Management Of Paradoxical Amino Acid Reactions
Most Parkinsons disease patients treated under this novel approach do not achieve gradual relief of symptoms as the l-dopa dosing values are increased. Symptom cessation tends to be abrupt, analogous to turning a light switch from off to on.,,
Paradoxical reactions with concomitant administration of serotonin and dopamine amino acid precursors occur in approximately 5% of patients. A paradoxical reaction is defined as an outcome to treatment that is the opposite of what is expected. In the Parkinsons disease patients being treated with balanced amino acid precursors, the most common paradoxical reactions are agitation and confusion, although any disease process related to monoamine diseases may be exacerbated such as depression, insomnia, or anxiety. With most Parkinsons disease patients, paradoxical reactions occur after many weeks or months when the l-dopa dosing value is on the threshold needed for control of Parkinsons disease symptoms late in treatment.,,
Add Medication For A Winning Combo
Diet and exercise are important for managing PD, but dont forget about medications. Take them regularly and exactly as your doctor prescribes.
If you tend to forget your medication, set an alarm to remind you. You can also use a pillbox thats labeled with days and times of day. Take your meds on a set schedule, dont skip doses and dont double dose, says Dr. Gostkowski. When youre diligent about taking your medications and following a healthy lifestyle, youll feel your best.
Aromatic Amino Acid Decarboxylase Deficiency
Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder that combines serotonin and catecholamine deficiency. The gene locus is 7p11. Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase catalyzes the decarboxylation of L-DOPA and 5-hydroxytryptophan to dopamine and serotonin, respectively. Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase deficiency is characterized by a CSF profile of low homovanillic acid and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid, high L-DOPA, 5-hydroxytryptophan, and 3-O-methyldopa , and normal pterin levels. Clinical onset is typically by 6 months of age. The associated features are hypotonia and extrapyramidal movement disorders such as torticollis, dystonia, blepharospasm, athetosis, and myoclonus. Other manifestations are profound developmental delay, irritability, sleep disturbances, and autonomic manifestations such as temperature instability, impaired diaphoresis, hypersalivation, recurrent syncope, or cardiorespiratory arrest. Impaired sympathetic responses, with maintenance of systemic blood pressure following nitroprusside infusion, are demonstrable . The syndrome may present in the neonate with hypothermia, lethargy, poor sucking, ptosis, and hypotension . Typically, patients are initially diagnosed with cerebral palsy, epilepsy, suspected mitochondrial encephalopathies, myasthenia, or hyperekplexia. Neuroimaging is generally unremarkable but may reveal progressive cerebral atrophy.
James T. Boyd, … Karen M. Lounsbury, in, 2017
You May Like: Big And Loud Therapy For Parkinson’s
Human Trials Are Still Needed
If these results can be replicated in patients, it will be a major breakthrough in the treatment of this devastating neurological disorder, concludes Kalipada Pahana, who led the study which was published in Nature Communications. There are drugs that slow the progression of Parkinsons disease, such as levodopa, which replenishes the dopamine deficiency caused by neuronal death. It slows the loss of motor skills but does not prevent the death of dopaminergic neurons. For patients with the most severe impairments, deep brain stimulation may be an alternative.
Scientists are currently working on several lines of research, such as immunotherapy and gene therapy, to cure this disease, which we so far can only slow down.
References
Why Not Just Take Dopamine

In theory, the simplest way to treat Parkinsons would be to directly replace the dopamine lost via supplements. But, theres a complication. Dopamine itself is unable to cross the blood-brain barrier a natural barrier that protects the brain from bacteria and viruses that may be in the blood. This means that taking dopamine directly is ineffective as it cant get from the blood into the brain.
Fortunately, levodopa can cross the blood-brain barrier, into the brain, where its turned into dopamine.
Don’t Miss: Best Treatment For Parkinson’s
So What Does Nutrition Have To Do With Parkinsons
1. The neurotransmitter dopamine is made in the body from amino acids which are the building blocks of protein. Every time we eat a protein rich food we take in protein, which the body breaks down into its component amino acids. Two amino acids are converted in the body into L-Dopa, which is then converted into dopamine in the brain.
2. Nutrient co-factors are required for each stage of this conversion process, so deficiencies of these may reduce dopamine production.
