Latest Developments In Dbs Surgery And Future Enhancements
In this one hour and twenty one minute webinar Stanford neurosurgeon Jaimie Henderson, MD, reviewed the steps a person with Parkinson’s can expect before, during, and after DBS surgery. He also outlined the differences between DBS systems as well as recent and anticipated advancements in DBS technology before taking questions from listeners.
There Are A Few Different Types
Parkinsons disease surgery includes surgical procedures that involve device implantation in the brain or ablation to reduce some effects of the disease. For some people, this type of surgery can help improve symptoms and reduce the dose of medication needed, which may decrease medication side effects.
You would need to prepare for your operation by having preoperative brain imaging and other tests, and you can expect to recover and experience an improvement of your symptoms within a few weeks.
This surgery does not prevent Parkinsons disease from progressing, so you might experience worsening effects of the condition and need higher medication doses down the road. This article will cover the most common types of brain surgery for Parkinson’s disease, what to expect, and recovery.
Conflict Of Interest Statement
PH is the director of the Duke University Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorders fellowship, which receives grant support from Medtronic. MS works for Duke University, and has received consultancy fees from Eli Lilly, Merz, Osmotica, Pfizer, SK Life Sciences, Allergan, Avid, Best Doctors, Biotie, Lundbeck, Neuronova, Novartis Pharma , Saraepta Therapeutics, and Sunovion Pharmaceutics, Inc. Dr. MS has also received grants from the Michael J. Fox Foundation, the NIH, the Parkinson Study Group, and Pharma 2B, royalties from Informa Press for the Handbook of Dystonia and Duke University for the Wearing Off Questionnaire. He has also received payment for development of educational presentations from the University of Kansas, the University of Miami, and the University of Rochester. Dr. MS also received paid travel accommodations from the Cleveland Clinic Neurological Institute, the Movement Disorder Society, and the National Parkinson Foundation.
Read Also: Parkinson Silverware
What To Expect After Deep Brain Stimulation
- Reactions 0 reactions
Deep brain stimulation is a treatment option that works well for some people with Parkinsons disease . This chronic disorder affects the nervous system and can greatly impact daily life. At times, doctors suggest DBS to help manage PD symptoms caused by the decline of neurons in the brain.1
