Differential Diagnosis Of Parkinsonian Syndromes Using Quantitative Biomarkers
Several studies have suggested that the combination of R2* and FA markers may better differentiate people with PD from healthy aged subjects with greater than 95% global accuracy .
In MSA-P, increased diffusivity and reduced anisotropy was found in the putamen, pons and middle cerebellar peduncle and greater iron deposition in the putamen, using phase-contrast susceptibility imaging or relaxometry .
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Dark Pigment In Brain Cells
The brain cells affected by Parkinson’s contain a pigment called neuromelanin. This pigment gives the cells a characteristic dark colouring.
The technique may be sensitive enough to monitor the progression of Parkinson’s.
As these cells are lost in Parkinson’s, this pigmentation is reduced. Recent research has suggested MRI may be sensitive enough to detect this change.
However, there are many different machines and methods for taking MRI brain scans, which could affect how accurate the technique is at detecting Parkinson’s.
The team developed ways to standardise results from different types of machine to increase the accuracy of the technique as a diagnostic tool.
They also discovered that the technique may be sensitive enough to monitor the progression of Parkinson’s.
Read Also: On Off Phenomenon
How A Diagnosis Is Made
The bedside examination by a neurologist remains the first and most important diagnostic tool for Parkinsons disease . Researchers are working to develop a standard biological marker such as a blood test or an imaging scan that is sensitive and specific for Parkinsons disease.
A neurologist will make the diagnosis based on:
- A detailed history of symptoms, medical problems, current and past medications. Certain medical conditions, as well as some medications, can cause symptoms similar to Parkinsons.
- A detailed neurological examination during which a neurologist will ask you to perform tasks to assess the agility of arms and legs, muscle tone, gait and balance, to see if:
- Expression and speech are animated.
- Tremor can be observed in your extremities at rest or in action.
- There is stiffness in extremities or neck.
- You can maintain your balance and examine your posture.
Exclusion Of Alternative Diagnoses
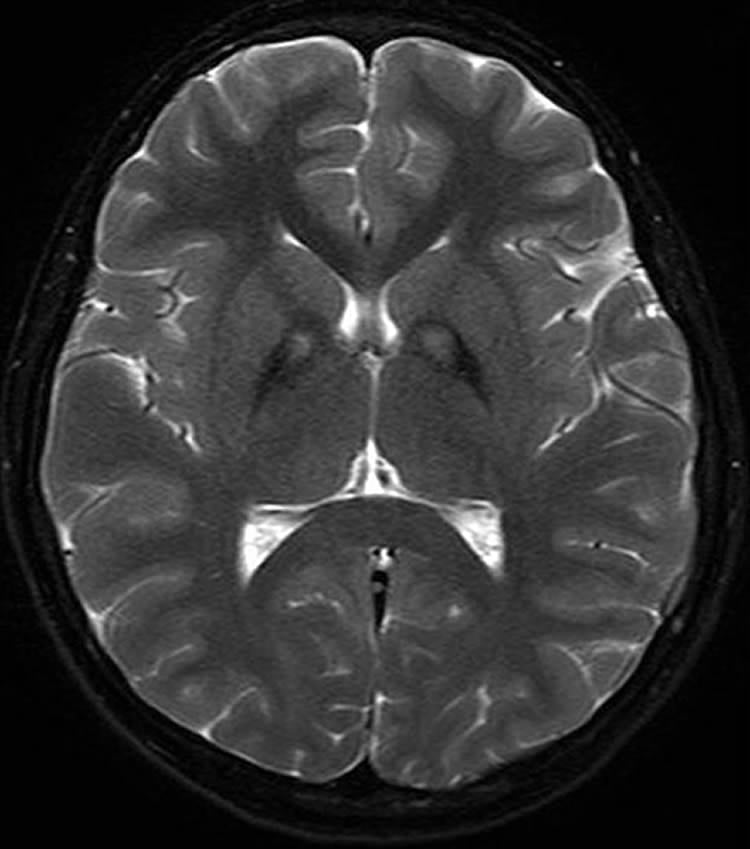
Structural MRI with conventional MR sequences is usually normal in early PD patients limiting its application in clinical routine for the detection of early PD. Recent studies, however, identified imaging correlates of underlying neuropathology in PD patients through advanced MRI techniques. These imaging abnormalities will be discussed in detail later in this review. Nevertheless, cMRI was repetitively shown to be useful in discriminating PD from APDs such as MSA and PSP. Latter are characterized by disease-specific atrophy patterns and signal intensity changes. In addition, current operational diagnostic criteria require the exclusion of symptomatic causes of parkinsonism in the work-up of patients with PD .
