What Happens To Someone Who Has Urinary Incontinence
The pelvic floor consists of a hammock of muscles, ligaments, and connective tissue, which covers the bottom of the pelvic cavity and assists in supporting the abdominal and pelvic organs. The pelvic floor maintains continence of bowel and bladder and plays an important role in sexual function.
The pelvic floor muscle consists of three layers and has fast and slow-twitch fibers to assist with support and sphincter properties. The muscle is the same in women and men and both sexes benefit from maintaining good strength and tone of the pelvic floor muscle.
As we age and with certain diseases such as PD our muscles become weak and the signals do not always tell the muscles to tighten up when they need too. Add a few pounds to the belly region also and you have the perfect storm for Peezing, Peelaughing, as well as a host of other words for embarrassing moments due to urinary incontinence or urgency!
Read Also: Diseases Similar To Parkinsons
Incomplete Emptying Of The Bladder
Parkinsons disease may also make it harder for you to empty your bladder completely. This occurs less frequently than the need for frequent urination, but it still affects many people with Parkinsons.
Your muscles are the culprit of this problem. When you urinate, you relax certain muscles, and Parkinsons can make it difficult to relax those muscles. Sometimes, it takes a long time to relax enough, and people may not spend long enough in the bathroom to empty their bladder.
Unfortunately, medications dont always help fully with bladder emptying in Parkinsons disease patients, although the drug urocholine or other medications designed to treat urinary retention may help. different.
Some people with urinary retention have to use a catheter to empty their bladder. If this is the case for you, your healthcare provider can instruct you on how to use the catheter.
Make Changes To Diet & Lifestyle
- Healthy and balanced diet means a happy bladder and bowels!
- A diet rich in veggies and fruits always helps with clean living.
- I have found that a diet rich in organic foods with less processed foods helps too.
- We get dehydrated easily! Drink fluids! Gatorade and water are great!!
- Alcohol, soda, and caffeine can irritate the bladder, so I try to drink those sparingly.
You May Like: What Foods Should You Avoid If You Have Parkinson’s Disease
Diagnosing A Urinary Tract Infection In Older Adults
Vague, uncommon symptoms such as confusion make UTIs challenging to diagnose in many older adults. Once your doctor suspects a UTI, its easily confirmed with a simple urinalysis.
Your doctor may perform a urine culture to determine the type of bacteria causing the infection and the best antibiotic to treat it.
There are home UTI tests that check urine for nitrates and leukocytes. Both are often present in UTIs. Because bacteria are often in the urine of older adults to some degree, these tests arent always accurate. Call your doctor if you take a home test and get a positive result.
Antibiotics are the treatment of choice for UTIs in older adults and younger people. Your doctor may prescribe amoxicillin and nitrofurantoin .
More severe infections may require a broad-spectrum antibiotic such as ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin .
You should start antibiotics as soon as possible and take them for the entire duration of treatment as prescribed by your doctor. Stopping treatment early, even if symptoms resolve, increases the risks of recurrence and antibiotic resistance.
Antibiotic overuse also increases your risk for antibiotic resistance. For this reason, your doctor will likely prescribe the shortest treatment course possible. Treatment typically lasts no more than 7 days, and your infection should clear up in a few days.
Its important to drink plenty of water during treatment to help flush out the remaining bacteria.
