Management Of Asymptomatic And Symptomatic Preexcitation
Blomström-Lundqvist, C, Scheinman, MM, Aliot, EM. ACC/AHA/ESC Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Supraventricular ArrhythmiasExecutive Summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines . Circulation. vol. 108. 2003. pp. 1871-1909.
Klein, GJ, Gulamhusien, SS. Intermittent preexcitation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Am J Cardiol. vol. 52. 1983. pp. 292-6.
Campbell, RWF, Smith, R, Gallagher, JJ. Atrial fibrillation in the preexcitation syndrome. Am J Cardiol. vol. 40. 1977. pp. 514-20.
Auricchio, A, Klein, H, Trappe, HJ. Lack of prognostic value of syncope in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. vol. 17. 1991. pp. 152-8.
Wellens, HJ, Bar, FW, Gorgels, AP. Use of ajmaline in patients with the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome to disclose short refractory period of the accessory pathway. Am J Cardiol. vol. 45. 1980. pp. 130-33.
Brembilla-Perrot, B, Ghawi, R. Electrophysiological characteristics of asymptomatic Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Eur Heart J. vol. 14. 1993. pp. 511-15.
Leitch, JW, Klein, GJ, Yee, R, Murdock, C. Prognostic value of electrophysiology testing in asymptomatic patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White pattern. Circulation. vol. 82. 1990. pp. 1718-23.
Atrial Fibrillation And Wpw
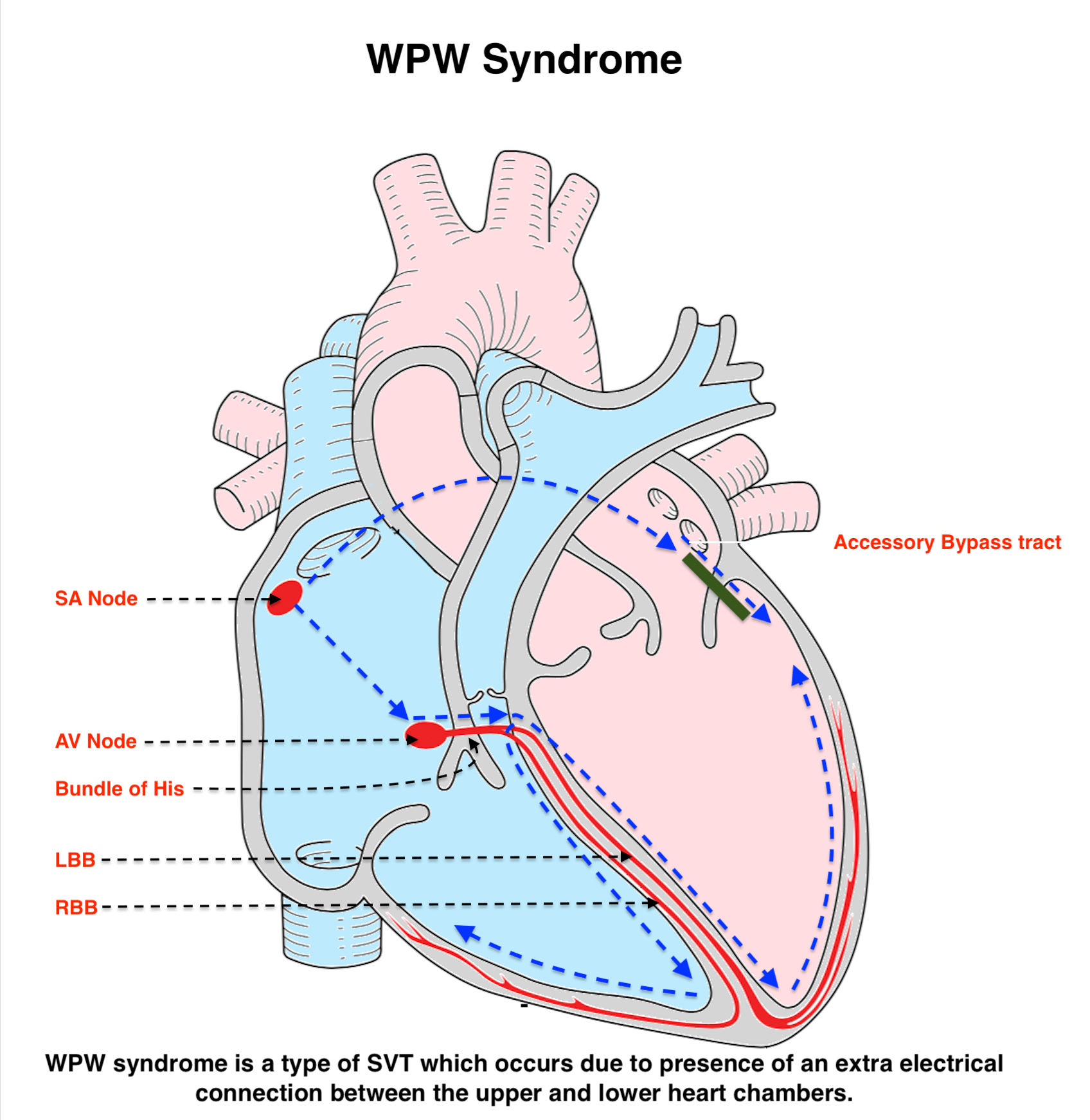
Patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome have an accessory pathway or a bypass tract that connects the electrical system of the atria directly to the ventricles, thereby allowing conduction to avoid passing through the AV node.
In normal individuals, when the sinus node creates an action potential it must pass through the AV node to get to the ventricles. When an accessory pathway is present, the sinus node action potential can pass through the bypass tract before the AV node, which causes the ventricles to become depolarized quickly. This is termed pre-excitation and results in a shortened PR interval on the ECG.
The combination of WPW and atrial fibrillation can potentially be fatal, especially if AV blocking agents are given . The medical treatment is procainamide, although electrical cardioversion is reasonable, especially if hemodynamically unstable.
