What Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Each person with Parkinsons disease experiences symptoms in in their own unique way. Not everyone experiences all symptoms of Parkinsons disease. You may not experience symptoms in the same order as others. Some people may have mild symptoms others may have intense symptoms. How quickly symptoms worsen also varies from individual to individual and is difficult to impossible to predict at the outset.
In general, the disease progresses from early stage to mid-stage to mid-late-stage to advanced stage. This is what typically occurs during each of these stages:
Early stage
Early symptoms of Parkinsons disease are usually mild and typically occur slowly and do not interfere with daily activities. Sometimes early symptoms are not easy to detect or you may think early symptoms are simply normal signs of aging. You may have fatigue or a general sense of uneasiness. You may feel a slight tremor or have difficulty standing.
Often, a family member or friend notices some of the subtle signs before you do. They may notice things like body stiffness or lack of normal movement slow or small handwriting, lack of expression in your face, or difficulty getting out of a chair.
Mid stage
Mid-late stage
Standing and walking are becoming more difficult and may require assistance with a walker. You may need full time help to continue to live at home.
Advanced stage
Stooping Or Hunching Over
Are you not standing up as straight as you used to? If you or your family or friends notice that you seem to be stooping, leaning or slouching when you stand, it could be a sign of Parkinson’s disease .
What is normal?If you have pain from an injury or if you are sick, it might cause you to stand crookedly. Also, a problem with your bones can make you hunch over.
Treatment For Early Stage Parkinsons
Several recent research developments have brought new hope for treating symptoms of Parkinsons disease and developing therapies to potentially slow disease process.
Medications such as dopamine replacement therapy and dopamine-inhibitors, which mimic the effect of dopamine on the brain, are among the main medication treatments for primary symptoms of PD.
Also Check: Sam Waterston Tremor
Discuss With Your Physician
Non-motor symptoms can sometimes be difficult to recognize. Therefore, it is important to make your doctor aware of them.
One useful resource is the PD NMS Questionnaire. You can use this to record your symptoms and discuss them with your doctor.
Dr. Ron Postuma, whose research was funded by donations to the Parkinson Canada Research Program, has also developed tools to help people with Parkinsons and their physicians identify and manage non-motor symptoms.
Breathing Problems And Parkinsons Disease
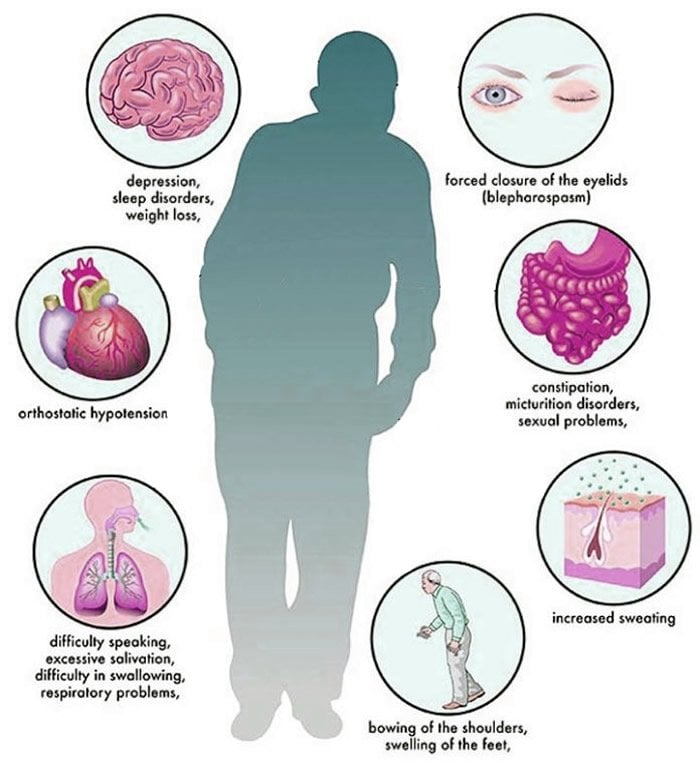
Usually, trouble breathing is not thought of as a symptom of PD. Those with PD who complain of this will typically have testing of their heart and lung function. This is necessary since, as we continue to emphasize, a person with PD can develop medical problems unrelated to PD and needs every new symptom evaluated like someone without PD. However, often the testing does not reveal a cardiac or pulmonary abnormality. Could difficulty breathing be a symptom of PD itself?