Also Check: How Does Someone Get A Urinary Tract Infection
Coping With Urinary Problems In Parkinsons Disease
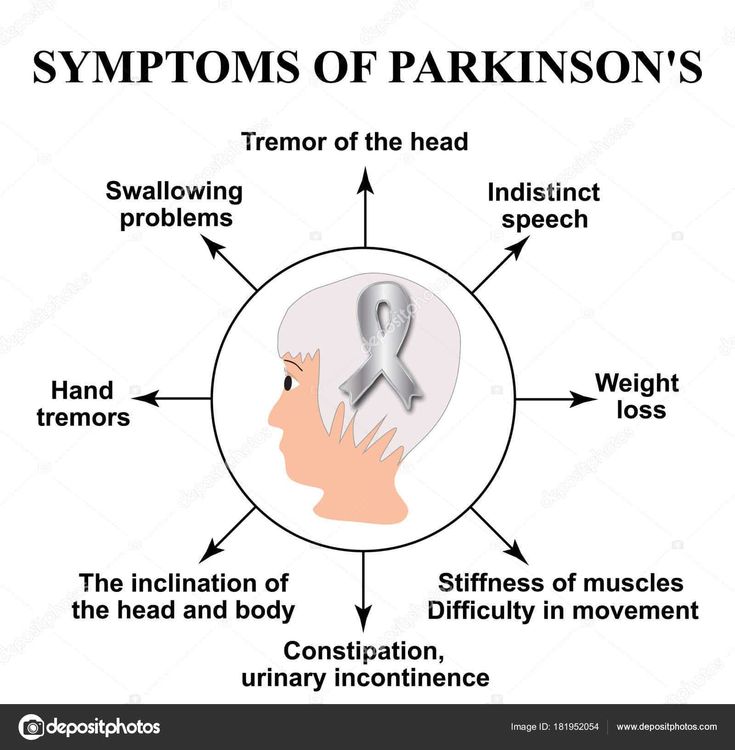
If you have Parkinsons disease, you may end up having to deal with urinary problems which research shows are common in addition to other symptoms of Parkinsons disease.Since urinary symptoms can lead to other problems, such as disrupted sleep and disruption to social activities, its important to be aware of these problems and know what you can do to help with this
You May Like: Sam Waterston Parkinsons
Don’t Miss: How To Improve Parkinson’s Gait
What Medications Help To Treat Urinary Incontinence
So back to the TV ads for urinary incontinence that have us adding MORE medication to our already full medication bag here are many medications that can help this problem. Medications include:
- Oxybutynin
- Mirabegron
- Phenoperidine fumarate
Do we really want to add that medication to the already growing list to our medications? The answer is YES!
Urinary Tract Infection In Parkinsons Disease
Article type: Review Article
Authors: Hogg, Elliota | Frank, Samuela | Oft, Jillianb | Benway, Brianc | Rashid, Mohammad Haruna | Lahiri, Shourid *
Affiliations: Department of Neurology, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, USA | Department of Infectious Diseases, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, USA | Department of Urology, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, USA | Departments of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Biomedical Sciences, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, USA
Correspondence: Correspondence to: Shouri Lahiri, MD, Departments of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Biomedical Sciences, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, 8700 Beverly Blvd., Los Angeles, CA 90048, USA. E-mail: .
Keywords: Parkinsons disease, urinary tract infection, delirium, falls, exacerbation
DOI: 10.3233/JPD-213103
Journal: Journal of Parkinson’s Disease, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 743-757, 2022
Abstract
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease And Walking
Management Of Sexual Dysfunction
Management of sexual dysfunction in patients with PD includes both behavioural and pharmacological options depending on the nature of the sexual dysfunction. Behavioural therapy may be used to treat SD, if considered as a learned maladaptive behaviour and may involve the use of psychodynamic psychotherapy and cognitive behavioural therapy . Pharmacological treatment of SD, on the other hand, requires either the reduction or elimination of drugs interfering with the sexual function or the introduction of drugs that improves sexual function . Ultimately, treatment options for SD may require multidisciplinary input from neurologists and psychologists for optimum results . Although phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors are standard treatment option for erectile dysfunction , intracavernosal alprostadil 1.2510 g injections can be used.
The management of hypersexuality as part of an impulse control disorder includes reduction/stopping of dopamine receptor agonist and practical therapeutic strategies including psychological therapies but not limited to counselling, psychotherapy, sex, couple and behavioural therapies . Hormonal treatment specifically testosterone has been tried in PD .
Urinary Tract Infections Which Are Very Frequent
Are other people out there being plagued by frequent infections? I am very fortunate that my Parkinsons is not severe but I am getting repeat infections which pull me down. I have been referred to a urologist.
I seem to have constant urinary infections and I am almost constantly on antibiotics. Im seeing a urologist tomorrow.
I hope the appointment goes well.
Frances
My wife who has PD has suffered with these infections for 5 years and only been dx for 3 years. For a long time we didnt know weather it was the infections or the PD that was making her bad. She saw a Urologist for the first time 2 years ago who came to the conclusion that my wife had nothing sinister and referred her back to her GP. The tablets she was on for bladder control that worked to a degree but these tablets mate her retain water in her bladder that was probably the cause of the infections. On Wednesday we are going to the clinic, after months of more investigations to discuss a catheter or botox. This is on top of trying to sort out her Parkinson meds because they are not working very well at all seeing PD nurse tomorrow.
