Movement Disorders Similar To Parkinsons
Conditions causing excess movement or decreased movement that are sometimes associated with Parkinsons disease-like symptoms include:
What Movement Disorder Could I Have?
When making a Parkinsons diagnosis, your doctor will review your medical history and symptoms, perform a careful neurological exam, and, if necessary, carry out further tests to rule out other movement disorders.
Your symptoms may be caused by a movement disorder other than Parkinsons disease if:
- You display Parkinsons disease symptoms and features that are characteristic of an additional movement disorder.
- The results of a brain imaging study or laboratory test, such as a blood test, confirm the presence of another movement disorder.
- Your symptoms do not respond to Parkinsons disease medication.
Because movement disorders are not all treated the same way, it is important to get a proper diagnosis as early as possible so you can formulate the right treatment plan with your doctor.
How Do You Treat Vascular Parkinsonism
There are several treatment options for parkinsonism including dopamine substitutes such as levodopa, dopamine agonists such as ropinirole, monoamine oxidase B inhibitors such as selegiline, and catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors such as entacapone, anticholinergics, and amantadine. Of all, levodopa, or syndopa, which is a combined preparation of levodopa with carbidopa, remains the most effective and widely used drug treatment in PD, possibly owing to the major neuropathological finding of degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra pars compacta leading to dopamine depletion in the striatum in PD.
However, the effectiveness of levodopa in VP is still an area under discussion. In a recent meta-analysis which included 14 cross-sectional studies, two case-control studies, two cohort studies, and two clinicopathological studies , it was concluded that the calculated event rate of levodopa response in VP patients was 0.304 , thus having a low response rate to levodopa. The analysis revealed that approximately only 30% of VP patients respond to levodopa therapy.
Zijlmans’ criteria were used for the diagnosis of VP in ten studies, while Winikates’criteria were used for five studies in the above meta-analysis. The rest did not have clear definitions of VP.
Are There Caveats Of Diagnosing Vascular Parkinsonism
The diagnostic criteria for VP as suggested by Zijlmans et al., which is widely used, were based on a study that compared the brains of 17 patients with suspected VP to those of 10 age-matched controls who had hypertension and other vascular risk factors in life, but no evidence of parkinsonism. The study observed macroscopically visible lacunar infarcts or lacunae caused by enlarged perivascular spaces which were seen in the caudate, putamen, globus pallidus, and thalamus in 11 of the parkinsonian brains, compared to only one control brain. It was also noted that the severity of microscopic small-vessel disease pathology was substantially greater in the VP cohort compared to controls.
However, there are several commonitions, worth highlighting about these observations which include the following: severity of microscopic small-vessel disease did not differ between frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital, and striatal regions and suggest lack of regional specificity 12/17 patients had nigral cell loss suggestive of underlying neurodegenerative parkinsonism and proposed VP criteria could be acute, delayed, or insidious in onset, with unilateral or bilateral parkinsonism, with or without gait impairment, and with focal or diffuse lesions, located anywhere in the parenchyma. Such imprecise clinical and neuroimaging criteria have contributed to less defined diagnostic boundaries, resulting in misrepresentation of other entities as VP.
You May Like: Fitflop Shoes For Parkinson’s
Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease
MedicationIn addition to combating the symptoms of Parkinsons with lifestyle changes such as exercise and/or physical therapy, medication therapy can help control Parkinsons symptoms. Because people with the disease have low levels of dopamine, the main drug therapy is based on increasing dopamine levels in the brain.
The drug levodopa contains a substance that occurs naturally in the body. When taken, the drug is converted to dopamine when it reaches the brain. Levodopa is combined with another substance to ensure it does not convert to dopamine before reaching the brain.
As Parkinsons disease progresses, the benefit from levodopa may become less reliable. In addition, levodopa side effects can include confusion, delusions and hallucinations, as well as involuntary movements called dyskinesia. The dose can be reduced to mitigate these side effects, but sometimes at the expense of losing the benefits of symptom control.
