Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinsons Disease
For people with severe motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease that are not adequately controlled by medication, a treatment called deep brain stimulation may offer some relief.
Deep brain stimulation requires the surgical placement of a small conductor called an electrode in the brain. The electrode delivers electrical stimulation that blocks the nerve signals that cause tremors.
Specialists at NYU Langones Center for Neuromodulation perform more than 100 deep brain stimulation procedures each year. Our neurologists, neurosurgeons, and psychiatrists provide a thorough evaluation to ensure youre a good candidate for the procedure.
Sites Of Deep Brain Stimulation And Symptom Control
While both subthalamic nucleus and globus pallidus internus stimulation help improve the motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease, studies have found a few differences.
DBS of the third target, the ventral intermediate nucleus, can be beneficial for controlling tremors but does not work as well at addressing the other motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
In a Canadian study, targeting the subthalamic nucleus allowed people to reduce the doses of their medications to a greater degree, while targeting the globus pallidus internus was more effective for abnormal movements .
In another study, STN deep brain stimulation also led to a greater reduction in medication dosages. However, GPi stimulation resulted in greater improvement in quality of life, and also appeared to help with the fluency of speech and depression symptoms.
Side effects of DBS can sometimes include subtle cognitive changes . A different study compared these effects with regard to these different areas.
GPi showed smaller neurocognitive declines than STN, though the effects were small with both. On a positive note, both procedures seemed to reduce symptoms of depression following surgery.
What Happens Before Surgery
In the doctor’s office you will sign consent forms and complete paperwork to inform the surgeon about your medical history, including allergies, medicines, anesthesia reactions, and previous surgeries. Presurgical tests may need to be done several days before surgery. Consult your primary care physician about stopping certain medications and ensure you are cleared for surgery.You may also need clearance from your cardiologist if you have a history of heart conditions.
Stop taking all non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines and blood thinners 7 days before surgery. Stop using nicotine and drinking alcohol 1 week before and 2 weeks after surgery to avoid bleeding and healing problems.
You may be asked to wash your skin and hair with Hibiclens or Dial soap before surgery. It kills bacteria and reduces surgical site infections.
No food or drink, including your Parkinson’s medication, is permitted after midnight the night before surgery.
Try to get a good night’s sleep. The DBS surgery involves multiple steps and lasts most of the day, during which you may be awake and off medication.
Morning of surgery
Arrive at the hospital 2 hours before your scheduled surgery time to complete the necessary paperwork and pre-procedure work-ups. An anesthesiologist will talk with you and explain the effects of anesthesia and its risks.
You May Like: Prayer For Parkinson’s Disease
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery
A team of experts, including a movement disorder specialist and a brain surgeon, conducts an extensive assessment when considering DBS for someone. They review your medications and symptoms, examine you when you’re on and off Parkinson’s medication, and take brain imaging scans. They also may do detailed memory/thinking testing to detect any problems that could worsen with DBS. If your doctors do recommend you for DBS and you are considering the surgery, discuss with your care team the potential benefits as each person’s experience is unique. It’s also critical to discuss the potential surgical risks, including bleeding, stroke and infection.
In DBS surgery, the surgeon places thin wires called electrodes into one or both sides of the brain, in specific areas that control movement. Usually you remain awake during surgery so you can answer questions and perform certain tasks to make sure the electrodes are positioned correctly. Some medical centers now use brain imaging to guide the electrodes to the right spot while a person is asleep. Each method has its pros and cons and may not be suitable for everyone or available everywhere.
Once the electrodes are in place, the surgeon connects them to a battery-operated device , which usually is placed under the skin below the collarbone. This device, called a neurostimulator, delivers continuous electrical pulses through the electrodes.
Deep Brain Stimulation Research Shows Promising Results For Treating Parkinsons Disease
Pulsed electrical stimulation drives cell-type specific neuromodulation. Credit: Rachel Keady Keeney
Researchers from Carnegie Mellon University have found a way to make deep brain stimulation more precise, resulting in therapeutic effects that outlast what is currently available. The work, led by Aryn Gittis and colleagues in CMUs Gittis Lab, will significantly advance the study of Parkinsons disease.
DBS allows researchers and doctors to use thin electrodes implanted in the brain to send electrical signals to the part of the brain that controls movement. It is a proven way to help control unwanted movement in the body, but patients must receive continuous electrical stimulation to get relief from their symptoms. If the stimulator is turned off, the symptoms return immediately.
Gittis, an associate professor of biological sciences in the Mellon College of Science and faculty in the Neuroscience Institute, said that the new research could change that.