In patients with WPW and atrial fibrillation, the erratic atrial action potentials can conduct through the accessory pathway very quickly . Therefore, WPW patients who develop atrial fibrillation have higher ventricular rates than those without WPW. If an AV blocking agent is given, fewer atrial action potentials will pass through the AV node and more will pass through the accessory pathway, paradoxically increasing the ventricular rate potentially causing ventricular fibrillation which is a fatal, hemodynamically unstable rhythm. Procainamide or electrical cardioversion is recommended in these situations.
Antidromic Svt In Wpw
In antidromic SVT, the action potential conducts to the ventricle initially via the accessory pathway, then wanders shambolically around the ventricles producing a weird wide QRS, and then propagates up the AV node in an unnatural retrograde manner. It then goes straight back down into the ventricle via the accessory pathway, and the whole thing repeats cyclically.
So, consider what might happen if the AV node were blocked. The ventricle is now only depolarised by the accessory pathway, so the QRS will be weird and wide, but now that the AV node is blocked, theoretically the block should have the exact same effect as in orthodromic SVT, i.e. the cycle is broken and the SVT should be aborted.
However, the authorities are not convinced. UpToDate hold forth that:
“Even though retrograde AV node conduction may be a “weak link” during antidromic AVRT, intravenously administered AV node-specific blocking drugs such as adenosine, verapamil, and beta blockers should be avoided unless the tachycardia is definitely known to be antidromic AVRT. …If the diagnosis is not certain, the patient should be considered to have an undiagnosed wide QRS tachycardia“
Which brings us to…
Don’t Miss: Wolf Parkinsons White Disease Treatment
Are There Different Types Of Accessory Pathways
Lown, B. The syndrome of short P-R interval, normal QRS complex and paroxysmal rapid heart action. Circulation. vol. 5. 1952 May. pp. 693-706.
James, TN. Morphology of the human atrioventricular node, with remarks pertinent to its electrophysiology. Am Heart J. vol. 62. 1961. pp. 756-71.
Lev, M, Leffler, WB, Langendorf, R. Anatomic findings in a case of ventricular preexcitation terminating in complete atrioventricular block. Circulation. vol. 34. 1966. pp. 718-33.
Murdock, CJ, Leitch, JW, Teo, WS. Characteristics of accessory pathways exhibiting decremental conduction. Am J Cardiol. vol. 67. 1991. pp. 506-10.
