Are There Medicines To Treat Dlb
Though there is no cure for DLB yet, there are medications that help manage the symptoms. These medications are called cholinesterase inhibitors, and they can help if a person with DLB is having memory problems. Some examples of these medicines are donepezil, rivastigmine and galantamine. If a person with DLB has movement symptoms they may be treated with medications used for Parkinsons disease, such as levodopa. Sleep problems may be managed by sleep medications including melatonin.
Because people with DLB are usually very sensitive to medications, any new medication, even one that is not being used for the brain, needs to be reviewed with the persons provider to avoid potential contraindication.
Lifespan In Parkinsons Nearly Identical To General Population
A new study finds that, overall, lifespan for those living with Parkinsons disease is nearly identical to those in the general population. The study looked at a group of diseases called synucleinopathies, including Parkinsons. The results appear in the May 15 online edition of JAMA Neurology.
Lewy bodies clumps of alpha-synuclein protein that accumulate in certain brain cells are the hallmark of PD. The clumps also occur in less common diseases such as multiple system atrophy , dementia with Lewy bodies , and PD dementia in which symptoms can be similar to those of typical Parkinsons.
Researchers led by Rodolfo Savica, M.D., Ph.D., at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, MN, compared lifespan and cause of death among people with synucleinopathies compared to the general population. They examined the medical records of all 461 people diagnosed with synucleinopathies in Olmsted County, MN, between 1991 and 2010. The scientists also analyzed records from individuals closely matched for age and sex who did not have these diagnoses.
Results
What Does It Mean?
Overall, the study reminds us that people with Parkinsons can live many years with the disease. With that in mind, people living with these diseases, their care partners and their families can take steps to plan for their health care and make important financial decisions.
Reference
Dont Miss: Stabilizing Spoon For Parkinsons
Common Symptoms Of Lewy Body Dementia
The disease of Lewy Body Dementia affects cognitive response, changes physical and sleep pattern along with changing behavioral features. Some people may start developing the disorder in movement in the initial stage that further leads to dementia. This is often termed as Parkinsons disease dementia.
Another group of people may start developing cognitive disorder with two or more distinctive features of dementia. There are very few people that come up with neuropsychiatric symptoms. These include hallucinations, behavioral problems, and complex mental activities.
Generic symptoms of Lewy Body Dementia include:
- Impaired thinking like loss of execution, planning, processing and/or ability to understand visual information
- Fluctuation in alertness, attention, and cognition
- Sudden tremors, stiffness, and difficulty in walking
- Changes in bodily functions like blood pressure, temperature regulation bowel and bladder function.
Don’t Miss: Holistic Chiropractic And Parkinson’s
Is Dementia A Symptom Of Both
One of the biggest similarities between PD and LBD is dementia. Some studies have found that approximately 78 percent of PD patients will eventually develop dementia.4 More specifically, almost half of Parkinsons patients will develop a certain type of dementia called Parkinsons Dementia, usually 10-15 years after their initial PD diagnosis.3 People with Parkinsons Dementia commonly experience poor memory and concentration, slowed thinking, confusion, depression, emotional changes, delusions, and visual hallucinations.
Parkinsons dementia is different than LBD, mainly in which symptoms occur first . Patients with Parkinsons Dementia will first show Parkinsons motor symptoms, followed by dementia many years after diagnosis. Conversely, LBD patients will first show dementia symptoms and may show motor symptoms later.3
Dementia With Lewy Bodies And Parkinson Disease Dementia
, MD, PhD, Department of Neurology, University of Mississippi Medical Center
Dementia with Lewy bodiesParkinson disease dementia
Dementia is chronic, global, usually irreversible deterioration of cognition.
Dementia with Lewy bodies is the 3rd most common dementia. Age of onset is typically > 60.
