What Is Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s Disease is a degenerative nervous system condition that affects one’s movement. Symptoms often start quite gradually, with minor issues such as small tremors within the extremities . Currently, there is no cure for Parkinson’s Disease but certain medications do have the capacity to help manage symptoms. Some doctors may also recommend surgery to address certain symptoms, which involves regulating certain areas of the brain.
The Promise And Potential Of Stem Cells In Parkinsons Disease
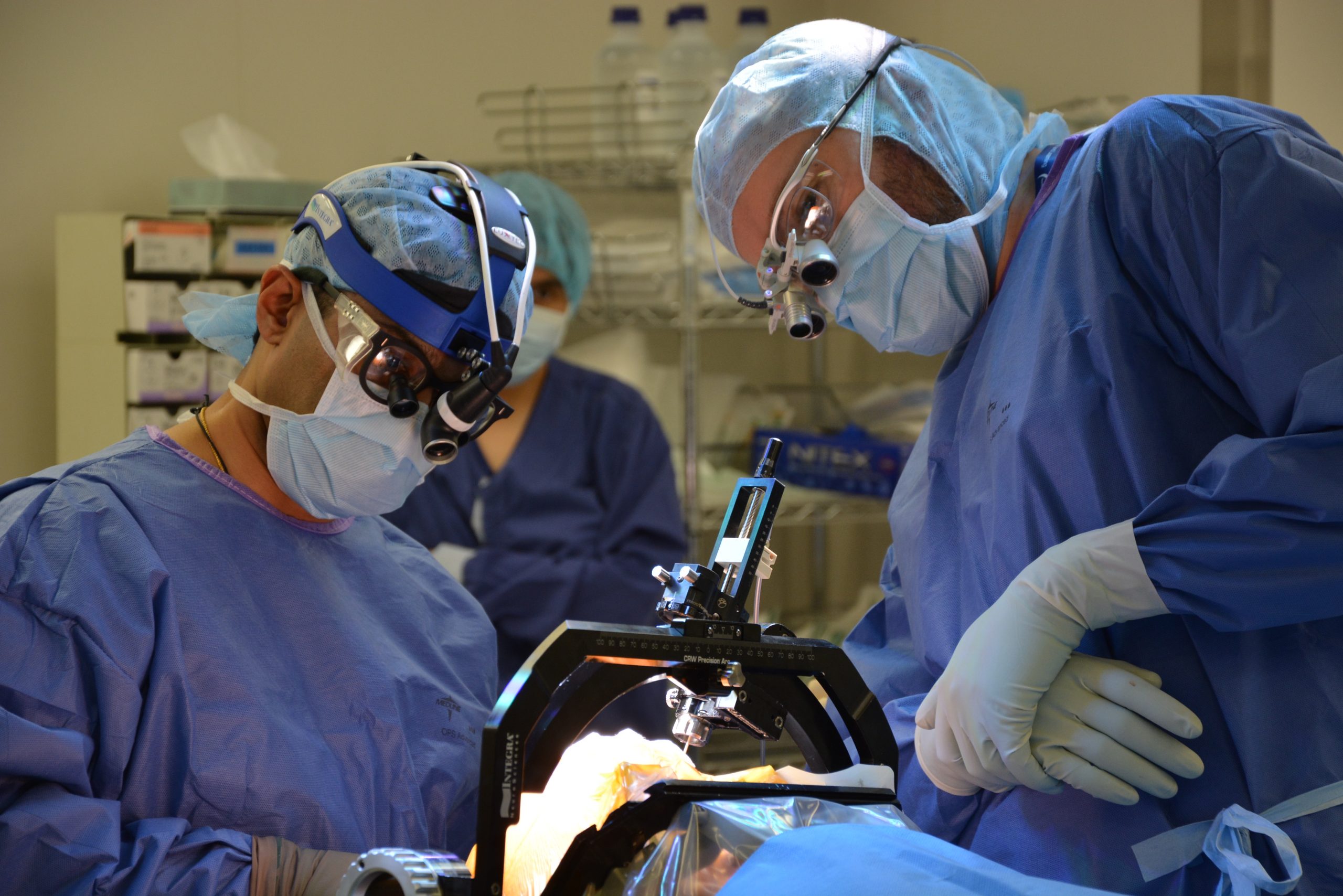
Neurosurgeon Viviane Tabar is co-leading a trial to inject stem cells into the brains of people with Parkinsons disease to restore dopamine levels.Credit: Courtesy of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
Neurosurgeon Viviane Tabar has scrubbed in. In front of her is the first participant in a clinical trial to determine whether stem cells can be safely injected into the brains of people with Parkinsons disease. The cells had been frozen, but they are now thawed and sitting on ice, waiting for their moment.
