Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Dementia with Lewy bodies is the third most common cause of dementia after Alzheimers disease and vascular dementia. This disease has symptomatic overlap with Parkinsons disease, such as rigidity, balance, and posture instability. However, dementia with Lewy bodies typically presents with more prominent cognitive problems, hallucination, and fluctuations in cognitive function. Other symptoms of DLB include dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, REM behavior sleep disorder, and memory changes.
What Are The Faces Of Msa
Given the multitude of features in MSA, clinical presentation is varied resulting in many faces of the disease. Since its first description in the 1960s the disease has been given different namesShy-Drager syndrome, striatonigral degeneration , and olivopontocerebellar atrophy depending on the predominant presenting symptoms. However, it was later discovered that each of these syndromes shared a similar pathology characterized by the presence of abnormal protein deposits in the brain, called glial cytoplasmic inclusions or GCIs. These inclusions are similar to Lewy bodies seen in PD, but unlike PD they are not found in neurons but rather in supporting glial cells. In the brain these glial cells are important for making myelin, a substance that insulates nerve fibers. The finding of this common pathological feature regardless of the clinical presentation led to the terminology used today, multiple system atrophy or MSA. Two clinical variants are generally still distinguished by clinicians based on the predominant presenting symptoms: parkinsonism or cerebellar ataxia . Both variants include autonomic dysfunction and as the disease progresses the features of these variants increasingly overlap.
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease Family Support
Diagnosis Of Multiple System Atrophy
The diagnosis of multiple system atrophy poses a challenge because there is no specific test to diagnose the condition. Parkinsonism can be confused with Parkinsons disease, whereas cerebellar ataxia can be confused with different forms of cerebellar ataxia, acquired or inherited. A definitive diagnosis can only be made on autopsy to find the characteristic pattern of degeneration. A probable diagnosis is made based on the exhibiting autonomic failure with either parkinsonism or cerebellar ataxia.
Autonomic system testing can be done, such as assessing for orthostatic hypotension, polysomnogram for sleep apnea, along with neurological examination, neuroimaging, including PET scan or MRI and DaTscan. MRI can help in identifying changes that may help rule out other causes or suggest multiple system atrophy. PET is used to check for metabolic functioning in specific parts of brain. DaTscan helps in assessing whether the disease is caused by dopamine system disorder, although the test is insufficient in differentiating between MSA and Parkinsons disease.
Signs It Might Be Multiple System Atrophy Instead Of Parkinsons Disease
Here are some clues as to whether it is multiple system atrophy or Parkinsons disease. One of the easier distinctions is between PD and MSA-C .If the patient presents with unsteadiness while walking, uncoordinated arms and legs, bladder disturbance and/or dizziness when standing the diagnosis is more likely to be MSA-C. On the other hand, if a person looks Parkinsonian the distinction can be harder, but there are clues:
- In the earlier stages of MSA-P , which is often when people have just been told they have Parkinsons disease, some patients will fall often.Frequent falls also occur in Parkinsons disease, but it typically occurs 10-15 years after diagnosis.
- In patients with MSA the classic Parkinsons drug L-Dopa may work initially but will stop working very quickly.It can continue working in PD patients for many years.
- Dementia is not associated with MSA however, it does occur in patients with lewy body Parkinsons disease.
- Early autonomic nervous system symptoms such as low blood pressure when standing and issues with the bladder are often signs of possible MSA in patients diagnosed with Parkinsons.
- Vocal cord issues are less common but very typical in MSA and much less common in PD.Some examples include difficulty getting words out, odd sighs and even falling asleep during a conversation.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Sleeping All The Time
Dti And Volumetry Data Of Subcortical Structures
Measures of mean FA and MD were calculated for each subcortical ROI to evaluate the microstructural diffusion properties of the 18 subcortical structures. Complementarily, the FreeSurfer volume-based stream was used to extract the volume of each ROI, which is often used as a marker of atrophy. Gender was included as a covariate in all analyses. Intracranial volume was also used as a covariate in the volumetric comparisons.
Whats The Difference Between Vascular Parkinsonism And Parkinsons
As the name implies, vascular parkinsonism is caused by cerebrovascular disease which affects the blood supply to the brain. Vascular parkinsonism is caused by one or more small strokes, while Parkinsons is caused by a gradual loss of nerve cells. One major difference from Parkinsons is that its not progressive, while Parkinsons becomes worse with time. Another difference is that there are no tremors in vascular parkinsonism.
For more information on vascular parkinsonism, read this journal article.
