Sensitivity To Clinical Conditions
When the group containing all individuals with PD was analyzed, increased sway was observed compared with the healthy subject group, but no other statistically significant differences in the LOS or gait-related variables were found . The in-depth analysis of participants with PD, when grouped by H& Y stage, showed the progressive decline of postural control and gait with increasing H& Y stages. The participants categorized as H& Y II showed the worst performance for all postural and gait measurements among the three groups. In contrast, participants categorized as H& Y II.5 not only showed better performance than individuals with more advanced pathological stages but also outperformed healthy subjects, including decreased sway and increased LOS and gait speed values .
Table 2 Performance of the participants in the instrumented tests of postural control and gait
All instrumented gait parameters during the single-task condition, except for stride width, showed significant correlations with conventional clinical scales, with variable strengths. Among these correlations, the strongest interactions were found for the 10-m Walking Test, which ranged from good to excellent. Independent of correlation strengths, the signs of the correlations were all coherent, and indicated that better performances on all postural and gait parameters were correlated with better performances on the clinical scales.
Trouble Moving Or Walking
People without PD do not think about their walking. Their arms naturally swing, and their feet naturally land on the heels with each step. They can walk and talk and carry bags, purses and plates of food without difficulty.
Individuals with PD tend to lose their automatic movements. Especially as Parkinsons advances, it may bring with it a variety of symptoms that are uncommon in early stages, such as problems with walking and poor balance . Feet begin to shuffle, and performing two tasks at once becomes more difficult. Turning becomes challenging, often leading to a freezing episode and sometimes a fall.
Parkinsons Disease Is a Movement and Sensory Disorder
People with PD have trouble regulating the speed and/or size of their movements. Movements are bradykinetic or hypokinetic .
Changes in the movement system lead to challenges controlling movements, including the following:
- Starting and stopping movements
- Linking different movements to accomplish one task
- Finishing one movement before beginning the next
Changes in the sensory system also lead to challenges, particularly noticing and correcting movement and voice issues, including the following:
- Slowness or smallness of movements
- Lack of movement
- Changes in posture
- Changes in voice volume
Walking Changes
There are many PD-related walking changes:
Managing Walking Changes
Walking Tips
Turning Tips
Freezing
Managing Freezing
Tips for Care Partners
Freezing is a significant cause of falls.
Common Motor Symptoms That Require Management
- Tremor is a prominent and early symptom of PD .
- Slowness, or bradykinesia, a core feature of PD.
- Rigidity is the third prominent feature on examination.
- A combination of bradykinesia and rigidity leads to some other characteristic features of PD, such as micrographia.
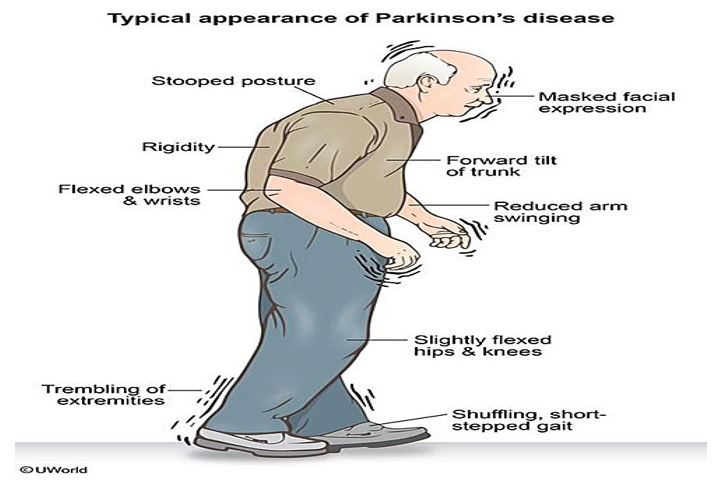
- The fourth prominent feature of PD is gait disturbance, although this is typically a late manifestation. Flexed posture, ataxia, reduced arm swing, festination, march-a-petits-pas, camptocormia, retropulsion, and turning en bloc are popular terms to describe the gait in PD. Gait disorder is not an early feature of PD but is frequently described as it is easy to recognize and cinches the diagnosis in later stages.
The rate of progression of the disease may be predicted based on the following:
- Males who have postural instability of difficulty with gait.