DBS treatment involves several steps. A doctor places a special device in the persons body during surgery. This device is designed to send electrical currents to certain parts of the brain. A doctor or DBS expert adjusts the devices settings based on how the person responds to the impulses.1
What Is Deep Brain Stimulation
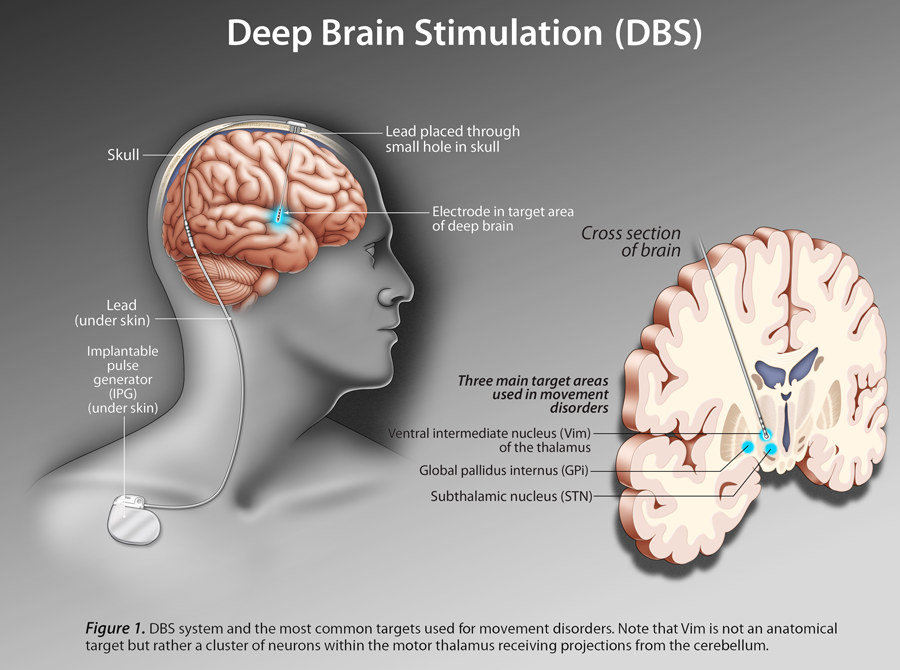
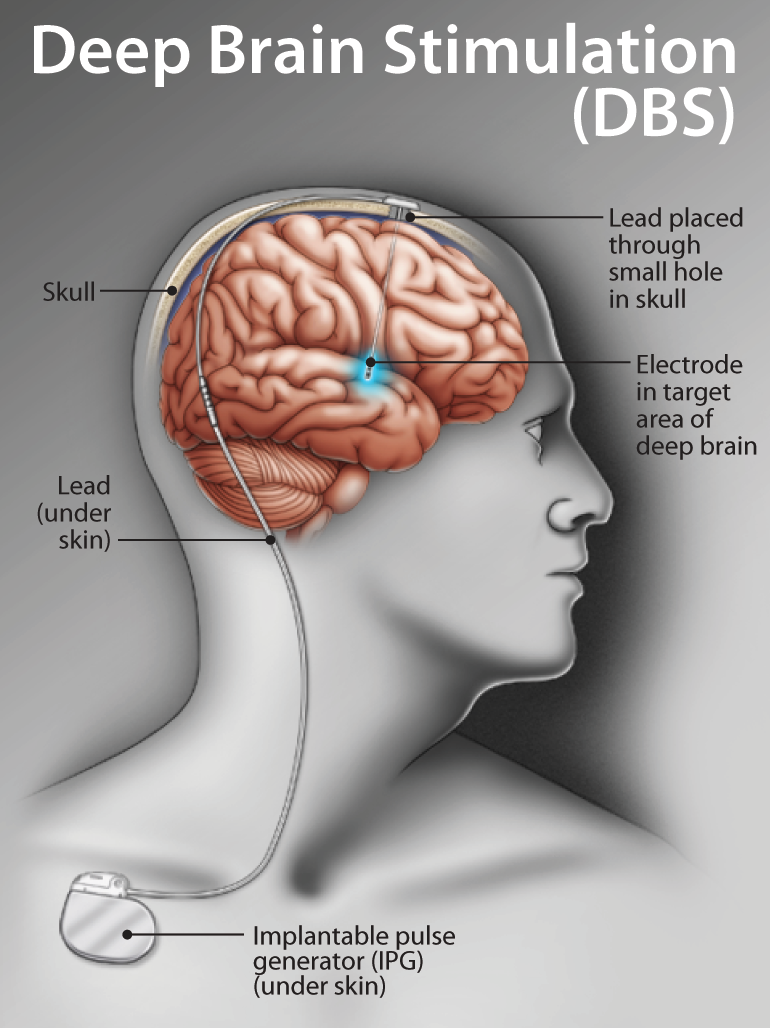
Deep brain stimulation is a surgical procedure that involves implanting electrodes in the brain, which deliver electrical impulses that block or change the abnormal activity that cause symptoms.
The deep brain stimulation system consists of four parts:
- Leads that end in electrodes that are implanted in the brain
- A small pacemaker-like device, called a pulse generator, that creates the electrical pulses
- Extension leads that carry electrical pulses from the device and are attached to the leads implanted in the brain
- Hand-held programmer device that adjusts the devices signals and can turn the device off and on.
In deep brain stimulation, electrodes are placed in the targeted areas of the brain. The electrodes are connected by wires to a type of pacemaker device placed under the skin of the chest below the collarbone.
Once activated, the pulse generator sends continuous electrical pulses to the target areas in the brain, modifying the brain circuits in that area of the brain. The deep brain stimulation system operates much the same way as a pacemaker for the heart. In fact, deep brain stimulation is referred to as the pacemaker for the brain.
Also Check: Sam Waterston Tremor
Surgical Procedure And Intraoperative Management
DBS surgery is preferentially performed in a relative medication-off state. To facilitate the rapid adaption of therapy, the authors recommend withdrawal of long-acting dopaminergic agents and temporary replacement by levodopa and continuous administration of apomorphine prior to surgery.34 At our center, levodopa is discontinued at least 12 h prior to surgery, similar to assessments of motor symptoms in the off state. Apomorphine in turn is continued until initiation of surgery. To prevent nausea and vomiting, domperidone should be considered one day before and during the first 2 days of using apomorphine. Any medication associated with an increased risk for cerebral hemorrhage must be discontinued appropriately.
How Should I Care For The Surgical Area Once I Am Home
- Your stitches or staples will be removed 10 to 14 days after surgery.
