Are There Different Types Of Accessory Pathways
Lown, B. The syndrome of short P-R interval, normal QRS complex and paroxysmal rapid heart action. Circulation. vol. 5. 1952 May. pp. 693-706.
James, TN. Morphology of the human atrioventricular node, with remarks pertinent to its electrophysiology. Am Heart J. vol. 62. 1961. pp. 756-71.
Lev, M, Leffler, WB, Langendorf, R. Anatomic findings in a case of ventricular preexcitation terminating in complete atrioventricular block. Circulation. vol. 34. 1966. pp. 718-33.
Murdock, CJ, Leitch, JW, Teo, WS. Characteristics of accessory pathways exhibiting decremental conduction. Am J Cardiol. vol. 67. 1991. pp. 506-10.
Ross, DL, Uther, JB. Diagnosis of concealed accessory pathways in supraventricular tachycardia. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. vol. 7. 1984. pp. 1069-85.
Anderson, RH, Becker, AE, Brechenmacher, C. Ventricular pre-excitation: a proposed nomenclature for its substrates. Eur J Cardiol. vol. 3. 1975. pp. 27-36.
Mahaim, I, Benatt, A. Nouvelles recherches sur les connections superieures de la branche du faisceau de His-Tawara avec cloison interventriculaire. Cardiologia. vol. 1. 1937. pp. 61
What Are The Two Forms Of Robinow Syndrome
Robinow syndrome is a rare disorder that affects the bones as well as other parts of the body. Two forms of Robinow syndrome have been described: autosomal recessive Robinow syndrome, and the milder autosomal dominant Robinow syndrome. They are distinguished based on their modes of inheritance, symptoms, and severity.
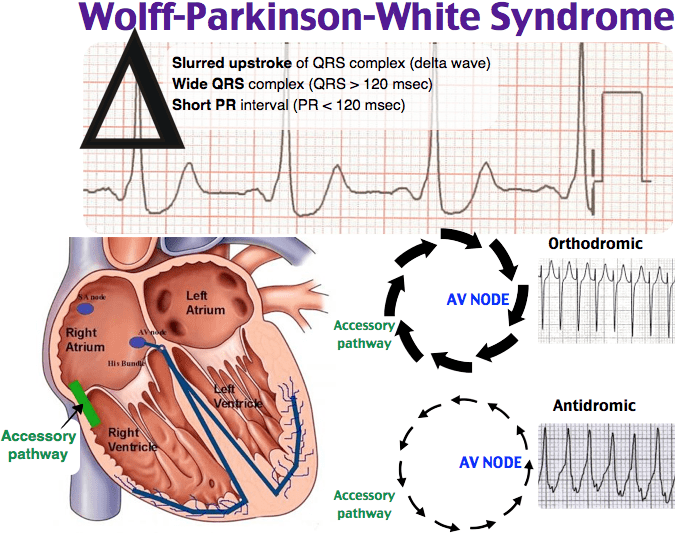
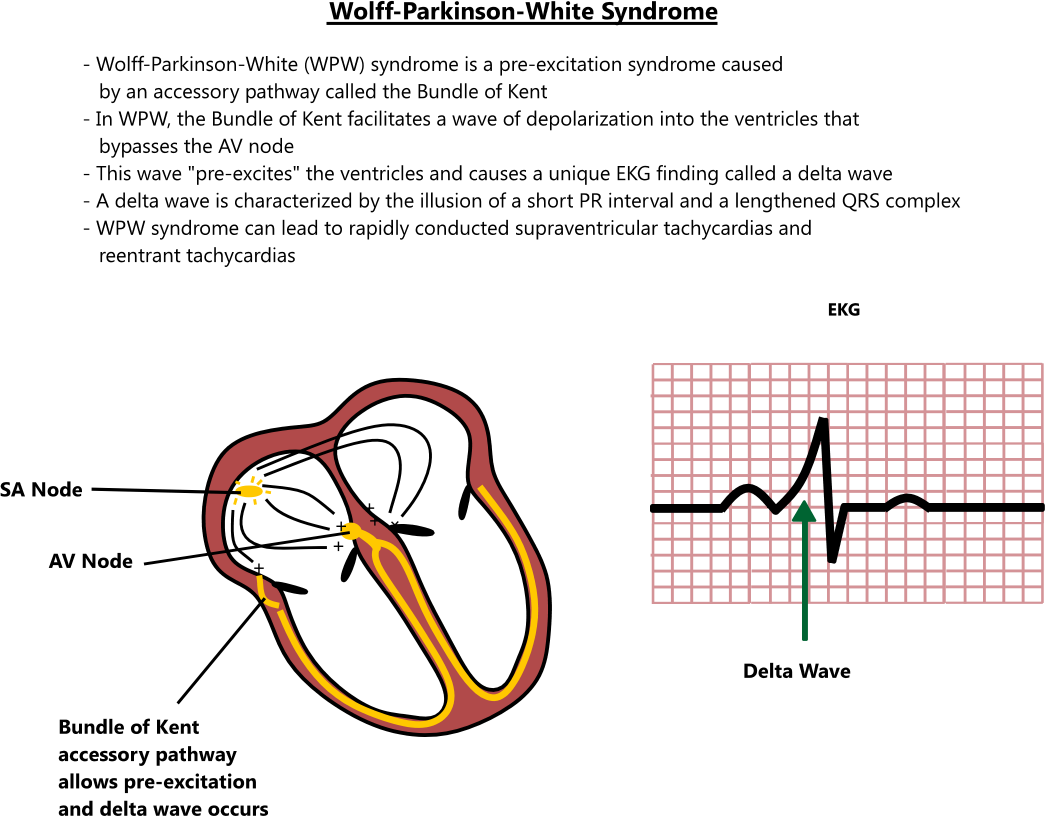
Prevalence Symptoms And Prognosis Of Wpw Syndrome
An electrocardiographic pattern of preexcitation occurs in the general population at a frequency of around 1.5 per 1000. Of these, 50% to 60% of patients become symptomatic. Approximately one-third of all patients with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia are diagnosed as having an AP-mediated tachycardia. Patients with AP-mediated tachycardias most commonly present with the syndrome of PSVT.