3. L-dopa medication competes for absorption with dietary amino acids, therefore the timing of taking L-dopa and the eating of protein needs to be managed for optimal absorption and effectiveness of the drug and the reduction of side-effects.
Therefore, the nutritional therapy approach to Parkinsons includes:
1. Supporting dopamine production by ensuring adequate precursors and co-factors
2. Considering drug-nutrient interactions to enhance effectiveness and reduce side-effects
3. Optimising nutritional status and addressing co-morbidities . These co-morbidities include constipation, depression, fatigue, and insomnia.
Two Amino Acids Administered Intranasally Could Cure Parkinsons Disease
In their quest for a cure for Parkinsons disease scientists have developed two peptides. These peptides when administered intranasally slowed the death of dopaminergic neurons thereby improving the symptoms of Parkinsons. Initial results in laboratory mice are very encouraging.
Man With Parkinsons
Parkinsons disease is the most common motor pathology in the world. Millions of people worldwide suffer from this degeneration of dopaminergic neurons, which causes many symptoms, including the characteristic tremor. The culprit of dopaminergic neuronal death is thought to be insoluble aggregates of abnormally shaped -synuclein, the so-called preformed fibrils. They are also present in Lewy bodies and are the cause of several neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinsons disease.
Read Also:French Study Shows That Lysosomes Act as Trojan Horses in Parkinsons Disease
Usually, neurons can eliminate -synuclein aggregates by exocytosis. These could then be transferred to other neurons by a hitherto unknown mechanism. Microglia, the immune cells of the brain are activated by preformed fibrils and release pro-inflammatory cytokines. Chronic inflammation in the brain accelerates the death of dopaminergic neurons and the release of -synuclein.
Also Check: Physical Therapy For Parkinson’s Disease
Side Effects And Adverse Reactions
The side effects of
- Hypertension, especially if the dosage is too high
- Arrhythmias, although these are uncommon
- Nausea, which is often reduced by taking the drug with food, although protein reduces drug absorption. l-DOPA is an amino acid, so protein competitively inhibits l-DOPA absorption.
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- A condition similar to stimulant psychosis
Although many adverse effects are associated with l-DOPA, in particular psychiatric ones, it has fewer than other antiparkinsonian agents, such as anticholinergics and dopamine receptor agonists.
More serious are the effects of chronic l-DOPA administration in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, which include:
- End-of-dose deterioration of function
- Dyskinesia at peak dose
- Possible dopamine dysregulation: The long-term use of l-DOPA in Parkinson’s disease has been linked to the so-called dopamine dysregulation syndrome.
Clinicians try to avoid these side effects and adverse reactions by limiting l-DOPA doses as much as possible until absolutely necessary.
Vitamin C And Vitamin E
Vitamin C and vitamin E are both antioxidants. One study that evaluated these vitamins found they helped delay the need for PD drugs. Taking vitamin E alone did not seem to have the same benefit. However, vitamin E supplements can increase the risk of bleeding, especially in those who take blood thinners. Vitamin E has also been studied for its potential to reduce the risk of developing PD. However, dietary intake of vitamin E did not show any reduction in the risk of developing PD.3,5
Also Check: Cialis And Parkinson’s Disease
Effect Of Dopamine And Dopamine Agonists On Gut Motility
Bacterial species from the Bacilli class, especially enterococci, are able to produce luminal dopamine . Importantly, dopamine and their agonists have been shown to affect the gut motility , which could potentially favor the colonization of levodopa decarboxylating bacteria . In addition, the dopamine agonists, which are usually used in combination with levodopa treatment, could have a similar effect on influencing gut motility to favor colonization of specific bacterial species. Therefore, studies investigating the effects of dopamine on gut motility of rodents, dogs, and humans were reviewed, with a complete overview in Table 1.
Table 1. Studies investigating the effects of dopamine and dopamine agonists on gut motility in rodents, dogs and humans.
Dietary Protein And Parkinsons
This known interaction between levodopa and amino acids in the gut means that people with Parkinsons need to be careful about their protein consumption around the time of taking their medication.
When you have a large amount of protein, they get broken down in the stomach into amino acids. And once these amino acids enter the small intestine, they start competing with levodopa to use the transporter system out into the blood. This competition can cause a reduction in the amount of levodopa reaching the brain, in turn reducing the effectiveness of the dose.