Other types of drugs can be used in combination with levodopa to prolong its beneficial effects. Some of these drugs work by blocking the enzymes known to break down dopamine, whether created naturally in the brain or by levodopa. Other types of medication, including anticholinergics and antivirals, are sometimes used to control physical symptoms such as tremor and involuntary movement. However, patients may find that their limited benefits do not offset the sometimes serious side effects.
External resources for Parkinsons disease:
Dopamine Transporter Single Photon Emission Computerised Tomography

In IPD and other atypical parkinsonism, DaTScan cannot be used to differentiate them. On the contrary, DaTScan was useful in distinguish VaP and IPD. Comparing IPD and VaP, the asymmetry index between the right to left 123FP-CIT striatal uptake was similar in VaP but higher in IPD, and the caudate and putamen uptake and the putamen to caudate ratio of the most affected side were higher in VaP than IPD both visually and semi-quantitatively .The result was reproducible by different studies . There was no significant difference in the asymmetry index of right to left striatum between VaP and healthy controls. These findings are consistent with the diffuse nature of the disease process underlying VaP versus persistent asymmetric nigrostriatal degeneration in IPD. The asymmetry index between bilateral striatal tracer uptake was a promising marker to differentiate VaP from IPD. In a meta-analysis, DaTScan was found to have a sensitivity of 80100% and specificity of 73100% to differentiate IPD and VaP . In summary, DaTScan would be a useful ancillary test in VaP that could improve the diagnostic accuracy and prognosticate patients response to levodopa treatment. If resources allowed, suspected VaP patients should undergo DaTScan.
You May Like: Sam Waterston Parkinson’s
Whats The Difference Between Vascular Parkinsonism And Parkinsons
As the name implies, vascular parkinsonism is caused by cerebrovascular disease which affects the blood supply to the brain. Vascular parkinsonism is caused by one or more small strokes, while Parkinsons is caused by a gradual loss of nerve cells. One major difference from Parkinsons is that its not progressive, while Parkinsons becomes worse with time. Another difference is that there are no tremors in vascular parkinsonism.
For more information on vascular parkinsonism, read this journal article.
Whats The Difference Between Dementia With Lewy Bodies And Parkinsons
In dementia with Lewy bodies, dementia always appears first. There can also be changes in alertness as well as visual hallucinations. However, because of the presence of Lewy bodies throughout the entire brain, characteristics of this disease not only include cognitive characteristics, but also physical, sleep, and behavioral changes. As the disease progresses, the motor symptoms common to Parkinsons such as tremor, slowness, stiffness, and walking and balance problems will appear.
For more information on dementia with Lewy bodies, visit www.lbda.org.
Also Check: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinson’s
Iron Sensitive And Neuromelanin Sensitive Mri
Dorsal nigral hyperintensity abnormalities can now be visualised by the recent development of MRI techniques. Within the substantia nigra, it contains iron and neuromelanin granules. Iron accumulation and neuromelanin loss are found to be associated with dopaminergic degeneration in the substantia nigra . The iron content in the substantia nigra was found to be 30% higher in IPD than healthy controls in pathological studies . The amount of neuromelanin was reduced when PD progressed and was confirmed in a number of post-mortem studies .
T2* and SWI sequences in 3Tesla or 7Tesla are sensitive to detect the iron load in the dorsolateral substantia nigra and these signals are inversely proportional to the iron content. Meta-analyses showed that in iron sensitive MRI sequences, there was loss of dorsal nigral hyperintensity in IPD and atypical parkinsonism due to the increased iron deposition . These techniques were used to differentiate nigrostriatal parkinsonism from healthy controls, but it cannot differentiate between IPD and atypical parkinsonism. The number of VaP patients included in substantia nigra imaging was small. In a study, 14 out of 19 VaP patients had intact dorsal nigral hyperintensity, which substantiated the observation that majority of VaP were not caused by substantia nigra degeneration .