Population-based studies have demonstrated a bimodal distribution of symptoms for patients with preexcitation, with a peak in early childhood followed by a second peak in young adulthood. Nearly 25% of infants who demonstrate preexcitation and/or have AP-mediated arrhythmias will lose evidence of preexcitation and/or become asymptomatic over time as the conduction property of the AP can degenerate with time.
Pappone et al reported that during a mean follow-up of 37.7 months, 18.2% and 30% of noninducible patients have lost the anterograde and retrograde conduction, respectively. The mean age of these patients was 33.6 ± 14.3. Compared to others who had persistent conductibility through the AP, these patients were asymptomatic, noninducible, and had longer minimal 1:1 conduction cycle length through the AP during the baseline EPS.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease Funding Opportunities
Symptoms Of Wpw Syndrome
Typically, when teenagers or people in their early 20s first experience an arrhythmia due to this syndrome, it is an episode of palpitations Palpitations Palpitations are the awareness of heartbeats. The sensation may feel like pounding, fluttering, racing, or skipping beats. Other symptomsfor example, chest discomfort or shortness of breathmay… read more that begins suddenly, often during exercise. The episode may last for only a few seconds or may persist for several hours. For most people, the very fast heart rate is uncomfortable and distressing. A few people faint.
In older people, episodes of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia due to Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome tend to cause more symptoms, such as fainting, shortness of breath, and chest pain.
How Is It Treated
During an episode, your doctor may suggest that you try vagal manoeuvres. These are things that might help slow your heart rate. Your doctor will teach you how to do vagal manoeuvres safely. Examples include bearing down or putting an ice-cold, wet towel on your face.
Catheter ablation, a non-surgical procedure, might be used to stop the rhythm problem. This procedure can successfully eliminate WPW most of the time. There is a small risk of the arrhythmia recurring even after successful ablation of WPW. But a second session of catheter ablation is usually successful.
