Which Body Parts Do Parkinsons Tremors Affect
There are five main places youâll have Parkinsonâs tremors:
1. Hands. Parkinsonâs disease tremors often start in the fingers or hands with whatâs called a pill-rolling motion. Imagine holding a pill between your thumb and index finger and rolling it back and forth.
2. Foot. A Parkinsonâs foot tremor is more likely to happen while youâre sitting or lying down with your feet at rest. If the tremor moves into your thigh muscles. It could look like your whole leg is shaking.
Foot tremors disappear when you stand or walk because those are active movements. A foot or leg tremor while youâre standing may be another condition.
3. Jaw. This is common in people with Parkinsonâs. It may look like youâre shivering. It can become bothersome if the tremor makes your teeth chatter. If you wear dentures, it could make them shift or fall out.
Chewing eases the tremor, so gum might help.
4. Tongue. Itâs rare, but a tongue tremor can cause your entire head to shake.
5. Internal. Some people with Parkinsonâs say they can feel a shaking sensation in their chest or abdomen. But canât be seen from the outside.
Types Of Tremor & Tremor Terminology
Before proceeding further, it is important to briefly delve into tremor nosology. There is a variety of tremor types that clinicians must consider when evaluating patients . Rest tremor occurs when voluntary muscle activity is absent. Action tremor can be subdivided into postural, kinetic and intention tremors. Postural tremor occurs when holding a body part motionless against gravity. Re-emergent tremor is a particular type of postural tremor when the patient holds their arms extended, the tremor commences after a variable latency of one to several seconds. Kinetic tremor occurs with voluntary movement . Intention tremor occurs with goal-directed movement and worsens as the body part approaches the target. Familiarity with the terms defined above is necessary in order to understand the diagnostic criteria, which have been proposed for both ET and PD.
What Are The Different Categories Or Types Of Tremor
Tremor is most commonly classified by its appearance and cause or origin. There are more than 20 types of tremor. Some of the most common forms of tremor include:
Essential tremor
Essential tremor is one of the most common movement disorders. The exact cause of essential tremor is unknown. For some people this tremor is mild and remains stable for many years. The tremor usually appears on both sides of the body, but is often noticed more in the dominant hand because it is an action tremor.
The key feature of essential tremor is a tremor in both hands and arms, which is present during action and when standing still. Additional symptoms may include head tremor without abnormal posturing of the head and a shaking or quivering sound to the voice if the tremor affects the voice box. The action tremor in both hands in essential tremor can lead to problems with writing, drawing, drinking from a cup, or using tools or a computer.
Tremor frequency may decrease as the person ages, but the severity may increase, affecting the persons ability to perform certain tasks or activities of daily living. Heightened emotion, stress, fever, physical exhaustion, or low blood sugar may trigger tremor and/or increase its severity. Though the tremor can start at any age, it most often appears for the first time during adolescence or in middle age . Small amounts of alcohol may help decrease essential tremor, but the mechanism behind this is unknown.
Dystonic tremor
Cerebellar tremor
Recommended Reading: What Is The Difference Between Alzheimer’s And Parkinson’s Disease
How Do I Know If I Am A Candidate For Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation works for people with PD who have responded to levodopa but now have developed dyskinesias or other off symptoms like a return of tremors, rigidity and slowness of movement. DBS doesn’t seem to help people with atypical Parkinson’s syndromes that also don’t seem to improve with Parkinson’s meds.
There are many important issues to be addressed when considering DBS to treat Parkinson’s disease. These issues should be discussed with a movement disorders expert or a specially trained neurologist. A movement disorders expert is someone who has trained specifically in movement disorders.
One of the most important criteria is that you try drug treatment first. Surgery is not recommended if medications can adequately control the disease. However, surgery should be considered if you do not achieve satisfactory control with medications. Talk to your doctor to see if deep brain stimulation is right for you.
