What To Expect From Diagnosis
Theres no single test for Parkinsons, so it can take some time to reach the diagnosis.
Your doctor will likely refer you to a neurologist, who will review your symptoms and perform a physical examination. Tell your doctor about all the medications you take. Some of these symptoms could be side effects of those drugs.
Your doctor will also want to check for other conditions that cause similar symptoms.
Diagnostic testing will be based on your symptoms and neurologic workup and may include:
Study Design And Participants
All the clinical data and 123I-FP-CIT SPECT images used in this study were downloaded from the PPMI database. The PPMI is an ongoing longitudinal, international, multicentre, observational clinical study of patients with early Parkinsons disease aimed at identifying disease biomarkers . The study ascertains patients with a clinical disease duration of < 2 years who periodically undergo clinical motor evaluation and imaging with 123I-FP-CIT SPECT. The diagnosis of Parkinsons disease had to be supported by an in vivo evidence of nigrostriatal dopaminergic dysfunction all patients with tremor and normal scans were followed up as a separate group . The full list of inclusion and exclusion criteria can be found in the PPMI study protocol, available online at .
Our analysis was focused on the period from baseline to the 2-year follow-up, as not enough patients had completed longer follow-ups. We therefore downloaded clinical motor assessments and 123I-FP-CIT SPECT images at both baseline and 2-year follow-up from the PPMI database in August 2015. For patients who did not have a 2-year assessment the previous or successive one was used.
The Different Tremors Of Parkinsons Disease
PD harbors several different tremors that are variable in frequency, amplitude, distribution, constancy, context in which they occur, and provoking situations . The classical Parkinsons tremor occurs at rest, is often asymmetric, has a distal maximum and a typical frequency of 46Hz . Many PD patients also have a postural tremor of the hands, which can have many different origins . Most commonly this is the rest tremor returning when the hand has assumed a new stable position . Therefore, the term tremor of stability may be more appropriate than resting tremor . Although this has never been tested, re-emergent tremor probably has the same pathophysiology and response to treatment as resting tremor. Resting tremor does not necessarily disappear completely after a voluntary action, but its amplitude is reduced in 90% of PD patients. In contrast, tremor is suppressed in only 6.5% of ET patients with resting tremor . Other postural tremors often have a higher frequency than resting tremor. They may have different etiologies, e.g. occurring in a dystonic limb, or resemble ET overlap with that of Parkinsons tremor. Therefore, electrophysiological frequency analysis cannot serve as diagnostic criterion but may be a supportive ancillary test in unclear cases. Note that clinical tremor assessments are as good as objective tremor measurements in estimating tremor severity therefore, an adequately trained clinical eye remains crucial.
Also Check: Caring For Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s Disease And Manganese
The hallmark clinical features of Parkinson’s disease include resting tremor, bradykinesia, postural instability, and other signs of motor dysfunction. Motor symptoms generally appear when greater than 60% of dopaminergic neurons are lost and dopamine content in the striatum is reduced to below 20% of normal levels . Loss of dopaminergic neurons occurs with aging and the prevalence of Parkinson’s disease increases dramatically in elderly populations. This observation has led to the hypothesis that Parkinson’s disease may reflect an inability of the aging nervous system to remove reactive oxygen species and repair oxidative damage to proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids . The development of the neuronal aggregates of -synuclein and other proteins seen in Parkinson’s disease patients is consistent with this oxidative stress hypothesis .
A.M. Reynolds, in, 2021
What Is The Physiological Tremor

Tremor is a common side effect of many drugs . Various drugs and toxins can cause all types of tremor known clinically although increased physiological tremor is most commonly seen. Tremor is the dose limiting side effect of the ?2 adrenergic agonists, salbutamol and terbutaline, used to treat obstructive airway diseases. Tremor is usually seen within a month of starting valproic acid treatment and is more evident when a dose is > 750 mg/day although it can also occur when the dose is within therapeutic range. It is the most common tremorogenic drug among anticonvulsants, affecting up to 25% of patients. Intention tremor may occur in patients on lithium. The occurrence rate increases with increasing serum lithium levels and manifests almost 100% in patients with lithium toxicity. Tardive tremor, a rare disorder, represents a separate entity in which, by definition, is caused by exposure to a dopamine receptor blocking agent within six months of the onset of symptoms and persisting for at least one month after stopping the offending drug. It is usually static in nature but can occur at rest and on intentional movements, such as eating and writing. Tremor can also occur as a toxic reaction to marijuana, and 3,4-methylene-dioxymethamphetamine or ecstasy.