There are a number of ways in which difficulty breathing may be a symptom of PD:
Shortness of breath can be a wearing-OFF phenomenon
Some non-motor symptoms can fluctuate with brain dopamine levels, which means that they change as a function of time from the last levodopa dose. For some people, shortness of breath can be one of the non-motor symptoms that appears when medication levels are low. However, shortness of breath can be due to anxiety which can also be a wearing-OFF phenomenon. Sometimes it is not possible to determine whether the key symptom is anxiety or shortness of breath. Treatment involves changing medication dosing and timing so that OFF time is minimized. You can view this webinar which discusses the concept of wearing OFF and potential treatments.
Abnormal breathing can be a type of dyskinesia
Restrictive lung disease
Aspiration pneumonia
Sleep apnea
Don’t Miss: Cleveland Clinic Parkinson’s Bicycle Study 2017
Surgery For People With Parkinsons Disease
Deep brain stimulation surgery is an option to treat Parkinsons disease symptoms, but it is not suitable for everyone. There are strict criteria and guidelines on who can be a candidate for surgery, and this is something that only your doctor and you can decide. Surgery may be considered early or late in the progression of Parkinsons. When performing deep-brain stimulation surgery, the surgeon places an electrode in the part of the brain most effected by Parkinsons disease. Electrical impulses are introduced to the brain, which has the effect of normalising the brains electrical activity reducing the symptoms of Parkinsons disease. The electrical impulse is introduced using a pacemaker-like device called a stimulator. Thalamotomy and pallidotomy are operations where the surgeon makes an incision on part of the brain. These surgeries aim to alleviate some forms of tremor or unusual movement, but they are rarely performed now.
Hospice Eligibility Of End
Since Parkinsons disease is progressive, patients need hospice care. If your family member or any loved one has been diagnosed with Parkinsons disease, expect that there will be a decline in their motor abilities. They will need professional nursing care to attend to their needs because it will be harder for them to speak and express their struggles.
Here are the things you need to observe to determine if the patient already needs hospice care:
- Difficulty in breathing and oxygen supply is necessary
- Difficulty in walking where a wheelchair is already needed
- Hard to understand speech
- Difficulty in eating and drinking
- More complications occur, such as pneumonia, sepsis, pyelonephritis, decubitus ulcers, and other comorbidities
Recommended Reading: Parkinson Silverware
Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms Seen Years Before Diagnosis New Research Reveals
First of its kind UK study investigated risk factors and pre-diagnostic symptoms.
New research reveals early signs of Parkinson’s disease, that can be seen years before a diagnosis. The research, published in JAMA Neurology, is the first of its kind in the UK in analysing the neurodegenerative disorder in a largely diverse population in a bid to take a more in-depth look at how the disease affects all people.
Researchers found that neither ethnicity nor socio-economic status was linked to an increased or decreased risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. The study, conducted by a team at Queen Mary University of London, investigated both risk factors and pre-diagnostic symptoms.
The experts suggested that loss of hearing may be a part of the impairment in sensory processing that so often comes with the development of Parkinson’s disease. Sensory impairment manifests itself in different ways in different patients – through sight, hearing or even sense of smell, according to the researchers.
Read More: Elderly woman with dementia says ‘they’re kicking us out of Westbury Court’
Additionally, the study suggested new trends within the well known symptoms of Parkinson’s. Tremors – a common symptom of the disease – were found the show up as many as 10 years prior to diagnosis, becoming more frequent in the two years leading up to diagnosis.
Symptoms of Parkinson’s disease – Full list
According to the NHS, the three main symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are:
Incidence Of Parkinsons Disease
Its estimated that approximately four people per 1,000 in Australia have Parkinsons disease, with the incidence increasing to one in 100 over the age of 60. In Australia, there are approximately 80,000 people living with Parkinsons disease, with one in five of these people being diagnosed before the age of 50. In Victoria, more than 2,225 people are newly diagnosed with Parkinsons every year.
Also Check: Prayer For Parkinson’s Disease
Confusion With Essential Tremor
The tremor of Parkinsons disease is often confused with the tremor of a condition called Essential Tremor, or Benign Familial Tremor . Katherine Hepburn had Essential Tremor, and was originally misdiagnosed with Parkinsons. Ronald Reagan also had Essential Tremor. Both had a head tremor and a vocal tremor. In Essential Tremor, the hands are most commonly involved, followed by the head and then the voice. Essential Tremor can also cause the jaw to tremor, and it may be difficult to figure out if a jaw tremor is from Essential Tremor or Parkinsons. Unfortunately, some people may have both disorders. Some authorities believe that there is, in fact, an increased association between the two conditions, so that more people with Parkinsons disease have Essential Tremor than would be expected by chance alone, but this has not been established.
