What Tests Diagnose Parkinson’s Disease
There currently are no tests that can definitively diagnose Parkinsons Disease. A diagnosis is based on the clinical findings of your physician in combination with your report on the symptoms you are experiencing.
In situations where an older person presents with the typical features of Parkinsons and they are responsive to dopamine replacement therapy, there is unlikely to be any benefit to further investigation or imaging.
Early Signs Of Parkinsons
Early physical signs include the common motor symptoms: tremor, muscle rigidity and slowness. They may also include the following:
- Symptoms starting on one side of the body
- Change in facial expression
- Loss of sense of smell
- Depression or anxiety
Some of these symptoms are quite common and by no means exclusive to Parkinsons, so if you have some of them, it does not mean you have Parkinsons.
Understanding Parkinsons Disease: Getting A Parkinsons Diagnosis
Once you start noticing some changes in your body that impact your daily life or are just simply bothersome, you should begin the process of figuring out if you have Parkinsons disease. It may seem like a daunting undertaking, but dont let fear stop you. Once you are diagnosed, you can start treating your symptoms and learning strategies that will help you feel better.
Read Also: What Are The Effects From Having Parkinson’s Disease
Definition And Differential Diagnosis
There are many manifestations of but the classical diagnostic symptoms are:
- slowness and poverty of movement
The physical signs of include:
- slowness of movement
At diagnosis, these signs are usually unilateral, but they become bilateral as the disease progresses. Later in the disease additional signs may be present including postural instability , cognitive impairment and orthostatic hypotension .
There is no single way to define Parkinsons disease or what is often called idiopathic Parkinsons disease in order to differentiate it from other causes of parkinsonism, such as multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy .
is traditionally defined, pathologically, by the finding of Lewy bodies and degeneration of catecholaminergic neurones at post-mortem. Using a pathological definition of PD is problematic for a number of reasons:
- A pathological diagnosis is not practical in life.
- Lewy body inclusions in catecholaminergic neurones are seen in individuals without clinical evidence of it is presumed that these are pre-clinical cases.
- Lewy bodies have not been found in otherwise typical individuals with with Parkin mutations, although such rare young-onset genetic cases of PD might be said not to have idiopathic PD.
In recent years, attempts to define genetically have become possible with the discovery of monogenic forms of the disease. However, such families account for a very small proportion of cases.
Common causes of tremor.
New Laboratory Tests For Parkinsons Disease
Currently, Parkinsons disease diagnosis is based on a visual clinical exam, done by a doctor in their office. This means that motorsymptoms such as tremor, stiffness and slowness must be apparent before a diagnosis is made by the neurologist yet those visible symptoms dont often appear until long after the initial brain changes of PD are present. However, this is changing! There are two newly available laboratory tests that bring us closer to a new era in Parkinsons diagnosis.
For more background, continue reading. If youd like to skip down to learn about the two new lab tests for Parkinsons, .
Also Check: What Country Has The Highest Rate Of Parkinson’s Disease
Assessing Level Of Rigidity
Healthcare providers also look for rigidity by moving the joints in your elbows, wrists, knees, and ankles to see if there’s resistance. The resistance may be smooth or may appear as slight hesitations in movements, known as cogwheeling. This is sometimes made more obvious by the patient actively moving the opposite limb.
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose This Condition
When healthcare providers suspect Parkinsons disease or need to rule out other conditions, various imaging and diagnostic tests are possible. These include:
New lab tests are possible
Researchers have found possible ways to test for possible indicators or Parkinsons disease. Both of these new tests involve the alpha-synuclein protein but test for it in new, unusual ways. While these tests cant tell you what conditions you have because of misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins, that information can still help your provider make a diagnosis.
The two tests use the following methods.
- Spinal tap. One of these tests looks for misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins in cerebrospinal fluid, which is the fluid that surrounds your brain and spinal cord. This test involves a spinal tap , where a healthcare provider inserts a needle into your spinal canal to collect some cerebrospinal fluid for testing.
- Skin biopsy. Another possible test involves a biopsy of surface nerve tissue. A biopsy includes collecting a small sample of your skin, including the nerves in the skin. The samples come from a spot on your back and two spots on your leg. Analyzing the samples can help determine if your alpha-synuclein has a certain kind of malfunction that could increase the risk of developing Parkinsons disease.
Also Check: What Is Focused Ultrasound For Parkinson’s
New Skin Test Accurately Diagnoses Parkinsons Disease
11/23/2020
New research out of Banner Sun Health Research Institute shows for the first time a simple skin test can accurately identify Parkinsons disease. This is a real breakthrough since there is currently no reliable test for the disease.
The study was published this September in the scientific journal Movement Disorders. Tom Beach, MD, Ph.D., Director of the Brain and Body Donation Program at BSHRI, was a lead researcher on the study.