An early study, from 1987, found that on a low protein diet, 11 people with Parkinsons were more sensitive to the effects of levodopa, and saw reduced fluctuations in their symptoms throughout the day compared with a high protein diet. However, we now know that a low-protein diet is not advisable for people with Parkinsons. So, whats the answer?
Read Also: Is Constipation A Symptom Of Parkinson’s
What Is Parkinsons Disease
James Parkinson, a physician in 19th-century London, is credited with being the first to detail the symptoms of a neurodegenerative disorder now called Parkinsons disease. Symptoms of the disease, however, were described as far back as 5,000 BCE in ancient Indian medical writings, and 2500 years ago in Chinese medical texts.
Parkinsons disease, a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that impacts movement, muscle control, balance, and other bodily functions, is part of a group of conditions known as nervous system disorders.
Parkinson’s, which affects movement, develops gradually. It often begins with a slight tremor in one hand. It is the most frequently diagnosed movement disorder and second only to Alzheimers disease as the most prevalent neurodegenerative disorder.
Incidence of Parkinson’s ranges from 8.6 to 19 per 100,000 people. Statistics currently show that about 50,000 new cases are diagnosed in the United States every year, a number expected to rise as the population in the U.S. ages. Parkinson’s disease onset before age 40 is rare, with prevalence rates for the disease averaging between 1% and 2% for people over the age of 60 and 3% to 5% for people over age 85. The disease affects all races and ethnic groups equally.
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Treated
There is currently no cure for Parkinsons disease, which always gets worse over time. Death is usually because of complications, including pneumonia or falling-related injuries.
Parkinsons disease changes the quality of life for patients and their families. In order to make the most worthwhile treatment decisions, education is imperative. Some prescription drugs and surgical procedures may drastically improve symptoms.
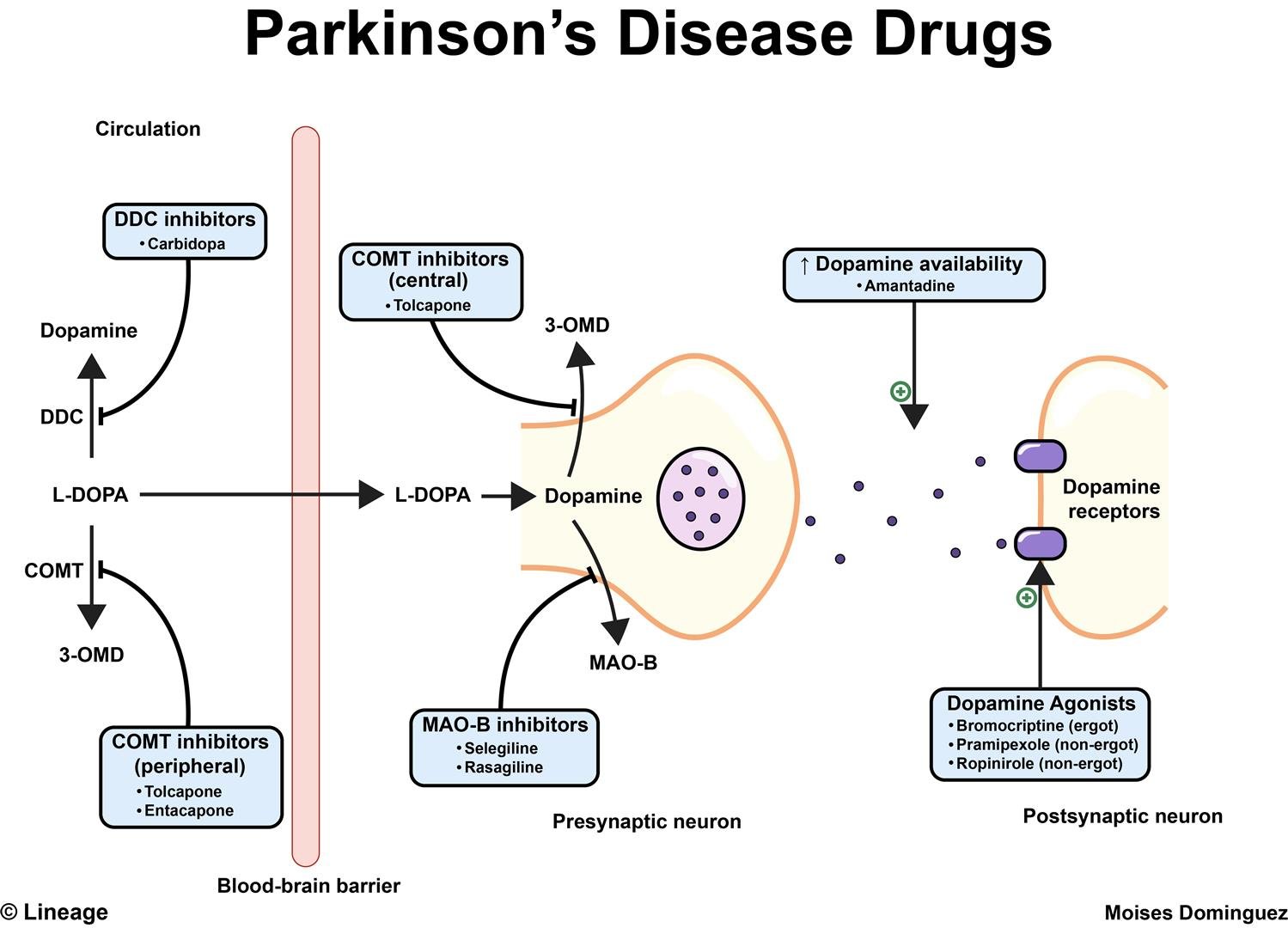
Treatment plans for Parkinson’s depend on symptoms, other health issues and medications used to treat them, metabolism, and age. Because most Parkinson’s symptoms result from a lack of dopamine in the brain, many drugs attempt to replenish proper levels of dopamine or mimic the action of dopamine. Termed dopaminergic medications, these treatments target muscle rigidity, speed and coordination of movement, and tremors.
Though these medications can decrease symptoms for some Parkinson’s patients, they do come with side effects, some of which can be severe. The list of reported side effects for top Parkinson’s drugs includes:
| Confusion |
| Difficult or painful urination |
Don’t Miss: How Does General Anesthesia Affect Parkinson’s
Administration Routes And Transport Process Of Levodopa
The most common route for levodopa administration is orally via immediate-release or extended-release formulations of levodopa, where the latter might have potential benefits over other levodopa formulations, reviewed in Mittur et al. . Parenteral administration via subcutaneous injections are impossible due to the low solubility of levodopa and continuous intravenous administration, although effective , is impractical, as it requires large volumes of daily injections. A promising alternative option to conventional levodopa therapy for advanced PD patients with motor fluctuations and dyskinesia is intestinal infusion of a levodopa/carbidopa gel via a nasoduodenal tube or via gastrojejunostomy .
Figure 1. Human and bacterial levodopa metabolism. Levodopa is produced by hydroxylation of the meta-position of the phenyl-ring from tyrosine by TH using molecular oxygen. Sequentially levodopa can be decarboxylated to the active neurotransmitter dopamine by the AADC , or can be methylated by COMT . Bacterial TDC can decarboxylate tyrosine to tyramine but also levodopa to dopamine. Furthermore, bacteria can dehydroxylate the para-hydroxyl group of either levodopa or dopamine and can sequentially deaminate the dehydroxylated products.
What Is Amino Acid Therapy For Parkinsons
As discussed earlier, many of the most prominent, motor function-related symptoms of Parkinson’s disease can be traced back to insufficient levels of a neurotransmitter called dopamine. However, other symptoms such as sleep issues, mood changes, and more, are not linked to dopamine levels. According to an article published in the European Journal of Neurology, those symptoms stem from the influence of “complex, interconnected neuronal systems regulated by a number of different neurotransmitters.” The authors go on to state that developing treatments that optimize levels of several neurotransmitters “could prove invaluable for the treatment of the disease.”
A study published in the journal PLOS One in January of 2018 evaluated the relationship between concentrations of various amino acids in the blood and the progression of Parkinson’s disease. The authors explained that amino acids are crucial to the central nervous system, serving as neurotransmitters, neuromodulators, and regulators of energy metabolism. Changes in blood concentrations of amino acids in Parkinson’s patients have been linked to the amount of damage to the nervous system. The researchers discovered significant differences in concentrations of four amino acids: alanine, arginine, phenylalanine, and threonine. This specific amino acid profile could serve as a biochemical marker of Parkinson’s progression, they concluded.