Tabar, a physician-scientist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, makes an incision in her patients scalp and drills a small hole in their skull. She then uses a brain scan almost like a GPS, she says, to guide her to the putamen a part of the brain in which levels of the neurotransmitter dopamine are unusually low in people with Parkinsons. Once she has confirmed that shes reached the right spot, she injects the stem cells, then repeats the process on the other side of the brain. She hopes these cells will take hold and eventually begin to produce dopamine where otherwise there would be little or none. The surgery itself is minor enough that the patient can go home the next day.
Well Be Watching Progress Closely
Claire Bale, Head of Research Communications at Parkinsons UK, said:
“We’re encouraged to hear that approval has been given to do the first ever trial for stem cell treatment in people with Parkinson’s.
“Stem cells carry real hope as a future treatment for the 127,000 people living with the condition in the UK. Parkinson’s UK has invested more than £3 million in cutting edge stem cell research to help develop new and better treatments for Parkinson’s, faster.
“With all clinical trials, ensuring that the treatment is safe and effective is paramount and along with the international research community we will be watching the progress of the trial very closely.
“If successful this could be the beginning to further, much larger studies with stem cells taking us closer to a new potential treatment for Parkinsons.”
Don’t Miss: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinson’s
Phase 1 Trial Of Stem Cells In Treating Bradykinesia To Open In Us
The participants will be followed for a year by IMAC doctors and physical therapists. The trial enrolled a total 15 patients five in each dosing group ages 55 or older, who began experiencing bradykinesia for at least three months before enrollment. Participants were allowed to continue treatment with levodopa or other standard treatment.
The trial is underway at three of IMACs U.S. clinical centers: Chesterfield, Missouri Paducah, Kentucky and Brentwood, Tennessee.
Bradykinesia is one of the early signs of Parkinsons disease. It is characterized by slow movements, delayed reaction times, and decreased amplitude of movements that is, smaller movements.
Although the mechanisms underlying bradykinesia are not completely understood, it is generally accepted that inflammation is one of its key drivers.
Stem cells are characterized by their ability to divide indefinitely while giving rise to various cell types, prompting its interest as a regenerative medicine for disorders like Parkinsons.
MSCs are a subtype of stem cells that are found across different tissues, but at high rates in the umbilical cord. Other tissues include the bone marrow and fat. They have anti-inflammatory properties, supporting their potential to treat bradykinesia by easing inflammation.
Ricardo Knight, MD, the medical director of the Mike Ditka IMAC Regeneration Center in Arlington Heights, Illinois, is the trials lead investigator.
Cell Assessment Of Differentiated Da Neurons
Understanding the key type of DA neurons required to achieve downstream restoration of PD pathology is essential. The mesotelencephalic DA system in the midbrain contains two main groups: the A9 neuronal clusters of the nigrostriatal DA pathway located in the zona compacta, the substantia nigra involved in the control of posture, and the A10 neurons located in the ventromedial mesencephalic tegmentum that regulates the locomotor activity and emotional behavior . Dysfunction of the nigrostriatal system has been linked to Parkinsonism and later to schizophrenia, drug addiction, and depression . Differences between the two DA cell populations have been observed in neurochemistry and in spontaneous neuronal firing . More importantly, A9 neurons display significantly enhanced levels of neuromelanin pigmentation as compared to other dopamine-producing neurons . This could account for the association of early loss of A9 DA neurons in Parkinsons disease with increased vulnerability upon disease progression with the relative preservation of A10 DA neurons .
