What Are The Causes
Drug-induced parkinsonism is caused by medications that reduce dopamine levels in the brain. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that works to control bodily movements.
Dopamine is also part of the brains reward system. It helps you feel pleasure and enjoyment, and it supports your ability to learn and focus.
Medications that bind to and block dopamine receptors are called dopamine antagonists. These medications arent used to treat Parkinsons disease. Rather, theyre used to treat other conditions that might seriously impact your quality of life.
If your doctor has prescribed a medication that causes unwanted side effects, you may have options. You may also decide that the side effects are worth it if the medication effectively treats your condition.
Some medications that cause drug-induced parkinsonism include:
Which Age Group Is Parkinsonism More Prevalent In
There is more data on the incidence of Parkinsons disease than there is for Parkinsonism. The incidence of Parkinsons disease increases with age, and the diagnosis is more likely in older populations.
About 4% of people with Parkinsons disease will be diagnosed before they turn 50 years old.
Anesthetic Drugs May Interact With Medications Used For Parkinsons Disease
Lorri A. Lee, MD Tricia A. Meyer, PharmD, MS, FASHP
An estimated one million people in the United States have been diagnosed with Parkinsons Disease making it one of the most common neurological disorders in patients. This number is estimated to double in the next 30 years as PD is associated with increasing age. PD patients have a deficiency of dopamine in their brain and many of their medications are used to increase this neurotransmitter. They are frequently very sensitive to missing even one dose of their Parkinson medications and may exhibit increased rigidity, loss of balance, agitation, and confusion if their dosing schedule is delayed. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome or parkinsonism-hyperpyrexia syndrome can develop if their medications are held too long or as a result of serious infection.1 Many drugs used in the perioperative period, such as metoclopramide, butyrophenones , and phenothiazines have anti-dopaminergic activity that can worsen the symptoms of PD.
PD patients may be prescribed selective MAOI-B medications such as selegiline and rasagiline that inhibit metabolism of dopamine. Though caution is still advised, several studies have demonstrated that the risk of serotonin syndrome with these selective MAOI-B drugs is extremely low, even in combination with serotonergic antidepressants.
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare for this article.
Patients With Parkinsons Disease Are At Risk For Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Recommended Reading: Judy Woodruff Parkinson’s Disease
What Is The Difference Between Parkinsons Disease And Parkinsonism
Parkinsons disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that leads to movement symptoms and non-movement symptoms. It is sometimes called idiopathic , but the cause is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Parkinsonism is a more general term that encompasses the symptoms of Parkinsons disease. A variety of disorders or syndromes can lead to Parkinsonism, and these syndromes can lead to faster progression of symptoms, increased falling, presence of hallucinations, and can be non-responsive to levodopa .
The majority of people with the symptoms of Parkinsons disease will be diagnosed with idiopathic Parkinsons disease. Between 10% to 15% of these people will be diagnosed with Parkinsonism that is caused by something else.
Diagnosis Of Dip And The Role Of Dat Imaging
The clinical diagnostic criteria for DIP are defined as 1) the presence of parkinsonism, 2) no history of parkinsonism before the use of the offending drug, and 3) onset of parkinsonian symptoms during use of the offending drug. Since asymmetrical rest tremors are common in many DIP patients and symptoms persist or progress after cessation of the offending drug, patients clinically diagnosed with DIP may include individuals in the preclinical stage of PD whose symptoms were unmasked by the drug.,,,
DATs are presynaptic proteins in the membrane on terminals of dopaminergic neurons. They take up dopamine from the synaptic cleft projections that extend from the substantia nigra to the striatum. These transporters control dopaminergic transmission by spatial and temporal buffering, rendering the molecule an imaging target in diseases affecting the dopaminergic nigrostriatal pathway. Single-photon-emission computed tomography and positron-emission tomography scans are available using several DAT ligands., SPECT radioligands include 123I-N-3-fluoropropyl-2-carbomethoxy-3-nortropane , 123I-ioflupane, DaTSCAN, and 123I-2-carbomethoxy-3-tropane . PET scans may be superior to SPECT for imaging DATs, in that the lower energy of positrons provides higher resolution, resulting in better image quality with widespread clinical applications. However, most DAT imaging studies, including those in patients with DIP, have utilized SPECT.,-
You May Like: Best Bed For Parkinson’s Patients
Parkinsonism Due To Other Neurological Disorders
The following neurological disorders are known to cause parkinsonian symptoms:
Vascular parkinsonism Also known as arteriosclerotic parkinsonism, this condition is caused by multiple small strokes.
The onset of symptoms can be sudden or gradual, and often includes mobility problems in your legs. Symptoms may level off for a period of time.