We conducted a blinded study of 50 skin samples provided by the Arizona Study of Aging and Neurodegenerative Disorders and the Brain and Body Donation Program based at Banner Sun Health Research Institute, said Dr. Beach. Half the skin samples came from people who had Parkinsons disease and half came from people without neurologic disease. Researchers diagnosed 24 out of the 25 Parkinsons disease patients accurately. The study was carried out in coordination with Iowa State University.
The next step in this research is to study the skin test on living people with and without Parkinsons disease. The first use of the new test could be in clinical trials where accurate diagnosis is key. There are several diseases that mimic the signs of Parkinsons, making clinical trials complicated. Current diagnosis techniques rely on observing symptoms, a method that is only 60-75% accurate at early stages of the disease according to Dr. Beach.
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed
Your doctor will ask questions about your symptoms and your past health and will do a neurological exam. This exam includes questions and tests that show how well your nerves are working. For example, your doctor will watch how you move. He or she will check your muscle strength and reflexes and will check your vision.
Your doctor also may check your sense of smell and ask you questions about your mood.
In some cases, your doctor will have you try a medicine for Parkinson’s disease. If that medicine helps your symptoms, it may help the doctor find out if you have the disease.
Tests
There are no lab or blood tests that can help your doctor know whether you have Parkinson’s. But you may have tests to help your doctor rule out other diseases that could be causing your symptoms. For example:
- An MRI or CT scan is used to look for signs of a stroke or brain tumor.
- Blood tests check for abnormal thyroid hormone levels or liver damage.
Another type of imaging test, called PET, sometimes may detect low levels of dopamine in the brain. These low levels are a key feature of Parkinson’s. But PET scanning isn’t commonly used to evaluate Parkinson’s. That’s because it’s very expensive, not available in many hospitals, and only used experimentally.
Also Check: Does Restore Gold Work For Parkinson’s
The Importance Of The Research
In the study, sebum samples were gathered from the upper backs of 79 people with Parkinsons and compared with a control group of 71 people. Concentrations of sebum are known to be highest in this part of the body.
The clinical study follows observational research involving Joy Milne, a person with hereditary Hyperosmia, or sensitivity to smells. Researchers working with Milne determined that she could correctly identify individuals with Parkinsons disease simply by smelling the sebum that accumulated on their skin.
If the sebum swab test is proven effective in further clinical trials, it would be the first biomarker-based diagnostic test for Parkinsons.
This test has the potential to massively improve the diagnosis and management of people with Parkinsons disease, said Dr. Monty Silverdale, a neurologist, professor at Manchester, and the clinical lead author of the study, in a press statement.
Developing such a test is part of the core mission of the Michael J. Fox Foundation , which provided funding for the research alongside the group Parkinsons UK, according to Dr. Samantha Hutten, director of discovery and translational research for the foundation.
Also unclear, said Diaz, is whether the sebum swab test can be used to differentiate between people with Parkinsons and those with other forms of degenerative neurological diseases that also are characterized by altered sebum levels.
Passive Manipulation Of Limbs
To test for the presence of rigidity, we need to passively manipulate the limbs of the patient. However, If the disease is in its early stage or the symptoms are well controlled with medications, we may not be able to see rigidity. We will need to use some activation maneuvers, that basically consist in performing repetitive movements with the limb contralateral to the one that is being tested.
Also, there are two types of rigidity:
Lead-pipe rigidity: where the tone is uniformly and smoothly increased throughout the entire range of movement
Cogwheel rigidity: where a tremor is superimposed on the hypertonia, making the movement irregular due to intermittent increase and reduction of tone
Upper Extremity Testing
For the upper extremity the most sensitive joint where to check for rigidity is the wrist. To uncover rigidity, passively rotate the wrist and feel for a resistance to the movement. It is very important that the arm of the patient is fully relaxed when rotating the wrist. To do this, place your proximal hand under the patients forearm, while your distal hand grabs and rotates the wrist of the patient. When rigidity is present, the range of motion will be preserved but you will feel a resistance in performing the movement.
Wrist rotation with activation maneuver.
It is also possible to test for rigidity in the elbow by passively flexing and extending the forearm.
Elbow flexion-extension with activation maneuver.
Lower Extremity Testing
Also Check: Parkinson’s Foods To Eat
How Is It Treated And Is There A Cure
For now, Parkinsons disease is not curable, but there are multiple ways to manage its symptoms. The treatments can also vary from person to person, depending on their specific symptoms and how well certain treatments work. Medications are the primary way to treat this condition.
A secondary treatment option is a surgery to implant a device that will deliver a mild electrical current to part of your brain . There are also some experimental options, such as stem cell-based treatments, but their availability often varies, and many aren’t an option for people with Parkinsons disease.
Imaging And Lab Tests

Your doctor may order some imaging tests and laboratory tests. Imaging tests can include computed tomography scans and magnetic resonance imaging scans. Laboratory tests can include blood tests and urine tests.