I hope you get things sorted FrancesBilly
Update, My wife has had a catheter fitted which she is trying to get use to, it has a fip flow valve that opens and closes. Its so you dont need to wear a bag all the time, of a night you fit a bag so you dont have the problem of getting out of bed all the time During the day you open it every 2 hours to empty you bladder.
Billy
Also Check: Difference Between Parkinson’s And Dementia
Addressing Practical Aspects Of Eating And Drinking
Some people with Parkinsons have problems chewing and swallowing. This can make it difficult to eat a diet with plenty of fibre. A speech and language therapist can give advice about this. Ask your GP, specialist or Parkinsons nurse for a referral. If it takes a long time to eat and your meal goes cold, eat smaller portions and go back for seconds that have been kept warm. You can also get special plates that keep your meals hot the Disabled Living Foundation has more information.
An occupational therapist will also be able to give you some tips and practical advice.
What Is The Cause
While motor problems of the body and limbs are often the most visible symptom of PD, other symptoms occur as well. Parkinsons disease can affect the autonomic nervous system. This is the nervous system responsible for automatic bodily functions like bowel movements and urination.2
The area of the brain that is most heavily damaged by PD makes dopamine. Dopamine is a chemical messenger that allows for smooth and controlled muscle movement. Also, protein deposits in the brain called Lewy bodies contribute to autonomic nervous system problems in PD.9
You May Like: Medications Used For Parkinson’s Disease
Why Do Urgency And Frequency Occur
Bladder difficulties in Parkinsons are related to changes in the level of dopamine affecting the function of the bladder muscle. Parkinsons is also thought to affect the nerve pathway between the bladder and the part of the brain controlling bladder function. Some of the symptoms that affect bladder control are related to the level of dopamine in your body which will rise and fall depending on your medication level.
Other conditions such as weak pelvic floor muscles or an enlarged prostate will contribute to bladder symptoms. Constipation can also worsen bladder symptoms by putting pressure on the bladder.
Strategies For Managing Nocturia In Pd
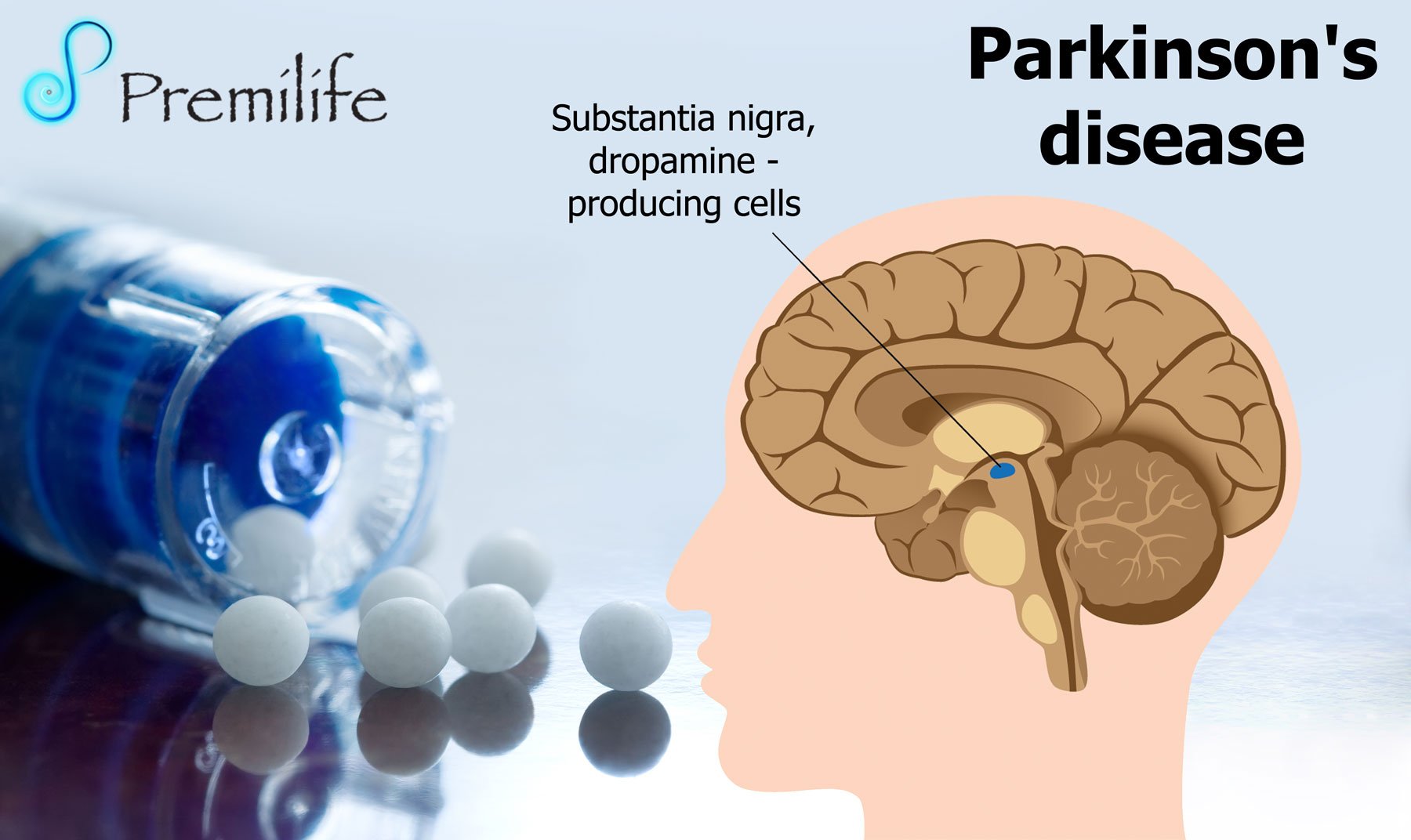
Despite the high prevalence of nocturia and impact on QoL, treatment options for managing this problem are currently limited and are often poorly tolerated or ineffective in PD. Guidance on nocturia treatment is limited, and most treatment options are derived from guidance around general management of urinary symptoms in neurological patients.57, 76, 79
Also Check: How To Live With Parkinson’s