Vascular parkinsonism has the slowest rate of progression of all atypical parkinsonisms. It doesn’t usually cause tremors, either.
Post-traumatic parkinsonism Also known as post-traumatic encephalopathy or “punch-drunk syndrome,” this condition may be caused by a severe head injury or by frequent head trauma, such as from boxing or football.
Post-traumatic parkinsonism can lead to a type of dementia called chronic traumatic encephalopathy . In March 2016, the National Football League admitted that there might be a link between CTE and head trauma.
Essential tremor This is a tremor that tends to run in families and become worse over time. It’s usually seen most severely in the hands, especially when the hands are moving.
Normal pressure hydrocephalus This condition is caused by an abnormal increase in fluid in the cavities of the brain.
NPH can sometimes be treated by draining the extra fluid into your abdomen using a shunt.
Environmentally Caused Parkinsonism
The following disorders are caused by outside factors like drugs and infection:
The following substances can cause drug-induced parkinsonism:
What To Expect From Your Doctor
Your doctor is likely to ask you a number of questions. Being ready to answer them may reserve time to go over any points you want to spend more time on. Your doctor may ask:
- When did you first begin experiencing symptoms?
- Do you have symptoms all the time or do they come and go?
- Does anything seem to improve your symptoms?
- Does anything seem to make your symptoms worse?
© 1998-2019 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research . All rights reserved.Terms of use.
You May Like: Patch For Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsonism Falls And Fracture Risk
All forms of parkinsonism, both PD and DIP, have implications for bone health. A 2014 meta-analysis on PD and fracture risk concludes that PD increases the risk of fracture.4
Given that the symptoms of parkinsonism affect balance, motor skills, gait, and the bodys ability to control movement, it is no surprise that people with PD are more likely to experience a fall than people without PD. Here is an excerpt from a 2016 study comparing the incidence of falls and fracture in PD patients:
It is estimated that 60.5% of patients with PD experience at least one fall and 39% have recurrent falls. The high frequency of falls consequently contributes to the increased risk for fractures in PD patients, which has been estimated to be approximately two times the risk in healthy controls. It has been estimated that 76% of falls in PD patients require health care services and 33% result in fractures. Falls and fractures may result in a series of unfavorable outcomes, such as disabilities and death. Furthermore, among PD patients with fractures, the mortality rate is approximately 10.6%.5
All too often, doctors prescribe these drugs without appropriate consideration of this risk. This excerpt from a study on DIP clarifies the danger of accepting a prescription of an unnecessary or inappropriate prescription drug:
Shockingly, the drugs that cause DIP are still being prescribed. This yet one more example further proving that the FDAs drug approval process is useless.
Synopsis
A Critical Reappraisal Of The Worst Drugs In Parkinsons Disease
What are the worst drugs for Parkinsons disease patients? Couldnt a simple list be assembled and disseminated to the Parkinson community? Recently Ed Steinmetz, an experienced neurologist in Ft. Meyers, FL pointed out to me, a list approach published in the Public Citizen Newsletter . The approach was to list every drug associated with a single confirmed or unconfirmed symptom of Parkinsons disease or parkinsonism. Parkinsons disease is defined as a neurodegenerative syndrome , whereas parkinsonism encompasses a wider net of drug induced and other potential causes. In parkinsonism symptoms are similar to Parkinsons disease, but patients do not have Parkinsons disease. Patients and family members confronted with a simple drug list approach may falsely conclude that most medicines are bad for Parkinsons disease, and that any medicine may cause parkinsonism. This concept is in general, incorrect. Although the approach is well-meaning, it is in need of a major revision, as Parkinsons disease and parkinsonism are too complex to summarize by simple lists. In this months column I will try to summarize the key information that patients and family members need to know about the worst pills, for Parkinsons disease and parkinsonism.
A Florida Parkinsons Treatment Blog by Michael S. Okun, M.D.
UF Center for Movement Disorders & Neurorestoration, Gainesville FL
Read Also: Leg Weakness Parkinson’s Disease
Disadvantages Of Regional Anesthesia Over General Anesthesia
Regional anesthesia will not eliminate Parkinsons symptoms, such as tremor or rigidity, except in the areas directly affected by the anesthetic.
Tremor can interfere with some monitoring device and makes it more difficult to interpret.
If the surgery is delicate, the surgeon may want the patient to be absolutely still.
The surgical procedure may not be possible under regional anesthesia.