Generally, stem cells are differentiated into specific nigra A9 DA neurons in large quantities prior to PD transplantation. This step has been thoroughly reviewed by many articles such as in Fan et al. and, thus, will not be further discussed here. However, we focus on developments in technology in cell assessment of differentiated DA neurons.
You May Like: Judy Woodruff Parkinson’s
Giving Stem Cells Outside Of The Brain
There are a number of trials looking that the potential of using different types of adult stem cells for Parkinsons happening all over the world. One example is a phase 1/2 trial based in Texas that started in 2015. The study is using stem cells collected from bone marrow, and aims to recruit 20 participants to see if injection of these cells into the blood is safe. It will also collect results on if this type of therapy can improve movement symptoms of Parkinsons, among other measures.
Another study worth note, although not for its scientific merit, is taking a slightly different tack to getting stem cell into the body. In a rather ambitious phase 2/3 trial happening in China, researchers will attempt to give neural stem cells through the nasal track of 12 participants to see if it can cause Parkinsons to go into remission. Personally I dont hold out much hope for the success of this particular trial.
Potential of this type of therapy: Stem cells produce a range of protective factors that could help to protect brain cells and slow the progression of Parkinsons. The pros of this technique are that various types of adult stem cells such as those from bone marrow are easily accessible and the therapy doesnt involve brain surgery so would be less invasive than other therapies in this post. The cons are that these cells will be unable to get into the brain, and the lack of proximity could hamper their effectiveness.
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s DIsease can include a variety of symptoms that vary in severity and type amongst the affected population. Early signs of the condition can sometimes go unnoticed but as the disease progresses one can expect these symptoms:
- Difficulty speaking
- Difficulty writing
- Loss of automatic movements
- Slowed overall movement
- Muscle stiffness
Read Also: Parkinson’s Bike Therapy
We Take A Look At The Science Behind Trials That Aim To Slow And Reverse Parkinsons By Using Stem Cells Or Other Cell Therapies
Parkinsons is caused by the loss of brain cells that produce the chemical dopamine. Research over the last few decades has focused on finding ways to slow or stop this loss to slow the progression of Parkinsons. Indeed, there are ongoing trials of promising therapies that aim to protect and nurture remaining dopamine-producing cells. But with half these cells lost or damaged by the point of diagnosis, a cure for Parkinsons may also require a therapy that can reverse the damage that has already been done this is where cell-based therapies that aim to replace those cells come into their own.
Transplanting Stem Cells Into The Brain
The first trial of this kind came early in 2016 when California-based company, the International Stem Cell Corporation , announced their phase I trial that aims to inject a type of neural stem cells into the brains of 12 people with Parkinsons.
The 12 month trial is taking place in Melbourne, Australia, and is currently recruiting people with moderate to severe Parkinsons. During the trial, doctors will transplant brain stem cells grown from human stem cells, into participants brains. However these cells are not the same type of cell that is lost in Parkinsons and when the trial was first announced, world-leading scientific experts, including Parkinsons UK researcher Professor Roger Barker from the University of Cambridge, raised questions about the approach being used in an article in the Journal of Parkinsons Disease.
Since this first trial was announced, other transplant trials using neural stem cells have reportedly begun, including a phase I/II trial in China that is currently recruiting 50 participants.
These early-stage clinical trials will focus on the safety of the therapy, so we may have to wait for further trials before we know if transplanting neural stem cells can help in Parkinsons.