Misperception #: Action Tremor = Et & Not Pd
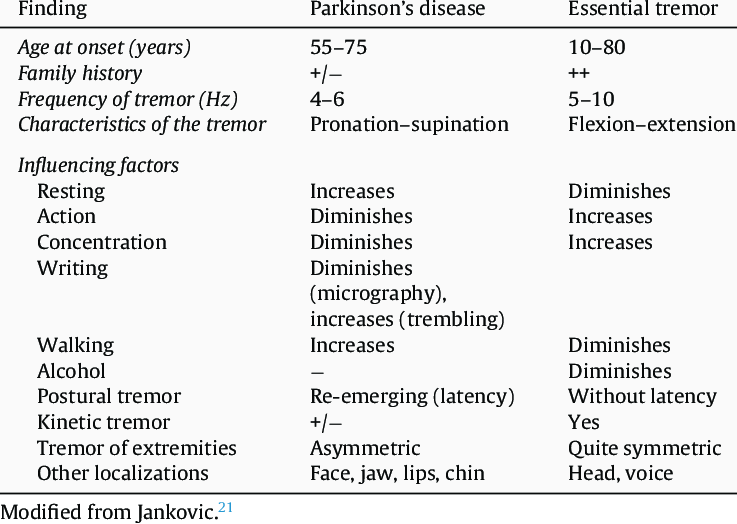
Action tremor is the hallmark feature of ET and can be further subdivided into postural, kinetic and intention tremors. Yet just as rest tremor may occur in patients with ET, conversely, action tremor may be found in patients with PD. Indeed, it is not uncommon to encounter patients with PD who have various forms of action tremor. Below, we discuss postural, kinetic and intention tremors separately.
Clinical pearl #2: Although action tremor is the hallmark feature of ET, it is commonly found in patients with PD as well. When evaluating kinetic tremor in a particular patient, comparing it to other tremor types within that patient may help distinguish PD from ET. Thus, kinetic tremor is generally of greater amplitude than postural tremor in ET whereas the converse has been reported in PD. Intention tremor with limb dysmetria is more suggestive of ET than PD. Some of the clinical features of action tremor may similarly suggest one disorder or another. Thus, a postural tremor whose frequency is similar to the 4- to 6-Hz rest tremor of PD is suggestive of PD. A postural tremor with a significant latency is also more characteristic of PD.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Symptom Tracker App
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Knowing the early warning signs of Parkinsons disease is very important for your health. Non-motor and motor symptoms can vary slightly from case to case in PD patients. Early signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease may be too mild to notice or may be mistaken for other similar conditions.
As mentioned, tremors are typically the most common symptom in all Parkinsons patients. Action tremor is characterized by involuntary shaking that usually begins in the limbs, like your hand shaking even when you are at rest. They may manifest as pill-rolling tremors, wherein you rub your thumb and index finger together.
Slow movement, medically known as bradykinesia, is another common symptom of Parkinsons disease. As the disease progresses, all of your movements may get slower and slower, making everyday tasks difficult or more time-consuming. What are some motor symptoms? You may have trouble walking or lifting yourself out of chairs. Your feet may drag or feel like they are stuck to the floor, and your steps may get shorter.
Your limbs may also become rigid. Muscle rigidity and stiffness can be painful and reduce your full range of motion. Furthermore, your posture may begin to deteriorate, resulting in you stooping, slouching, postural instability, or hunching over even when you think you are standing straight. Performing coordination exercises for Parkinsons patients may be beneficial for their physical health.
Is There A Link
Some people have MS and Parkinsonâs, but it could be a coincidence.
Research suggests that the damage that MS causes to your brain can lead some people to develop Parkinsonâs later on.
If you have MS, your immune system triggers ongoing inflammation. This can create lesions in your brain that cause Parkinsonâs disease. If lesions form in certain spots in your brain, they can affect how it makes dopamine.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Leaning To One Side
Where Can I Get More Information
For more information on neurological disorders or research programs funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, contact the Institute’s Brain Resources and Information Network at:
Office of Communications and Public LiaisonNational Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeNational Institutes of HealthBethesda, MD 20892
NINDS health-related material is provided for information purposes only and does not necessarily represent endorsement by or an official position of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke or any other Federal agency. Advice on the treatment or care of an individual patient should be obtained through consultation with a physician who has examined that patient or is familiar with that patient’s medical history.
All NINDS-prepared information is in the public domain and may be freely copied. Credit to the NINDS or the NIH is appreciated.