By finding a way to intervene that has long-lasting effects, our hope is to greatly reduce stimulation time, therefore minimizing side effects and prolonging battery life of implants.
Since then, she has been trying to find a strategy that is more readily translated to patients suffering from Parkinsons disease. Her team found success in mice with a new DBS protocol that uses short bursts of electrical stimulation.
Recommended Reading: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinson’s
Tremor Detection And Assessment
Various types of sensors, such as motion sensors, mechanical sensors and electrophysiological signals, can be used to detect the hand movement with tremors. Tremor-related features could be distinguished from voluntary movements and identified with the use of machine learning methods. The approaches for tremor detection usually fall into two main categories based on the type of sensor feedback, respectively, electromyography -based and inertial-based approach.
As surface EMG represents the activity of motor neurons reflecting the neural mechanisms in the central nervous system, the tremor EMG signals from one or more antagonistic muscle pairs were investigated while the tremor characteristics can be estimated . Studies showed that PD tremor exhibits distinguished features in the amplitude- and spectral-domain of EMG signals compared to healthy elders and patients with essential tremor. An additional frequency of 4.55 Hz in PD was observed as shown in Figure 5A . The fixed amplitude or frequency threshold based on EMG signal have been commonly used in an online tremor suppression system, however, adaptive threshold can be considered to improve the performance of tremor detection . Multilayer perceptron and recurrent neural network models were also used to predict the EMG envelop or raw signals for forecasting the tremor amplitude and frequency used as input in a closed-loop strategy for tremor suppression .
How Deep Brain Stimulation Works
Exactly how DBS works is not completely understood, but many experts believe it regulates abnormal electrical signaling patterns in the brain. To control normal movement and other functions, brain cells communicate with each other using electrical signals. In Parkinson’s disease, these signals become irregular and uncoordinated, which leads to motor symptoms. DBS may interrupt the irregular signaling patterns so cells can communicate more smoothly and symptoms lessen.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Bike Therapy
What You Need To Know
- Surgeons implant one or more small wires in the brain during a surgical procedure.
- The leads receive mild electrical stimulation from a small pulse generator implanted in the chest.
- Proper patient selection, precise placement of the electrodes and adjustment of the pulse generator are essential for successful DBS surgery.
- DBS does not fully resolve the symptoms of PD or other conditions, but it can decrease a patients need for medications and improve quality of life.
How Effective Is Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinsons Disease
Deep brain stimulation provides excellent relief for most patients symptoms including tremor, stiffness , slowed movement , freezing of gait and dyskinesias. Long-term studies have shown continued improvement in tremor, bradykinesia, and dyskinesia. Many patients are able to reduce their medications and maintain their level of function including independent participation in activities of daily living required to care for oneself. One of the distinct advantages, is that after DBS, patients on average improve their daily on timewhen they are at their best, without troublesome dyskinesiaby half a day.
Also Check: Pfnca Wellness Programs
Who Is A Candidate
You may be a candidate for DBS if you have:
- a movement disorder with worsening symptoms and your medications have begun to lose effectiveness.
- troubling “off” periods when your medication wears off before the next dose can be taken.
- troubling “on” periods when you develop medication-induced dyskinesias .
DBS may not be an option if you have severe untreated depression, advanced dementia, or if you have symptoms that are not typical for Parkinson’s.
DBS can help treat many of the symptoms caused by:
- Parkinson’s disease: tremor, rigidity, and slowness of movement caused by the death of dopamine-producing nerve cells responsible for relaying messages that control body movement.
- Essential tremor: involuntary rhythmic tremors of the hands and arms, occurring both at rest and during purposeful movement. Also may affect the head in a “no-no” motion.
- Dystonia: involuntary movements and prolonged muscle contraction, resulting in twisting or writhing body motions, tremor, and abnormal posture. May involve the entire body, or only an isolated area. Spasms can often be suppressed by “sensory tricks,” such as touching the face, eyebrows, or hands.
After your evaluation and videotaping is complete, your case will be discussed at a conference with multiple physicians, nurses, and surgeons. The team discusses the best treatment plan for each patient. If the team agrees that you are a good candidate for DBS, you will be contacted to schedule an appointment with a neurosurgeon.
Precision Of Temporal Interference Stimulation
One important requirement of DBS is high spatial precision . Stimulating brain regions unrelated to the disease might reduce the effectiveness of treatment or cause undesired side effects. In their study, the authors both built computer models to simulate the stimulation effects and demonstrated their spatial precision via two sets of experiments in anaesthetised mice.