- Patients with older age at onset, dementia, and failure to respond to traditional dopaminergic medications tend to have early admission to nursing homes and diminished survival.
- Individuals with just tremors at the initial presentation tend to have a protracted benign course.
- Individuals diagnosed with the disease at older age combined with hypokinesia/rigidity tend to have a much more rapid progression of the disease.
The disorder: leads to disability of most patients within ten years has a mortality rate three times the normal population.
Parkinsons cannot yet be cured . A lot of financial and other resources are being expended on research to find a cure.
Also Check: How Long Do You Live With Parkinson’s Disease
How Do I Maintain Good Posture
Use a mirror to check posture throughout the day. Be aware of posture changes. Try to catch yourself stooping or leaning and take action to make corrections. Ask people to tell you if they notice you stooping. Change position often. Take movement breaks! Get back or neck rolls or cushions for better postural alignment when sitting. Consider yoga or tai chi classes. Seek a physical therapy referral for specific posture recommendations and treatment. Perform simple posture exercises/ stretches throughout the day.
The Influence Of Education In Pd
The concept of an education-augmented cognitive reserve has been extensivelyinvestigated in studies focusing on dementia, normal aging, and PD. However, few studies have exploredthe relationship between education and motor outcomes. The possible mechanisms thatmight explain this relationship include: greater education-associated cerebralvolumes that are more resilient to neurodegenerative changes more efficientrecruitment of alternative brain networks that may be used for neurologicalfunction or enhanced brain repair/recovery mechanisms.
Kotagal et al. conducted across-sectional clinical imaging study of 142 subjects with PD. All subjectsunderwent dihydrotetrabenazine PET to confirmnigrostriatal dopaminergic denervation and also brain MRI to estimate adjustedcortical gray matter volume . After adjusting for possible confounders,including cognitive and dopaminergic covariates, as well as nonspecificneurodegeneration covariates , lower years of education remained a significant predictor of higher totalMDS-UPDRS motor scores. Educational level was inversely associated with white matter hyperintensities. Higher educational attainment is associated with lowerseverity of motor impairment in PD, and this association may reflect an extranigralprotective effect upon WM integrity.
These results are also consistent with previous studies that have shown inversecorrelations between balance performance in PD and educational attainment.,
You May Like: Cleveland Clinic Parkinson’s Center Of Excellence
Gait And Balance Problems
Parkinsons disease is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive damage to dopamine-producing nerve cells in a specific region of the brain. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter, or cell signaling molecule, that relays information between nerve cells and muscles. One of the most debilitating effects of Parkinsons disease is the loss of coordination and control in body movements, which in many cases leads to severe walking disabilities.
Tremor Rigidity Bradykinesia And Dyskinesia
One of the first visible motor symptoms to emerge in PD is resting tremor of a limb that is supported and at rest. Tremor typically begins on one side of the body with a tremor rate of 3 to 7 cycles per second. Tremors are usually less severe or even absent with voluntary movement and can increase during times of emotional stress. Tremor is considered one of the cardinal symptoms of Parkinsons diseasesome studies report it to be present in up to 80% of patients with autopsy-proven PD .
Rigidity is another common visible motor symptom associated with PD. It is a type of increased muscle tone generally defined as an increased resistance to passive movement of a joint. Rigidity tends to be more prominent in the flexor muscles of the trunk and limbs, causing a characteristic stooped posture. There are two types of rigidity: lead pipe and cogwheel. Lead pipe rigidity is defined as a constant resistance to motion throughout the entire range of movement. Cogwheel rigidity refers to resistance that stops and starts as the limb is moved through its range of motion.
Bradykinesia, another cardinal motor feature of PD, is of unknown cause and remains the subject of debate. It is defined as slowed voluntary movement, although we now know that rigidity also affects automatic movements such as arm and leg swing during gait.
Also Check: Sole Support For Parkinson’s
Improving Flexibility And Range Of Motion
Improving your flexibility can help you improve your balance and gait, as well as reduce rigidity. Try these exercises:
- Sit in a chair and bend your upper body at the waist to your right and left.
- Get on all fours and turn your upper body to the right and left. Lift your arm on the side youre turning to as you turn.