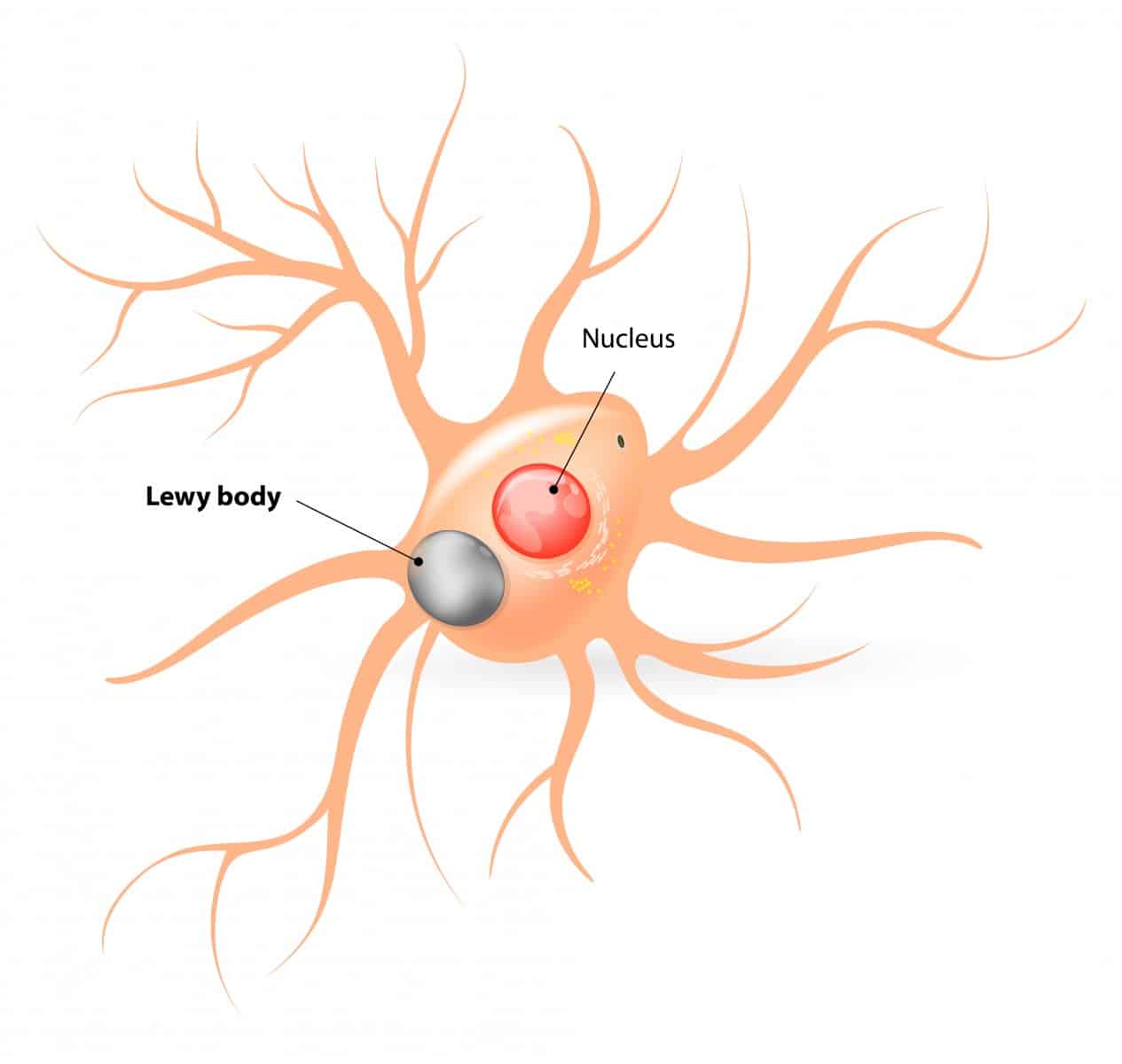
Lewy bodies are spherical, eosinophilic, neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions composed of aggregates of alpha-synuclein, a synaptic protein. They occur in the cortex of some patients who have dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurotransmitter levels and neuronal pathways between the striatum and the neocortex are abnormal.
Lewy bodies also occur in the substantia nigra of patients with Parkinson disease Parkinson Disease Parkinson disease is a slowly progressive, degenerative disorder characterized by resting tremor, stiffness , slow and decreased movement , and eventually gait and/or… read more , and dementia may develop late in the disease. About 40% of patients with Parkinson disease develop Parkinson disease dementia, usually after age 70 and about 10 to 15 years after Parkinson disease has been diagnosed.