Signs Of Parkinsons Disease
In 1817, Dr. James Parkinson published An Essay on the Shaking Palsy describing non-motor, as well as, motor symptoms of the illness that bears his name. Parkinsons is not just a movement disorder, explained Dr. Shprecher. Constipation, impaired sense of smell, and dream enactment can occur years before motor symptoms of Parkinsons. The latter, caused by a condition called REM sleep behavior disorder, is a very strong risk factor for both Parkinsons and dementia . This has prompted us to join a consortium of centers studying REM sleep behavior disorder.
Recommended Reading: On And Off Phenomenon
Support For People With Parkinsons Disease
Early access to a multidisciplinary support team is important. These teams may include doctors, physiotherapists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, dietitians, social workers and specialist nurses. Members of the team assess the person with Parkinsons disease and identify potential difficulties and possible solutions.There are a limited number of multidisciplinary teams in Victoria that specialise in Parkinsons disease management. But generalist teams are becoming more aware of how to help people with Parkinsons disease.
How Is Parkinsons Disease Treated
There is no cure for Parkinsons disease. However, medications and other treatments can help relieve some of your symptoms. Exercise can help your Parkinsons symptoms significantly. In addition, physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech-language therapy can help with walking and balance problems, eating and swallowing challenges and speech problems. Surgery is an option for some patients.
Recommended Reading: Judy Woodruff Parkinson’s
Symptoms That Are Commonly Associated With Pd
These symptoms include sleep disorders, abnormalities in blood pressure, urinary problems, constipation, depression, and anxiety. Even though these symptoms are so commonly seen in PD, they are also commonly associated with other issues that have nothing to do with PD, so it is vital to keep an open mind about their cause. If any symptom is new or worsening, it could be an indication of a new medical problem. For example, urinary problems are extremely common in PD, but may be a sign of an enlarged prostate, which can be treated in an entirely different way.
Is Parkinsons Disease Inherited
Scientists have discovered gene mutations that are associated with Parkinsons disease.
There is some belief that some cases of early-onset Parkinsons disease disease starting before age 50 may be inherited. Scientists identified a gene mutation in people with Parkinsons disease whose brains contain Lewy bodies, which are clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to understand the function of this protein and its relationship to genetic mutations that are sometimes seen in Parkinsons disease and in people with a type of dementia called Lewy body dementia.
Several other gene mutations have been found to play a role in Parkinsons disease. Mutations in these genes cause abnormal cell functioning, which affects the nerve cells ability to release dopamine and causes nerve cell death. Researchers are still trying to discover what causes these genes to mutate in order to understand how gene mutations influence the development of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists think that about 10% to 15% of persons with Parkinsons disease may have a genetic mutation that predisposes them to development of the disease. There are also environmental factors involved that are not fully understood.
Read Also: What Foods Should Be Avoided When Taking Levodopa
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Managed
Your doctors will tailor your treatment based on your individual circumstances. You will manage your condition best if you have the support of a team, which may include a general practitioner, neurologist, physiotherapist, occupational therapist, psychologist, specialist nurse and dietitian.
While there is no cure for Parkinson’s disease, symptoms can be treated with a combination of the following.
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinsons disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinsons disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
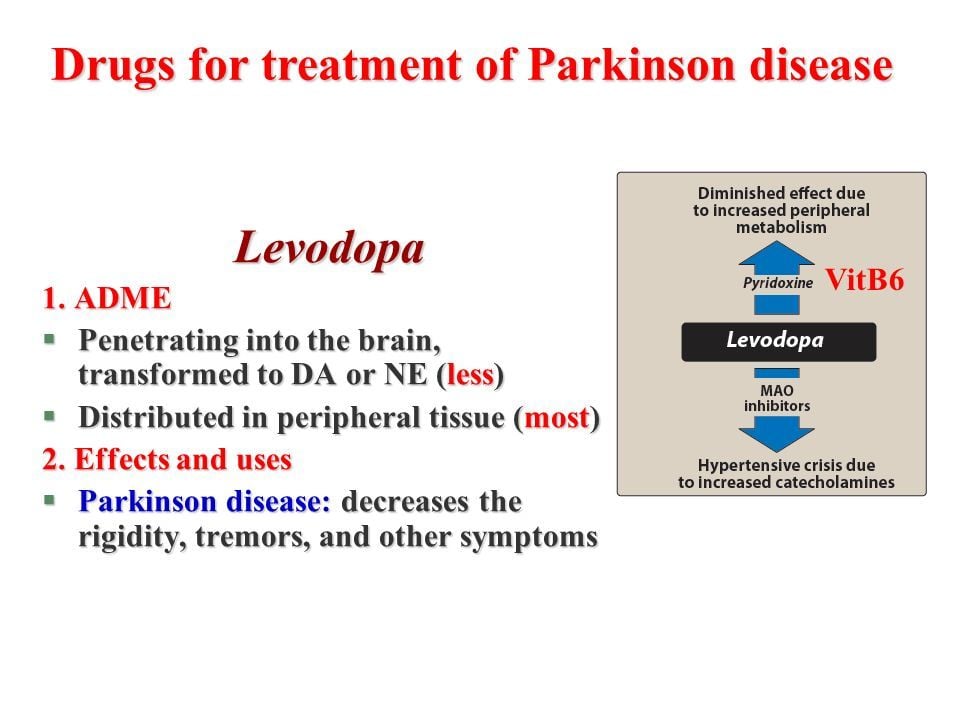