Read Also: Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease In Women
Global Plasma Antibody Concentrations
The global antibody concentrations are shown in Table 2 and presented in Figure 2. Interestingly, we observed significantly lower global IgG1 levels described by group in MSA compared to PD and controls . The levels of IgG2 were also significantly lower described by group in MSA compared to PD patients , but not compared to controls .
Table 2. Global plasma immunoglobulin levels.
Figure 2. Global plasma antibody levels. Distribution of global plasma amounts of antibodies in patients with Multiple System Atrophy divided into subtypes , patients with Parkinson’s disease , and controls . Absolute plasma concentrations to ELISA of total IgG, IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4, and IgM antibodies. Dot plots show plasma Ig concentrations with mean values ± SEM. Differences were tested using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test adjusted for age and sex.
Similar to IgG1 findings, there were significantly lower global IgM levels described only by group in MSA compared to PD and controls . Besides being described by group, the IgM levels were to a minor extent further described by sex , indicating sex as a confounding factor in IgM plasma levels. For detailed statistics see Table S2. Further, our model showed IgG3 levels to be significantly different , however, this difference was not described by group, age, or sex. No significant differences were observed between the groups for IgG4 or total IgG levels.
So What Is It Is It Parkinsons Disease Or Is It Something Else
The answer is not easy, but many who feel they have more than Parkinsons may in fact have multiple system atrophy .MSA is a very rare disorder that has similarities and features of Parkinsonism.However, it is so rare that many physicians are unfamiliar with it and so the diagnosis is not considered. As a result, a likely diagnosis of MSA might be delayed by years and even missed all together. Whats more, due to many symptoms that could possibly be attributed to other conditions diagnosing MSA can be challenging, even to the most experienced doctors. This can be very frustrating to those who know it is more than PD.
You May Like: Fluid Retention And Parkinson’s
What The Research Says
Little is known about the mechanisms at work in multiple system atrophy. Researchers at the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke are currently trying to figure out why the protein alpha-synuclein builds up in the glial cells of people with MSA and the neuronal cells of people with Parkinsons disease. A clinical trial tried using the drug rifampicin to slow down disease progression, but the treatment was ineffective. Data from this study is now being used in other MSA studies.
How Is Msa Diagnosed
Making a diagnosis of MSA can be difficult, particularly in the early stages, in part because many of the features are similar to those observed in Parkinsons disease.
After taking a clinical history and performing a brief neurological examination, a doctor may order a number of tests to help make the diagnosis. These tests might include autonomic testing , assessment of bladder function, and/or neuroimaging such as an MRI or PET scan. An MRI of the brain may identify changes which might suggest MSA or rule out other causes of the observed symptoms.
A PET scan is sometimes used to see if metabolic function is reduced in specific parts of the brain. DaTscan can assess the dopamine transporter in a part of the brain called the striatum and can help physicians determine if the condition is caused by a dopamine system disorder however this test cannot differentiate between MSA and Parkinsons disease. Individuals with MSA typically do not have sustained improvement in their symptoms with levodopa , a finding that often supports the diagnosis of MSA.
Recommended Reading: Stage 5 Parkinson’s Disease Life Expectancy
How Is It Treated
Currently, there are no treatments to delay the progressive neurodegeneration of MSA, and there is no cure. There are treatments to help people cope with the symptoms of MSA.
In some individuals, levodopa may improve motor function however, the benefit may not continue as the disease progresses.
The fainting and lightheadedness from orthostatic hypotension may be treated with simple interventions such as wearing compression stockings, adding extra salt and/or water to the diet, and avoiding heavy meals. The drugs fludrocortisone and midodrine sometimes are prescribed. In 2014, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved the medication droxidopa for the treatment of orthostatic hypotension seen in MSA. Dihydroxyphenylserine helps to replace chemical signals called neurotransmitters which are decreased in the autonomic nervous system in MSA. Some medications used to treat orthostatic hypotension can be associated with high blood pressure when lying down, so affected individuals may be advised to sleep with the head of the bed tilted up.
Bladder control problems are treated according to the nature of the problem. Anticholinergic drugs, such as oxybutynin or tolteridine, may help reduce the sudden urge to urinate.
Fixed abnormal muscle postures may be controlled with injections of botulinum toxin.
Sleep problems such as REM sleep behavior disorder can be treated with medicines including clonazepam, melatonin, or some antidepressants.
