Oral Dysfunction In Parkinsons: Swallowing Problems And Drooling
Two common and distressing problems that can develop in Parkinsons disease are swallowing dysfunction and drooling. I want to help you better understand these issues and learn what you can do to improve them so read on!
Thank you to Christine Sapienza, PhD, CCC-SLP and Bari Hoffman Ruddy, PhD, CCC-SLP for providing some of the material below.
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
How Do I Know If I Have A Speech Or Voice Problem
- My voice makes it difficult for people to hear me.
- People have difficulty understanding me in a noisy room.
- My voice issues limit my personal and social life.
- I feel left out of conversations because of my voice.
- My voice problem causes me to lose income.
- I have to strain to produce voice.
- My voice clarity is unpredictable.
- My voice problem upsets me.
- My voice makes me feel handicapped.
- People ask, “What’s wrong with your voice?”
Also Check: What Is Parkinson Disease In Layman Terms
Swallowing Difficulties And Parkinsons Medication
If swallowing tablets or capsules becomes difficult, it may be tempting to crush tablets or open capsules, but this should never be done, as it can cause serious side effects and/or prevent the medication working properly. Always ask your pharmacist or doctor, or check the patient information leaflet before tampering with medicines in any way. Swallowing medications with jelly, yoghurt or apple sauce may help you swallow medication more comfortably.
Many Parkinsons medicines are prepared or designed to work in a particular way that will be harmed by crushing or opening capsules. For example, some medicines have:
- Sugar or film coating: This is usually to make them taste better, but crushing may make them taste unpleasant.
- Enteric coating: This coating is designed to keep the tablet whole in the stomach, in some cases to protect the stomach or to protect the medicine from stomach acid so that it is released after passing through the stomach, for example in the intestine. This type of tablet should never be crushed.
- Modified or controlled release: These medications have been designed to release slowly and act over a longer period, so they can be taken less often. Crushing this type of tablet would lead to a rapid release of the medicine which could be harmful.
If you experience any problems you should talk to your doctor, so that he or she can prescribe medication in a form that is easier to take. Some medicines are available in liquid form.
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
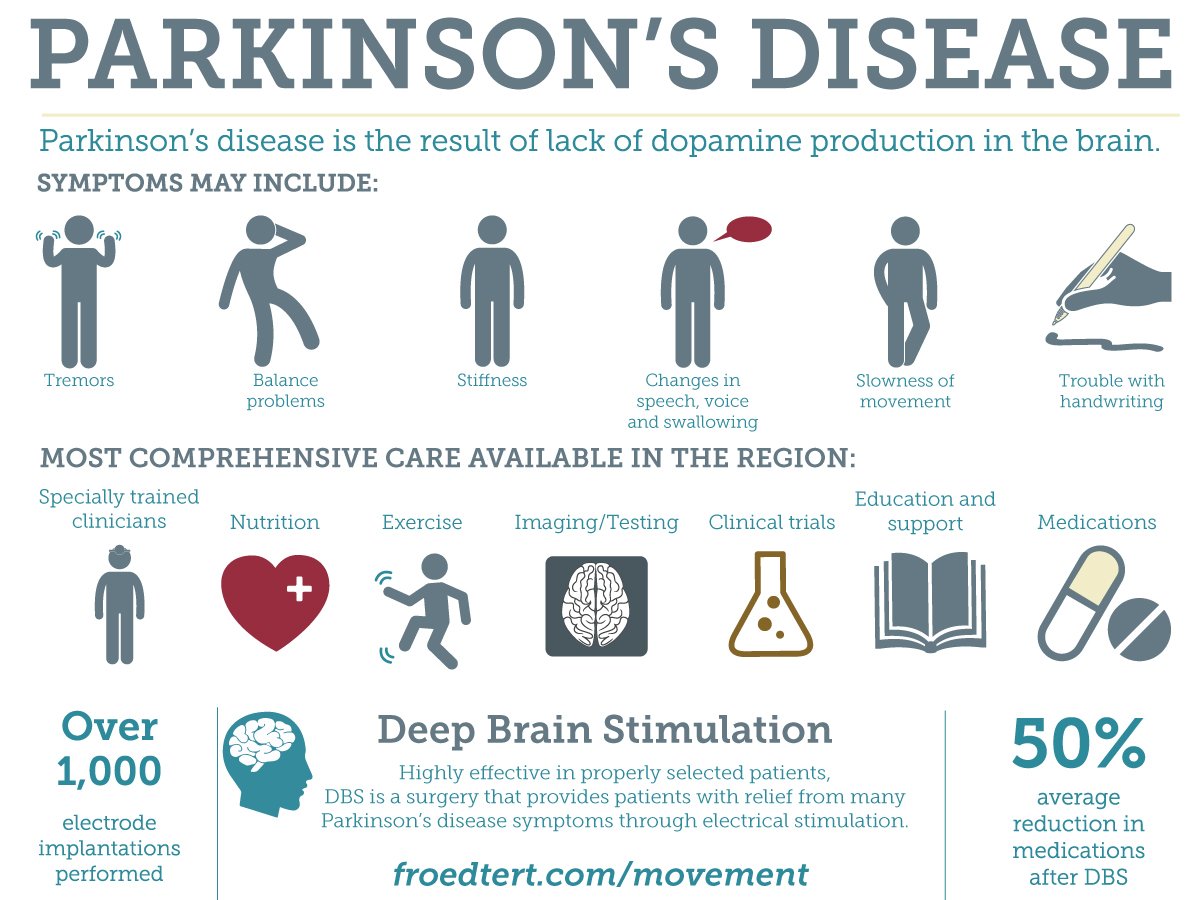
Parkinson’s disease has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Stiffness of the limbs and trunk
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination, sometimes leading to falls
Other symptoms may include depression and other emotional changes difficulty swallowing, chewing, and speaking urinary problems or constipation skin problems and sleep disruptions.