Up to 25% off Amino
Don’t Miss: 10 Symptoms Of Parkinson’s
Levodopa Combined With Decarboxylase Inhibitors
Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase is responsible for the enzymatic decarboxylation of levodopa to dopamine. Carbidopa is a commonly used decarboxylase inhibitor. The decarboxylase inhibitors do not penetrate the bloodbrain barrier and inhibit only the peripheral conversion of levodopa to dopamine, including the conversion that occurs in the intestinal lumen. Carbidopa allows an 80% decrease in the dosage of levodopa necessary to control parkinsonian symptoms . Carbidopa is relatively nontoxic but is inactive as an antiparkinson drug in the absence of levodopa.
The levodopa-carbidopa combination is not recommended in pregnancy or in patients younger than 18 years. Carbidopa is available as a single agent or formulated with levodopa in a fixed ratio of 10 mg/100 mg, 25 mg/100 mg, and 25 mg/250 mg and controlled-release preparations with fixed ratios of 25 mg/100 mg and 50 mg/200 mg . Packaged alone , carbidopa is useful for patients who require greater amounts of the drug than provided in the standard ratios.
Combine Exercise With Diet
Dr. Gostkowski says if you want to feel your best, combine a healthy diet with exercise. Research has shown that regular exercise can improve PD symptoms.
Do exercise that raises your heart rate, Dr. Gostkowski says. Aim for about 30 minutes a day, five days a week. Dont worry about specific exercises. Do an activity you enjoy, as long as it gets your heart rate up. Try brisk walking or biking or more advanced exercise for veteran athletes. I recommend seeing an occupational therapist. They can tailor an exercise program to your needs.
You May Like: Does Alan Alda Have Parkinson’s
How Does It Produce In The Brain
Levodopa is naturally produced in the brain as a precursor of dopamine, a well-known neurotransmitter that is responsible for controlled body movement. It represents a key step in the pathway that synthesized dopamine in the brain.
In this pathway, levodopa is formed from the amino acid L-tyrosine, which is produced from phenylalanine obtained from food. This reaction is catalyzed by an enzyme called tyrosine hydrolase. Immediately after its formation, levodopa is metabolized to dopamine with the help of dopa decarboxylase enzyme. The newly formed dopamine is then taken up by neurons and distributed to different parts of the brain to perform its functions.
A More Effective And Safer Approach To Parkinsons Disease
Based on the research of Dr. Mary Hinz, a safer and more effective approach to Parkinsons therapy exists. The successful implementation of Dr. Hinzs Parkinsons Therapy requires a thorough understanding of the underlying factors that cause the symptoms of Parkinsons disease and many years of practice, but the results can be amazing. Learn more about the causes and implementation of this therapy and if you are ready to get started, please contact us.
Also Check: What Diseases Are Similar To Parkinson’s
What Gets Stored In A Cookie
This site stores nothing other than an automatically generated session ID in the cookie no other information is captured.
In general, only the information that you provide, or the choices you make while visiting a web site, can be stored in a cookie. For example, the site cannot determine your email name unless you choose to type it. Allowing a website to create a cookie does not give that or any other site access to the rest of your computer, and only the site that created the cookie can read it.
Dyskinesia Uncontrolled Involuntary Movement
This is the most unpleasant side effect that appears within 2 years of using levodopa therapy, although in some patients, it may appear after 5 years.
It refers to the abnormal uncontrolled involuntary movements that mostly affect the arms, legs, and face. In this condition, the tremor becomes more aggressive and results in the wiggly movement.
You May Like: Alcohol And Parkinson’s Disease
How To Take It
Take tyrosine supplements at least 30 minutes before meals, divided into 3 daily doses. Taking vitamins B6, B9 , and copper along with tyrosine helps the body convert tyrosine into important brain chemicals.
Pediatric
Don’t give tyrosine supplements to a child without first asking your doctor.
Adult
Doses vary. Talk to your nutritionist or doctor about what dose is right for you. To treat symptoms of sleep deprivation, one study used 150 mg per kilogram of body weight per day.