hypotension need to have electrolytes, renal function and supine blood pressures closely monitored.
Parkinsonian psychosis, depression and dementia
Psychotic symptoms such as visual hallucinations and persecutory delusions occur most commonly in the setting of dementia, which may be mild and therefore easily missed. Most drugs for Parkinson’s disease make these symptoms worse. Depression is also common and requires treatment in its own right.
Recommended Reading: Physical Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
Basics Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease , or paralysis agitans, is a common neurodegenerative condition, which typically develops between the ages of 55 and 65 years. This disease was first named and described by James Parkinson in 1817. The progression of this disease is gradual and prolonged. It has a plausible familial incidence, although the estimates of these occurrences are low and usually sporadic. This disease is organized into two classifications: genetic and sporadic. Genetic PD follows Mendelian inheritance. Sporadic PD, which accounts for about 90% of all Parkinsons cases, is a more complex category in which the pathogenic mechanisms that underlie it are not yet fully understood. Nonetheless, it is known that the byzantine interactions of genetic and environmental influences play roles in the determination of sporadic PD. Several subtypes of PD exist. Each has its own set of causative factors and susceptibilities, pathology, and treatment courses. General risk factors, symptoms, and pathology will be discussed first, before addressing some of the subtypes.
Neurosurgical Treatments Of Parkinsons Disease
It is beyond the scope of this manuscript to comprehensively review neurosurgical treatment of PD. Only a brief review will be provided here and the reader is referred to other published literature on for additional information about this important therapeutic strategy. The renewed interest in surgical treatment of movement disorders has been stimulated in part by improved understanding of the functional anatomy underlying motor control, as well as refinement of methods and techniques in neurosurgery, neurophysio logy, and neuroimaging .
Besides thalamotomy and pallidotomy, another promising surgical approach for the treatment of tremors and other movement disorders is high-frequency DBS via electrodes implanted in the VIM nucleus of the thalamus, GPi, STN or other subcortical nuclei. The mechanism of electrical stimulation is not known, but the following explanations have been offered: 1) disruption of the network , 2) depolarization block, 3) preferential activation of inhibitory neurons, and 4) a functional ablation by desynchronizing a tremorogenic pacemaker.
Also Check: Early Parkinson’s Symptoms In Young Adults
Surgical Therapies With Transplantation And Gene Therapy
Cell transplantation is regarded as a potential future PD treatment. There have been trials using autologous and non-autologous cells. Human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells are few of the cells that have been included in these transplantation studies. One of the concerns with cell transplantation using stem cells is the ethical bounds that must be considered.
Since the first clinical trial in 1987 involving the transplantation of dopaminergic- neuron-rich human fetal mesencephalic tissue into PD patients striatums, more research has aimed to explore whether the grafted dopaminergic neurons will live and form connections in the brain, if the patients brain can harmonize and make use of the grafted neurons, and if the grafts can generate significant clinical improvement. Clinical trials with cell therapy intend to discover if there are long-lasting improvements following restoration of striatal DA transmission by grafted dopaminergic neurons. Experimental data from rodents and nonhuman primates show that fetal ventral mesencephalon intrastriatal grafted DA neurons demonstrate many morphological and functional characteristics of normal DA neurons. Significant improvements of PD-like symptoms in animal models have been demonstrated after successful reinnervation by the grafts. Dopaminergic grafts can reinnervate the striatum in the brain, restore regulated release of DA in the striatum, and can become functionally integrated into neural circuitries.