Ross, DL, Uther, JB. Diagnosis of concealed accessory pathways in supraventricular tachycardia. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. vol. 7. 1984. pp. 1069-85.
Anderson, RH, Becker, AE, Brechenmacher, C. Ventricular pre-excitation: a proposed nomenclature for its substrates. Eur J Cardiol. vol. 3. 1975. pp. 27-36.
Mahaim, I, Benatt, A. Nouvelles recherches sur les connections superieures de la branche du faisceau de His-Tawara avec cloison interventriculaire. Cardiologia. vol. 1. 1937. pp. 61
How Can We Tell The Location Of The Ap Based On The Superficial 12
The ECG hallmark of an antegradely conducting AP is the delta wave along with a shorter than usual PR interval and a widened QRS complex. Conversely, the presence of retrograde conduction only in an AP will not be apparent on a surface ECG during sinus rhythm . Whereas ECG during ORT has a normal QRS complex with retrogradely conducting P wave after the completion of the QRS complex in the ST segment or early in the T wave, the QRS during ART is fully preexcited.
Numerous algorithms have been described to localize the site of the AP using the axis of the delta wave and QRS morphology. The location of the AP along the AV ring is classified variously into five or ten regions, which can be broadly divided into those on the left and the right of the AV groove. Distribution along these lines is not homogenous. Some 46% to 60% of the pathways are found on the left free wall space. Nearly 25% are within the posteroseptal and midseptal spaces, 15% to 20% in the right free wall space, and 2% in the anteroseptal space.
The positive predictive value of these algorithms is better when the delta wave polarity is included and when algorithms involve fewer than six locations. Two simple algorithms that include both the delta wave axis and the QRS axis are shown . For the purpose of localization of the APs, delta wave is defined as the first 20 ms of the earliest QRS deflection.
Don’t Miss: Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Mill Hill Ave Command: Can You Give Adenosine To A
· 2) Second, there was a concern in the past that a certain percentage of wide-complex tachycardia were actually WPW with antidromic conduction, and so the advice was to avoid adenosine. The rationale was that since the bypass tract was capable of retrograde conduction, shutting down the AV node could expose the ventricles to potentially unregulated pacing.
Which Drugs Are Used To Treat Wolff
Class Ic drugs are typically used with an AV nodal blocking agent in low doses to avoid atrial flutter with a 1:1 conduction. class III drugs are also reasonable choices, although these agents are less effective for altering accessory pathway conduction properties. Class Ic drugs should not be given if the patient has structural heart disease . Class Ic drugs are typically used with an AV nodal blocking agent.
Recommended Reading: How Serious Is Parkinson’s Disease
What Are Wpw And Avrt
Preexcitation describes the situation in which impulses from the SA node or atrium reach the ventricle through an accessory pathway in addition to the AV node. WPW is a type of preexcitation syndrome in which there are ECG findings of an atrial-ventricular bypass tract and the patient demonstrates related tachydysrhythmias. The most common tachydysrhythmia seen in WPW is atrioventricular re-entrant tachycardia this is seen in 80% of patients with WPW and is what paramedics would most commonly be called for.
Recall that there are three mechanisms for the development of cardiac dysrhythmias:
Catheter Ablation Of Accessory Pathways
Lesh, MD, Van Hare, G, Scheinman, MM. Comparison of the retrograde and transseptal methods for ablation of left free-wall accessory pathways. J Am Coll Cardiol. vol. 22. 1993. pp. 542-9.
Jackman, WM, Wang, X, Friday, KJ. Catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular pathways by radiofrequency current. N Engl J Med. vol. 324. 1991. pp. 1605-11.
Kuck, KH, Schluter, M, Geiger, M. Radiofrequency current catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular pathways. Lancet. vol. 337. 1991. pp. 1557-61.
Calkins, H, Langberg, J, Sousa, J. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular connections in 250 patients: abbreviated therapeutic approach to Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Circulation. vol. 85. 1992. pp. 1337-46.
Kay, GN, Pressley, JC, Packer, DL. Value of 12-lead electrocardiogram in discriminating atrioventricular nodal reciprocating tachycardia from circus movement atrioventricular utilizing a retrograde accessory pathway. Am J Cardiol. vol. 59. 1987. pp. 296-300.