Both dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson disease dementia have a progressive course with a poor prognosis.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease Non Motor Symptoms
What Is Vascular Dementia
Vascular dementia is the second most common type of dementia in the UK after Alzheimers disease. It occurs when the brain is damaged due to a lack of blood flow.
Sometimes people have both vascular dementia and Alzheimers, giving them a diagnosis of mixed dementia.
If the vascular system within the brain becomes damaged so that the blood vessels leak or become blocked then blood cannot reach the brain cells and they will eventually die.
This death of brain cells can cause problems with memory, thinking or reasoning, and when these cognitive problems are bad enough to impact on daily life, it is known as vascular dementia.
Dementia symptoms specific to vascular dementia include stroke-like symptoms, suchas as muscle weakness, movement and thinking problems and mood changes, such as depression.
There are several different types of vascular dementia, due to the varying levels of damage on the affected part of the brain.
They include stroke-related dementia, single-infarct and multi-infarct dementia and subcortical vascular dementia.
Parkinson’s Disease Dementia And Dementia With Lewy Bodies
The key pathological hallmark found in brains of Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s disease dementia patients are abnormal microscopic deposits composed of -synuclein. This protein is found widely in the brain and its normal function is not yet well understood. The deposits are called “Lewy bodies”. Lewy bodies are also found in several other neurodegenerative brain disorders, including dementia with Lewy bodies . Evidence suggests that Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s disease dementia, and dementia with Lewy bodies, may be linked to the same underlying abnormalities in caused by the deposition of -synuclein.
Also Check: Is Dementia And Parkinson’s The Same
How Is Lbd Different From Parkinsons Or Alzheimers
These diseases are similar in a lot of ways. But there are some key differences in the symptoms that affect people with LBD and when those symptoms happen.
LBD may not cause short-term memory loss like Alzheimerâs. People with both conditions have trouble with thinking, alertness, and paying attention. But in LBD, those problems come and go. The disease can also cause hallucinations, often in the first few years someone has LBD. People with Alzheimerâs usually donât have hallucinations until the later stages.
People with LBD also often act out their dreams and make violent movements when theyâre asleep. Itâs called REM sleep behavior disorder. Sometimes, itâs the first sign that someone has LBD.
LBD and Parkinsonâs disease both cause movement problems, like stiff muscles and tremors. But most people with Parkinsonâs donât have problems with their thinking and memory until the very later stages of their disease. Sometimes, they donât have it at all. In the type of LBD known as Parkinsonâs disease with dementia, these problems begin much sooner.
People with LBD also need different drugs for their condition than the ones that treat Parkinsonâs or Alzheimerâs.
Dont Miss: Que Es El Mal De Parkinson
How Is Lewy Body Disease Treated
There is no cure for Lewy body disease, but a doctor may treat the symptoms with:
- Alzheimers disease medications to reduce hallucinations and behavioural problems
- Parkinsons disease medications to improve rigid muscles and slow movement
- antidepressants
- sleep medicines
Some medicines, such as antipsychotics, can make symptoms worse and may be dangerous. There are, however, other ways of dealing with symptoms, including:
- learning to manage a persons behaviour
- learning how to calm the person down
- changing their environment to help them function
- creating daily routines
- using therapies, such as physiotherapy, occupational therapy and speech and language therapy
- providing cognitive stimulation
People with Lewy body disease usually need help at home and eventually care in a nursing home. The disease progresses differently in different people. After they develop symptoms, people live on average for another 6 to 12 years, although some live much longer.
Recommended Reading: Best Diet For Parkinson’s Patients
Relationship With Alzheimers And Parkinsons Dementias
Lewy bodies not only appear in dementia before us, but are also present in Parkinsons disease, multiple systemic atrophy, and Alzheimers disease in the latter case, they are found specifically in the CA2-3 region of the hippocampus, the fundamental structure of memory consolidation.
