Strategy For Identifying Mechanism Based Ad/pd Subtypes
Before going into more detail, we briefly outline our general approach for identifying subtypes of sporadic AD and PD idiopathic patients : Following Tan et al. it is largely driven by the idea of a genetic sub-classification followed by a clinical, imaging based and biological characterization of patients in each cluster to test disease relevance.
Figure 1
Genetic commonalities between AD and PD can only be expected at the biological function level. Hence, the starting point of our work was a comprehensive mapping of the molecular disease landscape of AD and PD based on the scientific literature . The result was a set of 15 molecular mechanisms comprising 27 proteins that have been implicated in both diseases . We mapped 148 SNPs to these genes based on proximity as well as eQTL analysis, see details in Supplements. Using ADNI and PPMI as discovery cohorts , we calculated for each of the 15 molecular mechanism an aggregate burden score via sparse autoencoders and then used sparse non-negative matrix factorization to identify 4 distinct patient subgroups in AD and PD, see section. These subgroups were found independently in both diseases as well as in a merger of ADNI and PPMI patients .
Figure 2
Possible Link To Alzheimers
Though Alzheimers, Huntingtons, and Parkinsons are distinctly different diseases, some evidence has emerged that shows a common link between the three.
All three diseases have proteins within the cells that do not assemble properly. Though the molecular and cellular changes that occur in each disease vary greatly, this protein degradation has been shown to precede early clinical signs in each disease. This is promising news, as more studies are being done to determine whether this can either predict or prevent these neurodegenerative diseases.
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
- Apathy
- Feeling, seeing, smelling, hearing and tasting things that arent there
- Hallucinations and delusions
Parkinsons disease is usually expressed through the following five stages:
- Stage one Mild symptoms dont interfere with daily tasks, tremors occur on one side of the body, and posture, gait and facial expression changes may happen.
- Stage two Symptoms worsen, tremors and stiffness affect the entire body and walking and standing are more difficult. At this stage, people may have some trouble performing daily activities.
- Stage three Trouble moving quickly, and balance issues can make it hard to eat or get dresses. Patients may be more likely to fall.
- Stage four Patients may need a walker to move around. Most people are unable to live alone at this stage because they need help with daily activities.
- Stage five It may be impossible to stand or walk. A wheelchair may help with mobility. A caregiver should be present at all times during this stage.
Don’t Miss: Nad Therapy For Parkinson’s Disease
Treatments For Parkinsons Disease Dementia And Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Treatments for DLB are similar to PDD and are aimed at symptom control. The motor symptoms of slowness, stiffness and walking difficulties can be treated with Levodopa. However, Levodopa can cause or exacerbate hallucinations, making it difficult to use it as a treatment for patients who have or are at risk of having hallucinations. Sometimes, clinicians will need to treat the hallucinations more aggressively in order for a patient to tolerate Levodopa given to help the motor symptoms. On the flipside, anti-psychotic medications to control hallucinations can worsen motor symptoms, so treating all the symptoms of LBD simultaneously can be a tricky balancing act.
Dementia With Lewy Bodies And Parkinson Disease Dementia
, MD, PhD, Department of Neurology, University of Mississippi Medical Center
Dementia with Lewy bodiesParkinson disease dementia
Dementia is chronic, global, usually irreversible deterioration of cognition.
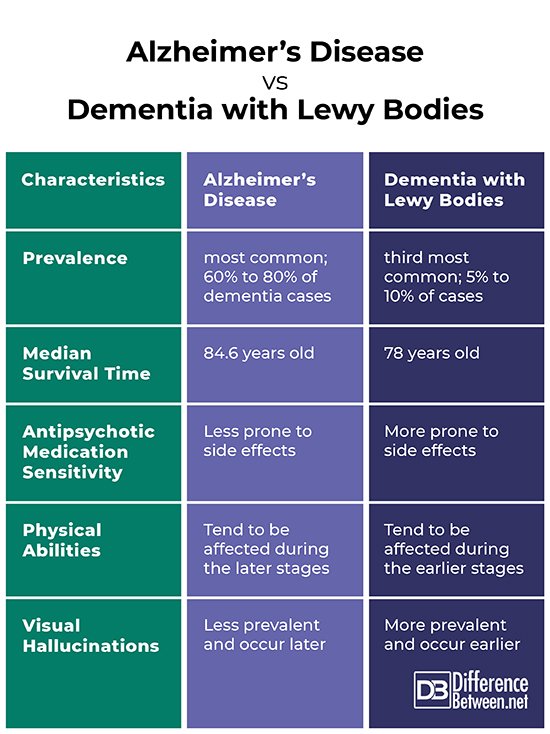
Dementia with Lewy bodies is the 3rd most common dementia. Age of onset is typically > 60.