While these tests and scans will not help diagnose Parkinsons disease, they can help rule out other conditions that have similar symptoms.
Your doctor may also suggest that you get a dopamine transporter scan . This scan requires a single-photon emission computed tomography scanner. It involves an injection of a small amount of a radioactive drug so that your doctor can study the dopamine systems in your brain .
While a DaTscan cannot conclusively prove that you have Parkinsons, it can help confirm your doctors diagnosis and eliminate other conditions.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson Silverware
Don’t Miss: Why Do Parkinson’s Patients Have Trouble Sleeping
I Have Pd And Several Symptoms Should I Get A Datscan
Likely no. There is no need for DaTscan when your history and exam suggest Parkinsons disease and you meet the diagnostic criteria. Occasionally, if signs and symptoms are mild or you dont meet the diagnostic criteria, your doctor will refer you for a DaT scan. Keep in mind that ultimately the diagnosis is based on your history and physical exam. The DaT scan is most commonly used to complete the picture and is not a test for a diagnosis.
Why Genetic Testing For Parkinsons Disease Is Complex:
- There are many genes that are associated with the development of PD. This list continues to grow as more genes are discovered. Testing of only some of these genes is available in commercial labs.
- The majority of people with PD, even those with a family history of PD, do not harbor one of these identified abnormal genes. The genetic contribution to PD in these people is yet to be discovered.
- For a particular gene there may be a number of different mutations associated with disease, some of which are more common than others. Commercial testing may identify only the most common of the mutations, and therefore not capture everyone who carries a disease-causing mutation.
- Conversely, only particular mutations in a gene may be associated with disease. Commercial testing may identify changes in a gene that may not have clinical consequences. This can be confusing for patients who even after genetic testing may not know whether they harbor a disease-causing mutation.
- Different mutations can be enriched in different ethnic populations. For example, Ashkenazi Jews and North African Berbers have an increased risk of carrying Leucine rich repeat kinase 2 mutations. Glucocerebrosidase mutation frequency also varies greatly with ethnicity and is also increased among Ashkenazi Jews.
In addition to the above, it is important to realize that not all genes associated with PD contribute to disease in the same way:
Dont Miss: 1st Sign Of Parkinsons
Also Check: Stabilizing Pen For Parkinson’s
Surgery For People With Parkinsons Disease
Deep brain stimulation surgery is an option to treat Parkinsons disease symptoms, but it is not suitable for everyone. There are strict criteria and guidelines on who can be a candidate for surgery, and this is something that only your doctor and you can decide. Surgery may be considered early or late in the progression of Parkinsons. When performing deep-brain stimulation surgery, the surgeon places an electrode in the part of the brain most effected by Parkinsons disease. Electrical impulses are introduced to the brain, which has the effect of normalising the brains electrical activity reducing the symptoms of Parkinsons disease. The electrical impulse is introduced using a pacemaker-like device called a stimulator. Thalamotomy and pallidotomy are operations where the surgeon makes an incision on part of the brain. These surgeries aim to alleviate some forms of tremor or unusual movement, but they are rarely performed now.
Recommended Reading: Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Parkinsons
Who Does It Affect
The risk of developing Parkinsons disease naturally increases with age, and the average age at which it starts is 60 years old. Its slightly more common in men or people designated male at birth than in women or people designated female at birth .
While Parkinsons disease is usually age-related, it can happen in adults as young as 20 .
Also Check: What Fruits Are Good For Parkinson’s
Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease
There are currently no blood or laboratory tests to diagnose non-genetic cases of Parkinsons. Doctors usually diagnose the disease by taking a persons medical history and performing a neurological examination. If symptoms improve after starting to take medication, its another indicator that the person has Parkinsons.
A number of disorders can cause symptoms similar to those of Parkinsons disease. People with Parkinsons-like symptoms that result from other causes, such as multiple system atrophy and dementia with Lewy bodies, are sometimes said to have parkinsonism. While these disorders initially may be misdiagnosed as Parkinsons, certain medical tests, as well as response to drug treatment, may help to better evaluate the cause. Many other diseases have similar features but require different treatments, so it is important to get an accurate diagnosis as soon as possible.
Learn More About Parkinsons Disease: Overview
Read Also: Huntington’s Disease Vs Parkinson’s Disease
Physical Examination And Tests
A trip to the neurologists office often includes what seems like dozens of questions, along with multiple tests.
There currently are no diagnostic blood tests for Parkinsons disease, but your doctor may do some routine blood and urine tests to assess your overall health. Your blood pressure will be taken sitting and standing to look for orthostatic hypotension.
A movement disorder specialist will do a variety of physical tests to assess you as well.