In addition to Lewy bodies we can find amyloid plaques, One of the typical signs of Alzheimers dementia and dopamine and acetylcholine neurotransmitter deficiencies, as in Parkinsons disease. This is why Lewy disease is often referred to as a midpoint between the other two, etiologically and symptomatically.
Unlike what happens in Alzheimers disease, in Lewy body dementia no atrophy is observed in the cortex of the middle part of the temporal lobes during the early stages of the disease. This fact explains some of the symptomatic differences between the two dementias, especially the evolution of memory problems.
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
The most prominent signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease occur when nerve cells in the basal ganglia, an area of the brain that controls movement, become impaired and/or die. Normally, these nerve cells, or neurons, produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems associated with the disease. Scientists still do not know what causes the neurons to die.
People with Parkinsons disease also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinsons, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinsons disease contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons andLewy body dementia.
You May Like: Best Antidepressant For Parkinson’s Disease
Tests For Dementia With Lewy Bodies
There’s no single test for dementia with Lewy bodies.
The following may be needed to make a diagnosis:
- an assessment of symptoms for example, whether there are typical symptoms of dementia with Lewy bodies
- an assessment of mental abilities this will usually involve a number of tasks and questions
- blood tests to rule out conditions with similar symptoms
- brain scans, such as an MRI scan, CT scan or a SPECT scan these can detect signs of dementia or other problems with the brain
Cognitive Symptoms Of Lewy Body Dementia
LBD causes changes in thinking abilities. These changes may include:
- Visual hallucinations, or seeing things that are not present. Visual hallucinations occur in up to 80 percent of people with LBD, often early on. Nonvisual hallucinations, such as hearing or smelling things that are not present, are less common than visual ones but may also occur.
- Unpredictable changes in concentration, attention, alertness, and wakefulness from day to day and sometimes throughout the day. Ideas may be disorganized, unclear, or illogical. These kinds of changes are common in LBD and may help distinguish it from Alzheimer’s disease.
- Severe loss of thinking abilities that interfere with daily activities. Unlike in Alzheimer’s dementia, memory problems may not be evident at first but often arise as LBD progresses. Other changes related to thinking may include poor judgment, confusion about time and place, and difficulty with language and numbers.
Recommended Reading: Experimental Drugs For Parkinson’s Disease
Find Time To Care For Yourself
As a caregiver, it is critical for you to take care of to maintain your own health and well-being. You may be at increased risk for poor sleep, depression, or illness as a result of your responsibilities. Watch for signs of physical or emotional fatigue such as irritability, withdrawal from friends and family, and changes in appetite or weight.
All caregivers need time away from caregiving responsibilities to maintain their well-being. Learn to accept help when it’s offered, and learn to ask family and friends for support. One option is professional respite care, which can be obtained through home care agencies and adult day programs. Similarly, friends or family can come to the home or take the person with LBD on an outing to give you a break.
Medications For Other Symptoms Of Dementia
People with LBD may often experience a sleep disorder called rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. This can sometimes be treated with sedatives like clonazepam or with melatonin . Other more severe symptoms of LBD including fluctuating levels of alertness , hallucinations, agitation, severe confusion, and delirium can be challenging to treat. Doctors must first rule out underlying causes like infection or other medications that can be triggering these symptoms. If unable to find a treatable cause, doctors may use a low dose of the atypical antipsychotic medication quetiapine to treat these symptoms. However, people with LBD must not be given typical antipsychotics or high-potency atypical antipsychotics , as people with LBD are very sensitive to these medications and may develop neuroleptic malignant syndrome if they take them. This is a life-threatening condition that causes fever, muscle stiffness, and racing heart, and can lead to heart and kidney failure. Talk with your doctor about medication options.
Read Also: Apda Parkinsons Disease Handbook
Also Check: How To Test For Parkinson’s Symptoms
Parkinsons Disease: Causes Symptoms And Treatments
Parkinsons disease is a brain disorder that causes unintended or uncontrollable movements, such as shaking, stiffness, and difficulty with balance and coordination.
Symptoms usually begin gradually and worsen over time. As the disease progresses, people may have difficulty walking and talking. They may also have mental and behavioral changes, sleep problems, depression, memory difficulties, and fatigue.