Symptoms of Parkinsons and the rate of progression differ among individuals. Sometimes people dismiss early symptoms of Parkinson’s as the effects of normal aging. In most cases, there are no medical tests to definitively detect the disease, so it can be difficult to diagnose accurately.
Early symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are subtle and occur gradually. For example, affected people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. They may notice that they speak too softly, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. Friends or family members may be the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinson’s. They may see that the person’s face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
People with Parkinson’s often develop a parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward, small quick steps as if hurrying forward, and reduced swinging of the arms. They also may have trouble initiating or continuing movement.
You May Like: Early Stages Of Parkinson’s
Breathing & Respiratory Difficulties
Some people with Parkinsons disease may experience shortness of breath. There is no clear cause underlying respiratory dysfunction in PD, its frequency or the effect that medications have on respiration. Several reasons for shortness of breath in PD include:
- Wearing off is a common experience among people with PD who have been taking levodopa for several years. These occur when the medication benefit wears off and PD symptoms return before the next dose.
- Respiratory dyskinesia refers to an occurrence of irregular and rapid breathing when levodopa medications reach their peak effect. These may accompanied by involuntary body movements, typically experienced as dyskinesia.
- Anxiety is a common symptom of PD that may also exacerbate shortness of breath, whether by itself or as a consequence of wearing off of the medication.
- Aspirationpneumonia is a pneumonia that develops after food or liquid goes down the wrong pipe. Advanced PD can increase the risk of swallowing difficulties, choking and aspiration pneumonia.
- Non-PD health issues include conditions such as asthma, allergies, lung disease, heart disease and other conditions that may cause shortness of breath.
Exercises For Restoring Health Breathing
There are various suggested types of exercise which can help gradually shift the equilibrium point of CO2 intolerance back to healthy states. However, all of these emphasize nose breathing over mouth breathing , and diaphragmatic breathing over chest breathing. This represents an immediate roadblock for people with PD, for whom mouth breathing is likely to have become so ingrained that it feels like the nose is permanently stuffed up, and who have diaphragms which are so frozen that it cannot voluntarily be flexed. However, it is possible to open the nose in the majority cases through some simple exercises. Robert Litman in the above video demonstrates this, and below is another video of Patrick McKeown on the topic. See also my article on how I restored nose breathing with the help of a red light anti-allergy device. It is also possible to restore access to diaphragmatic breathing, as I covered in another article, which explains how I used Block Therapy to achieve this.
Once nasal and diaphragmatic breathing is made possible there are a few different types of breathing exercises one try for restoring CO2 tolerance to more normal levels. It is important to note that these exercises are not necessarily targeted at immediate regulation of the Nervous System, unlike breathing methods designed for in-the-moment relaxation or mobilization, but are aimed at long term retraining of breathing patterns in order to restore healthy oxygenation levels to the brain and muscles.
You May Like: Flexibility Exercises For Parkinson’s Disease
Foods That Are Hard To Chew
Many people with Parkinsons have difficulty with chewing and swallowing foods. A person needs medical help if this is the case. A speech and language therapist may be able to help a person overcome this issue.
However, if a person is finding certain foods hard to chew and swallow, they may wish to avoid these foods.
Such foods include:
- dry, crumbly foods
- tough or chewy meats
If a person does wish to eat chewy meats, they could try using gravy or sauce to soften them and make eating easier.
They could also try chopping meat into smaller pieces or incorporating meat into casseroles, which can make it more tender.