Also work on lower-body strength training. Strength training can help you improve your balance, walk further distances, and potentially increase your walking speed. Some exercises to try include:
- Leg presses. While sitting down, push a weight away from your body using your legs.
- Squats. Start in an upright position with your legs slightly wider than hip distance. Bend your knees while pushing your glute muscles back, so that your knees dont come over your toes. You can hold onto something if necessary. You dont have to go down more than a few inches.
- Exercise bike. If you have access to a recumbent exercise bike , using the bike can help strengthen your legs.
- Repeatedly sit in and rise out of a chair. Repeating the motions of sitting down and rising helps strengthen your leg and core muscles. It also helps you practice a functional activity.
What Is Parkinsonian Gait
Parkinsonian gait is a defining feature of Parkinsons disease, especially in later stages. Its often considered to have a more negative impact on quality of life than other Parkinsons symptoms. People with Parkinsonian gait usually take small, shuffling steps. They might have difficulty picking up their feet.
Parkinsonian gait changes can be episodic or continuous. Episodic changes, such as freezing of gait, can come on suddenly and randomly. Continuous changes are changes in your gait that happen all the time while walking, such as walking more slowly than expected.
You May Like: Seroquel And Parkinson’s Disease
Balance Orientation And Postural Control
Balance is the ability to automatically and accurately maintain your center of mass over your base of support. Postural orientation is the ability to control the segments of your body in relation to one another and to gravity, taking into account the environment and whatever task is being performed. Postural control involves both balance and postural orientation.
Control of posture has both musculoskeletal components and motor processes, which organize the muscles into neuromuscular synergies. Balance also involves neural componentssensory and perceptual processesthat integrate input from the somatosensory, visual, and vestibular systems, as well as higher level processes that contribute to anticipatory and adaptive aspects of postural control .
Poor balance and unstable posture are commonly observed motor symptoms in those with PD. Until recently, it was thought to occur relatively late in the course of the disease. This is reflected by the Hoehn and Yahr scale, in which postural instability is represented only in the advanced stages of the disease . However, there is significant evidence that changes in postural control occur even in the early stages of Parkinsons and, although there is fluctuation, generally increase over time .
What Causes Gait To Change
PD causes damage to the nerves in the brain and in the body, as well as causing accumulations of the protein alpha-synuclein, called Lewy bodies.
The motor symptoms of PD, like Parkinsonian gait, are caused by damage to the part of the brain called the substantia nigra pars compacta. The neurons in the substantia nigra produce dopamine, a neurotransmitter that transmits signals from the substantia nigra to other parts of the brain to produce smooth, purposeful movement.2,4
Damage to the neurons in the substantia nigra causes a reduction in dopamine, creating the motor symptoms seen in people with PD.2,4
You May Like: Joy Milne Parkinson’s Disease
Disorders Of Posture Balance And Gait In Parkinson’s Disease
Disorders of movement function related to posture, balance, and gait are common occurrences for many persons with Parkinson’s disease. Numerous studies have identified a broad variety and heterogeneous distribution of postural and locomotor changes. These alterations are often associated with diminished functional ability, poor prognosis, and frequent falls. Present pharmacologic management appears to have a limited influence on postural instability and associated falls, and, despite anecdotal information, there is scant information on the therapeutic effectiveness of physical interventions aimed at enhancing these functions. Future advances would likely be facilitated by: determining the nature and extent of the specific involvement of postural and locomotor control
- Previous article in issue
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Read Also: What Is Parkinson Disease In Layman Terms
Vertical Ground Reaction Force
In normal gait, the vertical ground reaction force plot has two peaks â one when the foot strikes the ground and the second peak is caused by push-off force from the ground. The shape of the vertical GRF signal is abnormal in PD. In the earlier stages of the disease, reduced forces are found for heel contact and the push-off phase resembling that of elderly subjects. In the more advanced stages of the disorder where gait is characterized by small shuffling steps, PD patients show only one narrow peak in the vertical GRF signal.
Dropped Head Syndrome And Camptocormia
Approximately 5-10% of people with PD have a more pronounced problem with their posture. One potential difficulty is a pronounced forward flexion of their head, called dropped head syndrome . Another, is a pronounced flexion of their entire trunk, called camptocormia or bent spine syndrome . These two conditions have many causes besides PD including other neurodegenerative diseases such as the Parkinson plus syndrome, multiple system atrophy , amyotrophic lateral sclerosis , and muscle or nerve diseases such as chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy .
Typically, in dropped head syndrome and camptocormia, the forward flexion is present with sitting and increases with walking. When lying down on the back however, the neck and trunk can mostly or completely straighten out. This distinguishes it from a fixed posture of the neck or back called kyphosis or kyphoscoliosis, which does not straighten out when lying on the back. Kyphosis is common as people age and is not related to PD. It can be caused by osteoporosis, leading to compression fractures of the spine, arthritic changes in the spine, and degenerative disc disease. Both kyphosis and camptocormia can co-exist in one person, which complicates the diagnosis. Both are also more common in women than men.
You May Like: Que Es La Enfermedad De Parkinson Y Sus Sintomas
Why Do Truncal Abnormalities Occur In Pd
The reason that these syndromes occur in PD are not clear. There are four potential causes, and likely each of these play a role in some of the cases that are seen:
- Myopathy of the muscles of the back that are meant to hold up the neck or trunk, or to keep the trunk in midline.
- Dystonia or over-activity of muscles that either pull the neck forward, pulling the trunk forward, or pull the trunk to the side.
- Medication side effect this needs to be considered if the postural change occurs over a short period of time after a medication change. This has been described in rare cases after starting dopamine agonists , for example.
- Part of PD progression that is not explained by the above three reasons.
Machine Learning Algorithms Application For Gait Analysis
There has been increasing use of machine learning in medicine including neurology to aid diagnosis, and patient management using risk stratification . ML algorithms learn from data by identifying underlying patterns and relationships. The field of ML can broadly be categorized into supervised, unsupervised and reinforcement learning.
Supervised learning begins with the aim of predicting a known output or target. Indeed, an SL algorithm takes a known set of input data and known responses to the data , and trains a model to generate reasonable predictions for the response to new input data. In such algorithms, the artificial intelligence is approximating what a trained physician is already able to perform with high accuracy. This approach means that the learning algorithm generalized the training data to previously unobserved situations in a reasonable way.
All forms of SL algorithms can be classified as either classification or regression. Classification techniques predict discrete responses. Regression techniques, instead, are used to predict continuous responses. They can also be used for modeling the risk, meaning that the computer is doing more than merely reproducing the physician skills. These algorithms are also capable of discovering new associations not apparently evident to humans preliminary interpretation.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Loss Of Taste
What Is Parkinson’s Gait
Parkinsons gait is a symptom of Parkinsons disease that usually develops as the condition becomes more severe. Effect of the disease such as a lack of balance and strength contribute to an unsteady, stooped gait. Often, Parkinsons gait is mistaken for a walking style thats consistent with old age, until the condition gets worse. Other common signs of Parkinsons gait include short steps, difficulty in turning or stopping and the patient feeling as if he or she is constantly leaning forward.
Parkinsons disease affects the human brain and slows the speed of signals traveling through the nervous system. This reduced speed of transmission can have a major effect on everyday activities, including walking, showering and getting dressed. Other problems include a lack of balance and fatigue. As the condition gets worse, the symptoms become more apparent, including Parkinsons gait.
Assessment Of Gait Therapy Effectiveness In Patients With Parkinsons Disease On The Basis Of Three
- 1Department of Clinical Rehabilitation, University of Physical Education, Krakow, Poland
- 2Department of Physical Education and Sport, University of Physical Education, Krakow, Poland
- 3Department of Neurology, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland
Objective: The aim of this study was to assess the effect of physical exercise on gait pattern disorders, based on three-dimensional gait analysis in the sagittal plane in a group of people with Parkinsons disease .
Methods: Thirty-two subjects with PD were qualified for the study, which ran for 3 weeks and included 18 therapeutic sessions. Thirty-five control subjects were included in the research . Gait analysis using the Vicon 3D system took place in the Biokinetics Laboratory. The research group was tested before and after treatment, and the control group was tested once.
Exercise therapy slightly increased the range of movement in the examined joints of PDs patients. Results of pathological walking patterns occurring prior to treatment improved after treatment and moved closer to the physiological gait pattern.
Also Check: Medical Marijuana And Parkinson’s Disease