Lewy bodies are spherical, eosinophilic, neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions composed of aggregates of alpha-synuclein, a synaptic protein. They occur in the cortex of some patients who have dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurotransmitter levels and neuronal pathways between the striatum and the neocortex are abnormal.
Lewy bodies also occur in the substantia nigra of patients with Parkinson disease, and dementia may develop late in the disease. About 40% of patients with Parkinson disease develop Parkinson disease dementia, usually after age 70 and about 10 to 15 years after Parkinson disease has been diagnosed.
Because Lewy bodies occur in dementia with Lewy bodies and in Parkinson disease dementia, some experts think that the two disorders may be part of a more generalized synucleinopathy affecting the central and peripheral nervous systems. Lewy bodies sometimes occur in patients with Alzheimer disease, and patients with dementia with Lewy bodies may have neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Dementia with Lewy bodies, Parkinson disease, and Alzheimer disease overlap considerably. Further research is needed to clarify the relationships among them.
Read Also: Cleveland Clinic Parkinson’s Doctors
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease was described by James Parkinson nearly 100 years before Dr. Alois Alzheimer described the dementia later named Alzheimers disease . Called the shaking palsy by Parkinson, PD is diagnosed when a person shows at least two of these three symptoms: slowed movements , muscle rigidity, and tremor . We recognize many other associated signs of PD, including expressionless face, quiet speech, cramped handwriting, shuffling gait, trouble getting out of a chair, and difficulty swallowing. Many of the symptoms of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease result when certain nerve cells that produce dopamine in the brain begin to malfunction and die.
Most cases are called idiopathic, meaning the cause remains unknown, although a small number of cases are linked with poisoning , head trauma, more complex PD-like neurological disorders , or reversible toxic medication effects ,
Movement Problems And Lewy Body Dementia
Some people with LBD may not experience significant movement problems for several years. Others may have them early on. At first, movement symptoms, such as a change in handwriting, may be very mild and easily overlooked. Movement problems may include:
- Muscle rigidity or stiffness
Recommended Reading: Michael J Fox Cure For Parkinson’s
What Is Lewy Body Dementia Causes Symptoms And Treatments
On this page:
Lewy body dementia is a disease associated with abnormal deposits of a protein called alpha-synuclein in the brain. These deposits, called Lewy bodies, affect chemicals in the brain whose changes, in turn, can lead to problems with thinking, movement, behavior, and mood. Lewy body dementia is one of the most common causes of dementia.
LBD affects more than 1 million individuals in the United States. People typically show symptoms at age 50 or older, although sometimes younger people have LBD. LBD appears to affect slightly more men than women.
Diagnosing LBD can be challenging. Early LBD symptoms are often confused with similar symptoms found in other brain diseases or in psychiatric disorders. Lewy body dementia can occur alone or along with other brain disorders.
It is a progressive disease, meaning symptoms start slowly and worsen over time. The disease lasts an average of five to eight years from the time of diagnosis to death, but can range from two to 20 years for some people. How quickly symptoms develop and change varies greatly from person to person, depending on overall health, age, and severity of symptoms.
In the early stages of LBD, symptoms can be mild, and people can function fairly normally. As the disease advances, people with LBD require more help due to a decline in thinking and movement abilities. In the later stages of the disease, they often depend entirely on others for assistance and care.
How Is Age Related To Pdd
Both PD and PDD are more common with increasing age. Most people with PD start having movement symptoms between ages 50 and 85, although some people have shown signs earlier. Up to 80% of people with PD eventually develop dementia. The average time from onset of movement problems to the development of dementia is about 10 years.