Other Tremors And How It Differs
The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke notes that some common tremors include:
Other causes of tremors unrelated to Parkinsons disease can include:
- certain medications
You May Like: Parkinson’s Lewy Body Disease
What Treatments Are There For Tremors
Parkinsons tremors cannot be cured. However, there are several options to manage them.
Many of the typical Parkinsons drug treatments are associated with a reduction in tremors, including levodopa and dopamine agonists. A surgical procedure called deep brain stimulation also may be offered to control unmanageable tremors.
Physical therapy can help some patients control their tremors better, as can reducing the intake of substances such as caffeine, which can induce tremors. Many patients experience an increase in the severity of their tremors when they are stressed. Therefore, trying to reduce sources of anxiety and engaging in complementary therapies may help some patients.
Note: Parkinsons News Today is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
What Causes Essential Tremors
It is generally accepted that tremor is caused when problems arise in the thalamus, which is the structure of the brain that is responsible for coordinating and controlling muscle activity. However, at this time, researchers and medical professionals are not exactly certain what causes essential tremor.
Researchers are currently analyzing changes in specific chromosomes that have been linked to the development of essential tremor, but there have been no confirmed genetic connections as of yet.
In patients with a family history of ET, the specific manner in which essential tremor is inherited can vary. Most of the time, ET is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, which means that one altered copy of a gene can cause essential tremor. However, this inheritance pattern is not found in other families with ET, making it an unclear and unconfirmed connection to family history and genetics.
You May Like: How To Test For Parkinson’s Symptoms
What Else Can I Do To Sleep Better With Parkinsons Disease
Practicing healthy sleep hygiene habits may also promote more restful sleep.
- Get outside during the day. Bright light tells your body its time to be awake.
- Keep your body moving during the day. Even if all you feel up to is a short walk or two, all physical activity offers benefits.
- Try at-home remedies, such as massage or a warm bath. Relaxing your mind may help your body fall asleep.
Dont:
- Take long naps during the day.
- Use stimulants, such as caffeine, within six hours of bedtime.
- Use your bedroom for activities other than sleeping. Go to another room to read, watch TV or work.
How To Investigate Parkinsons Tremor
1. Tremor distribution. Parkinsons tremor can affect several parts of the body, typically involving the limbs, but sometimes also the lips and chin . Some patients have signature features such as a pill-rolling tremor, where there is a thumb flexion from neutral position. Such a pill-rolling tremor has important diagnostic value, as it is seen in only a limited number of conditions: apart from PD, it can also be seen in drug induced parkinsonism or in a limited number of atypical parkinsonism . In contrast, however, patients with dystonic tremor often have a thumb extension tremor . The form and distribution of tremor can vary within a single patient, depending on the limb position. Therefore, it is useful to look for resting tremor in different arm positions . In many patients, the resting tremor amplitude reachesits maximum during walking, and sometimes the tremor is only visible during walking . Tremor assessment can therefore already start when walking with the patient to the examination room.
To assess postural tremor, we use a few different postures: arms stretched out, the bat-winging position , and wrist extension . It is useful to expose the patients chest during these tasks, because the pectoral muscles may contract during dystonic posturing of the arm. Furthermore, asking the patient to slowly rotate the outstretched arms from pronation to supination may show a position-specific tremor which is a sign of dystonic tremor.