Medicines For Parkinsons Disease
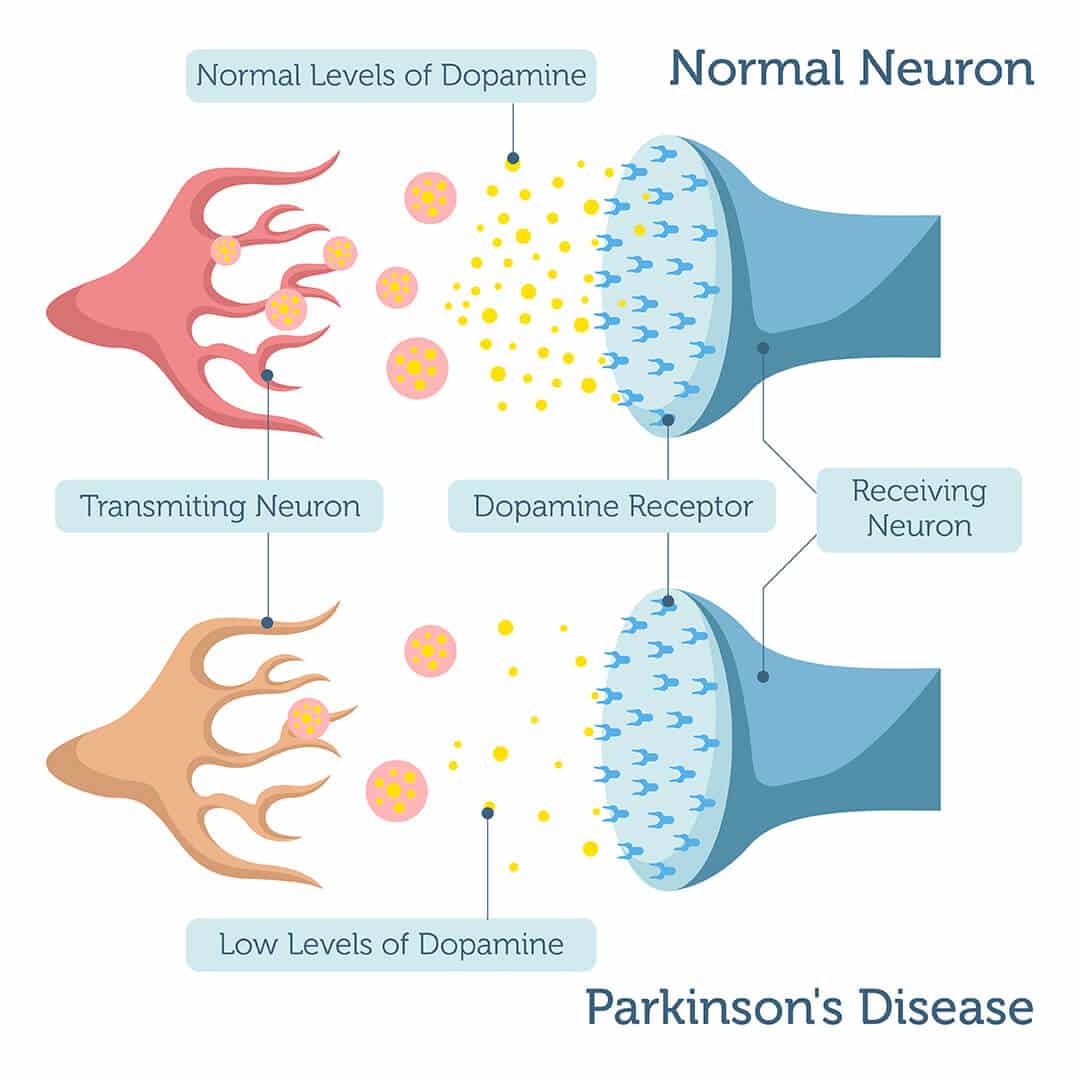
Medicines can help treat the symptoms of Parkinsons by:
- Increasing the level of dopamine in the brain
- Having an effect on other brain chemicals, such as neurotransmitters, which transfer information between brain cells
- Helping control non-movement symptoms
The main therapy for Parkinsons is levodopa. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brains dwindling supply. Usually, people take levodopa along with another medication called carbidopa. Carbidopa prevents or reduces some of the side effects of levodopa therapy such as nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and restlessness and reduces the amount of levodopa needed to improve symptoms.
People living with Parkinsons disease should never stop taking levodopa without telling their doctor. Suddenly stopping the drug may have serious side effects, like being unable to move or having difficulty breathing.
The doctor may prescribe other medicines to treat Parkinsons symptoms, including:
- Dopamine agonists to stimulate the production of dopamine in the brain
- Enzyme inhibitors to increase the amount of dopamine by slowing down the enzymes that break down dopamine in the brain
- Amantadine to help reduce involuntary movements
- Anticholinergic drugs to reduce tremors and muscle rigidity
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease Young Age