Is Multiple System Atrophy A Form Of Parkinson
Multiple system atrophy is a progressive disorder of the nervous system.1 MSA leads to degeneration of multiple areas of brain, mainly, basal ganglia, brain stem and cerebellum. The particular areas affected in the brain can lead to symptoms related to the function of these parts, which include coordination, balance, movement and control of autonomic functions in the body. Autonomic functions are functions that are beyond our control and done involuntarily by the body.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Shaking In Parkinson’s Disease
Low Blood Pressure When Standing Up
Someone with MSA will often feel lightheaded, dizzy and faint after standing up. This is known as postural hypotension and is caused by a drop in blood pressure when you stand up or suddenly change position.
When you stand up after lying down, your blood vessels usually narrow quickly and your heart rate increases slightly to prevent your blood pressure from dropping and decreasing blood flow to your brain.
This function is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. But with MSA, this system does not work properly, so the control is lost.
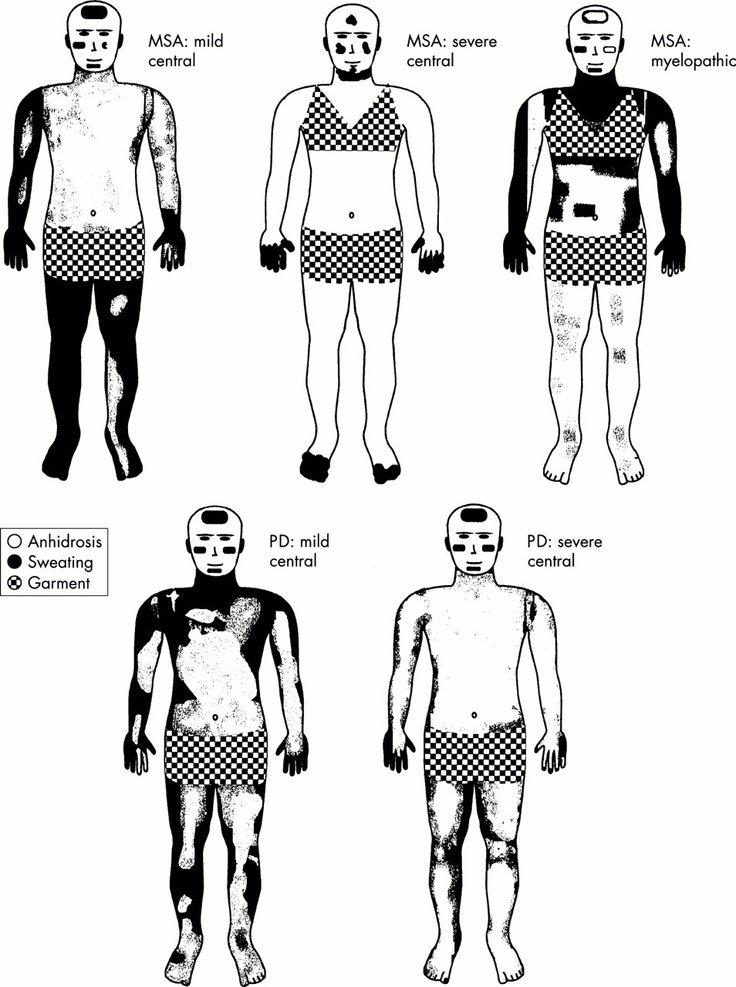
Signs And Symptoms Of Dysautonomia
Dysautonomia refers to a disturbance of the autonomic nervous system, the nerve pathways which regulate unconscious bodily functions including heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, salivation, perspiration, micturition , and some sexual functions. Patients with dysautonomia experience symptoms of fainting or dizziness when changing to an upright position . The lightheadedness results from a decrease in blood pressure upon rising which decreases the amount of blood working against gravity to reach the brain. When a patient collapses to the floor, the amount of blood reaching the brain increases as the blood pressure rises, and the patient regains consciousness. Other typical symptoms of autonomic nervous system dysfunction are constipation, impotence in males, and loss of bladder or bowel control leading to incontinence or constipation. Some patients experience abnormal sweating and develop reddish-blue discoloration of the skin known as the cold hand or cold foot sign. MSA patients also frequently snore, have longer than normal pauses in breathing during sleep , and exhibit combative behavior while asleep, known as REM sleep behavioral disorder .
You May Like: Parkinson’s And Personality Changes
The Rare Nervous System Disorder Often Mistaken For Parkinson’s
Multiple system atrophy is a disorder which causes multiple parts of the nervous system to degenerate. The older names for MSA include three syndromes: Shy-Drager syndrome, striatonigral degeneration, and olivopontocerebellar atrophy. MSA is a progressive disease affecting the autonomic nervous system, the part of your body that controls unconscious actions like blood pressure, digestion, and breathing.