You might take medicine to control or prevent episodes.
Don’t Miss: What Is An Off Period In Parkinson’s
Are There Any Specific Tachycardias Associated With Accessory Pathways
Cain, ME, Luke, RA, Lindsay, BD. Diagnosis and localization of accessory pathways. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. vol. 15. 1992. pp. 801-24.
Reyes, W, Milstein, S, Dunnigan, A. Indications for modification of coexisting dual atrioventricular node pathways in patients undergoing surgical ablation of accessory atrioventricular connections. J Am Coll Cardiol. vol. 17. 1991. pp. 1561-7.
Klein, GJ, Bashore, TM, Sellers, TD. Ventricular fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. N Engl J Med.. vol. 301. 1979. pp. 1080-5.
Dreifus, LS, Haiat, R, Watanabe, Y. Ventricular fibrillation: a possible mechanism of sudden death in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Circulation. vol. 43. 1971. pp. 520-7.
Wellens, HJJ, Durrer, D. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome and atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. vol. 34. 1974. pp. 777-82.
Campbell, RWF, Smith, R, Gallagher, JJ. Atrial fibrillation in the preexcitation syndrome. Am J Cardiol. vol. 40. 1977. pp. 514-20.
Sharma, AD, Klein, GJ, Guiraudon, GM. Atrial fibrillation in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: incidence after surgical ablation of the accessory pathway. Circulation. vol. 72. 1985. pp. 161-9.
Dagres, N, Clague, JR, Lottkamp, H. Impact of radiofrequency catheter ablation of accessory pathways on the frequency of atrial fibrillation during long-term follow-up: high recurrence rate of atrial fibrillation in patients older than 50 years of age. Eur Heart J. vol. 22. 2001. pp. 423-7.
How Can We Tell The Location Of The Ap Based On The Superficial 12 Lead Ecg
Gallager, JJ, Pritchett, ELC, Sealy, WC. The preexcitation syndromes. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. vol. 20. 1978. pp. 285-327.
Ross, DL, Uther, JB. Diagnosis of concealed accessory pathways in supraventricular tachycardia. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. vol. 7. 1984. pp. 1069-85.
Arruda, MS, McClelland, JH, Wang, X. Development and validation of an ECG algorithm for identifying accessory pathway ablation site in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. vol. 9. 1998. pp. 2-12.
Fitzpatrick, AP, Gonzales, RP, Lesh, MD. New algorithm for the localization of accessory atrioventricular connections using a baseline electrocardiogram. J Am Coll Cardiol. vol. 23. 1994. pp. 107-16.
Lindsay, BD, Crossen, KJ, Cain, ME. Concordance of distinguishing electrocardiographic features during sinus rhythm with the location of accessory pathways in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Am J Cardiol. vol. 59. 1987. pp. 1093-1102.
Cain, ME, Luke, RA, Lindsay, BD. Diagnosis and localization of accessory pathway. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. vol. 15. 1992. pp. 801-24.
DAvila, A, Brugada, J, Skeberis, V. A fast and reliable algorithm to localize accessory pathways based on the polarity of the QRS complex on the surface ECG during sinus rhythm. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. vol. 18. 1995. pp. 1615-27.
Xie, B, Heald, SC, Bashir, Y. Localization of accessory pathways from the 12-lead electrocardiogram using a new algorithm. Am J Cardiol. vol. 74. 1994. pp. 161-5.
You May Like: First Stage Of Parkinson’s Disease
How Is The Problem Treated
See supraventricular tachycardia. Patients may be treated with heart medicines to prevent episodes of SVT. In general, infants are treated until their first birthday and then the medicines can be stopped. In older children, radiofrequency ablation has become first line treatment as it is safe with high success rates.