- Each of the four pin sites should be kept covered with band aids until they are dry. You will be able to wash your head with a damp cloth, avoiding the surgical area.
- You may only shampoo your hair the day after your stitches or staples are removed, but only very gently.
- You should not scratch or irritate the wound areas.
You May Like: Prayer For Parkinson’s Disease
What Happens Before Surgery
In the doctor’s office you will sign consent forms and complete paperwork to inform the surgeon about your medical history, including allergies, medicines, anesthesia reactions, and previous surgeries. Presurgical tests may need to be done several days before surgery. Consult your primary care physician about stopping certain medications and ensure you are cleared for surgery.You may also need clearance from your cardiologist if you have a history of heart conditions.
Stop taking all non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines and blood thinners 7 days before surgery. Stop using nicotine and drinking alcohol 1 week before and 2 weeks after surgery to avoid bleeding and healing problems.
You may be asked to wash your skin and hair with Hibiclens or Dial soap before surgery. It kills bacteria and reduces surgical site infections.
No food or drink, including your Parkinson’s medication, is permitted after midnight the night before surgery.
Try to get a good night’s sleep. The DBS surgery involves multiple steps and lasts most of the day, during which you may be awake and off medication.
Morning of surgery
Arrive at the hospital 2 hours before your scheduled surgery time to complete the necessary paperwork and pre-procedure work-ups. An anesthesiologist will talk with you and explain the effects of anesthesia and its risks.
A Stanford Neurosurgeon Answered Questions About Deep Brain Stimulation
Stanfords Parkinsons Community Outreach Program hosts a quarterly deep brain stimulation support group meeting for those wanting to learn more about this surgical treatment for Parkinsons disease . The June 2020 meeting featured Dr. Daniel Kramer, a neurosurgeon and clinical instructor at Stanford, who answered audience questions pertaining to DBS.
You May Like: Judy Woodruff Parkinson’s
Is Deep Brain Stimulation Right For You
While deep brain stimulation is shown to offer long-term benefits, the treatment does come with some risks. According to the Parkinsons Foundation, there is a 1% to 3% chance of developing an infection, cranial bleeding, stroke, or other complications from the treatment.
Furthermore, deep brain stimulation might work better for some people than others. It might be an option worth considering if youve experienced symptoms of Parkinsons for at least five years, are struggling with side effects of Parkinsons medications, or your symptoms make it difficult to perform everyday activities, among other factors.
The decision for or against deep brain stimulation should be made by having the potential candidate evaluated by a multidisciplinary team who can together construct a risk-benefit profile for a potential candidate, explains Dr. Okun. The team commonly is made up of a neurologist, a neurosurgeon, a neuropsychologist, a psychiatrist, and rehabilitation specialists.
Talk with a neurologist if you have Parkinsons disease and youre interested in exploring deep brain stimulation.
How Effective Is It
DBS does not cure or slow the progression of Parkinsons disease. However, many people report that it helps them control the motor symptoms of the condition.
The Parkinsons Foundation says that DBS improves symptoms in many people. However, it is different for everyone.
Some people experience a mild improvement, while others experience a significant improvement. Some people may be able to stop taking their Parkinsons disease medication, while others will not.
DBS is not the right treatment choice for everyone. Doctors tend to only recommend it in advanced Parkinsons disease and when more standard medications are not working as well as they should.
According to the Parkinsons Foundation, people who are best suited to DBS:
- have had Parkinsons disease symptoms for at least 5 years
- experience on/off fluctuations in symptoms, even though they are taking medications
- have dyskinesia
There are three components of the DBS system:
- The lead: This is also called an electrode. It is a thin, insulated wire.
- The extension: This is another insulated wire that connects the lead to the neurostimulator.
- The neurostimulator, or IPG: This is essentially the battery pack.
According to Johns Hopkins, during the procedure, a surgeon will implant the three pieces of the DBS system into the persons body.
Also Check: Cleveland Clinic Parkinson’s Bicycle Study 2017
Deep Brain Stimulation For The Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease And Other Movement Disorders
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that leads to resting tremor, rigidity, slowness of movement, and postural instability. These symptoms are caused by degeneration of neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta , one of a group of brain structures known as the basal ganglia and part of a circuit crucial for coordinating purposeful movement. This circuit relies on the chemical messenger dopamine, which is produced by SNc neurons. As PD progresses and these neurons are lost, reduced dopamine results in abnormal circuit activity and motor symptoms.