MSA affects anywhere from two to 15 individuals per 100,000. It can take a while to receive an MSA diagnosis because of the similarities between MSA and other conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease. MSA is usually diagnosed around 50 years of age and is seen in people of all ethnic backgrounds. Once symptoms begin, the disease tends to progress quite rapidly.
Research To Find Msa Biomarkers And An Earlier Msa Diagnosis
An important goal of the Coalitions MSA Research Program is to fund and encourage the development of biomarkers to distinguish PD from MSA at a much earlier stage.The stakes are high.An accurate biomarker could lead to quicker development of treatments.In fact, a concern in past clinical trials of MSA treatments that failed is that maybe the patients in the trial are too late stage to show effectiveness.Increasing the number of known early stage MSA patients could improve the likelihood of finding treatments and even a cure.
Also Check: How Is Michael J Fox Doing With His Parkinson’s
Signs And Symptoms Of Multiple System Atrophy
Multiple system atrophy is classified under two categories based on the presenting symptoms at the time of evaluation. These include:
MSA-P or parkinsonian type. It consists of primary characters of Parkinsons disease, such as slow, shuffling gait, stiffness of muscles, and mild tremors, along with imbalance, incoordination and autonomic nervous system dysfunction.3
MSA-C or cerebellar type. It consists of primary characters of ataxia, such as imbalance, incoordination, dysphagia, speech problems and abnormal eye movements
The progression of multiple system atrophy symptoms is usually rapid and eventually requires walking assistance such as cane, walker or wheelchair, within years of initiation of symptoms as compared to Parkinsons in which the progression is slow.
Treating Multiple System Atrophy
There’s currently no cure for MSA and no way of slowing its progression.
People with the condition typically live for 6 to 9 years after their symptoms start and may get worse quickly during this time. Some people may live for more than 10 years after being diagnosed.
The symptoms can be managed so that the person is as independent and comfortable as possible.
Find out how to manage:
Physiotherapy and occupational therapy can help people with MSA stay mobile and maintain their fitness and muscle strength.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Support Group Long Island
Signs And Symptoms Of Parkinsonism
The parkinsonian features of MSA typically include a slowed and shuffling gait, difficulty with balance, stiffness of muscles, particularly those of the neck, and slurred and low-volume speech. Neck and trunk muscle rigidity or weakness may result in abnormal postures such as forward bending of the neck or a body tilt when sitting . Tremor, if present, is usually mild. Patients also may develop hoarseness, difficulty breathing due to vocal cord weakness, and frequent involuntary sighing.Initial symptoms of MSA overlap with those of Parkinson’s disease and many patients with MSA are first diagnosed with classic Parkinson’s disease. Some patients initially respond to the same medications used for Parkinson’s disease but unfortunately, the benefit is usually transient. The course of MSA-P varies markedly from one individual to another. While some patients live for up to 20 years after the onset of symptoms, most patients reach severe disability, requiring assistance with walking and other activities of daily living within five to eight years. It usually progresses much more rapidly than classic Parkinson’s disease.
Similar Symptoms Between Multiple System Atrophy And Parkinsons

Initially, it is difficult to differentiate multiple system atrophy from Parkinsons. The similar symptoms that present in both the diseases include, tremors, rigidity and slowing of movements, incoordination and lack of balance, speech problems with difficulty speaking, orthostatic hypotension leading to spells of lightheadedness and fainting especially from seated position to standing position, bladder problems including both urinary urgency and urinary hesitancy and difficulty emptying bladder.
You May Like: Is Constipation A Symptom Of Parkinson’s
Signs And Symptoms Of Cerebellar Dysfunction
MSA-C is characterized by poor coordination and progressive loss of balance . In addition, patients with MSA-C may have tremor with action, which is different from the resting tremor seen in typical Parkinson’s disease. This tremor is present during activities, such as reaching for objects or eating, and can be elicited on examination by the finger-to-nose maneuver. Other features include slurring of speech, difficulty with swallowing, and progressive weakness. The first symptom is usually mild incoordination in the hands and legs, which eventually progresses to loss of balance requiring a walker or a wheelchair.
Whats The Difference Between Drug
Parkinsons is a progressive disorder, which will become worse over time, while DIP does not. In DIP, Parkinson-like symptoms can begin within four days to one month of starting the medication. However, all the symptoms could completely subside once the effecting medication is stopped, though it may take up to 18 months for all the symptoms to subside.
For more information on drug-induced parkinsonism, read this journal article and/or information sheet.
You May Like: Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome Drugs To Avoid