Are You Always Short With Turner Syndrome
Girls with Turner syndrome are typically short in relation to the height of their parents. On average, adult women with untreated Turner syndrome are 20cm shorter than adult women without the syndrome. Treatment with additional high-dose growth hormone reduces this difference by about 5cm on average.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take Parkinson’s To Progress
Symptmes Du Syndrome De Wpw
Le syndrome de Wolff-Parkinson-White est une cause fréquente de tachycardie paroxystique supraventriculaire Tachycardie paroxystique supraventriculaire La tachycardie paroxystique supraventriculaire est un rythme cardiaque rapide et régulier qui débute et sarrête brutalement et qui a son origine au niveau… en apprendre davantage . Très rarement, ce syndrome provoque un rythme cardiaque extrêmement rapide et potentiellement mortel pendant la fibrillation auriculaire Fibrillation auriculaire et flutter auriculaire La fibrillation et le flutter auriculaires sont des formes de décharges électriques très rapides qui entraînent une contraction très rapide des oreillettes quelques-unes… en apprendre davantage .
Si les nourrissons développent des arythmies dues à ce syndrome, ils peuvent devenir essoufflés ou léthargiques, perdre leur appétit, ou présenter des pulsations de thorax rapides et visibles. Une insuffisance cardiaque peut se développer.
Lorsque des épisodes de tachycardie paroxystique supraventriculaire due à un syndrome de Wolff-Parkinson-White surviennent chez des personnes plus âgées, ils provoquent en général plus de symptômes, comme un évanouissement, un essoufflement et une douleur thoracique.
Pearls And Other Issues
Patients with atrial fibrillation and rapid ventricular response are often treated with amiodarone or procainamide. Procainamide and cardioversion are accepted treatments for conversion of tachycardia associated with Wolff Parkinson White syndrome . In acute AF associated with WPW syndrome, the use of IV amiodarone may potentially lead to ventricular fibrillation in some reports and thus should be avoided.
AV node blockers should be avoided in atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter with Wolff Parkinson White syndrome . In particular, avoid adenosine, diltiazem, verapamil, and other calcium channel blockers and beta-blockers. They can exacerbate the syndrome by blocking the heart’s normal electrical pathway and facilitating antegrade conduction via the accessory pathway.
An acutely presenting wide complex tachycardia should be assumed to be ventricular tachycardia if doubt remains about the etiology.
Read Also: What Is Drug Induced Parkinson’s Disease
Management Of Asymptomatic And Symptomatic Preexcitation
Blomström-Lundqvist, C, Scheinman, MM, Aliot, EM. ACC/AHA/ESC Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Supraventricular ArrhythmiasExecutive Summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines . Circulation. vol. 108. 2003. pp. 1871-1909.
Klein, GJ, Gulamhusien, SS. Intermittent preexcitation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Am J Cardiol. vol. 52. 1983. pp. 292-6.
Campbell, RWF, Smith, R, Gallagher, JJ. Atrial fibrillation in the preexcitation syndrome. Am J Cardiol. vol. 40. 1977. pp. 514-20.
Auricchio, A, Klein, H, Trappe, HJ. Lack of prognostic value of syncope in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. vol. 17. 1991. pp. 152-8.
Wellens, HJ, Bar, FW, Gorgels, AP. Use of ajmaline in patients with the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome to disclose short refractory period of the accessory pathway. Am J Cardiol. vol. 45. 1980. pp. 130-33.
Brembilla-Perrot, B, Ghawi, R. Electrophysiological characteristics of asymptomatic Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Eur Heart J. vol. 14. 1993. pp. 511-15.
Leitch, JW, Klein, GJ, Yee, R, Murdock, C. Prognostic value of electrophysiology testing in asymptomatic patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White pattern. Circulation. vol. 82. 1990. pp. 1718-23.
What Are The Typical Electrophysiologic Findings Of Wpw Syndrome
Electrophysiology study in patients with WPW syndrome can help to confirm the presence of an AP, differentiate this condition from other forms of SVT, and to localize the pathway participating in the tachycardia for ablative therapy.
Figure 8.
Eccentric retrograde conduction through the accessory pathway located in left free wall. Note the eccentric activation of the atrium with pacing from the ventricle, with earliest atrial depolarization at the distal CS lead . The panel shows right ventricular apical pacing at 200 beats/min . His p, proximal His His d, distal His V, ventricular electrogram A, atrial electrogram CS, coronary sinus CS 9-10, the most proximal electrode in the CS catheter RVa, right ventricular apex RVa d, distal right ventricular apex.