The Role Of Mri And Datscan In Vascular Parkinsonism: A Case Report
A. Tran, M. Amin, R. Burns
Location: Exhibit Hall C
Objective: The role of MRI and DAT scan in Vascular Parkinsonism: A Case Report
Background: DaTscan has become a widely used clinical tool to help clinicians with challenging diagnoses. DaTscan can help distinguish idiopathic Parkinson Disease from secondary forms of Parkinsonism such as vascular Parkinsonism . The integrity of the nigrostriatal dopamine pathway can be assessed using single photon emission computed tomography with dopamine transporter radioligands. DaTscan would be abnormal in PD and normal in VD. While a meta-analysis by Brigo showed high sensitivity and specificity in differentiating PD and VD using DaTscan, reliance on DaTscan alone may be misleading in certain cases.
Methods: Case study
: Although DaTscan has been shown to have high sensitivity and specificity by many studies, the test has limitations because in most studies the gold standard used is the clinical diagnosis made by a movement disorders neurologist and not a neuropathological confirmation. Therefore, the true diagnosis is unknown false positive or false negative scans can occur, which highlights the needs for integration of various clinical findings and imaging tools . This case illustrates an abnormal DaTscan in a patient with VD.
References: Brigo F, et al. FP-CIT SPECT may be a useful tool to differentiate between Parkinsons disease and vascular or drug-induced parkinsonisms: A meta-analysis. Eur J Neurol 2014 21:1369-1376.
Also Check: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinsons
Whats The Difference Between Progressive Supranuclear Palsy And Parkinsons
People with PSP generally progress more rapidly than people with Parkinsons. A person with Parkinsons tends to lean forward while a person with PSP tends to lean backward. Tremors are common in people with Parkinsons and rare in people with PSP. Speech and swallowing abnormalities are more severe and show up sooner in those living with PSP.
For more information on progressive supranuclear palsy, read this fact sheet and insights from the CurePSP organization website.
Is There A Proposed Mechanism Of Vascular Parkinsonism
Ischemic basal ganglia or subcortical white matter lesions disrupt interconnecting fiber tracts between the basal ganglia, thalamus, and motor cortex leading to disruption of sensory-motor integration as well as descending reticular pathways to major centers of the brain stem.
Infarctions affecting basal ganglia lacunae, including the thalamus, external globus pallidus, and putamen, that extend into the caudate and internal capsule, can mimic features of idiopathic PD. The second form with subcortical white matter lesions often produces clinical features resembling the classical lower body parkinsonism and has a more relentless rather than step-wise progression.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson Silverware
What Is Vascular Parkinsonism
Parkinsonism is a hypokinetic movement disorder characterized by akinesia/bradykinesia, resting tremors, and extrapyramidal rigidity. Vascular parkinsonism is a form of atypical parkinsonism, in which the parkinsonian features are of vascular origin in contrast to typical Parkinson’s disease which is neurodegenerative in etiology. It accounts for 4.4%12% of all cases of parkinsonism.
The Association Between Vascular Disease And Pd
The association between ischaemic stroke and vascular risk factors on the one hand and PD on the other has been addressed in several studies. The incidence of ischaemic stroke among PD patients was lower than that of controls in one study , but an association was found in another . Cigarette smoking is recognised as protective for PD and a low incidence of both smoking and myocardial infarction is seen in PD patients . A retrospective case-control study of 178 patients with newly diagnosed PD, and 533 age- and sex-matched controls showed that diabetes, history of smoking, high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol and triglycerides were significantly less frequent in PD than controls . Another study looked at the frequency of cerebrovascular lesions in 617 patients with autopsy-proven idiopathic PD and 535 age-matched controls. It found that 44.0% of PD patients had vascular lesions, more than was seen in controls , while acute, often fatal ischaemic or hemorrhagic strokes were less frequent in parkinsonian patients . The study concluded that there is neither a protective effect of PD against stroke nor a greater susceptibility to death from stroke in the populations examined .