Two Areas In Which Parkinsons Disease May Bring About Death
I. Falls
PD patients are at an increased risk of falling and bad falls can lead to death. This usually occurs as a complication of a fall that requires hospitalization, particularly if it involves surgery. While most people do not fracture their hips when they fall, some do, and hip surgery, while routine, is still major surgery. It carries the risk of infection, delirium related to pain medications and anesthesia, heart failure, pneumonia, blood clots in the legs that then go to the lungs, and general weakness from immobility. Hip fractures are probably the main cause for death for those who fall, but people can fracture other bones and require surgery. They may fracture their ribs, which leads to reduced coughing, because of the pain, and an increased risk of lung infections . It is surprisingly uncommon for Parkinsons Disease patients to die from brain injuries related to falls, but it still may occur.
II. Pneumonia
What Causes Pain In Cases Of Parkinsons Syndrome Sufferers
Common Symptoms Of Drug
The motor features of PD are often very easy to see via a neurologic exam in a doctors office. Rest tremor for example, is seen in virtually no other illness and can therefore be very important in diagnosing PD. But there is one other common condition that induces the symptoms of PD, including a rest tremor, which must be considered every time PD is being considered as a diagnosis, and that is drug-induced parkinsonism.
Parkinsonism is not technically a diagnosis, but rather a set of symptoms including slowness, stiffness, rest tremor, and problems with walking and balance. This set of symptoms can be caused by PD, but also can occur as a side effect of certain prescription medications .
A number of medications can cause parkinsonism because they block the dopamine receptor and thereby mimic the symptoms of PD that are caused by loss of dopamine neurons in the brain. Reviewing a patients medications is therefore a critical step for a neurologist when seeing someone with parkinsonism. Anti-psychotics and anti-nausea treatments make up the bulk of the problematic medications, although there are other medications that can also cause parkinsonism. The primary treatment for this type of parkinsonism is weaning off of the offending medication, if possible.
Read Also: What Is The Difference Between Alzheimer’s And Parkinson’s Disease
Atypical Parkinsonism Or ‘parkinson’s Plus Syndromes’
“Parkinson’s Plus Syndromes” are less common than Parkinson’s disease.
Some atypical parkinsonism syndromes include:
Multiple system atrophy This is a category of several disorders in which one or more body systems deteriorate.
Your doctor may classify you as having MSA-P, in which parkinsonian symptoms are dominant or MSA-C, in which dysfunction of the cerebellum is dominant.
The names of some of these syndromes include olivopontocerebellar atrophy , Shy-Drager syndrome , and striatonigral degeneration .
Progressive supranuclear palsy Symptoms of this condition usually begin after age 50 and proceed more rapidly than Parkinson’s disease.
In people with PSP, problems with eye movement can lead to blurry vision. Falls tend to occur early in the course of the disease, and dementia may occur later in the disease.
Corticobasal degeneration This condition may cause jerking and loss of control in a limb, often without weakness in that limb.
If you have this disorder, you may be given Botox to help your limb relax.
Lewy body dementia LBD is the second leading cause of dementia in the elderly, after Alzheimer’s disease.
In this condition, the same Lewy bodies occur in the brain as in Parkinson’s disease, but in multiple areas of the brain.
If you have LBD, you may experience speech problems, hallucinations, and gradual cognitive decline.
Delayed Administration And Contraindicated Drugs Place Hospitalized Parkinsons Disease Patients At Risk

Problem: One-third of all patients with Parkinsons disease visit an emergency department or hospital each year, making it a surprisingly common occurrence.1 The disease affects about 1 million people and is currently the fourteenth leading cause of death in the US. Hospitalization can be risky for patients with Parkinsons disease when viewed from the perspective of pharmacological management.