Retrograde conduction over most APs is nondecremental. Hence, in the absence of intraventricular conduction delay or the presence of multiple bypass tracts, the VA conduction time is the same over a range of pace cycle lengths. The exception to this is the slowly conducting decremental posteroseptal pathway found in the permanent form of junctional reciprocating tachycardia, in which the VA conduction time increases with increasing ventricular pacing rate.
It is important and often challenging to differentiate retrograde conduction over septal pathway from conduction over the normal AV system. One maneuver that can make this differentiation is differential pacing and measuring the VA conduction time.
Read Also: How Does Parkinson’s Disease Kill You
Atrial Fibrillation And Wolff
Atrial fibrillation may be particularly dangerous for people with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. The extra pathway can conduct the rapid impulses to the ventricles at a much faster rate than the normal pathway can. The result is an extremely fast ventricular rate that may be life threatening. Not only is the heart very inefficient when it beats so rapidly, but this extremely fast heart rate may also progress to ventricular fibrillation Ventricular Fibrillation Ventricular fibrillation is a potentially fatal, uncoordinated series of very rapid, ineffective contractions of the ventricles caused by many chaotic electrical… read more , which is fatal unless treated immediately.
Treatments For Wpw Syndrome
In many cases, episodes of abnormal heart activity associated with WPW syndrome are harmless, don’t last long, and settle down on their own without treatment.
You may therefore not need any treatment if your symptoms are mild or occur very occasionally, although you should still have regular check-ups so your heart can be monitored.
If your cardiologist recommends treatment, there are a number of options available. You can have treatment to either stop episodes when they occur, or prevent them occurring in the future.
Read Also: Glove For Parkinson’s Tremors
Catheter Ablation Of Accessory Pathways
Lesh, MD, Van Hare, G, Scheinman, MM. Comparison of the retrograde and transseptal methods for ablation of left free-wall accessory pathways. J Am Coll Cardiol. vol. 22. 1993. pp. 542-9.
Jackman, WM, Wang, X, Friday, KJ. Catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular pathways by radiofrequency current. N Engl J Med. vol. 324. 1991. pp. 1605-11.
Kuck, KH, Schluter, M, Geiger, M. Radiofrequency current catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular pathways. Lancet. vol. 337. 1991. pp. 1557-61.
Calkins, H, Langberg, J, Sousa, J. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular connections in 250 patients: abbreviated therapeutic approach to Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Circulation. vol. 85. 1992. pp. 1337-46.
Kay, GN, Pressley, JC, Packer, DL. Value of 12-lead electrocardiogram in discriminating atrioventricular nodal reciprocating tachycardia from circus movement atrioventricular utilizing a retrograde accessory pathway. Am J Cardiol. vol. 59. 1987. pp. 296-300.
Tchou, PJ, Lehmann, MJ, Donga, J. Effect of sudden rate acceleration on the human His-Purkinje system: adaptation of refractoriness in a damped oscillatory pattern. Circulation. vol. 73. 1986. pp. 920-9.
Drago, F, DeSantis, A, Grutter, G, Silverti, MS. Transvenous cryothermal catheter ablation of re-entry circuit located near the atrioventricular junction in pediatric patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. vol. 45. 2005. pp. 1096-103.
Fibrillation Auriculaire Et Syndrome De Wolff
La fibrillation auriculaire peut être particulièrement dangereuse en cas de syndrome de Wolff-Parkinson-White. La voie accessoire peut conduire les impulsions rapides vers les ventricules à un rythme beaucoup plus rapide que celui de la voie normale . Il en résulte une fréquence ventriculaire extrêmement rapide et potentiellement mortelle. Le cur est non seulement très peu efficace lorsquil bat aussi rapidement, mais ce rythme cardiaque extrêmement élevé peut également évoluer en une fibrillation ventriculaire Fibrillation ventriculaire La fibrillation ventriculaire est une série non coordonnée, potentiellement mortelle, de contractions très rapides et inefficaces des ventricules , provoquée par… en apprendre davantage , qui est mortelle si elle nest pas rapidement traitée.