Having a drink with a meal can also make chewing and swallowing easier.
The Gastrointestinal Tract And Parkinsons
As promised in a previous blog, I now return to the topic of the gastrointestinal tract and Parkinsons disease . As most of you know, GI symptoms are very common in PD. We will discuss what those symptoms are, why they occur, and the current research that links what is happening in the gut to theories as to why PD occurs at all. Many of you have suggested gut-related topics for this blog including a discussion of symptoms such as bloating and constipation, and a discussion of the use of probiotics in PD. I will address these issues as well. Submit additional topics that you would like to read about here.
GI symptoms can be among the most bothersome of the non-motor symptoms of PD. Constipation is the most common of these symptoms, affecting 80-90% of people with PD. APDA has a helpful brochure with practical tips to prevent and treat constipation in PD.
GI pathology in Parkinsons disease however, can involve the entire GI tract and includes sialorrhea and dysphagia . In addition, delayed gastric emptying, in which the digestive contents are held up in the stomach and do not move normally into the small intestine, can cause sensations of nausea and bloating.
The gut has its own nervous system
The gut as a biomarker
Entry to the brain
How do Lewy bodies propagate?
Recommended Reading: What Classes Of Drugs Are Used To Treat Parkinson’s Disease
What Causes Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease occurs when nerve cells, or neurons, in an area of the brain that controls movement become impaired and/or die. Normally, these neurons produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems of Parkinson’s. Scientists still do not know what causes cells that produce dopamine to die.
People with Parkinson’s also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinson’s, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying-down position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinson’s contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons disease and Lewy body dementia.
Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease
A number of disorders can cause symptoms similar to those of Parkinson’s disease. People with Parkinson’s-like symptoms that result from other causes are sometimes said to have parkinsonism. While these disorders initially may be misdiagnosed as Parkinson’s, certain medical tests, as well as response to drug treatment, may help to distinguish them from Parkinson’s. Since many other diseases have similar features but require different treatments, it is important to make an exact diagnosis as soon as possible.
There are currently no blood or laboratory tests to diagnose nongenetic cases of Parkinson’s disease. Diagnosis is based on a person’s medical history and a neurological examination. Improvement after initiating medication is another important hallmark of Parkinson’s disease.
Read Also: Lewy Body Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms
Problems With Tongue Muscles
Parkinsons can also cause problems in the tongue muscles. The tongue is important in swallowing. We use it to move food around and push it to the back of the mouth to trigger the swallowing reflexes. Parkinsons can also impair the reflexes that protect our windpipe from food and drink. A problem coordinating breathing and swallowing may make this problem worse.
Medicines For Parkinson’s Disease

Medicines prescribed for Parkinson’s include:
- Drugs that increase the level of dopamine in the brain
- Drugs that affect other brain chemicals in the body
- Drugs that help control nonmotor symptoms
The main therapy for Parkinson’s is levodopa, also called L-dopa. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brain’s dwindling supply. Usually, people take levodopa along with another medication called carbidopa. Carbidopa prevents or reduces some of the side effects of levodopa therapysuch as nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and restlessnessand reduces the amount of levodopa needed to improve symptoms.
People with Parkinson’s should never stop taking levodopa without telling their doctor. Suddenly stopping the drug may have serious side effects, such as being unable to move or having difficulty breathing.
Other medicines used to treat Parkinsons symptoms include:
- Dopamine agonists to mimic the role of dopamine in the brain
- MAO-B inhibitors to slow down an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain
- COMT inhibitors to help break down dopamine
- Amantadine, an old antiviral drug, to reduce involuntary movements
- Anticholinergic drugs to reduce tremors and muscle rigidity
Also Check: Drugs Prescribed For Parkinson’s Disease
Sidebar: Advances In Circuitry Research
The brain contains numerous connections among neurons known as neural circuits.
Research on such connections and networks within the brain have advanced rapidly in the past few years. A wide spectrum of tools and techniques can now map connections between neural circuits. Using animal models, scientists have shown how circuits in the brain can be turned on and off. For example, researchers can see correlations between the firing patterns of neurons in a zebrafishs brain and precise behavioral responses such as seeking and capturing food.
Potential opportunities to influence the brains circuitry are starting to emerge. Optogenetics is an experimental technique that involves the delivery of light-sensitive proteins to specific populations of brain cells. Once in place, these light-sensitive proteins can be inhibited or stimulated by exposure to light delivered via fiber optics. Optogenetics has never been used in people, however the success of the approach in animal models demonstrates a proof of principal: A neural network can be precisely targeted.