Recommended Reading: Best Stationary Bike For Parkinson’s
Epidemiology Of Dementia And Parkinson’s Disease
Dementia and PD are both diagnosed frequently and increase mortality . Perhaps dementia is perceived more so as a memory problem and a disease of old age, but the incidence of dementia and PD in younger age is similar. In the Netherlands, for dementia, the incidence per 1,000 person-years is 0.4 among those aged 6064 , and for PD, it is 0.3 . Dementia incidence patterns, however, show a much steeper increase with age mounting to 27 per 1,000 person-years for those 85 and over, compared to 4 for PD over 85. In view of similar mortality , therefore, the prevalence of dementia in the general population is much higher than prevalence of PD . However, adjusted for age and other factors, 6-year mortality in PD is higher than in Alzheimer’s dementia . Age adjustment is relevant also as it shows that comorbid disease may be equally prevalent for Alzheimer’sa main type of dementiaand PD across the same age groups .
What Are The Complications Of Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease causes physical symptoms at first. Problems with cognitive function, including forgetfulness and trouble with concentration, may arise later. As the disease gets worse with time, many people develop dementia. This can cause profound memory loss and makes it hard to maintain relationships.
Parkinson disease dementia can cause problems with:
- Speaking and communicating with others
- Problem solving
- Forgetfulness
- Paying attention
If you have Parkinson disease and dementia, in time, you likely won’t be able to live by yourself. Dementia affects your ability to care of yourself, even if you can still physically do daily tasks.
Experts don’t understand how or why dementia often occurs with Parkinson disease. Its clear, though, that dementia and problems with cognitive function are linked to changes in the brain that cause problems with movement. As with Parkinson disease, dementia occurs when nerve cells degenerate, leading to chemical changes in the brain. Parkinson disease dementia may be treated with medicines also used to treat Alzheimer’s disease, another type of dementia.
Recommended Reading: Grants For Parkinson’s Patients
Types Of Lewy Body Dementia And Diagnosis
LBD refers to either of two related diagnoses dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson’s disease dementia. Both diagnoses have the same underlying changes in the brain and, over time, people with either diagnosis develop similar symptoms. The difference lies largely in the timing of cognitive and movement symptoms.
In DLB, cognitive symptoms develop within a year of movement symptoms. People with DLB have a decline in thinking ability that may look somewhat like Alzheimer’s disease. But over time, they also develop movement and other distinctive symptoms of LBD.