Parkinson’s Disease And The Bladder
In this 30-minute video lecture Dr. Donna Deng explains the cause of bladder dysfunction and quality of life consequences. Treatment options include behavioral modification, pharmacologic, nerve stimulation , Implantable Impulse Generator, and Botox injections. Last line of treatment for older men with Parkinsons should be prostate surgical procedures.
Same Types Of Bladder Issues
The most common type of bladder problem has been difficulties in holding urine. As a result, individuals are unable to hold urine for sufficient lengths of time and this results in an increased frequency to urinate in the day and night. Individuals may need to rush to the toilet and this may sometimes lead to incontinence. Additionally, individuals may report problems with urination such as difficulties in starting their urinary stream, known as urinary hesitancy, a weak and interrupted urinary stream and, occasionally, may also experience retention of urine. Difficulties in urination are not as noticeable as problems with holding urine, and some individuals may unknowingly leave behind urine in their bladder after urinating. This is known as the post-void residual volume, and as a routine should be measured through a simple bedside ultrasound scan. Holding back a significant quantity of urine in the bladder after urinating can increase the risk for developing urinary tract infections.
You May Like: Can Stem Cells Help Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons Disease And Your Bladder
Many diagnosed with Parkinsons disease experience urinary tract issues. A Michigan Medicine urologist discusses treatment options for patients to consider.
Anne Pelletier-Cameron, M.D., often jokes to her patients that shes a female plumber of the lower urinary tract. On a more professional note, however, shes a urologist in the Michigan Medicine Department of Urology.
In this role, Pelletier-Cameron treats patients with a variety of lower urinary tract symptoms. Some of her patients have been diagnosed with Parkinsons disease, a progressive nervous system disorder that impacts movement. But the breakdown of nerve cells that characterize Parkinsons disease can also cause non-movement symptoms, including bladder issues.
Half of all women and 17% of men will experience urinary incontinence, or the inability to hold urine, she says, noting that for Parkinsons disease patients, those numbers escalate.
Many of my PD patients end up having other bladder problems, including issues with urgency and frequency, says Pelletier-Cameron. Nocturia, or the need to urinate many times during the night, is also common, along with difficulty in emptying the bladder.
Pelletier-Cameron says the impact of bladder symptoms cant be ignored.