Tchou, PJ, Lehmann, MJ, Donga, J. Effect of sudden rate acceleration on the human His-Purkinje system: adaptation of refractoriness in a damped oscillatory pattern. Circulation. vol. 73. 1986. pp. 920-9.
Drago, F, DeSantis, A, Grutter, G, Silverti, MS. Transvenous cryothermal catheter ablation of re-entry circuit located near the atrioventricular junction in pediatric patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. vol. 45. 2005. pp. 1096-103.
Recommended Reading: Drugs To Treat Parkinson’s
Understanding Medications Versus Catheter Ablation
Medications Versus Catheter Ablation Very often, when a patient complains of heart rhythm issues, their primary care physician or cardiologist will start them on medication to try to improve symptoms or restore normal rhythm. Medications are, after all, easy to TachycardiaTachycardia is the medical term for a heart rate over 100 beats per minute. There are many heart rhythm disorders that can cause tachycardia. Sometimes, its normal for you to have a fast heartbeat. For instance, its normal for your heart rate to rise
Serotonin Syndrome : Symptoms Causes &
Serotonin syndrome, also known as serotonin toxicity, is a potentially life-threatening condition resulting from having too much serotonin in your body. Learn about serotonin syndrome symptoms, the medications that can cause the condition, and how it can beWebMDWebMD Better information. Better health.Treatment of atrial flutter · After atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter is the most important and most common atrial tachyarrhythmia. Although it was first described 80 years ago, techniques for its diagnosis and management have changed little for decades. The diagnosis rested almost entirely with the 12 lead ECG, and treatment options included only the use of a digitalis compound to slow and control the ventricular
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Mucuna Pruriens For Parkinson’s
How Is Wpw Treated
Treatment will depend on how severe your symptoms are, and how often you have them. You may only need to be observed by your healthcare provider if you are not having symptoms. You may need any of the following:
- Medicines may be given to slow or regulate your heartbeat.
- Radiofrequency ablation is a procedure used to send energy to the area of your heart that has an electrical problem. The energy causes an area of the heart muscle to scar. This stops the electrical problem and allows your heart to beat normally.
- Cardioversion is a procedure used to give your heart an electrical shock. The shock may help put your heartbeat back into a normal rhythm. Cardioversion may be needed if other treatments do not work.
How Is Wpw Syndrome Treated
If youre diagnosed with WPW syndrome, you have several treatment options, depending on your symptoms. If youre diagnosed with WPW syndrome but dont have any symptoms, your doctor may recommend that you wait and continue follow-up appointments. If youre having symptoms, the treatment may include the following:
Don’t Miss: Can A Blood Test Detect Parkinson’s
Safe Practice In Svt With Wpw
So, in summary, what can we safely say about the management of acute SVT in WPW?
- Theoretically, AV nodal blockers should be safe in WPW-associated SVT, be it antidromic or orthodromic. If one thinks for a minute about the epidemiology of SVT, one will come to the conclusion that a large proportion of SVT is in fact caused by WPW or some other sort of preexcitaton syndrome, which is usually not known at the time of their first presentation. Many of these people get adenosine, which then reveals their delta waves to the horrified emergency personnel. Most of them do not die of VF. On the basis of this, we may conclude that it is probably reasonably safe.
- Practically, antidromic SVT in WPW may be difficult to discriminate from AF or VT. Broad complexes and 300+ heart rates could be anything in WPW. Sure, it could be supraventricular, and respond to adenosine. Or it could be AF, and turn into VF. Or it could be VT, which will not benefit from an AV nodal blocker, in which case you have wasted precious time.
The table below has been compiled with the use of the belowlisted references and the UpToDate article on this topic
How Is Wpw Syndrome Diagnosed
People experiencing a fluttering or racing heartbeat usually tell their doctors. The same applies to those experiencing chest pain of difficulty breathing. However, if you dont have symptoms, the condition may go unnoticed for years.
