Huntingtons Disease Vs Alzheimers
Huntingtons disease is a cause of chorea usually appearing in the middle years of life and later becoming complicated with psychiatric and cognitive abnormalities Alzheimers disease is a neurodegenerative condition of the brain which is characterized by the atrophy of brain tissues, and it has been identified as the most common cause of dementia. Impairment
- Anosognosia
Management There is no disease-modifying drug at present. Progressive neurodegeneration leads to dementia and death after 10-20 years. There is no definitive treatment for the Alzheimers disease.
Cholinesterase inhibitors can be given to control the neuropsychiatric manifestations such as depression.
Memantatidine has also proven to be effective in controlling the disease progression and symptoms.
Anti-depressants are prescribed when necessary along with the drugs such as zolpidem that can that can minimize the sleep disturbances.
Comparison Table Between Huntingtons And Parkinsons
| Parameters of Comparison | ||
| Lack in production of dopamine from nerve cells. | ||
| Symptoms | Change in moods, triggering in mood swings, lack of coordination, slow understanding towards things, indecisive behaviour etc. | Loss of smell, Difficulty in digestion, change in voice, poor And minuscule handwriting, change in posture, movements become slow, clumsiness etc. |
| Treatment | No permanent cure is available but a patient can try several ways prescribed by the doctors to cope with the disease. | Various treatments are available. |
Diagnosis Of Huntington Disease
-
A doctor’s evaluation, confirmed by genetic testing
-
Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging
or magnetic resonance imaging Magnetic Resonance Imaging In magnetic resonance imaging , a strong magnetic field and very high frequency radio waves are used to produce highly detailed images. MRI does not use x-rays and is usually very safe… read more is done to check for the degeneration of the basal ganglia and other areas of the brain usually affected by the disease and to rule out other disorders.
Genetic testing is done to confirm the diagnosis. Genetic testing and counseling are important for people who have a family history of the disease but no symptoms because people are likely to have children before symptoms appear. For such people, genetic counseling should precede genetic testing. They are referred to centers that have expertise in dealing with the complex ethical and psychologic issues involved.
Don’t Miss: Cleveland Clinic Parkinson’s Bicycle Study 2017
How Are They Alike
MS and Parkinsonâs both affect your central nervous system, which includes your brain and spinal cord. Thatâs why they both can affect how you move, sleep, feel, and talk.
These diseases both affect your nerves. MS can break down the coating, called myelin, that surrounds and protects your nerves. In Parkinsonâs, nerve cells in a part of your brain slowly die off.
Both can start out with mild symptoms, but they get worse over time.
Common symptoms of both diseases include:
- Shaky fingers, hands, lips, or limbs
- Slurred speech thatâs hard for others to understand
- Numb or weak limbs that make your walk unsteady
- Loss of muscle control that often affects one side of your body at first, then later both
- Spastic limb movements that are hard to control
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
- Poor balance
Depression is another symptom common to both conditions.
Clinical Features Of Alzheimers
The key clinical features of this condition are,
- Memory impairment
- Frontal executive function- impairment in planning, organizing, and sequencing
- Visuospatial difficulties
- Difficulties with orientation in space and navigation
- Posterior cortical atrophy
- Personality
- Anosognosia
Although the vast amount research carried out on this subject has not been able to find the exact cause of the disease, it has unveiled a lot about the molecular pathology related to the disease progression. Deposition of beta-amyloid in amyloid plaques and the formation of tau-containing neurofibrillary tangles are the hallmark features of Alzheimers disease. Laying down of amyloid in the cerebral blood vessels can give rise to amyloid angiopathy
First degree relatives have a two times higher risk of getting Alzheimers than the normal population. Mutations in the following genes are the cause of autosomal dominant forms of the Alzheimers disease.
- Amyloid precursor protein
- E4 allele of apolipoprotein E
Figure 02: Alzheimers
- Family history
- Genetic predisposition
Whenever there is a clinical suspicion of Alzheimers disease, a CT scan of the brain is carried out this will show degenerative changes such as atrophy in the presence of Alzheimers disease.