While virtually anyone could be at risk for developing Parkinsons, some research studies suggest this disease affects more men than women. Its unclear why, but studies are underway to understand factors that may increase a persons risk. One clear risk is age: Although most people with Parkinsons first develop the disease after age 60, about 5% to 10% experience onset before the age of 50. Early-onset forms of Parkinsons are often, but not always, inherited, and some forms have been linked to specific gene mutations.
Diagnosis Of Lewy Body Dementia
No single test can be used to definitively diagnose Lewy Body Dementia. Currently, Lewy bodies can only be identified through autopsy. Therefore, the process of diagnosis is similar to that of diagnosing Alzheimers Disease and is designed to rule out other possible causes of a persons symptoms.
A thorough diagnostic evaluation will include physical and neurological examinations , patient and family interviews , and psychological/psychiatric and neuropsychological testing. Click here to return to our previous in-depth discussion of each of these components of a diagnostic workup. In addition, brain imaging scans may be performed.
The following tests may be used in a psychological/psychiatric evaluation:
Read Also: Does Susan Collins Have Parkinson Disease
Recommended Reading: What Are Parkinson’s Tremors Like
Lewy Body Dementia: A Common Yet Underdiagnosed Dementia
While its not a household word yet, Lewy body dementia is not a rare disease. It affects an estimated 1.4 million individuals and their families in the United States. Because LBD symptoms can closely resemble other more commonly known disorders like Alzheimers disease and Parkinsons, it is often underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed. In fact, many doctors or other medical professionals still are not familiar with LBD.
What Are The Symptoms Of Lewy Body Dementia
Lewy body dementia symptoms may resemble those of other neurological disorders, like Alzheimers disease and Parkinsons disease. Symptoms fluctuate over time and vary from person to person.
There are several possible symptoms of LBD, which can be grouped into the following categories:
- Movement issues.
- Smaller handwriting than whats normal for the person.
Cognitive symptoms of Lewy body dementia
Fluctuating cognitive function is a relatively specific feature of Lewy body dementia. A person with LBD may experience periods of being alert and coherent in between periods of being confused and unresponsive to questions. This can change from day to day or within the same day.
Other cognitive symptoms include a decline in:
- Planning abilities.
- Problem-solving skills.
- Ability to focus.
- Understanding information in visual form.
Visual hallucinations, or seeing things that arent there occur in up to 80% of people with LBD and often early on in the condition. Other types of hallucinations, such as hearing or smelling things that arent there, are less common than visual ones but may also occur.
Visuospatial difficulties, including decreased depth perception, trouble recognizing familiar objects and impaired hand-eye coordination, are also common in people with LBD.
Sleeping problems in Lewy body dementia
Other sleep issues associated with LBD include:
- Excessive daytime drowsiness.
Dysautonomia in Lewy body dementia
- Changes in body temperature.
Don’t Miss: Can Head Injury Cause Parkinson’s
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Lewy Body Dementia
The most common symptoms of LBD include changes in thinking abilities, movement, sleep, and behavior. The degree of symptoms can vary widely and people with LBD may not have every symptom. Common symptoms include:
- Trouble with attention, planning, multitasking, problem-solving, and reasoning. Memory problems are also common but may not be noticeable early on.
- Problems with visual and spatial abilities, such as judging distance and depth or misidentifying objects.
- Unpredictable changes in concentration, attention, alertness, and wakefulness.
- Visual hallucinations, which occur in up to 80% of people with LBD, often early on.
- Movement changes, such as tremor or muscle stiffness, known as parkinsonism.
- Sleep disorders, including rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder in which a person seems to act out dreams while asleep, excessive sleep or lack of sleep, and restless leg syndrome.
- Depression, lack of interest, anxiety, ideas not based in reality, and other changes in mental health.
- Sensitivity to heat and cold, dizziness, poor sense of smell, and other changes in automatic functions of the body.
Individuals with mild symptoms can often function close to normally. As the disease progresses and thinking and movement abilities decline, people with LBD will need more help and may depend on caregivers full time.