In Parkinson’s disease dementia, cognitive symptoms develop more than a year after the onset of movement symptoms . Parkinson’s disease dementia starts as a movement disorder, with symptoms such as slowed movement, muscle stiffness, tremor, and a shuffling walk. These symptoms are consistent with a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Later on, cognitive symptoms of dementia and changes in mood and behavior may arise.
Not all people with Parkinson’s disease develop dementia, and it is difficult to predict who will. Many older people with Parkinson’s develop some degree of dementia.
Caregivers may be reluctant to talk about a person’s symptoms when that person is present. Ask to speak with the doctor privately if necessary. The more information a doctor has, the more accurate a diagnosis can be.
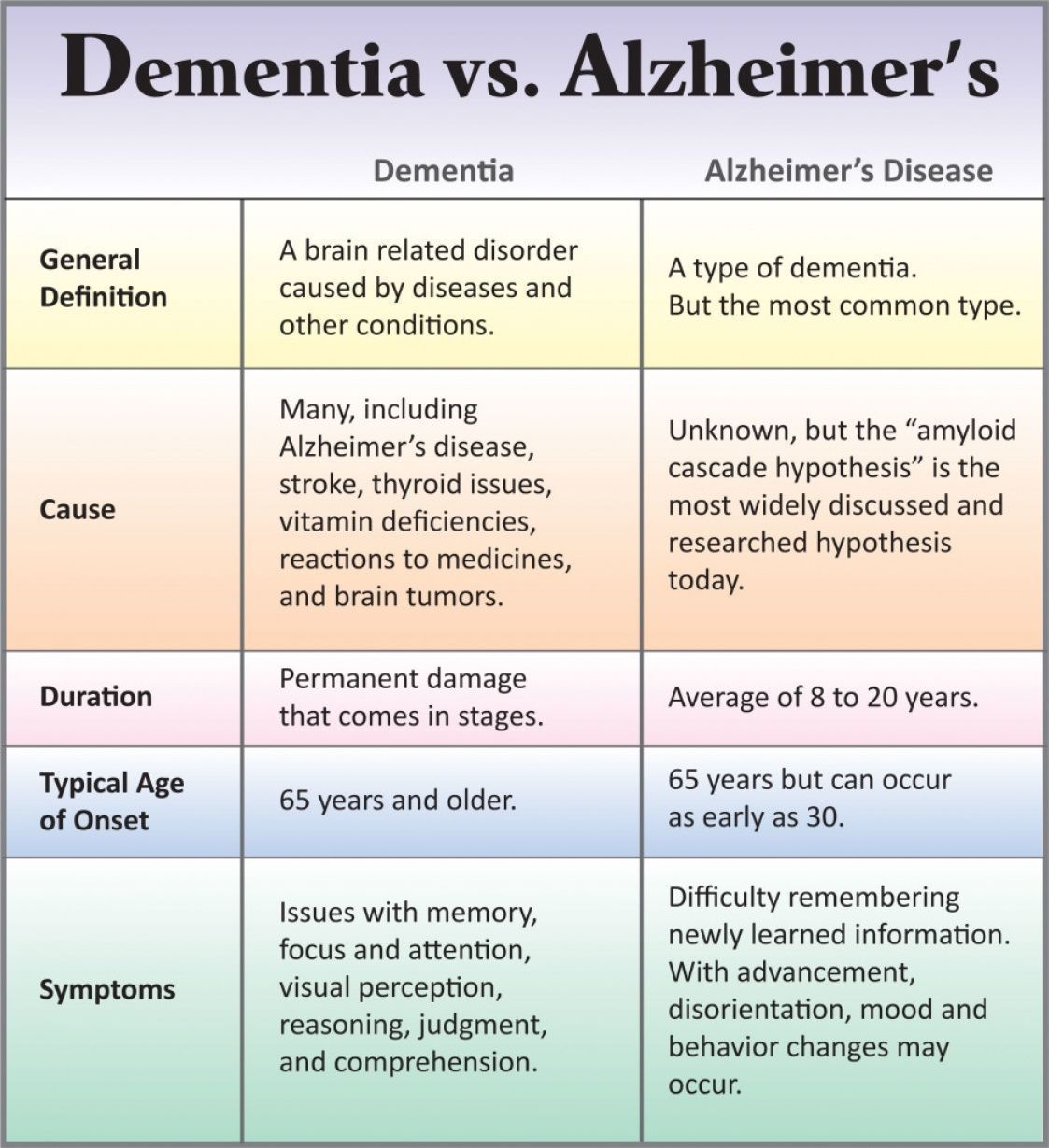
The Differences Between Alzheimers And Parkinsons
16 October, 2020
Do you know the differences between Alzheimers and Parkinsons? First of all, we must say that both diseases constitute two of the causes of dementia. Now, lets be a bit more specific. According to data from the WHO , dementia due to Alzheimers disease represents 60-70% of all cases of dementia in the world.
However, its important to keep in mind that theyre very different diseases. Additionally, we must make clear that having either condition doesnt always lead to the development of dementia . In this sense, we know that between 20-60% of people with Parkinsons disease end up developing dementia.
Buter et al. conducted a study that was published in the journal Neurology. It was conducted with 233 patients with Parkinsons disease. The researchers were able to observe that about 60% of them developed Parkinsons dementia in a period of 12 years.
So whats dementia? It refers to the set of symptoms that arise as a consequence of neurological damage or disease. These symptoms involve the loss or weakening of the mental faculties and mainly affect three different areas: cognitive , behavioral , and personality .
Dont Miss: How Many Caregivers Are Caring For Parents With Dementia
Recommended Reading: Lifestyle Changes For Parkinson’s Disease
Differences Between Delirium Dementia Alzheimer’s And Parkinson’s
Your brain doesnt finish developing until your mid-to-late 20s. Is it all downhill from there? Neuroscientists are discovering that you can continue to rewire your brain to encourage growth and prevent your brain cells from dying, but everyone experiences age-related cognitive decline.
Its often lumped into an umbrella category of mental slowdown that happens as you get older.
However, there are a few different brain diseases that affect aging adults. Heres how to understand the difference between delirium, dementia, Alzheimers and Parkinsons.
How Is Parkinsons Disease Dementia Diagnosed
No single test can diagnose Parkinsons disease dementia. Instead, doctors rely on a series or combination of tests and indicators.