Read Also: Is Parkinson’s Disease Serious
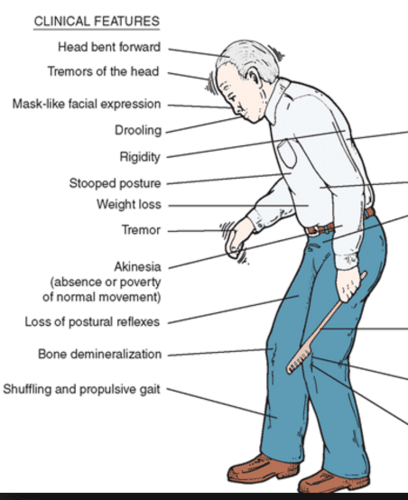
What Are The Motor Symptoms Of Parkinsons
Parkinsons is officially classified as a movement disorder because it involves damage to the areas of the brain, nerves and muscles that influence the speed, quality, fluency and ease of movement. Motor symptoms are usually the most visible elements of Parkinsons. Motor symptoms of Parkinsons also respond well to Parkinsons medications.
Although motor symptoms of Parkinsons often get the most attention and treatment, researchers estimate motor symptoms dont actually appear in most people until around 60?80% of the nerve cells in the brain that make dopamine have stopped working because of Parkinsons.
In this article, we will help you identify and learn about the various motor symptoms of Parkinsons so you can be proactive in the management of your symptoms.
The impacts of Parkinsons on movement are called motor symptoms.
Strategies To Help Manage Tremor Include:
- Take your medication on time! This helps minimize off times that can make tremor worse.
- Streamline your focus to reduce multitasking. Rest your elbow on the table when taking a drink to stabilize yourself or sit down when you button your shirt to concentrate more intently on the task at hand.
- Reduce stress. Nerves and feeling stressed, in general, can make tremor worse, as can fatigue.
- Consider adaptive technologies and products designed to make everyday tasks easier, such as specially-designed razors, pens, keyboards, utensils, cups and dishes.
Learn more about Bradykinesia and Rigidity
What Makes A Parkinsons Tremor Different
The tremor that occurs in Parkinsons disease is different from almost all other tremors because it is a resting tremor since it presents primarily at rest. It goes away with movement, but often returns when the limb, usually a hand or fingers, are held in one position. While holding a spoon or fork to the mouth, the tremor can reappear which is why those with Parkinsons are known to spill things. Parkinsons disease tremor may affect almost any part of the body, but most commonly involves the fingers, followed next most commonly by the hands, jaw, and feet.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease Disability Benefits Questionnaire
Myoclonus In Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease
Unilateral resting tremor in the distal limb is usually the first motor manifestation in the majority of patients with PD. While tremor, either at rest or during muscle activation, is common in PD, myoclonus is much less prevalent and was originally described as a consequence of levodopa therapy. In a study of 12 PD patients who developed myoclonus after taking levodopa for 12 months, abnormal movements consisted of single, abrupt jerks of the extremities, which were bilateral and symmetrical or occasionally in an arm or leg on the same side . In general, the trunk and limbs are most commonly affected, whereas facial muscle involvement is unusual. Myoclonus can occur during sleep, fatigue, dozing or even wakefulness, but abates with levodopa cessation. Luquin et al. reported spontaneous and action myoclonus with multifocal distribution in only 6 out of 168 patients with levodopainduced dyskinesias, whereas Marconi et al. observed sporadic myoclonic jerks in most patients during the 1020 minutes following absorption of levodopa. Methylsergide, a serotoninspecific antagonist, has been reported to improve levodopainduced myoclonus, without worsening levodopainduced dyskinesias .
S.A. Gunzler, D.E. Riley, in, 2014
Pathophysiology Of Parkinsonian And Non
It is assumed that tremor networks within the brain are responsible for the different tremors. These circuits are not yet precisely known. Some nodes seem to play an important role. Ventral intermediate nucleus of the thalamus is the relay site in cerebellar outflow pathway where deep brain stimulation can improve almost all tremors indicating that cerebellum and its outflow pathway may involve in tremor genesis .
Emerging neuroimaging evidence showed that both the basal ganglia and the cerebellum are involved in Parkinsonian tremor . It was reported that PD with rest tremor had more grey matter volume decrease in the right quadrangular lobe and declive of the cerebellum and more iron accumulation in dentate nucleus, relative to those with akinetic-rigid type . Data from functional neuroimaging indicates that dopaminergic dysfunction in pallidum triggers the onset of tremor, whereas, the tremor amplitude is regulated within the cerebello-thalamo-cortical circuit .