In the first set of experiments, the researchers selectively targeted a small region found deep in the brain called the hippocampus, and they proved that stimulation of this area does not affect an overlaying brain region called the cortex. The stimulation effect was validated with two laboratory techniques. The first method was an electrical recording technique called in vivo whole cell patch clamp, which uses a glass tube called a patch pipette to acquire signals from neurons in the brains of live animals. This method requires open-skull surgery on mice to place the patch pipette deep into the stimulated brain region, and it demonstrated the stimulation effect with single-cell precision. The second method was a technique called c-fos labeling, which can reveal neurons that have recently been stimulated. After the noninvasive stimulation experiment, the authors dissected the mouses brain and found that the only neurons that had been activated resided in the hippocampus region and not in the overlaying cortex region.
You May Like: Judy Woodruff Health Problems
Living With A Dbs Device
Batteries most often last three to five years, but this can vary. Rechargeable batteries may last up to 15 years.
There are several precautions related to electrical/magnetic devices that are important, but usually easy to accommodate. Items such as cell phones, computers, and home appliances do not generally interfere with the stimulator. Keep your stimulator identification card handy when you are out and about, in your wallet or purse.
Theft Detectors
Be aware that some devices may cause your transmitter to turn on or off. This includes security monitors that might be found at the library and retail shops.
If this occurs accidentally, it is not usually serious, but may be uncomfortable or result in your symptoms worsening if the stimulator is turned off. When you visit stores with these devices, you can ask to bypass the device by presenting your stimulator identification card.
Home Electronics
Keep the magnet used to activate and deactivate the stimulator at least 12 inches away from televisions, computer disks, and credit cards, as the magnet could potentially damage these items.
Air Travel/Metal Detectors
Talk to TSA personnel when traveling by plane, as the metal in the stimulator may set off the detector. If you are asked to go through additional screening with a detector wand, its important to talk to the person screening you about your stimulator.
Medical Diagnosis and Treatment
Occupational Electromagnetic Concerns
How Does Deep Brain Stimulation Work
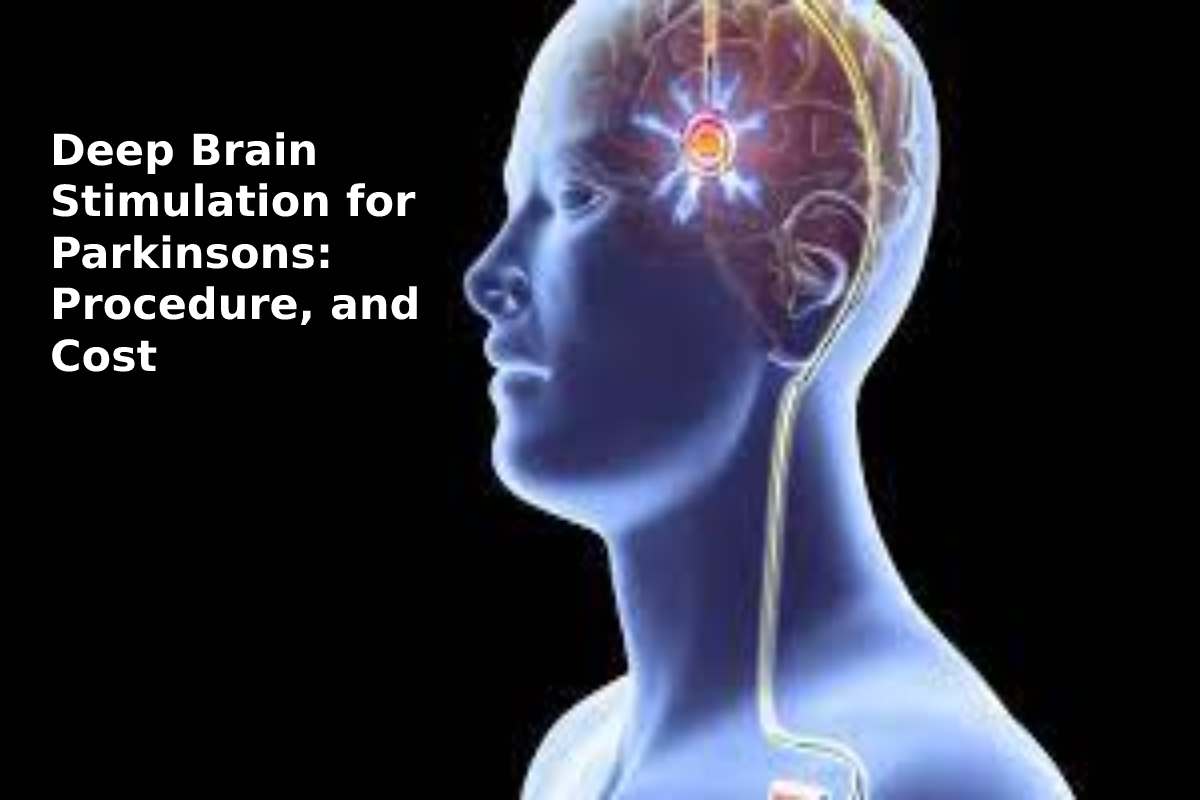
Movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease and other neurological conditions are caused by disorganized electrical signals in the areas of the brain that control movement. When successful, DBS interrupts the irregular signals that cause tremors and other movement symptoms.