You May Like: Weighted Silverware
Electrical Neuromodulation Therapies For Pd And Hd
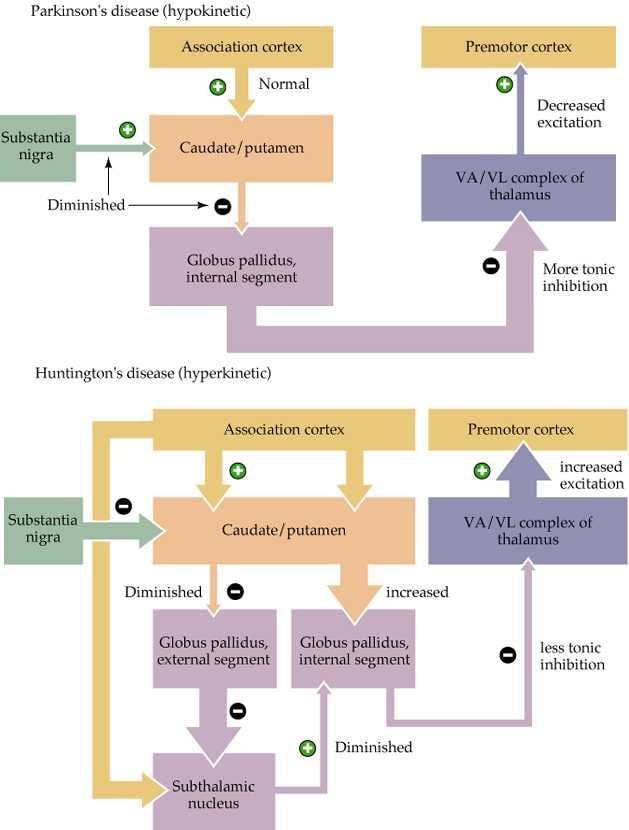
The cardinal motor symptoms of PD and chorea in HD are caused by the progressive degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the SNpc and the loss of MSNs in the striatum , respectively. In both cases, the motor impairment is attributed to alteration of functional connectivity of the striatum, a principal input of the basal ganglia .
Hyperkinetic movement disorders are characterized by uncontrollable and excessive motor activity, as chorea in HD. Reports published between 1987 and 1989 showed that blocking the activity of the STN produces hyperkinetic motor symptoms. Similar results are observed when the GABAergic inputs from the striatum are blocked, favoring the inhibitory modulation of the GPe over the STN . On the other hand, hypokinetic disorders like akinesia and bradykinesia have been described in PD. In this case, the decrease in striatal DA levels, as a result of the decrease in its synthesis, release, and reuptake alter the corticostriatal balance causing an increase in the activity of the indirect pathway and reducing the activity of the direct pathway, that leads to a breakdown of the internal balance of the basal ganglia, and consequently the loss of movement control . These symptoms, unlike hyperkinetic movements, are treated with DA agonists as L-dopa . However, as stated in previous sections, the chronic use of this pharmacological therapy has a limited effect, which in the case of PD can induce a motor complication known as LID and on-off phenomenon .
More About Cjd Huntington’s Disease Korsakoff Syndrome And Parkinson’s Disease
In Alzheimer’s & Dementia,Main
This article below shares more details about different types of dementia. To explore other types of dementia,
4. Creutzfeldt- Jakob Disease is a fatal brain disorder that affects people and other certain mammals. This occurs with a person whose prion protein begins folding into an abnormal three-dimensional shape. The mis-folded prion protein destroys brain cells which leads to rapid decline in thinking, reasoning, confusion, involuntary muscle movements and difficulty walking. CJD is a type of dementia that gets worse unusually fast.
Prion Protein is found throughout the entire body. The specific function is not yet known for the prion protein but scientists do know that the protein starts to fold into an abnormal three-dimensional shape in the brain. These misfolded proteins eventually start to destroy brain cells in a domino effect.
CJD is so rare that it occurs about 1 in 1 million people annually worldwide which breaks down to about 300 new cases each year in the United States. There is no single test yet to diagnose CJD. The following tests may help to determine if a person has CJD. There is no known specific cause for CJD but there is an estimated 90 percent of those diagnosed with sporadic CJD die within one year. Those affected lose their ability to speak or move and they require full-time daily care.
There is no treatment for CJD yet but these tests below can help determine a diagnosis.