Thanks in part to the BRAIN Initiative, research on neural circuitry is gaining momentum. The Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies Initiative is accelerating the development and application of new technologies that enable researchers to produce dynamic pictures of the brain that show how individual brain cells and complex neural circuits interact at the speed of thought.
NIH Publication No. 15-5595
Breathing Problems In Parkinsons Disease: A Common Problem Rarely Diagnosed
Parkinsons disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimers disease. It is characterized by bradykinesia tremor, rigidity, and postural instability. Potential non-motor manifestations of PD include depression, anxiety, constipation, overactive bladder symptoms, dementia, and sleep disturbances.
Although James Parkinson, in 1817, described breathing abnormalities in his Essay on the shaking palsy, there has been limited research on this important non-motor symptom.
People living with Parkinsons may present with a wide variety of respiratory symptoms, ranging from shortness of breath at rest to acute stridor. Shortness of breath can be very distressing for patients and clinicians alike. Multiple investigations may be undertaken, looking for infection, blood clots and heart problems. Although these potential causes of breathing abnormalities need to be excluded, clinicians must remember that PD itself and its medications can cause SOB and that normal investigations should not automatically lead to a diagnosis of anxiety, depression or lead to inappropriate treatment plans.
Several different patterns of breathing abnormality may be found in PD:
KM Torsney, D Forsyth
Also Check: What Benefits Can You Claim For Parkinson’s Disease
Slow Muscles Carrying Food To Your Stomach
Parkinsons may also slow down the muscles carrying food down into your stomach. Food moving slowly down your food pipe to your stomach can make you feel full up. But once it arrives at your stomach you realise youre still hungry. By this time the food on your plate may have gone cold and be unappealing.
Living Well With Parkinson’s
While medication and DBS surgery are the most effective treatments for PD, individuals often choose to delay these treatments because of their adverse side effects. Until a therapy is developed that can halt the progression of PD, there is a significant need for strategies that provide symptom relief without causing negative side effects.
Diet, Exercise, and Stress Reduction
Findings from several studies suggest that exercise has the potential to provide relief from certain PD symptoms. Anecdotally, people with Parkinsons disease who exercise typically do better. However, many questions remain. Among them is whether exercise provides a conditioning effect by strengthening muscles and improving flexibility or whether it has a direct effect on the brain.
In an NINDS-funded trial comparing the benefits of tai chi, resistance training, and stretching, tai chi was found to reduce balance impairments in people with mild-to-moderate PD. People in the tai chi group also experienced significantly fewer falls and greater improvements in their functional capacity.
Technologies that Improve Quality of Life
Don’t Miss: What Drugs Can Cause Parkinson’s Disease
Swallowing Difficulties In Parkinsons Disease
The act of swallowing involves a complex series of activities that begin in the mouth, continue in the pharynx and end in the esophagus. These include chewing, using the tongue to move the bolus of food to the back of the throat and then coordinating the muscles that both propel the food into the esophagus and protect the airway or trachea from food penetration. Swallowing dysfunction can be considered both a motor and a non-motor symptom of PD. Loss of dopamine neurons in the substantia nigra area of the brain can cause the motor dysfunction that impairs swallowing. However, loss of neurons in other areas of the brain, such as the cortex and lower brain stem can also affect the overall control and coordination of swallowing, and can be thought of as a non-motor symptom of PD. Swallowing issues are very important to diagnose. Impacts on your daily life and your health can range from difficulties with meals to more extreme cases where it could lead to choking and aspiration which can be very serious or even fatal.
Medication Side Effects And The Gut
The interactions between PD medication ingestion and the gut can play a major role in motor fluctuations the phenomenon in which a patients response to Levodopa varies widely during the day. A recent APDA webinar helps to explain this interplay.
Delayed gastric emptying
Delayed gastric emptying can interfere with medication absorption. Medication doses that are ingested by mouth may sit in the stomach before being transported to the small intestine where they are absorbed. Delayed gastric emptying could be responsible for dose failures when a dose of medication does not have a robust enough effect.
Protein effect
Levodopa crosses the wall of the small intestine via a molecule in the intestinal wall that transports amino acids, the building blocks of protein. When dietary protein is also present in the small intestine, then there are fewer transporters available for Levodopa to use. A patient may therefore experience the protein effect, in which he or she feels that medication is not as effective after a high-protein meal. Sources of dietary protein include: beef, chicken, pork, fish, eggs, nuts and dairy.
Helicobacter pylori and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth
About a third of PD patients are infected with Helicobacter pylori, a common bacteria which can cause gastritis and ulcers. Infection with Helicobacter pylori has been linked to worsened motor fluctuations. It can be diagnosed with a urea breath test that analyzes exhaled air.
Read Also: Emotional Symptoms Of Parkinson’s