After a series of tests that determines the optimal placement, neurosurgeons implant one or more wires, called leads, inside the brain. The leads are connected with an insulated wire extension to a very small neurostimulator implanted under the persons collarbone, similar to a heart pacemaker. Continuous pulses of electric current from the neurostimulator pass through the leads and into the brain.
A few weeks after the neurostimulator has been in place, the doctor programs it to deliver an electrical signal. This programming process may take more than one visit over a period of weeks or months to ensure the current is properly adjusted and providing effective results. In adjusting the device, the doctor seeks an optimal balance between improving symptom control and limiting side effects.
You May Like: On-off Phenomenon
Conflict Of Interest Statement
UCSF has submitted two pending/provisional patents related to use of particular brain signals for closed loop DBS. Drs. NS and CH are included as co-inventors on these patents.
References
Little, S., Brown, P. 2014. The functional role of beta oscillations in Parkinsons disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 20:S44S48. doi:10.1016/S1353-802070013-0
de Hemptinne, C., Swann, N. C., Ostrem, J. L., Ryapolova-Webb, E. S., San Luciano, M., Galifianakis, N. B., et al. 2015. Therapeutic deep brain stimulation reduces cortical phase-amplitude coupling in Parkinsons disease. Nat Neurosci. 18:779786. doi:10.1038/nn.3997
Little, S., Pogosyan, A., Neal, S., Zavala, B., Zrinzo, L., Hariz, M., et al. 2013. Adaptive deep brain stimulation in advanced Parkinson disease. Ann. Neurol. 74:449457. doi:10.1002/ana.23951
What Happens During Surgery
For stage 1, implanting the electrodes in the brain, the entire process lasts 5 to 7 hours. The surgery generally lasts 3 to 4 hours.
Step 1: attach stereotactic frameThe procedure is performed stereotactically, which requires attaching a frame to your head. While you are seated, the frame is temporarily positioned on your head with Velcro straps. The four pin sites are injected with local anesthesia to minimize discomfort. You will feel some pressure as the pins are tightened .
Step 2: MRI or CT scanYou will then have an imaging scan, using either CT or MRI. A box-shaped localizing device is placed over the top of the frame. Markers in the box show up on the scan and help pinpoint the exact three-dimensional coordinates of the target area within the brain. The surgeon uses the MRI / CT scans and special computer software to plan the trajectory of the electrode.
Step 3: skin and skull incisionYou will be taken to the operating room. You will lie on the table and the stereotactic head frame will be secured. This prevents any small movements of your head while inserting the electrodes. You will remain awake during surgery. Light sedation is given to make you more comfortable during the initial skin incision, but then stopped so that you can talk to the doctors and perform tasks.
Recommended Reading: Voice Amplifiers For Parkinson’s
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery And Implantation
DBS consists of two surgeries, spaced approximately three to six weeks apart to ensure the patient has adequate time to recover. Throughout your experience, you will be attended to by a top team of physicians and other medical experts including a neurosurgeon, an electrophysiologist, and an anesthesiologist.
It should be noted that DBS offers many benefits. The generator can be programmed by a neurologist, and customized to each individual patient. The procedure is also reversible. Most patients experience a significant improvement of symptoms. However, as with any brain surgery, there are risks. With DBS, the risk of stroke is 1 in 100 and infection is 1 in 50.
Today, many more patients could be helped by DBS than are currently benefiting from the procedure. Statistics show only 7 percent of Parkinsons disease and 1 percent of tremor patients in Michigan who would benefit from the procedure have undergone DBS. At U-M, we are proud to have one of the superior DBS programs in the country. We have developed a wide array of ways to improve DBS, including special imaging tools that help doctors more accurately place the electrodes, and lead intraoperative motor and speech testing that result in fewer side effects for the patient.
U-M is also home to an active research program, where our team of experts is always working on ways to make DBS faster and more accurate. We also regularly have clinical trials available for patients interested in participating.
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Don’t Miss: Weighted Silverware