What Is A Parkinsons Tremor
Other health issues can also cause tremors, like multiple sclerosis or essential tremor. But Parkinsonâs tremors are different because theyâre usually:
- Resting. Parkinsonâs tremors happen when your muscles are still. They go away when you move. They also lessen while you sleep. For example, if youâre sitting in a chair with your arm relaxed, you may notice that your fingers twitch. But if youâre using your hand, like when you shake someone elseâs hand, the tremor eases or stops.
- Rhythmic. Parkinsonâs tremors are slow and continuous. They arenât random tics, jerks, or spasms.
- Asymmetric. They tend to start on one side of your body. But they can spread to both sides of the body.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease And Brain Function
Other Tremors And How It Differs
A Parkinsonian tremor has a few distinct characteristics, though it may be easy to confuse with other types of tremors depending on the other symptoms a person shows. Doctors will look for and rule out other types of tremors to confirm their diagnosis.
The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke notes that some common tremors include:
Dopamine is an important neurotransmitter that plays a critical role in a number of bodily functions, such as movement and coordination. People with Parkinsons disease produce less dopamine, which may cause them to experience movement-related problems, such as rigidity, slowness of movement, poor balance, and tremors.
Low levels of dopamine may disrupt the way the brain processes movement, which can result in movement problems. Evidence suggests that many people with Parkinsons disease lose 6080% of dopamine-producing cells in the brain by the time they present symptoms.
Other causes of tremors unrelated to Parkinsons disease can include:
- certain medications
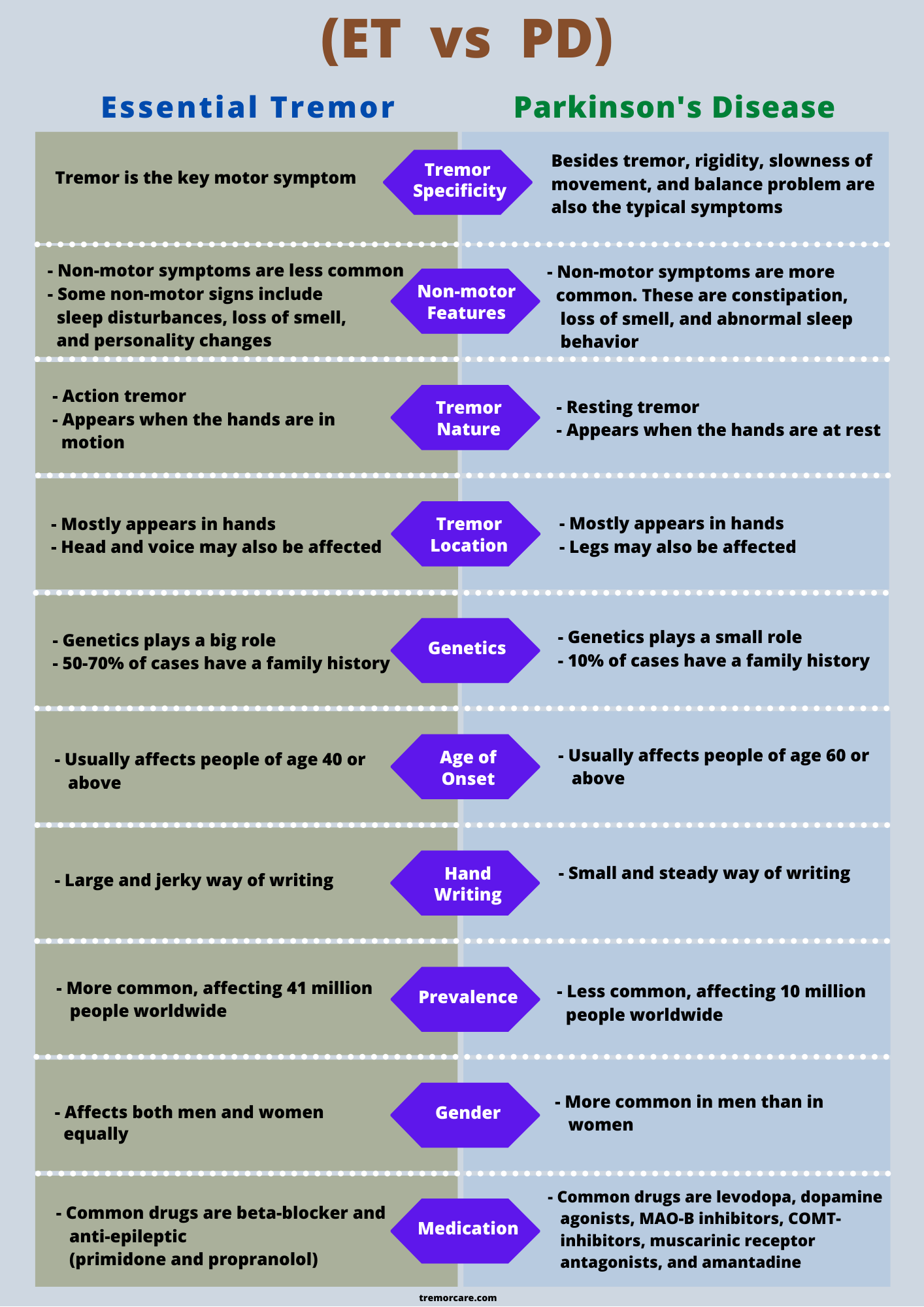
Parkinsons Tremors Vs Essential Tremors
Because they can be similar to Parkinsons tremors, essential tremors are often confused as symptoms of the disease. Just as with Parkinsons, essential tremor can cause uncontrollable rhythmic shaking in different parts of the body.
Up to 10 million people are affected by this common nervous system disorder. While genetics and environment likely play a role in essential tremor, the cause is unknown, according to the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
Essential tremors in the hands or arms can be distinct from Parkinsons because they typically happen when the hands are in use.
The essential tremor can get really bad when youre using your limb when drinking or eating soup, for example, says Gilbert. The Parkinsons tremor is usually not as disabling whereas the essential tremor can be life-altering.