Your neurologist will likely diagnose you with Parkinsons and then track your progression. They may monitor you for signs of dementia. As you get older, your risk for Parkinsons dementia increases.
Your doctor is more likely to conduct regular testing to monitor your cognitive functions, memory recall, and mental health.
You May Like: Is Drooling A Sign Of Parkinson’s Disease
Whats The Difference Between Lewy Body Dementia Parkinsons Disease And Alzheimers Disease
Lewy body dementia is an umbrella term for two related clinical diagnoses: dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinsons disease dementia. These disorders share the same underlying changes in the brain and very similar symptoms, but the symptoms appear in a different order depending on where the Lewy bodies first form.
Dementia with Lewy bodies is a type of dementia that causes problems with memory and thinking abilities that are severe enough to interfere with everyday activities. It specifically affects a persons ability to plan and solve problems, called executive function, and their ability to understand visual information. Dementia always appears first in DLB. The motor symptoms of Parkinsons such as tremor, slowness, stiffness and walking/balance/gait problems usually become more evident as the disease progresses. Visual hallucinations, REM sleep behavior disorder, fluctuating levels of alertness and attention, mood changes and autonomic dysfunction are also characteristic of DLB.
Finally, Alzheimers is characterized by different abnormal clumps called amyloid plaques, and jumbled fiber bundles called tau tangles. These microscopic structural changes in the brain were discovered by Dr. Alois Alzheimer in 1906. These plaques and tangles, together with loss of connections between nerve cells, contribute to loss of coherence and memory, as well as a progressive impairment in conducting normal activities of daily living.
Living With Parkinson Disease
These measures can help you live well with Parkinson disease:
- An exercise routine can help keep muscles flexible and mobile. Exercise also releases natural brain chemicals that can improve emotional well-being.
- High protein meals can benefit your brain chemistry
- Physical, occupational, and speech therapy can help your ability to care for yourself and communicate with others
- If you or your family has questions about Parkinson disease, want information about treatment, or need to find support, you can contact the American Parkinson Disease Association.
You May Like: Average Age Of Parkinson’s Onset
Lewy Bodies: More Than Lbd
LBD is characterized by the presence of Lewy bodies in the nerve cells of the brain, meaning that LBD patients have Lewy bodies in the brain.2 However, Lewy bodies are also common with other conditions, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinsons disease. In fact, most people with PD also have Lewy bodies in their brain. However, even if they have Lewy bodies, not all Parkinsons patients will also develop LBD.2
What Causes Parkinsons Disease Dementia
A chemical messenger in the brain called dopamine helps control and coordinate muscle movement. Over time, Parkinsons disease destroys the nerve cells that make dopamine.
Without this chemical messenger, the nerve cells cant properly relay instructions to the body. This causes a loss of muscle function and coordination. Researchers dont know why these brain cells disappear.
Parkinsons disease also causes dramatic changes in a part of your brain that controls movement.
Those with Parkinsons disease often experience motor symptoms as a preliminary sign of the condition. Tremors are one of the most common first symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
As the disease progresses and spreads in your brain, it can affect the parts of your brain responsible for mental functions, memory, and judgment.
Over time, your brain may not be able to use these areas as efficiently as it once did. As a result, you may begin experiencing symptoms of Parkinsons disease dementia.
You have an increased risk of developing Parkinsons disease dementia if:
- youre a person with a penis
- youre older
Don’t Miss: Sole Support For Parkinson’s
Behaviors Seen In Parkinsons Disease Dementia
As dementia progresses, managing disorientation, confusion, agitation, and impulsivity can be a key component of care.
Some patients experience hallucinations or delusions as a complication of Parkinsons disease. These may be frightening and debilitating. Approximately 50 percent of those with the disease may experience them.
The best thing to do when giving care to someone experiencing hallucinations or delusions from Parkinsons disease dementia is to keep them calm and reduce their stress.
Take note of their symptoms and what they were doing before they exhibited signs of hallucinating and then let their doctor know.
This element of the disease can be particularly challenging for caregivers. Patients may become unable to care for themselves or be left alone.
Some ways to make caregiving easier include:
- sticking to a normal routine whenever possible
- being extra comforting after any medical procedures
- limiting distractions
- using curtains, nightlights, and clocks to help stick to a regular sleep schedule
- remembering that the behaviors are a factor of the disease and not the person