Also Check: Prayer For Parkinson’s Disease
A Patient Disease Model
HSCI Principal Faculty member and Director of the Neuroregeneration Research Institute at McLean Hospital Ole Isacson, MD, with funding from HSCI, the Harvard Miller Consortium for the Development of Nervous System Therapies, and the National Institutes of Health, has generated brain cells that produce dopamine, collected from the skin cells of patients with Parkinsons.
Isacson orchestrated the transformation by biologically reprogramming the mature skin cells into induced pluripotent stem cells, and then encouraging the stem cells to become dopaminergic neurons. Neurons were also made from skin cells collected from individuals with genetic mutations associated with high risk for Parkinsons disease.
The creation of this in vitro disease model provides a powerful platform for studying Parkinsons outside of the body. In the journal Science Translational Medicine, Isacson and his team reported that many of the mutations implicated in Parkinsons affect the function of the mitochondria, the cellular organelle responsible for energy production. In collaboration with HSCI Director of Translational Medicine Lee Rubin, PhD, Isacsons lab started to identify compounds that could eliminate disease symptoms in cell lines derived from people carrying Parkinsons mutations.
The Many Types Of Stem Cells
While the regenerative power of stem cells is at the cutting-edge of research, people have known that our tissues and organs have the capacity to regrow for thousands of years. The regenerative ability of the liver even features in Greek mythology. The myth goes that when Prometheus defied the gods they sentenced him to eternal torment, each day a vulture would eat his liver only for it to regrow as fast as it was damaged.
We now know that the ability of our tissues to regrow is due to the presence of stem cells. But its not just when cells get damaged that stem cells are activated, there are types of stem cells that are active throughout our lives.
Whatever your age, your body is many years younger. This is because almost all of our organs and tissues contain adult stem cells that can turn into many different types of cells and help our body to replace old or damaged tissues. But adult stem cells can only develop into a limited number of cell types. For example, bone marrow stem cells naturally develop into blood cells but not brain cells.
Adult stem cells were first discovered in the 1960s, and we now know they can be found all over the body, including in our brains. Some forms of adult stem cells already provide vital treatments. For instance, bone marrow contains adult stem cells that make all our different blood cells which means that bone marrow transplants from healthy donors can be used to treat blood disorders like leukaemia.
You May Like: Sam Waterston Parkinson’s
Gmp Cryopreservation Of Cells
The generation of good manufacturing practice -compliant, deliverable midbrain DA progenitors/neurons optimized for cell-based therapy for PD is a major challenge. Currently, a diverse collection of clinical-grade hESC lines are available as starting material to generate GMP-compliant mDA progenitors/neurons. In fact, GMP compliant differentiation protocols and reagents have been successfully applied to generate GMP mDA neurons .
Does It Work Efficacy Of Commercial Stem Cell Clinics
Commercial clinics do not as a rule publish their results in peer-reviewed journals to demonstrate to the scientific community that the treatments work. Rather, they usually rely on anecdotes from patients as proof of efficacy. Some clinics are tracking their results by measuring variables such as quality of life before or after the procedure. However, without comparing the patients to a similar group who does not receive the treatment, it is hard to know whether any improvement is due to placebo effect or to the treatment itself.
You May Like: Pfnca Wellness Programs
Why Is Stem Cells Treatment Better Than Conventional Treatment Approach For Treating Parkinsons
Conventional treatment approaches highly invasive associated with many side effects. Although stem cells can naturally heal the body from damage and regenerate lost neurons to improve impaired functions. Additionally, since the bodys own cells are used for repairing, the entire treatment is minimally invasive without any side effects.
Recommended Reading: On Off Phenomenon
Stem Cell Research And Parkinsons
The aim of stem cell research in Parkinsons is to understand how nerve cells develop, why some die and how healthy cells can be used to replace damaged brain cells. With this knowledge it may be possible to replace the damaged cells in the brain by introducing healthy dopamine-producing cells generated from stem cells grown in the laboratory. Healthy dopamine-producing cells derived from stem cells could also be useful to researchers in testing new treatments.