Also Check: Parkinsons Disease And Sleep
Also Check: Prayers For Parkinson’s Disease
Description Of The Test
A routine brain MRI study, at 1.5T or 3T magnetic field strength, takes about 30 minutes and includes different acquisitions, also referred to as sequences. We recommend to include T1-weighted and T2 FLAIR, either as 2D or 3D acquisitions. Both transversal and sagittal planes should be available. Furthermore, the protocol should include diffusion-weighted imaging and a susceptibility sensitive sequence, either T2* or susceptibility weighted imaging . For a more detailed evaluation of the basal ganglia and small areas of tissue loss, it is advisable to also include a T2-weighted sequence. The purpose and limitations of these various sequences are described in Table 1.
What Is Parkinsons And How Can Mri Help
More than ten million people are living with Parkinsons disease worldwide, with about one million cases expected to be in the United States by 2020.1 This is more than the number of people with multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy and Lou Gehrigs disease combined.1 With the rising prevalence of Parkinsons disease, its important to understand the signs and symptoms of the disease. Likewise, physicians and radiology departments may need to know what role magnetic resonance imaging may play.
Don’t Miss: Prayer For Parkinson’s Disease
The First Full Body Mri Conditional Portfolio3
Medtronic offers the world’s first full-body MRI capable DBS device portfolio. People with Parkinsons with implanted DBS systems feel reassured knowing that with proper safeguards, MRI is an option for them.
PerceptTM PC neurostimulator is the first and only device to have full-body MR Conditional4 access anywhere on the body for both 1.5T and 3T MRI scans.
Diffusion Mri For The Study Of Parkinsons Disease
Diffusion changes in PD has been the subject of many studies over the years. They are generally based on two measures accounting for mean diffusivity and fractional anisotropy . These measures describe the diffusion of water molecules in the brain, MD accounts for the their overall displacement and FA indicates the orientation of diffusion. The meta-analysis proposed by Cochrane and Ebmeier, 2013 put into evidence important discrepancies between the diffusion scans of PD patients across studies between 1946 and 2012, notably regarding acquisition parameters, analysis methods and the introduction of medication. Most studies focused on the SN as Region Of Interest and often reported FA reductions in different segments with a slight tendency towards the caudal segment. However, no significant association was detected between disease severity and FA values. The first studies were carried out on small cohorts and presented opposing results. We can notably cite the work of Schwarz et al., 2013 where, in contrast to the work of Du et al., 2011, no differences were found in SN for FA values between PD patients and controls but a significant increase of MD in the SN was reported.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Double Vision
What Can You Detect With A Parkinsons Mri
Generally, you can receive a Parkinsons diagnosis in a clinical setting, but an MRI can help to assess various aspects of the disease and its progress. In particular, a Parkinsons MRI can do the following for patients who have or are suspected to have Parkinsons disease:
- Evaluate tissue loss and how the brain is atrophying
- Check for changes to the basal ganglia region of the brain
- Find out if there are abnormal iron deposits in the basal ganglia or brainstem
- Look at changes to white matter
- Examine the diffusion of restricted tissues in acute infarction and neurodegenerative diseases
- Help to diagnose atypical parkinsonism
- Exclude treatable causes of parkinsonism such as normal pressure hydrocephalus
You May Like: Parkinsons Life Center Of Southern New Jersey
How Parkinsons Disease Affects The Autonomic Nervous System And The Heart
In PD, there are two major reasons why the automatic control of the cardiac system is impaired. First, areas of the brain that control this system often contain Lewy bodies and have undergone neurodegeneration. In addition, the autonomic nervous system itself is directly affected by Lewy body-like accumulations and neurodegeneration. This means, when the baroreceptors in the heart and carotid artery sense a drop in blood pressure and try to generate a signal to the heart and blood vessels to increase the blood pressure, the message may not get through. This results in neurogenic orthostatic hypotension , or drops in blood pressure upon standing due to autonomic nervous system dysfunction. There are no medications that can cure nOH by restoring the autonomic nervous system in PD. nOH however, can be treated. Read more about nOH and its treatments here.
Structural problems of the heart such as coronary artery disease or cardiomyopathy are not thought to be part of the pathology of PD, although of course, could co-exist with PD.