The shaking from an essential tremor typically improves when using both hands to bring a cup to the mouth but the same action can amplify the tremor in Parkinson’s, according to Gilbert.
Dr. Beck points out that an essential tremor may be faster than a Parkinsons tremor, which tends to be milder. A difference can often be seen in a persons handwriting. Those with essential tremor tend to have more unsteady and wavy writing, whereas Parkinsons patients are more apt to display micrographia, or abnormally small handwriting.
They have low amplitude movement so their writing gets smaller and smaller to a point where it can be barely legible, he says.
Read Also: My Dad Died From Parkinson’s
Depression With Huntingtons Disease
Due to the nature and lower life expectancy of Huntingtons disease, it is common for a diagnosis to lead to depression. Patients with Huntingtons are at a higher risk of suicide.
If you are struggling with your Huntingtons diagnosis or prognosis, contact the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration National Helpline online or call 1-800-662-4357 to seek help.
For more mental health resources, including a helpful list of links and hotline numbers, see our National Helpline Database.
What Makes Them Different
MS and Parkinsonâs have different causes. They usually start to affect you at different ages, too.
MS often affects people between ages 20 and 50, but children get it, too. Parkinsonâs usually starts at age 60 or older, but some younger adults get it.
MS is an autoimmune disease. That means your bodyâs immune system goes haywire for some reason. It attacks and destroys myelin. As myelin breaks down, your nerves and nerve fibers get frayed.
In Parkinsonâs, certain brain cells start to die off. Your brain makes less and less of a chemical called dopamine that helps control your movement. As your levels dip, you lose more of this control.
Some genes may put you at risk for Parkinsonâs, especially as you age. Thereâs a small chance that people who are exposed to toxic chemicals like pesticides or weed killers can get it, too.
These symptoms are more common if you have MS. They not usually found in Parkinsonâs:
You May Like: Does Alan Alda Have Parkinson’s
Are Tremors Or Dyskinesias Painful
Tremors are almost never painful, says Herrington. And unless the dyskinesias are very severe, they also hardly ever cause pain.
However, Herrington says that when a persons medication wears off, the person can experience a condition called dystonia, which is related to dyskinesia. Dystonia is a potentially painful, cramping condition that can occur in the face, arms, or legs and can be very uncomfortable.
Possible Link To Alzheimers
Though Alzheimers, Huntingtons, and Parkinsons are distinctly different diseases, some evidence has emerged that shows a common link between the three.