You May Like: Parkinson’s Foundation San Diego
Parkinsons Tremors Vs Essential Tremors
Because they can be similar to Parkinsons tremors, essential tremors are often confused as symptoms of the disease. Just as with Parkinsons, essential tremor can cause uncontrollable rhythmic shaking in different parts of the body.
Up to 10 million people are affected by this common nervous system disorder. While genetics and environment likely play a role in essential tremor, the cause is unknown, according to the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
Essential tremors in the hands or arms can be distinct from Parkinsons because they typically happen when the hands are in use.
The essential tremor can get really bad when youre using your limb when drinking or eating soup, for example, says Gilbert. The Parkinsons tremor is usually not as disabling whereas the essential tremor can be life-altering.
The shaking from an essential tremor typically improves when using both hands to bring a cup to the mouth but the same action can amplify the tremor in Parkinsons, according to Gilbert.
Dr. Beck points out that an essential tremor may be faster than a Parkinsons tremor, which tends to be milder. A difference can often be seen in a persons handwriting. Those with essential tremor tend to have more unsteady and wavy writing, whereas Parkinsons patients are more apt to display micrographia, or abnormally small handwriting.
They have low amplitude movement so their writing gets smaller and smaller to a point where it can be barely legible, he says.
In Vivo Dopaminergic And Serotonergic Imaging
Neurochemical correlates of Parkinson’s disease tremor. Correlation between age-normalized striatal I beta-CIT binding and UPDRS motor subscores for speech, facial expression, tremor , rigidity, bradykinesia, and posture and gait . Reprinted from Pirker , with permission from John Wiley and Sons. Correlation between 11C-WAY 100635 PET in the raphe and total UPDRS tremor score . Reprinted from Doder et al. , with permission from Wolters Kluwer. Correlation between pallidal FP-CIT binding and resting tremor severity , using within-patient difference scores . This procedure controls for non-specific differences between patients. Reprinted from Helmich et al. , with permission from John Wiley and Sons. These data show that tremor severity is correlated with dopamine depletion in the pallidum , but not the striatum , and also with serotonin depletion in the raphe .
You May Like: What Medications Should Parkinson’s Patients Avoid
How Does Essential Tremor Develop
Essential tremor symptoms often first appear in a persons 40s, when delicate movements such as threading a needle become difficult. But its usually not until people reach their 50s or 60s that the tremor becomes troublesome for example, making it difficult to use a fork, drink from a cup, or write a letter. Essential tremor progresses slowly. Though essential tremor may eventually affect the voice and head, many people find that their symptoms dont progress beyond mild hand and arm tremor. Tremors are usually absent during sleep.
We dont know the precise cause of essential tremor. Some experts believe that the problem lies in the cerebellum or its connections with the brainstem, which lies at the base of the brain. Essential tremor is a heritable condition. If you have essential tremor, your children will have a 50% chance of developing it as well.
How Can I Reduce Tremors
In the early stages of Parkinsons disease, some people can reduce tremors by pressing or rolling a ball, pen or other small object. Tremors can also increase during stressful situations, during which you should take some time to breath and relax.
Tremors are more difficult to control during the more advanced stages of the disease. Here are some ways to better manage your tremors if they interfere with daily activities:
- Write on a keyboard rather than by hand
- Use speech-to-text cell phone apps
- Drink with a straw
- Use heavier utensils. If this does not help, you can purchase electronic utensils designed to counter your tremors
- Purchase clothing and shoes that are easy to put on
Also Check: Natural Herbal Gardens Parkinson’s Herbal Formula
Clinical Presentation And Treatment
The classic parkinsonian tremor is an asymmetrical resting tremor. The tremor reemerges after 2 or more seconds of a new posture. PT can affect the upper and lower limbs, and sometimes the jaw, chin, and lips. PD patients can also have a bilateral postural/action tremor. PT is usually less responsive to levodopa compared to the other parkinsonian symptoms. Dopamine agonists and selective inhibitors of monoamine oxidase B may improve tremor. The three main targets for tremor in DBS are the Vim, GPi, and subthalamic nucleus .
Martin Niethammer, David Eidelberg, in, 2019