Symptoms of Korsakoff Syndrome:
Read Also: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinsons
Human Fetal Tissue As A Source Of Progenitor Cells
The first study demonstrating that dopaminergic neurons could be replaced using fetal tissue was performed using 6-hydroxydopamine -lesioned rats that were implanted with DA-rich ventral mesencephalic tissue from rat fetuses . These studies were followed by the generation of the first non-human primates PD model: monkeys lesioned with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine . This model manifested several of the patients symptoms, and transplanting primate fetal mesencephalic tissue into their striatum showed to alleviate these symptoms . These studies set foot for the first PD cell replacement therapy in humans. These clinical trials were performed using dopaminergic neuron precursors from human fetal tissue, which were transplanted into the striatum of PD patients . Transplanted tissue presented no negative effects at the transplantation site, was functional and survived in the transplanted brain region, but clinical benefits were variable .
Table 3. Common animal models of Parkinsons Disease.
Table 4. Common animal models of Huntingtons disease.
How Do Treatments Differ
MS treatments can ease your symptoms during an attack or slow down the diseaseâs effects on your body.
Steroids like prednisone calm the inflammation that damages your nerves.
Plasma exchange is another therapy if steroids donât work. Your doctor will use a machine to remove the plasma portion of your blood. The plasma gets mixed with a protein solution and put back into your body.
Some people with both diseases who take anti-inflammatory medicines like steroids see their Parkinsonâs symptoms get better.
Disease-modifying treatments slow down MS nerve damage and disability. They include:
Also Check: Similar To Parkinsons
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a degenerative disorder of the central nervous system mainly affecting the motor system. The motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease result from the degeneration of dopamine generating cells in the substantia nigra in the midbrain. The causes of this cell death are poorly understood. Early in the course of the disease, the most obvious symptoms are shaking, rigidity, slowness of movement and difficulty in walking and gait. Later, thinking and behavioral problems arise, with dementia commonly occurring in the advanced stages of the disease. Depression is the most common psychiatric symptom. Other symptoms include sensory, sleep problems and emotionally related problems.
Parkinsons disease is more common in older people, and most cases occur after the age of 50 when it is seen in young, it is called young onset Parkinsons disease.Diagnosis is by medical history and physical examination. There is no cure for PD, but medications, surgery, and multidisciplinary management can provide relief from the disabling symptoms. The main classes of drugs useful for treating motor symptoms are levodopa, dopamine agonists, and MAO-B inhibitors. These drugs too can cause disabling side effects. Deep brain stimulation has been tried as a treatment modality with some success.
On The Right Track To Treat Movement Disorders: Promising Therapeutic Approaches For Parkinsons And Huntingtons Disease
- 1Center for Integrative Biology, Faculty of Sciences, Universidad Mayor, Santiago, Chile
- 2Faculty of Medicine, Biomedical Neuroscience Institute, University of Chile, Santiago, Chile
- 3Program of Cellular and Molecular Biology, Institute of Biomedical Sciences, University of Chile, Santiago, Chile
- 4Center for Geroscience, Brain Health, and Metabolism, University of Chile, Santiago, Chile
Don’t Miss: Pfnca Wellness Programs
Main Differences Between Huntingtons And Parkinsons
Key Difference Huntingtons Disease Vs Alzheimers
Huntingtons disease is a cause of chorea, usually appearing in the middle years of life and later becoming complicated with psychiatric and cognitive abnormalities. Alzheimers disease is a neurodegenerative condition of the brain, which is characterized by the atrophy of brain tissues and it has been identified as the most common cause of dementia. In Huntingtons disease, there is a predominant motor impairment which is not observed in the Alzheimers disease. This is the key difference between Huntingtons disease and Alzheimers.
Also Check: Prayers For Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons Disease Vs Als Differences In Symptoms Causes And Treatment
Written byDevon AndrePublished onJuly 25, 2016
Parkinsons disease and ALS can cause difficulties in movement and are both known to be progressive neurological diseases.
ALS is part of a cluster of disorders known as motor neuron diseases that involve gradual degeneration and death of motor neurons. In a healthy individual, messages from motor neurons in the brain are transmitted to the motor neurons in the spinal cord and sent to the particular muscles. In ALS, this communication degenerates and cells begin to die. As a result, the message that is transmitted is incomplete. Unable to function, the muscles begin to weaken and waste away over time. Eventually, communication from the brain to muscles is lost completely.