Patients with Parkinsons disease require strict adherence to an individualized, timed medication regimen of antiparkinsonian agents. Dosing intervals are specific to each individual patient because of the complexity of the disease. It is not unusual for patients being treated with carbidopa/levodopa to require a dose every 1 to 2 hours. When medications are not administered on time, according to the patients unique schedule, patients may experience an immediate increase in symptoms.2,3 Delaying medications by more than 1 hour, for example, can cause patients with Parkinsons disease to experience worsening tremors, increased rigidity, loss of balance, confusion, agitation, and difficulty communicating.2 Studies show that three out of four hospitalized patients with Parkinsons disease do not receive their medications on time, or have had doses entirely omitted.4 According to the National Parkinson Foundation, 70% of neurologists report that their patients do not get the medications they need when hospitalized.2
Two case examples
References
Don’t Miss: Symptoms Of Parkinson Disease Webmd
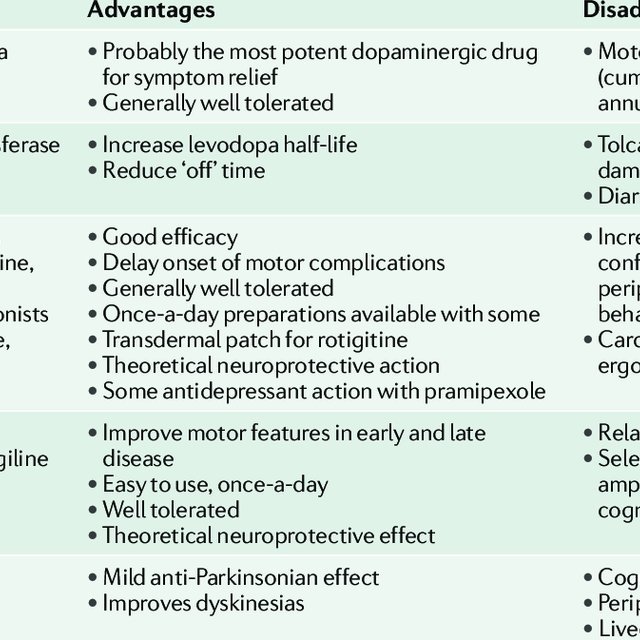
An Approach To The Treatment Of Parkinson’s Disease
No treatment can arrest or slow neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. The aim is to relieve symptoms and avoid the complications of therapy.
Early Parkinson’s disease
Many studies have shown that early treatment with dopamine agonists reduces the incidence of dyskinesia.1Fewer motor fluctuations were shown in some but not all of the studies. We recommend a dopamine agonist as the first treatment in younger patients who have mild disease and no cognitive deficit. It is necessary to add levodopa within 1-5 years in most patients. In more severe disease, treatment begins with levodopa but a dopamine agonist may be added to keep the daily dose of levodopa in the lower range if there is no cognitive deficit. Dopamine agonists are used infrequently and with caution in patients more than 70 years old because of the risk of neuropsychiatric adverse effects and postural hypotension. They are contraindicated in the presence of dementia.
Isolated resting tremor is rarely disabling, but if it interferes with function it can usually be managed with levodopa. When this is ineffective at low to moderate doses, the addition of an anticholinergic can sometimes be useful.
Patients with motor fluctuations
Role of physical therapy and surgery
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons disease is a degenerative, progressive disorder that affects nerve cells in deep parts of the brain called the basal ganglia and the substantia nigra. Nerve cells in the substantia nigra produce the neurotransmitter dopamine and are responsible for relaying messages that plan and control body movement. For reasons not yet understood, the dopamine-producing nerve cells of the substantia nigra begin to die off in some individuals. When 80 percent of dopamine is lost, PD symptoms such as tremor, slowness of movement, stiffness, and balance problems occur.
Body movement is controlled by a complex chain of decisions involving inter-connected groups of nerve cells called ganglia. Information comes to a central area of the brain called the striatum, which works with the substantia nigra to send impulses back and forth from the spinal cord to the brain. The basal ganglia and cerebellum are responsible for ensuring that movement is carried out in a smooth, fluid manner .
The action of dopamine is opposed by another neurotransmitter called acetylcholine. In PD the nerve cells that produce dopamine are dying. The PD symptoms of tremor and stiffness occur when the nerve cells fire and there isn’t enough dopamine to transmit messages. High levels of glutamate, another neurotransmitter, also appear in PD as the body tries to compensate for the lack of dopamine.
Don’t Miss: Treatment For Parkinson’s Disease Usually Includes
How To Talk To Someone With Hallucinations Or Delusions
- It is usually not helpful to argue with someone who is experiencing a hallucination or delusion. Avoid trying to reason. Keep calm and be reassuring.
- You can say you do not see what your loved one is seeing, but some people find it more calming to acknowledge what the person is seeing to reduce stress. For example, if the person sees a cat in the room, it may be best to say, I will take the cat out rather than argue that there is no cat.
Page reviewed by Dr. Chauncey Spears, Movement Disorders Fellow at the University of Florida, a Parkinsons Foundation Center of Excellence.
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease and the rate of decline vary widely from person to person. The most common symptoms include:
Other symptoms include:
- Speech/vocal changes: Speech may be quick, become slurred or be soft in tone. You may hesitate before speaking. The pitch of your voice may become unchanged .
- Handwriting changes: You handwriting may become smaller and more difficult to read.
- Depression and anxiety.
- Sleeping disturbances including disrupted sleep, acting out your dreams, and restless leg syndrome.
- Pain, lack of interest , fatigue, change in weight, vision changes.
- Low blood pressure.
Also Check: Can Vyvanse Cause Parkinson’s