Read Also: Effect Of Exercise On Parkinsons Disease
You May Like: Pfnca Wellness Programs
Brain Imaging In Parkinsons Disease
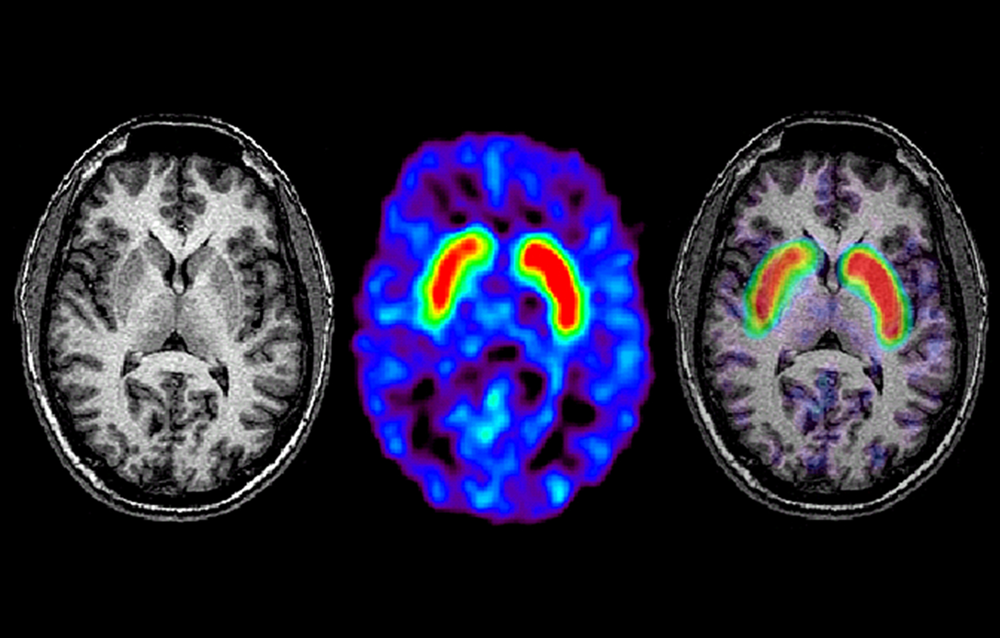
Traditional brain imaging with CT and MRI scans do not show changes in the brain when someone has Parkinsons disease and are generally not helpful in diagnosis. A new kind of brain scan, called a DaT scan, does show changes in persons with Parkinsons disease and may someday become an important tool in diagnosing Parkinsons.
The dopamine transporter, or DaT, scan uses a chemical that labels the dopamine transporter in the area of the brain known as the striatum. Dopamine is a neurochemical that is decreased in persons with Parkinsons disease.
The dopamine transporter, which moves dopamine in and out of cells, is also decreased in the striatum in persons with Parkinsons disease and related disorders. The chemical that labels the transporter is injected into the vein and can be imaged by using something called single photon emission computerized tomography, or SPECT scanning. This technique has been registered in the European Union since 2000 for differentiating a diagnosis of essential tremor and a parkinsonian syndrome. It was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2011 for this same indication and recently became available at the OHSU Brain Institute.
Response To Parkinsons Drugs
After examining you, and depending on the severity of your symptoms, your specialist may suggest you take medication for Parkinsons. If your symptoms improve after taking Parkinsons medication for a few weeks or months, your specialist may confirm a Parkinsons diagnosis. However, some people with other forms of parkinsonism will also respond well to these drugs.
Your specialist may suggest you have a scan to help make a diagnosis. However, scans alone cant make a definite diagnosis of Parkinsons, so they are not commonly used.
Read Also: Parkinson Bicycle Cleveland Clinic
Preparing For A Parkinsons Mri
A Parkinsons MRI is completely painless, but you do have to lie still while being scanned. Some patients feel claustrophobic in this situation. If youre worried about that, talk with your doctor about the possibility of having an anti-anxiety medication before the procedure.
On the day of the appointment, follow any instructions provided to you by your doctor. Remove metal jewelry and dont wear make-up as that can also have metal in it. If you are in the advanced stages of Parkinsons or if you are taking a sedative, you should arrange transportation to and from the appointment.
Determining Diagnosis Through Response To Parkinsons Medication
If a persons symptoms and neurologic examination are only suggestive of Parkinsons disease or if the diagnosis is otherwise in doubt, the physician may, nevertheless, prescribe a medication intended for Parkinsons disease to provide additional information. In the case of idiopathic Parkinsons, there is typically a positive, predictable response to Parkinsons disease medication in the case of some related Parkinsonian syndromes, the response to medication may not be particularly robust, or it may be absent entirely.