The molecular precursor to dopamine, L-DOPA , is used to treat PD. However, people in later stages of the disease experience off periods when this medication does not work well, and L-DOPA treatment can also trigger uncontrolled involuntary movement, a condition called dyskinesia. deep brain stimulation can offer symptomatic relief in later stages of PD and may reduce requirements for L-DOPA treatment and exposure to its side effects. DBS is also used to treat other movement disorders, including essential tremor, which causes involuntary shaking that worsens during movement, and dystonia, which causes involuntary muscle contractions and slow, repetitive movements or abnormal postures.
How Does The Neurosurgeon Know Where To Place The Electrodes In My Brain
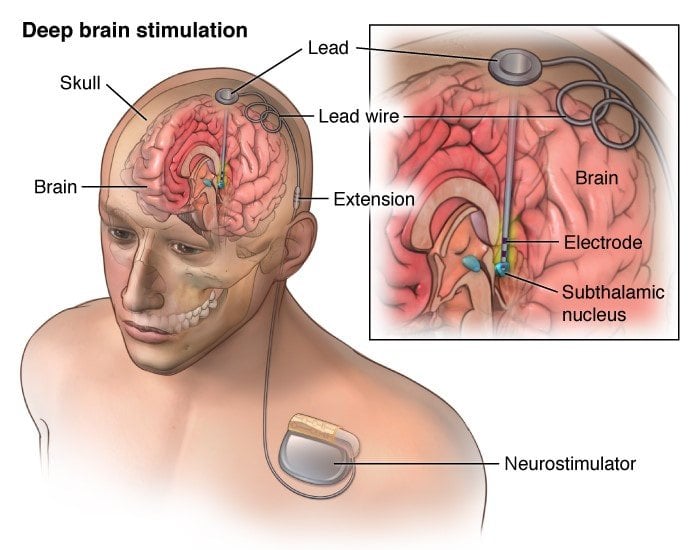
Positioning the electrodes in the brain is the most critical step. The electrodes have to be placed in an exact location in the brain to improve symptoms. Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging scans are taken before and/or during the procedure to pinpoint the exact areas to target and guide the lead and electrode placement. Many times an electrode may be used to record brain cell activity at the target site to improve lead placement.
Don’t Miss: On Off Phenomenon
How Does It Work
A small device placed inside your chest sends electrical pulses to your brain. The pulses block nerve signals that cause Parkinson’s symptoms.
A DBS system has four parts:
- A thin wire, called a lead, that’s placed in the part of your brain causing symptoms
- A pulse generator, like a pacemaker, that sends tiny electrical signals to the lead
- A wire that connects the lead to the pulse generator
- A remote control to program the system — the only part outside your body
After the system is in place and turned on, a DBS expert will adjust it so you get the best relief for your symptoms.
You can also control the system yourself. You can turn it off and on, check the battery, and tweak the settings.
Will I Have To Limit My Activity Following Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery
- You should not engage in light activities for 2 weeks after surgery. This includes housework and sexual activity.
- You should not engage in heavy activities for 4 to 6 weeks after surgery. This includes jogging, swimming, or any physical education classes. Anything strenuous should be avoided to allow your surgical wound to heal properly. If you have any questions about activities, call your doctor before performing them.
- You should not lift more than 5 lbs. for at least 2 weeks.
- You should not raise your arms above your shoulders or over bend or stretch your neck.
- Depending on the type of work you do, you may return to work within 4 to 6 weeks.
Don’t Miss: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinsons
What Care Is Needed After
On top of the wound care required with any surgery, DBS calls for special follow-up and ongoing care. Depression, falls, nausea, and problems with motor skills and swallowing can occur after DBS. In a follow-up appointment, doctors can address these issues and any other side effects of the device and/or the stimulation.1,2
Some follow-up care will last only a short time, depending on the issue. For instance, DBS can alter a persons mood, personality, and speech. Counseling, drugs, and speech therapy may help with these issues. A doctor can help find the best course of action in each case.1,2
People treated with DBS will need some extra care for the rest of their lives. Each persons device must be maintained and adjusted to meet their unique needs. Dosages of other drugs used to treat PD may also need to change over time.1,2,4
Clinical Experience With Deep Brain Stimulation
The advent of modern DBS led to a major change in the therapeutic armamentarium for movement disorders. DBS rapidly overtook lesioning as the surgical treatment of choice for refractory movement disorders due to a number advantages: it is nondestructive and several stimulation parameters, including the location, size, intensity, and the shape of the stimulating current field can be adjusted following surgical implantation. These properties allow clinicians to program the DBS device in such a way as to maximize motor benefits while minimizing side effects, most of which are caused by the inadvertent stimulation of structures adjacent to the intended target. Perhaps most importantly for patients with PD, DBS has a lower reported complication rate when used bilaterally .