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinsons disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
Also Check: Parkinson’s Double Vision
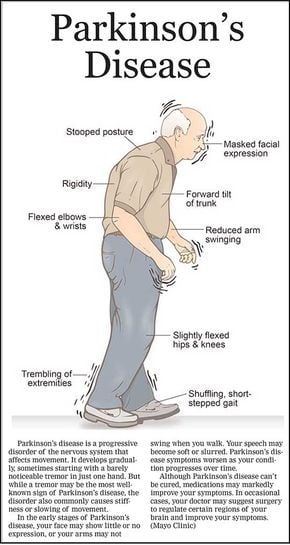
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a movement disorder that progresses slowly. Some people will first notice a sense of weakness, difficulty walking, and stiff muscles. Others may notice a tremor of the head or hands. Parkinson’s is a progressive disorder and the symptoms gradually worsen. The general symptoms of Parkinson’s disease include:
- Slowness of voluntary movements, especially in the initiation of such movements as walking or rolling over in bed
- Decreased facial expression, monotonous speech, and decreased eye blinking
- A shuffling gait with poor arm swing and stooped posture
- Unsteady balance difficulty rising from a sitting position
- Continuous “pill-rolling” motion of the thumb and forefinger
- Abnormal tone or stiffness in the trunk and extremities
- Swallowing problems in later stages
- Lightheadedness or fainting when standing
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a nervous system disease that affects your ability to control movement. The disease usually starts out slowly and worsens over time. If you have Parkinsons disease, you may shake, have muscle stiffness, and have trouble walking and maintaining your balance and coordination. As the disease worsens, you may have trouble talking, sleeping, have mental and memory problems, experience behavioral changes and have other symptoms.
You May Like: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinson’s
Environmental Factors And Exposures
Exposure to pesticides and a history of head injury have each been linked with PD, but the risks are modest. Never drinking caffeinated beverages is also associated with small increases in risk of developing PD.
Low concentrations of urate in the blood is associated with an increased risk of PD.
Drug-induced parkinsonism
Different medical drugs have been implicated in cases of parkinsonism. Drug-induced parkinsonism is normally reversible by stopping the offending agent. Drugs include:
What Causes Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons disease occurs when nerve cells in the basal ganglia, an area of the brain that controls movement, become impaired and/or die. Normally, these nerve cells, or neurons, produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems of Parkinson’s. Scientists still do not know what causes cells that produce dopamine to die.
People with Parkinson’s also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinson’s, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying-down position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinson’s contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons disease and Lewy body dementia.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Hallucinations Commercial
What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Most patients with Parkinsons disease can maintain a good quality of life with medications. However, as the disease worsens, medications may no longer be effective in some patients. In these patients, the effectiveness of medications becomes unpredictable reducing symptoms during on periods and no longer controlling symptoms during off periods, which usually occur when the medication is wearing off and just before the next dose is to be taken. Sometimes these variations can be managed with changes in medications. However, sometimes they cant. Based on the type and severity of your symptoms, the failure of adjustments in your medications, the decline in your quality of life and your overall health, your doctor may discuss some of the available surgical options.
Other Reasons For Cognitive Symptoms
Besides PD, there are other important causes of cognitive dysfunction to keep in mind. Medical illnesses such as thyroid disease or vitamin B12 deficiency can cause cognitive symptoms. Urinary tract infections or pneumonia can acutely cause confusion or hallucinations. In these settings, the cognitive symptoms are generally reversible after the infection or medical condition is treated. One should be aware that some medications for pain or bladder problems may cause sedation/sleepiness or confusion, and, thereby, impair cognitive function.
Also Check: Fitflop Shoes For Parkinson’s