All three diseases have proteins within the cells that do not assemble properly. Though the molecular and cellular changes that occur in each disease vary greatly, this protein degradation has been shown to precede early clinical signs in each disease. This is promising news, as more studies are being done to determine whether this can either predict or prevent these neurodegenerative diseases.
Recommended Reading: Where Is The Lesion In Parkinson’s Disease
How Do Treatments Differ
MS treatments can ease your symptoms during an attack or slow down the diseaseâs effects on your body.
Steroids like prednisone calm the inflammation that damages your nerves.
Plasma exchange is another therapy if steroids donât work. Your doctor will use a machine to remove the plasma portion of your blood. The plasma gets mixed with a protein solution and put back into your body.
Some people with both diseases who take anti-inflammatory medicines like steroids see their Parkinsonâs symptoms get better.
Disease-modifying treatments slow down MS nerve damage and disability. They include:
National Institute for Neurological Disorders and Stroke: âTremor Fact Sheet.â
Neurology: âParkinsonâs Disease in Multiple Sclerosis – A Population-Based, Nationwide Study in Denmark .â
Mayo Clinic: âMultiple Sclerosis: Overview,â âMultiple Sclerosis: Symptoms and Causes,â âMultiple Sclerosis: Treatment,â âParkinsonâs Disease: Causes,â âParkinsonâs Disease: Definition,â âParkinsonâs Disease: Risk Factors,â âParkinsonâs Disease: Symptoms.â
Christopher Reeve Foundation: âHow the spinal cord works.â
National Association for Continence: âParkinsonâs Disease.â
National Multiple Sclerosis Society: âMS Symptoms,â âWho Gets MS? .â
National Parkinson Foundation: âNon-Motor Symptoms.â
Multiple Sclerosis Trust: âLhermitteâs sign.â
Johns Hopkins Medicine: âPlasmapheresis.â
FDA.
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease And Essential Tremor
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is caused by a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. A deficiency in the chemical dopamine can cause symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
In about 15% of cases, Parkinsons occurs in individuals with a family history of the disease, due to gene mutations and alterations that are passed down.
Age is a large risk factor for developing Parkinsons. People over the age of 60 have the highest risk of developing the disease.
Studies show that men are 1.5 times more likely to develop Parkinsons than women.
Other environmental risk factors that can lead to Parkinsons include:
- Head injury
- Exposure to pesticides and herbicides
- Exposure to toxins such as trichlorethylene and polychlorinated biphenyls
Signs & Symptoms: Is It Essential Tremor Or Parkinsons
In order to start managing your condition and receive the treatment you need, you should be aware of the most common signs and symptoms as well as the key differences between essential tremor and Parkinsons. After all, the first step in getting care as early on as possible is self-awareness that you might be suffering from one of these conditions.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease Mental Health
Handwriting: A Strange Clue
Micrographia, very small and crowded handwriting, is one of the hallmark signs of Parkinson’s disease that doctors will look for it’s even one of the main reasons they’ll ask patients to fill diagnostic questionnaires out themselves. This handwriting may start off having a normal “font size”, but then gradually become smaller and smaller as the patient writes more.
People with Essential Tremor don’t have micrographia their handwriting can be affected by their condition, but it’s much more likely to become larger and more shaky .
How Are Tremors And Dyskinesia Experienced By Caregivers

People with Parkinsons disease can experience their condition much differently than do their caregivers or spouses. Sometimes being in the off state looks more comfortable to the caregiver because the person is still, and can even seem kind of calm, says Herrington. But for the person with Parkinsons, they experience that off state as very uncomfortable. They may describe it as feeling trapped because they want to move but and they cant.
In this case, he continues, the person might say, Look, I know I have dyskinesia, but I prefer being free to move than feeling stuck and trapped. The caregiver, however, may feel bothered by the increased movement, he says, and think that the person is taking too much medication.
There can be a real disconnect there between what the patient would want and what the caregiver might think is best, says Herrington. Its not always the best thing to try to get rid of every last bit of dyskinesia, because the person might be less comfortable in that state.
Also Check: Stage 5 Parkinson’s Disease Life Expectancy