Since the first application of DBS for PD in 1993, several thousand patients worldwide have undergone surgical implantation. While many studies have reported the benefits and durability of this therapy , six large-scale, randomized, controlled clinical trials have been performed . Given the pervasive nature of this disease, the end points of these trials have appropriately included quality of life measures, the severity of motor symptoms in the medication off state, and time spent in the on state without troublesome motor symptoms .
Don’t Miss: Prayers For Parkinson’s Disease
Historical Perspective Of Deep Brain Stimulation
Prior to the discovery of levodopa, surgical interventions were the most efficacious treatment for PD symptoms, but primarily focused on the reduction of bothersome tremor. Early approaches targeted the pyramidal tracts, with lesioning either at the point of origin in the cortex or the descending pathways through the brainstem and cervical spinal cord . Although tremor was reliably improved following surgery, hemiparesis was an inevitable consequence. However, in 1952, Dr. Irving Cooper inadvertently interrupted the anterior choroidal artery while performing a mesencephalic pedunculotomy in a patient with PD. Ligation of the vessel was required, though what resulted was a serendipitous reduction in rigidity and tremor with preservation of motor and sensory function. Cooper reasoned the favorable outcomes were due to infarction of the medial globus pallidus. An expansion of ablative stereotactic surgery followed, aided by the earlier development of the stereotactic frame and methods of targeting deep brain structures, including the basal ganglia and thalamus. However, the success of these approaches was limited, partly because of inaccurate, imprecise, and inconsistent targeting. Moreover, intentionally created bilateral brain lesions frequently led to irreversible deficits in speech, swallowing, and cognition.
Pallidal Stimulation Versus Subthalamic Stimulation
As mentioned, there are two main anatomic targets for using DBS to treat PD the STN and the GPi. There have been several large randomized studies comparing STN and GPi DBS in PD. It is suggested that both STN DBS and GPi DBS overall equally and successfully improve motor symptom, and are similar in cost-effectiveness. However, although no differences were observed in the on phase between STN DBS and GPi DBS, significant differences were seen in the off phase STN DBS was more effective in terms of motor function improvement in the off phase. There are different opinions in terms of effects of STN DBS and GPi DBS on quality of life. Some authors have found no significant difference between the STN and GPi targets. However, others agree with that greater improvements in quality-of-life measures are achieved in patients with GPi DBS.
GPi DBS can be used for patients with more axial symptoms, gait issues, dyskinesias, depression, and word fluency problems. STN DBS is often favored in reducing medication post surgery, and for patients with greater tremor. STN-DBS has also demonstrated an improvement in the quality of sleep for patients.
You May Like: Pfnca Wellness Programs
What Benefits Does The Procedure Offer
DBS is not a cure for Parkinsons, but it may help control motor symptoms while allowing a reduction in levodopa dose. This can help reduce dyskinesias and reduce off time. DBS does not usually increase the peak benefits derived from a dose of levodopa the best levodopa response before DBS is a good indicator of the best response after DBS. But it can help extend the amount of on time without dyskinesias, which may significantly increase quality of life.
DBS does not provide most patients benefit for their non-motor symptoms, such as depression, sleep disturbance, or anxiety. DBS also does not usually improve postural instability or walking problems. If a symptom you have does not respond to levodopa, it is not likely to respond to DBS.
Spinal Cord Stimulation For Movement Disorders
Spinal cord stimulation has shown promising results in spinal cord injury and other movement disorders, such as multiple sclerosis. The stimulation, applied over the lumbar spinal cord, works by activating large diameter afferent fibers entering the spinal cord, which then transsynaptically activate and engage spinal neuronal networks. The same target structures can also be activated by transcutaneous electrodes placed over the lower thoracic spine and abdomen. Transcutaneous spinal cord stimulation is completely non-invasive and, as it uses TENS electrodes and stimulators, can be applied at low cost. Yet, in comparison to the implanted epidural variant, the efficacy of transcutaneous spinal cord stimulation depends on the body position and spinal alignment, which could lead to inconsistent result if the body position and posture isn’t controlled during the application.
Don’t Miss: Weighted Silverware