Read Also: Parkinson’s Hallucinations Commercial
How Is Parkinsons Disease Treated
There is no cure for Parkinsons disease. However, medications and other treatments can help relieve some of your symptoms. Exercise can help your Parkinsons symptoms significantly. In addition, physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech-language therapy can help with walking and balance problems, eating and swallowing challenges and speech problems. Surgery is an option for some patients.
Living With Parkinsons Disease
As Parkinsons develops, a person who has it may slow down and wont be able to move or talk quickly. Sometimes, speech therapy and occupational therapy are needed. This may sound silly, but someone who has Parkinsons disease may need to learn how to fall down safely.
If getting dressed is hard for a person with Parkinsons, clothing with Velcro and elastic can be easier to use than buttons and zippers. The person also might need to have railings installed around the house to prevent falls.
If you know someone who has Parkinsons disease, you can help by being a good friend.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson Life Expectancy Early Onset
Don’t Miss: Weighted Silverware
Main Difference Parkinsonism Vs Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsonism and Parkinsons disease are two medical conditions that occur due to the unusual functioning of brain processes and it is quite confusing to identify the line of demarcation which differentiates one from the other. However, health care professionals tend to observe various clinical features, findings on physical examination and investigations, in order to establish an accurate diagnosis, for the purpose of treatment and follow-ups. The main difference between Parkinsonism and Parkinsons disease is that Parkinsonism is a comparatively rapidly progressive condition than Parkinsons disease with additional features like hallucinations, delusions, and dementia.
Here, we will discuss,
1. What is Parkinsonism Clinical Features, Cause, Method of Treatment
2. What is Parkinsons Disease Clinical Features, Cause, Method of Treatment
3. Difference Between Parkinsonism and Parkinsons disease
What Doctors Look For When Diagnosing Parkinsons
Certain physical signs and symptoms noticed by the patient or his or her loved ones are usually what prompt a person to see the doctor. These are the symptoms most often noticed by patients or their families:
-
Shaking or tremor: Called resting tremor, a trembling of a hand or foot that happens when the patient is at rest and typically stops when he or she is active or moving
-
Bradykinesia: Slowness of movement in the limbs, face, walking or overall body
-
Rigidity: Stiffness in the arms, legs or trunk
-
Posture instability: Trouble with balance and possible falls
Once the patient is at the doctors office, the physician:
-
Takes a medical history and does a physical examination.
-
Asks about current and past medications. Some medications may cause symptoms that mimic Parkinsons disease.
-
Performs a neurological examination, testing agility, muscle tone, gait and balance.
Also Check: How Do People Get Parkinsons Disease
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Double Vision
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease and the rate of decline vary widely from person to person. The most common symptoms include:
Other symptoms include:
- Speech/vocal changes: Speech may be quick, become slurred or be soft in tone. You may hesitate before speaking. The pitch of your voice may become unchanged .
- Handwriting changes: You handwriting may become smaller and more difficult to read.
- Depression and anxiety.
- Sleeping disturbances including disrupted sleep, acting out your dreams, and restless leg syndrome.
- Pain, lack of interest , fatigue, change in weight, vision changes.
- Low blood pressure.
What Are The Symptoms
VP is often called ‘lower body parkinsonism’ because it affects the legs more than the upper body. People living with VP may experience:4
- Bradykinesia, or slow muscle movements
- Rigid muscles
- Dementia
- Incontinence
Muscle tremors can also occur but these are not as common. While the symptoms usually affect the legs, some people living with VP may also experience these symptoms in their upper body.2
These symptoms may come on suddenly or may take weeks to months to develop. VP is not as progressive as PD but symptoms may also worsen over time in some people with VP.3,4
Don’t Miss: Pfnca Wellness Programs
Continue Learning About Parkinson’s Disease
Important: This content reflects information from various individuals and organizations and may offer alternative or opposing points of view. It should not be used for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. As always, you should consult with your healthcare provider about your specific health needs.