Researchers are particularly interested in embryonic stem cells as they have the potential to develop into all types of cells in the body, including the brain. More research is needed in order to understand the way these cells work to ensure that replication can be controlled and a safe treatment developed.
Read Also: Parkinson Bicycle Cleveland Clinic
Don’t Miss: Diseases Similar To Parkinsons
Etiology And Risk Factors
Parkinsonian symptoms can arise from either the neuropathologic condition of PD or other forms of parkinsonism. For neuropathologic PD, about 90% of cases are sporadic, with no clear etiology an additional 10% have a genetic origin, and at least 11 different linkages with 6 gene mutations have been identified Genetic forms of PD are seen more frequently in young-onset PD. A combination of environmental factors or toxins, genetic susceptibility, and the aging process may account for many sporadic cases Secondary forms of parkinsonism can be caused by medications, the sequelae of central nervous system infection, toxins, or vascular/metabolic disorders . The only proven risk factor for PD is advancing age . Other environmental or lifestyle risk factors associated with development of PD are rural living, exposure to pesticides and herbicides, well-water drinking, and working with solvents . However, none of these factors unequivocally has been demonstrated to cause iPD .
Figure 1: Etiology of Parkinsons Disease . View Figure 1
Recommended Reading: Sam Waterston Tremor
How Commercial Stem Cell Clinics Work
A typical treatment at one of these clinics involves removing fat cells from the abdomen , treating the cells in various ways in order to isolate mesenchymal stem cells or stromal cells from the removed tissue, and finally injecting these cells back into the body. The cells are re-introduced into the body in different locations depending on which disease is being targeted. Such treatments are performed for a fee, sometimes a large one, and are not covered by insurance.
Also Check: Parkinson Bicycle Cleveland Clinic
Clinical Trials For Stem Cell
Table 3. Summary of clinical studies in cell transplantation for PD.
Figure 1. Systematic analysis of various factors associated with clinical outcomes using positron emission tomography readings of Parkinsons disease patients with fetal ventral mesencephalic cell transplantation. Statistical comparison was performed on various parameters against fold change of PET readings pre- and post-transplantation. Age on onset: old vs. young PD patients. Disease stage in mild and severe conditions. Disease duration: long vs. short . Student t-test, *p< 0.05, ***p< 0.001.
Figure 2. Systematic analysis of various factors associated with clinical outcome in fVM cell transplantation in PD patients using UPDRS motor scores. Statistical comparison was performed on varying parameters against the Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale motor scores of pre- and post-transplantation. Age on onset: old vs. young PD patients. Disease stage in severe vs. mild condition. Disease duration: long vs. short . Two-way ANOVA, Sidaks multiple comparisons test, **p< 0.005, ***p< 0.001.
First Transplant Trial Of Lab Made Dopamine
Following successes in monkeys, researchers in Japan have announced a clinical trial to transplant dopamine-producing brain cells made in the lab from iPS cells will start in 2018.
We will eagerly be awaiting more information and the outcome of this and the other trials mentioned in this post and hope that it will contribute to more research in this area, and future opportunities for those in the UK to take part.
Potential of this type of therapy: Dopamine-producing brain cells are the type of cell lost in Parkinsons and transplanting them into the brain may be the best hope for repairing the damage and reversing the condition, making this study one of the most exciting ones to follow going forwards. Potential challenges to this approach are all about safety these techniques are still very new, so we dont know much about the long-term safety of lab-made cells.
Stem cells definitely hold huge potential for developing therapies for Parkinsons, but we still have a number of questions to answer and challenges to address before they will be a therapeutic option for people with the condition. We still dont know enough about if these transplant therapies will improve both motor and non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons, such as problems with thinking, memory, pain, and anxiety. We also need to know:
Also Check: Voice Amplifiers For Parkinson’s