Read Also: Can Parkinsons Be Reversed With Exercise
How To Know If Unborn Baby Has Down Syndrome
An ultrasound can detect fluid at the back of a fetuss neck, which sometimes indicates Down syndrome. The ultrasound test is called measurement of nuchal translucency. During the first trimester, this combined method results in more effective or comparable detection rates than methods used during the second trimester.
Treatment Of Wpw Syndrome
-
Maneuvers and drugs to convert heart rhythm
-
Sometimes ablation
Destruction of the extra conduction pathway by catheter ablation Destroying abnormal tissue Abnormal heart rhythms are sequences of heartbeats that are irregular, too fast, too slow, or conducted via an abnormal electrical pathway through the heart. Heart disorders are… read more is successful in more than 95% of people. The risk of death during the procedure is less than 1 in 1,000. Ablation is particularly useful for young people who might otherwise have to take antiarrhythmic drugs for a lifetime.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Support Group Connecticut
How Is Wpw Diagnosed
WPW can only be diagnosed by reviewing an ECG . A holter or ambulatory monitor and exercise testing are also helpful in evaluating patients known to have WPW.
In the past, patients with WPW but without symptoms had been observed by a cardiologist for many years. Recently, new guidelines have been published for this group of patients. Your cardiologist may order a holter monitor or stress test to look for a persistent patter of WPW. If the WPW pattern persists, invasive electrophysiology testing is now recommended.
Your doctor will also ask you several questions:
- Do you have symptoms?
- Do you have a history of atrial fibrillation?
- Do you have a history of fainting?
- Do you have a history of sudden cardiac death or does anyone in your family?
- Are you a competitive athlete?
The results of your diagnostic tests and the answers to these questions will help guide your therapy.
Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome Drugs
If vagal maneuvers cant stop rapid heartbeat, you may need an injection of an anti-arrhythmia drug. Your doctor may also recommend a medication that can slow down the heart rate.
Heart-Augmentation.