In its early stage, ALS also known as Lou Gehrigs disease may appear as Parkinsons disease, which is also a neurological disease similar to ALS. Here we will outline the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for both ALS and Parkinsons disease to help you understand the differences between the two.
Possible Link To Alzheimers
Though Alzheimers, Huntingtons, and Parkinsons are distinctly different diseases, some evidence has emerged that shows a common link between the three.
All three diseases have proteins within the cells that do not assemble properly. Though the molecular and cellular changes that occur in each disease vary greatly, this protein degradation has been shown to precede early clinical signs in each disease. This is promising news, as more studies are being done to determine whether this can either predict or prevent these neurodegenerative diseases.
You May Like: Diseases Similar To Parkinsons
Cellular Replacement Therapies For Pd And Hd
In 1967, in an important breakthrough, Cotzias et al. demonstrated that the administration of a precursor of DA, L-dopa, improved motor function in PD patients, leading to the thought that the cure for PD was discovered. Also in the 1960s, tetrabenazine was introduced as an antipsychotic but also showed beneficial effects for the treatment of hyperkinetic motor symptoms, like chorea in HD patients . To date, it is known that these drugs do not reverse disease progression and in many cases do not have the desired effects. This has brought the idea that local production of DA and GABA, and therefore the replacement of the neurons that produce it, would be the ideal treatment for these diseases. The fact that the major symptoms present in PD and HD patients are due to the loss of dopaminergic and GABAergic neurons in specific brain regions, respectively, means that replacing these specific cell types could help relieve some of the symptoms present in patients. This has given rise to different branches of investigations seeking cellular replacement-based therapies, which have shown promising results in animal models for these diseases as well as in affected patients .
Genetic Testing For Huntington Disease
|
The genetic mutation that causes Huntington disease is located on chromosome 4. It involves repetition of a particular section of the genetic code in the DNA. The gene for Huntington disease is dominant. Thus, having only one copy of the abnormal gene, inherited from one parent, is sufficient to cause the disease. Almost all people with the disease have only one copy of the abnormal gene. Children of such people have a 50% chance of inheriting the abnormal gene and thus the disease. People who have a parent or grandparent with Huntington disease can find out whether they have inherited the gene for the disease by taking a genetic test. For the test, a blood sample is taken and analyzed. Such people may or may not want to know whether they have inherited the gene. This issue should be discussed with an expert in genetic counseling before genetic testing. |
You May Like: Parkinson’s Bike Therapy
What Makes Them Different
MS and Parkinsonâs have different causes. They usually start to affect you at different ages, too.
MS often affects people between ages 20 and 50, but children get it, too. Parkinsonâs usually starts at age 60 or older, but some younger adults get it.
MS is an autoimmune disease. That means your bodyâs immune system goes haywire for some reason. It attacks and destroys myelin. As myelin breaks down, your nerves and nerve fibers get frayed.
In Parkinsonâs, certain brain cells start to die off. Your brain makes less and less of a chemical called dopamine that helps control your movement. As your levels dip, you lose more of this control.
Some genes may put you at risk for Parkinsonâs, especially as you age. Thereâs a small chance that people who are exposed to toxic chemicals like pesticides or weed killers can get it, too.
These symptoms are more common if you have MS. They not usually found in Parkinsonâs:
Parkinsons Disease Vs Als: Us Prevalence
One million Americans live with Parkinsons disease. The average cost of Parkinsons disease including treatment, lost work wages, and social security payments is $25 billion annually in the U.S.
It is not clear how many people are affected by ALS, but the estimates range between 12,000 and 15,000. Doctors tell roughly 5,000 patients annually that they have ALS. Records on ALS have not been well kept across the country, so estimates may fall way below the actual rates. Common age of ALS diagnosis is between 55 and 75, and life expectancy is anywhere between two and five years after the onset of symptoms. Longevity in ALS is strongly linked to a persons age. Younger individuals with ALS tend to live longer than those diagnosed at an older age.
Also Check: Judy Woodruff Parkinson’s