What Is Parkinsons Disease Its A Movement Disorder

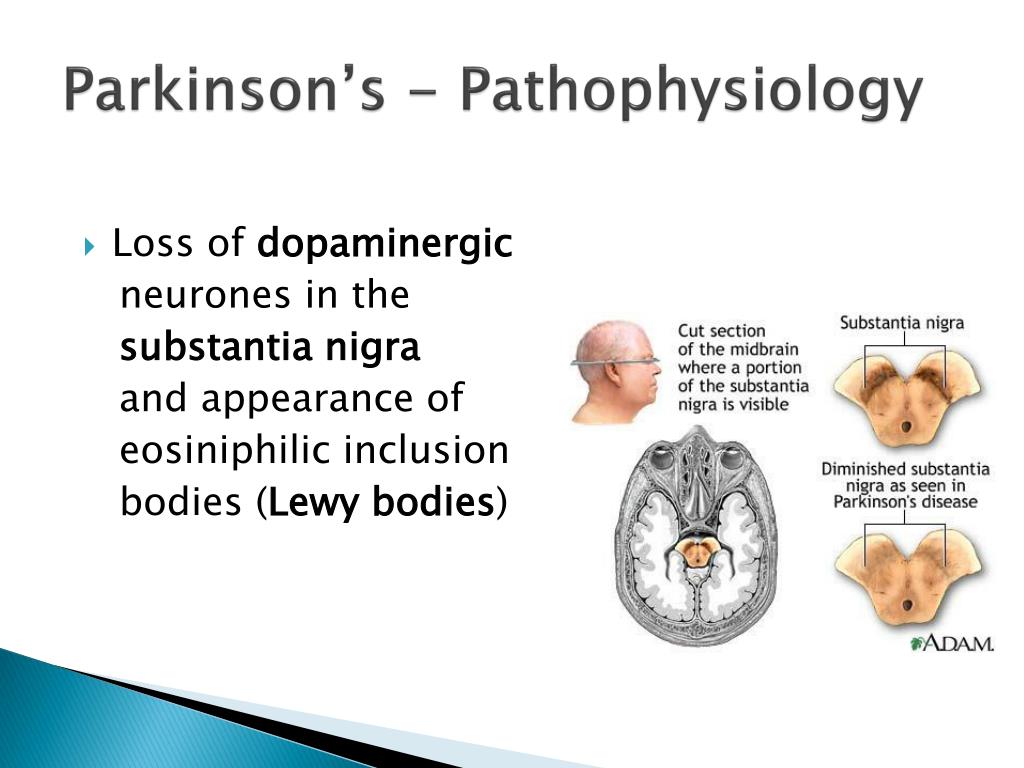
Parkinsons disease is a progressive brain illness that affects the way you move. In more clinical terms, Parkinsons disease is a neurodegenerative disorder of the central nervous system.
Normally, there are cells in the brain that produce a chemical called dopamine. Dopamine sends signals to the parts of your brain that control movement. When approximately 60-80% of the dopamine-producing brain cells are damaged, symptoms of Parkinsons disease appear, and you may have trouble moving the way you want.
Parkinsons disease is a chronic illness and it slowly progresses over time. While there is no therapy or medicine that cures Parkinsons disease, there are good treatment options available that can help you live a full life.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Diagnostic Tests For Parkinsons Disease
Recommended Reading: Prayer For Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Clinical Features Of Vascular Parkinsonism
VP is classically described as an entity characterized by predominant lower-body parkinsonism, postural instability, shuffling or freezing gait, absence of rest tremor, absent or poor response to dopamine, and presence of corticospinal tract signs. Gait abnormalities predominate with VP the base is not always as narrow in lower-body parkinsonism as it is in idiopathic PD and posture is unstable, with postural responses to maintain balance being poor. The occurrences of dementia, pseudobulbar palsy, and incontinence are other recognized features.
Clinical features that resemble the pattern seen in idiopathic PD have also been described as being attributable to lacunar infarcts in the basal ganglia. Although the parkinsonism is often only clinically evident on the contralateral side of the body to the brain lesion, ipsilateral clinical features have also been reported.
Diagnosis is supported by the history of prior stroke and vascular risk factors, namely hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, or carotid stenosis.