Pedals or patches on your chest can electrically blow your heart and help to restore a normal rhythm. Cardioversion is commonly used when maneuvers and medications are not effective.
Radiofrequency Catheter Isolated.
Thin, flexible ducts are fought through the blood vessels in your heart. The electrode on the catheter tips is destroyed due to your condition to the additional electrical pathway. Radiofrequency ablation permanently fixes heart-rhythm problems in most of the people with WPW syndrome.
| Footnote. Treatment of Wolff Parkinson White syndrome is treated through ablation procedure by destroying the extra electrical pathway which increases the heartbeats. Apart from that certain medications are also given in order to cure this syndrome. |
Recommended Reading: Amino Acid Used To Treat Parkinson’s Disease
How Can We Tell The Location Of The Ap Based On The Superficial 12
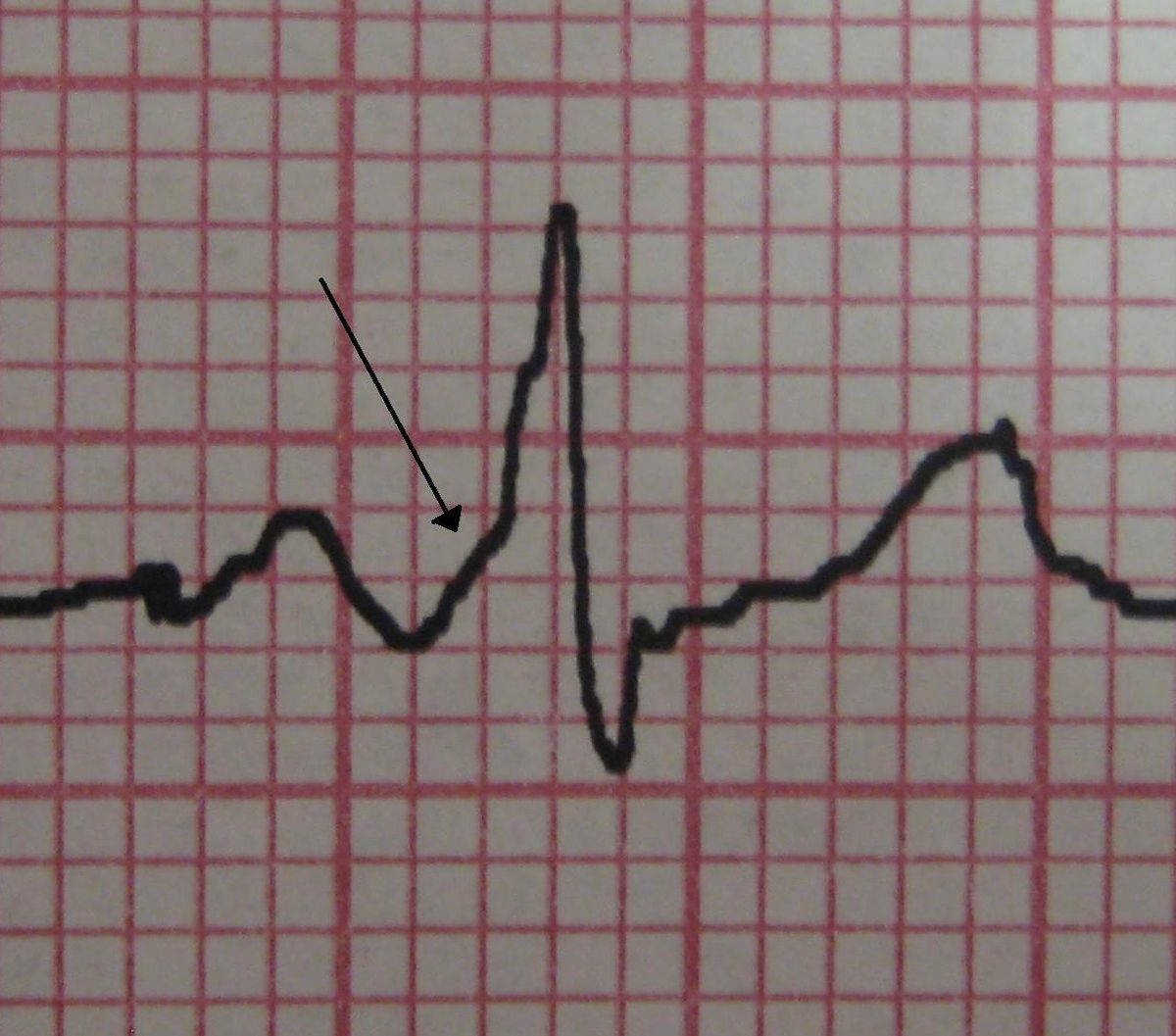
The ECG hallmark of an antegradely conducting AP is the delta wave along with a shorter than usual PR interval and a widened QRS complex. Conversely, the presence of retrograde conduction only in an AP will not be apparent on a surface ECG during sinus rhythm . Whereas ECG during ORT has a normal QRS complex with retrogradely conducting P wave after the completion of the QRS complex in the ST segment or early in the T wave, the QRS during ART is fully preexcited.
Numerous algorithms have been described to localize the site of the AP using the axis of the delta wave and QRS morphology. The location of the AP along the AV ring is classified variously into five or ten regions, which can be broadly divided into those on the left and the right of the AV groove. Distribution along these lines is not homogenous. Some 46% to 60% of the pathways are found on the left free wall space. Nearly 25% are within the posteroseptal and midseptal spaces, 15% to 20% in the right free wall space, and 2% in the anteroseptal space.
The positive predictive value of these algorithms is better when the delta wave polarity is included and when algorithms involve fewer than six locations. Two simple algorithms that include both the delta wave axis and the QRS axis are shown . For the purpose of localization of the APs, delta wave is defined as the first 20 ms of the earliest QRS deflection.