If you have a racing heartbeat, your doctor will likely perform a physical exam and conduct tests that measure your heart rate over time to check for tachycardia and diagnose WPW syndrome. These heart tests may include:
You May Like: Parkinson’s Phase 3 Trials
Treatment Of Atrial Fibrillation And Wpw Syndrome
-
Direct-current cardioversion
The treatment of choice for Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is direct-current cardioversion Direct-Current Cardioversion-Defibrillation The need for treatment of arrhythmias depends on the symptoms and the seriousness of the arrhythmia. Treatment is directed at causes. If necessary, direct antiarrhythmic therapy, including antiarrhythmic… read more . The usual rate-slowing drugs used in atrial fibrillation are not effective, and digoxin and the nondihydropyridine calcium channel blockers are contraindicated because they may increase the ventricular rate and cause ventricular fibrillation. If cardioversion is impossible, drugs that prolong the refractory period of the accessory connection should be used. IV procainamide or amiodarone is preferred, but any class Ia, class Ic, or class III antiarrhythmic drug Drugs for Arrhythmias The need for treatment of arrhythmias depends on the symptoms and the seriousness of the arrhythmia. Treatment is directed at causes. If necessary, direct antiarrhythmic therapy, including antiarrhythmic… read more can be used.
What Drugs Are Contraindicated In Wpw
atrial fibrillationdigoxincalcium channel blockers
. Also question is, what medications should not be taken with WPW?
Do not give digoxin or nondihydropyridine calcium channel blockers to patients with atrial fibrillation and Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome because these drugs may trigger ventricular fibrillation.
Also, why is digoxin contraindicated in WPW? The use of digoxin or verapamil for long-term therapy appears to be contraindicated for many patients with WPW syndrome, because these medications may enhance antegrade conduction through the AP by increasing the refractory period in the AV node.
Thereof, is adenosine contraindicated in WPW?
In the presence of WPW, traditional treatments may be contraindicated. Any AV nodal slowing agent, including adenosine, diltiazem and amiodarone, may cause an adverse reaction in the presence of WPW. Of those three medications, AHA recommends amiodarone. It is important to keep WPW in mind when treating a tachycardia.
What triggers WPW?
The extra electrical pathway that causes a rapid heartbeat is present at birth. An abnormal gene is the cause in a small percentage of people with WPW . The syndrome also is associated with some forms of congenital heart disease, such as Ebstein anomaly. Otherwise, little is known about why the extra pathway develops.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Quality Of Life
What Are The Symptoms Of Wolff
Symptoms occur only when the heart beats abnormally fast, so most of the time people have no symptoms. Episodes can start suddenly and last for a few seconds or several hours. They often happen during exercise. When symptoms do occur, they include rapid heartbeat, heart palpitations or heart fluttering, lightheadedness, chest pain, fatigue, fainting, dizziness, anxiety, loss of consciousness, and breathing problems. Sudden death can occur.
Orthodromic Svt In Wpw
In orthodromic SVT, the action potential enters the AV node, propagates down the bundle of His, depolarises the ventricles, reenters the atria via the accessory pathway, and stimulates the AV node again. As in any normal SVT, this is something that should respond well to AV nodal blockers. If you block the AV node, the reentry of the action potential will only stimulate the atria and then dissipate harmlessly against the blocked node, and propagate no further. That ends the cycle, as there will be no ventricular action potential to reenter and stimulate the atria, which means that the next pulse should be a good honest sinus beat. On the basis of this, the UpToDate boffins recommend standard anti-SVT pharmacotherapy:
“The approach to patients with orthodromic AVRT is similar to patients with other types of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia… AV nodal blocking agent should be instituted. We suggest intravenous adenosine rather than intravenous verapamil as the initial choice based on its efficacy and short half-life. “
You May Like: Bicycle Therapy For Parkinson’s Disease
When To Seek Medical Advice
See a GP if you keep getting a fast heartbeat. It’s important to get it checked out in case it could be something serious.
Dial 999 for an ambulance if:
- your heartbeat doesn’t go back to normal in a few minutes
- you have chest pain that lasts more than 15 minutes you may also have pain in your arms, back or jaw
- you have chest pain and other symptoms like feeling sick, being sick , shortness of breath or sweating
- someone passes out and doesn’t regain consciousness
If you’ve been diagnosed with WPW syndrome and you experience an episode, first try the techniques you’ve been taught or take any medication you’ve been given.
Dial 999 or go to your nearest accident and emergency department if these measures don’t stop the episode within a few minutes, or if someone you know has WPW syndrome and collapses or faints.