Unfortunately, there are no standard biological tests for the disease, such as a blood test. However, researchers are actively trying to find biomarkers in blood and other bodily fluids that could help confirm the diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: What Foods Should Be Avoided When Taking Levodopa
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
We do not know what causes Parkinsons disease. There is some evidence to suggest that there is a genetic factor which increases the risk of Parkinsons disease within some families. Also, there might be an increased risk if people have come into contact with a particular toxin or toxins found in the environment via pesticides and other chemicals used in agriculture. The specific toxin or toxins have not yet been identified but there is ongoing research into this possible cause.
Recommended Reading: Alternative Treatment For Parkinsons Disease
When People Talk About Parkinsons They May Mention The Effects It Has On The Substantia Nigra But Did You Know That There Are Other Areas Of The Brain That Are Affected By The Condition
Parkinsons is a condition that causes the gradual loss of the dopamine-producing brain cells of the substantia nigra an area of the brain located just above where the spinal cord meets the midbrain. It is these cells that produce and release the neurotransmitter dopamine, which has a key role in turning thought about movement into action.
While this definition of the condition is useful to briefly explain Parkinsons, the whole story is somewhat more complex. Over the last 30 years, it has become accepted that Parkinsons also causes a number of non-motor symptoms, such as changes in sleep, smell and even the way we think, which likely involve other areas of the brain.
Now scientists are looking at the broader effects of the condition on the brain in an attempt to better understand why people experience different symptoms. The finding could lead us to new treatments that tackle more than just the motor symptoms of the condition.
You May Like: Sam Waterston Tremor
The Role Of Magnetic Resonance Imaging For The Diagnosis Of Atypical Parkinsonism
- 1Institut du Cerveau et de la Moelle épinièreICM, INSERM U 1127, CNRS UMR 7225, Sorbonne Université, UPMC Univ Paris 06, UMRS 1127, CNRS UMR 7225, Paris, France
- 2ICM, Movement Investigations and Therapeutics Team , Paris, France
- 3ICM, Centre de NeuroImagerie de RechercheCENIR, Paris, France
- 4Service de Neuroradiologie, Hôpital Pitié-Salpêtrière, APHP, Paris, France
- 5Dynamics and Pathophysiology of Neuronal Networks Team, Center for Interdisciplinary Research in Biology, Collège de France, CNRS UMR7241/INSERM U1050, MemoLife Labex, Paris, France
- 6Department of Neurology, Avicenne University Hospital, Sorbonne Paris Nord University, Bobigny, France
- 7Département des Maladies du Système Nerveux, Hôpital Pitié-Salpêtrière, APHP, Paris, France
Structural And Functional Imaging
Traditional structural imaging modalities, such as X-ray computed tomography and brain MRI using anatomical T1 or T2-weighted sequences, are limited to use for identifying the dopaminergic deficits in the brain of patients with PD. However, MRI can be useful in the identification of structural lesions associated with other forms of parkinsonism, such as those underlined by vascular pathology or neoplasms. Structural MRI can also be useful for measuring the degree and distribution of brain atrophy. With regards to differential diagnosis, it has been shown that abnormal T2 MRI hypo-intensities in the putamen discriminate MSA-P from PD with 88% sensitivity and 89% specificity. Decreased putaminal signal intensities were higher using T2*-weighted gradient echo than T2-weighted fast-spin echo sequences and more useful in differentiating PD from MSA-P. Atrophy of the superior cerebellar peduncles and the frontal cortex also aid in discriminating PSP from PD with 74/94% and 95/91% specificity/sensitivity, respectively .
Diagnostic accuracy of MRI modalities.
You May Like: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinsons
What Is A Datscan
A DaTscan is an imaging drug, also called Ioflupane I 123 or phenyltropane, that acts as a radioactive tracer for dopamine transporters within the brain. This drug was approved by the FDA in 2011. It may help distinguish the diagnosis of essential tremor from Parkinson’s syndromes, like Parkinsons disease or Parkinsons disease dementia.
The drug is administered during the SPECT scan. This scanning technique gathers images of a particular area in the brain called the striatum, a cluster of neurons in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum helps facilitate the transportation of dopamine.
DaTscan is injected into the patients bloodstream and eventually circulates to the brain. The tracer attaches itself to a molecule found on dopamine neurons in the striatum called the dopamine transporter . The patient then undergoes a SPECT scan which will produce an image of the dopaminergic neuron terminals that remain available in the striatum.