Urinary Symptoms And Parkinsons Disease: The Patients Perspective
Research has found that urinary dysfunction can occur in up to 85% of individuals with PD and can adversely impact quality of life. Urinary symptoms can be experienced in many ways, including having an urgency to go to the bathroom, waking up to go to the bathroom, increased frequency, incomplete emptying, incontinence, among others. Urinary symptoms were reported to have a significant impact on day-to-day functions, engagement in public and social settings, and psychological well-being . Forty-one percent of the participants stated that urinary symptoms had a negative impact on quality of life.
Despite increased awareness of urinary symptoms for individuals with PD, greater insights from the patients perspective about the relationship between urinary symptoms, day-to-day living, and quality of life may help with adapting to and coping with PD. Our report provides you with the patients perspective.
Don’t Miss: Vibrating Pen For Parkinson Patients
Introduction Of Bacteria Via Catheterization
Indwelling urinary catheterization provides a direct pathway for pathogenic bacteria to ascend from the external environment to the lower urinary tract. There are three possible mechanisms by which catheterization may lead to bacterial colonization of the lower urinary tract and subsequent infection . First, bacteria may be introduced directly during catheter insertion if aseptic technique is not observed. Secondly, bacteria may travel along the outside of the catheter, between the urethral mucosa and the exterior of the catheter. Lastly, bacteria may ascend directly along the interior lumen of the catheter. Overall, extraluminal tracking of bacteria seems to be the predominant pathophysiologic mechanism of catheter-associated UTI , with biofilm formation playing a role in some cases . Bacteriuria is virtually guaranteed with indwelling urinary catheterization and is more likely with prolonged duration of catheterization.
Why Do Some People With Parkinsons Disease Experience Urinary Incontinence
Parkinsons is best known for its effects on balance and movement, but it impacts the autonomic nervous system as well. The autonomic nervous system controls specific bodily functions, like heart rate, blood pressure, libido, and urine production.
Over time, changes to the autonomic nervous system affect your bladders ability to store and release urine. That means you might have trouble making it to the bathroom on time or need to urinate more frequently.
You May Like: Zhichan Capsule
Read Also: Big Therapy For Parkinson Disease
Institutional Characteristics And Patient Selection
This study was approved by the institutional review board at Yale University School of Medicine. Subjects were selected from patients followed by 1 physician at the Yale Urology Medical Group Clinic. All patient visits at the clinic are logged by the Patient Financial Services Department under corresponding diagnosis codes. Follow-up notes from clinic visits or phone calls are recorded in patient charts by the same physician after each encounter.
Inclusion criteria for the study were as follows: neurogenic bladder dysfunction stable traumatic SCI at least 1 year after injury bladder management with CIC minimum of 1 year follow-up by the same physician at the Yale Urology Clinic seen between the 2000 and 2010. Exclusion criteria were other etiology for neurogenic bladder such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson disease, spina bifida, or diabetes other methods of bladder management, including other catheterization methods or Crede maneuver or had undergone urinary diversion.
| Age, years |
Note: Data presented as mean ±SD, unless noted otherwise data in parentheses are percentages. PRx = prophylaxis UTI = urinary tract infection.
Whats Next For Those Suffering From Urinary Incontinence

I decided I did not want to add another medication to the medicine bag. I was trying to see if there was something I could do besides resigning myself to wearing pads or some other incontinence protection all the time. At 53 years old, I wanted to see if there was a way I could help myself.
Part 2 of this article will address my experiences. I plan to discuss what I lovingly refer to as PEE PEE PT physical therapy to help treat urinary incontinence.
You May Like: Voice Amplifiers For Parkinsons
Also Check: Root Cause Of Parkinson’s Disease
Management Strategies To Prevent Uti In Pd
Although there is little in the way of high-quality data to prevent UTI in PD, several measures can be considered as part of a multifaceted approach. In general, all patients with PD and urinary retention should be counseled on maintaining adequate hygiene including perineal cleanliness and, if required, aseptic catheterization techniques . In addition, regular scheduled bladder and bowel emptying should be encouraged to reduce urinary retention and inadvertent fecal contamination from stool incontinence. There should be a low threshold to treat comorbid medical conditions that increase the risk of urinary retention and UTI, such as benign prostatic hyperplasia or diabetes, and adjustment of medications that promote urinary retention . More PD-specific research is urgently needed to address this important issue.
Table 1
Concomitant conditions that lead to recurrent UTI and recommendations for prevention
Table 2
Summary of interventions and recommendations from European Association of Urology