In patients with a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease, or parkinsonism , this area of the brain will show dark. This indicates the loss of dopamine-containing nerve cells within the brain, a hallmark of the disease.
When Brain Mri Is Recommended To Help Diagnose Parkinsonism
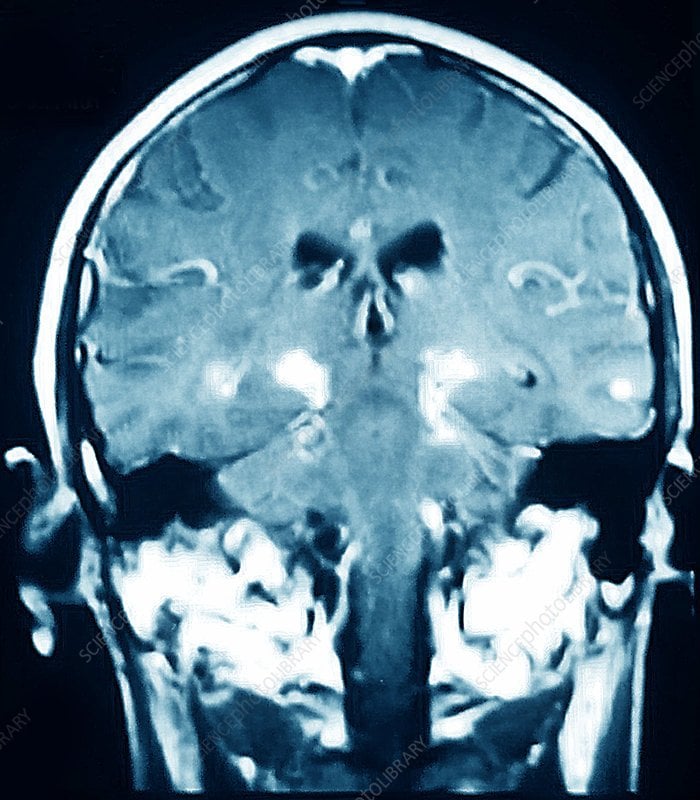
Differentiating atypical parkinsonism from Parkinsons disease can be a challenge in patients presenting with symptoms in early disease stages. A diagnosis cannot be made from a brain magnetic resonance imaging scan, but brain MRI can be of added value when there is uncertainty about the clinical diagnosis.
The appropriateness of and the added diagnostic value of a brain MRI scan in the work-up of parkinsonism is described in a newly published article in the Journal of Parkinsons Disease. Lead author Frederick J.A. Meijer, MD, PhD, a neuroradiologist in the department of radiology and nuclear medicine at Radboud University Medical Center in Nijmegen, The Netherlands, offers advice on the scanning protocol to use, and also discusses its diagnostic value with respect to specific abnormalities that can be seen.
The authors of the article, who also include neurologists from the Radboud University Medical Center and Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition and Behavior, conducted a 3-year long prospective study on the contribution of routine brain MRI to the differential diagnosis of parkinsonism.1 Based on this research, the authors refuted clinical guidelines recommending standard use of cerebral MRI for all patients presenting with parkinsonism.
3T brain MRI including DTI tractography in a patient presenting with parkinsonism.
Recommended Reading: Diseases Similar To Parkinsons
What Are The Treatments
Currently there is no cure for Parkinsons disease.
Symptoms can be mild in the early stages of the condition and people might not need immediate treatment. Your doctor and specialist will monitor your situation.
There are several different types of drugs used to treat Parkinsons disease. Drug treatments are tailored to each individuals needs and are likely to involve a combination of different drugs. Your medication should be reviewed regularly. It is likely that, over time, changes will be made to the types of drugs you take and the doses you take each day.
The main types of drug treatment for Parkinsons disease are:
- drugs which replace dopamine
- drugs which mimic the role of dopamine
- drugs which inhibit the activity of acetylcholine
- drugs which prevent the body breaking down dopamine
- other drugs such as anti-sickness medication
Everybody is affected differently by medication. The possible side effects of Parkinsons disease drugs include nausea , vomiting , tiredness and dizziness. Some people might experience confusion, nightmares and hallucinations. For some people, dopamine agonists have been linked to compulsive behaviour such as addictive gambling or hypersexuality .
The effectiveness of the main drug treatment levodopa can wear off over time and its long-term use can cause some people to develop involuntary twisting or writhing movements of the arms, legs or face . To reduce the risk, doctors might delay the use of levodopa for younger people.